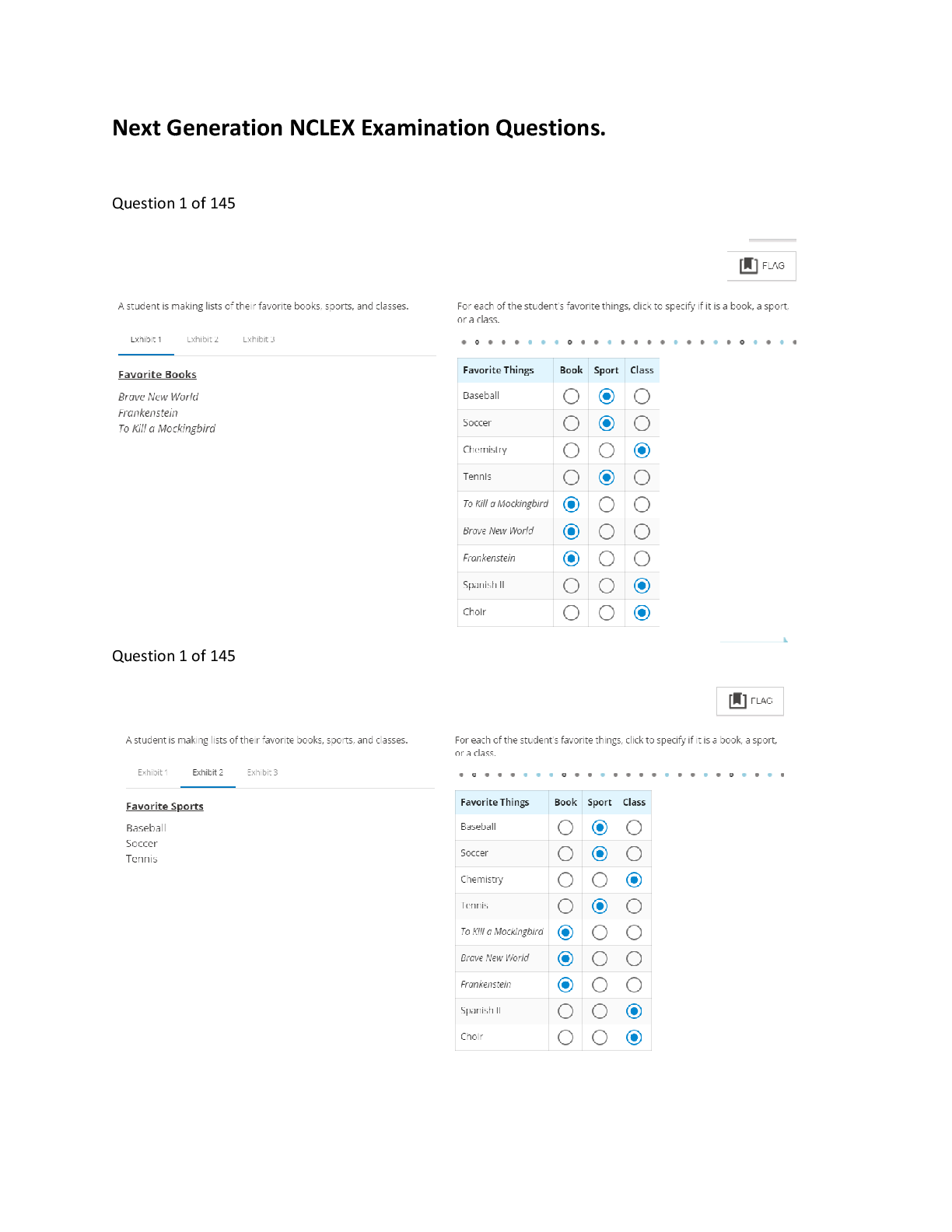
A patient with suspected acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is placed on a cardiac monitor. The patient is complaining of dyspnea and is given supplemental oxygen. The provider determines that the oxygen is effective based o
...
A patient with suspected acute coronary syndromes (ACS) is placed on a cardiac monitor. The patient is complaining of dyspnea and is given supplemental oxygen. The provider determines that the oxygen is effective based on which SaO2 level? - ANSWER When a patient presents with potential ACS, the patient should have oxygen administered to maintain an SaO2 of at least 94%.
A patient experiences cardiac arrest, and the resuscitation team initiates ventilations using a bag-valve-mask (BVM) resuscitator. The development of which condition during the provision of care would lead the team to suspect that improper BVM technique is being used? - ANSWER Complications can occur with the use of a BVM resuscitator due to improper technique. Delivering excessive volume or ventilating too fast creates excessive pressure that can damage the airways, lungs and other organs. Excessive volume can lead to tension pneumothorax.
Assessment of a patient reveals an ETCO2 level of 55 mmHg and an arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) level of 88%. The provider would interpret these findings as indicative of which condition? - ANSWER An SaO2 level of less than 90% (PaO2 of less than 50 mmHg) accompanied by ETCO2 values greater than 50 mmHg is indicative of respiratory failure.
A healthcare provider initiates ventilations to ensure adequate breathing and oxygenation. While ventilations are being performed, capnography is established to evaluate the adequacy of the ventilations. The healthcare provider determines that ventilations are adequate based on which end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) value? - ANSWER End-tidal carbon dioxide values in the range of 35 to 45 mmHg confirm adequacy of ventilation.
A patient comes to the emergency department complaining of palpitations and "some shortness of breath." Cardiac monitoring is initiated and reveals the following ECG rhythm strip. The provider interprets this strip as indicating which arrhythmia? - ANSWER In atrial flutter, atrial contraction occurs at such a rapid rate that discrete P waves separated by a flat baseline cannot be seen on the strip. Instead, the baseline continually rises and falls, producing the "flutter" waves. In leads II and III, the flutter waves may be quite prominent, creating a "sawtooth" pattern. Because of the volume of atrial impulses, the AV node allows only some of the impulses to pass through to the ventricles. In atrial flutter, a 2:1 ratio is the most common (i.e., for every two flutter waves, only one impulse passes through the AV node to generate a QRS complex). Ratios of 3:1 and 4:1 are also frequently seen.
A person suddenly collapses while sitting in the sunroom of a healthcare facility. A healthcare provider observes the event and hurries over to assess the situation. The healthcare provider performs which assessment first? - ANSWER A systematic approach to assessment is necessary. The healthcare provider should first perform a rapid assessment. A rapid assessment is a quick visual survey to ensure safety, to form an initial impression about the patient's condition, and to check for responsiveness, breathing and a pulse if the patient appears to be unresponsive. This would be followed by a primary assessment and then a secondary assessment.
A 35-year-old female patient's ECG is consistent with STEMI. The ECG reveals a new ST-segment elevation at the J point in leads V2 and V3 of at least which size? - ANSWER New ST-segment elevation at the J point in leads V2 and V3 of at least 0.15 mV (1.5 mm) in women 40 years or younger is considered diagnostic of STEMI.
An ECG strip of a patient in the emergency department reveals the following rhythm. Which feature would the healthcare provider interpret as indicating atrial fibrillation? - ANSWER The two key features of atrial fibrillation on ECG are the absence of discrete P waves and the presence of irregularly irregular QRS complexes.
A patient presents to the emergency department with mild to moderate recurrent chest pain, without any nausea or vomiting. A 12-lead ECG is obtained and shows ST-segment depression with transient T-wave
[Show More]