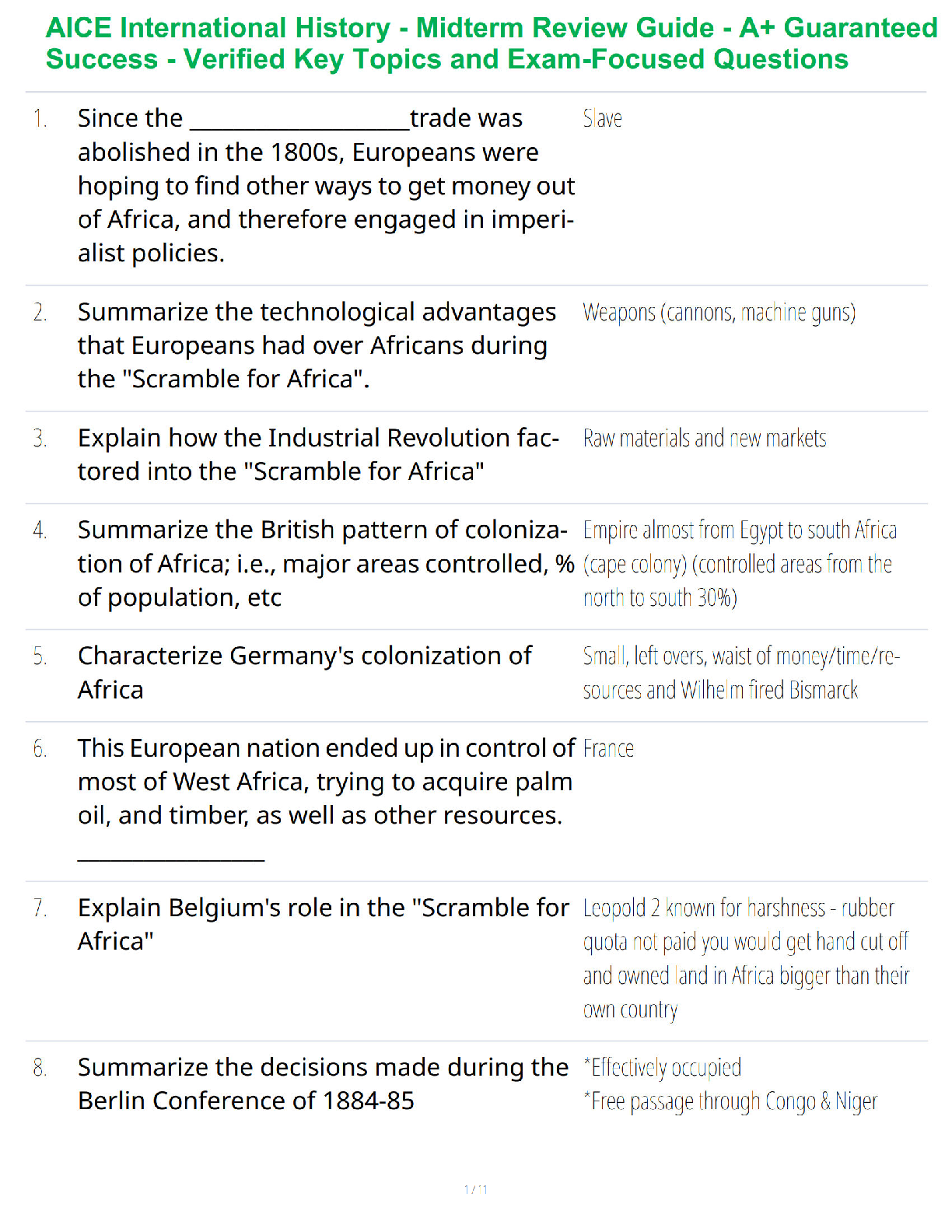
knowledge
(Ans- The awareness and understanding of a set of information and the ways that information can be made useful to support a specific task or reach a decision.
wisdom
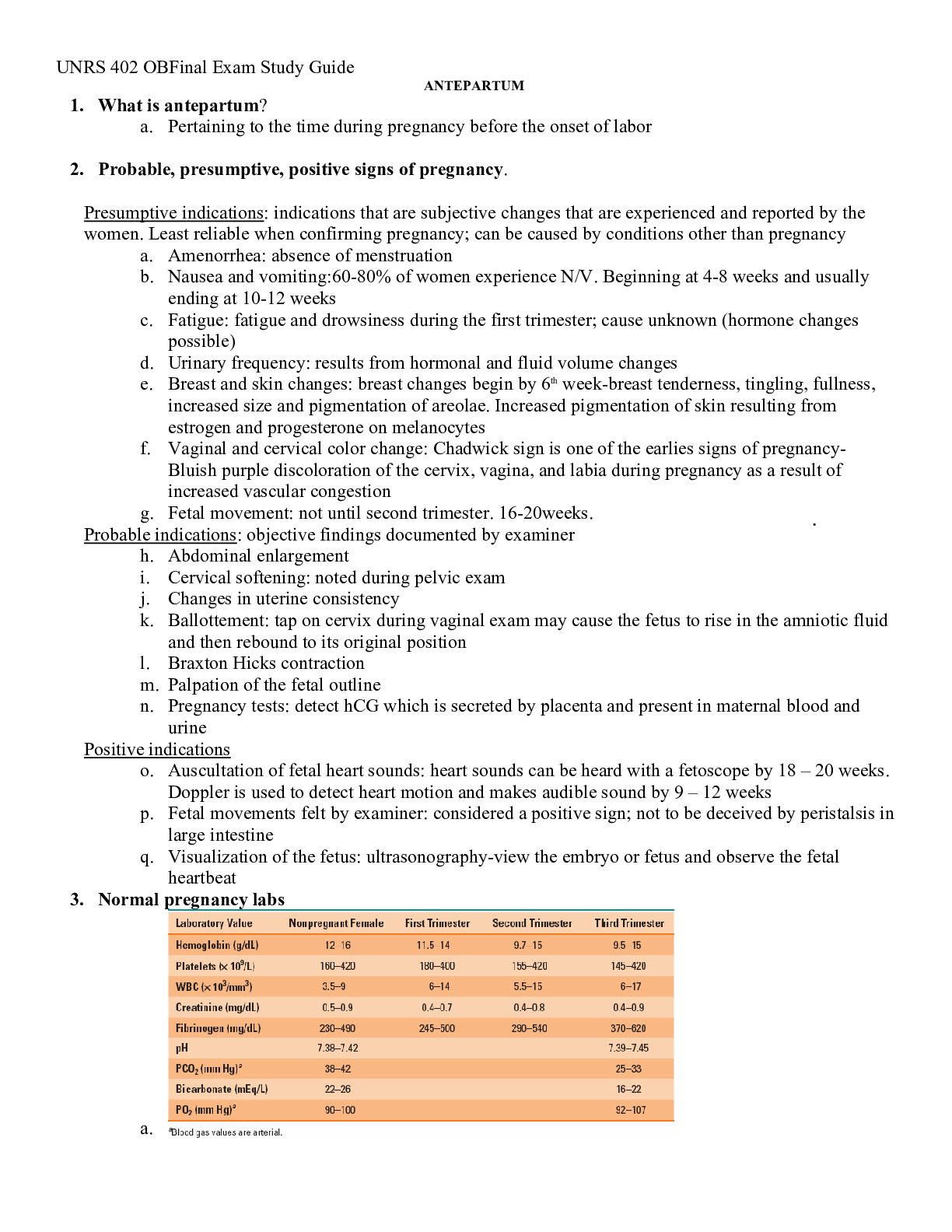
(Ans- knowledge applied in a practica
...
knowledge
(Ans- The awareness and understanding of a set of information and the ways that information can be made useful to support a specific task or reach a decision.
wisdom
(Ans- knowledge applied in a practical way or translated into actions: the use of knowledge and experience to heighten common sense and insight so as to exercise sound judgement in practical matters. Sometimes thought of as the highest form of common sense.
Wisdom is the ability to apply valuable and viable knowledge, experience, understanding , and insight while being prudent and sensible.
It is the appropriate use of knowledge to solve human problems. It is knowing HOW and WHEN to apply knowledge
general principles of informatics (NI)
(Ans-
1. specialty that integrates nursing science with multiple information and analytical sciences to identify, define, manage, and communicate data, information, knowledge, and wisdom in nursing practice.
2. NI supports nurses, consumers, patients, the interprofessional healthcare team, and all other stakeholders
3. support is accomplished through the use of information structures, information processes, and information technology
scientific underpinning
(Ans- the scientific underpinnings of practice provide the basis of knowledge for advanced practice nursing.
These scientific underpinnings includes sciences such as biology, physiology, psychology, ethics, and nursing.
Nursing science, information science, and computer science.
The Foundation of Knowledge Model definition
(Ans- Conceptual Framework or the basis for which knowledge is used to meet the needs of the healthcare delivery system
4 key Elements of The Foundation of Knowledge Model
(Ans- knowledge acquisition, knowledge processing, knowledge generation and knowledge dissemination
computer science
(Ans- Branch of engineering (application of science) that studies the theoretical foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. The study of storage/memory, conversion and transformation, and transfer or transmission of information in machines— that is, computers—through both algorithms and practical implementation problems. Algorithms are detailed, unambiguous action sequences in the design, efficiency, and application of computer systems, whereas practical implementation problems deal with the software and hardware.
cognitive science
(Ans- the interdisciplinary study of the mind, intelligence, and behavior that focuses on how people process information
information science
(Ans- information science enables the processing of information. KNOWLEDGE ACQUISITION
This processing links people and technology.
Humans are organic ISs, constantly acquiring, processing, and generating information or knowledge in their professional or personal lives.
standardized terminology (STs)
(Ans- standardized terminology (STs) contribute to the development of knowledge because they ensure that all professionals share the same understanding or meaning of a given concept, to clarify communication, facilitate research, and provide structure for decision support tools and EHRs.
STs are structured, controlled languages developed to represent concepts in a given domain in a clear, unambiguous fashion that conveys the exact same meaning for data, information, and even different countries.
STs are key to the development of an EHR in order to represent, communicate, exchange, reuse, and report data, information, and knowledge, including Meaning Use criteria
Informatics Competencies
(Ans- New nurses should have the following skills: use e-mail, operate windows applications, search databases, and know how to work with institution specific nursing software used for charting, and med. administration
1980s core groups were: 1. user, 2. developer., or expert
2001 groups: 1. entry level, 2. experienced nurse, 3. informatics nurse, 4. informatics nurse specialist
information literacy
(Ans-
-ability to identify when information is needed
-the skills to find, evaluate, and effective use it
-evaluation of online resources for quality
-ability to search literature databases
[Show More]