Education > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > GIS Applications Final Exam 2022 with complete solution (All)
GIS Applications Final Exam 2022 with complete solution
Document Content and Description Below
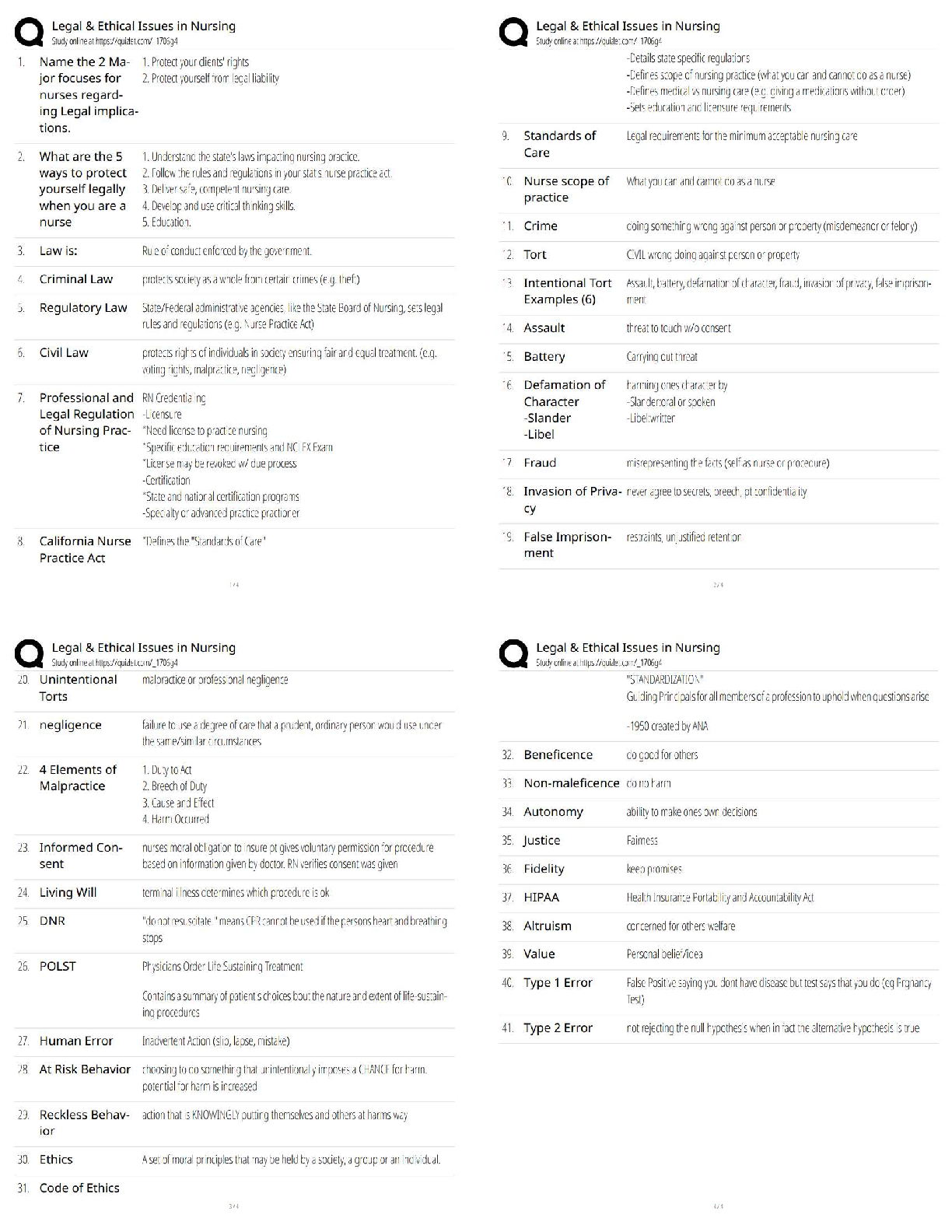
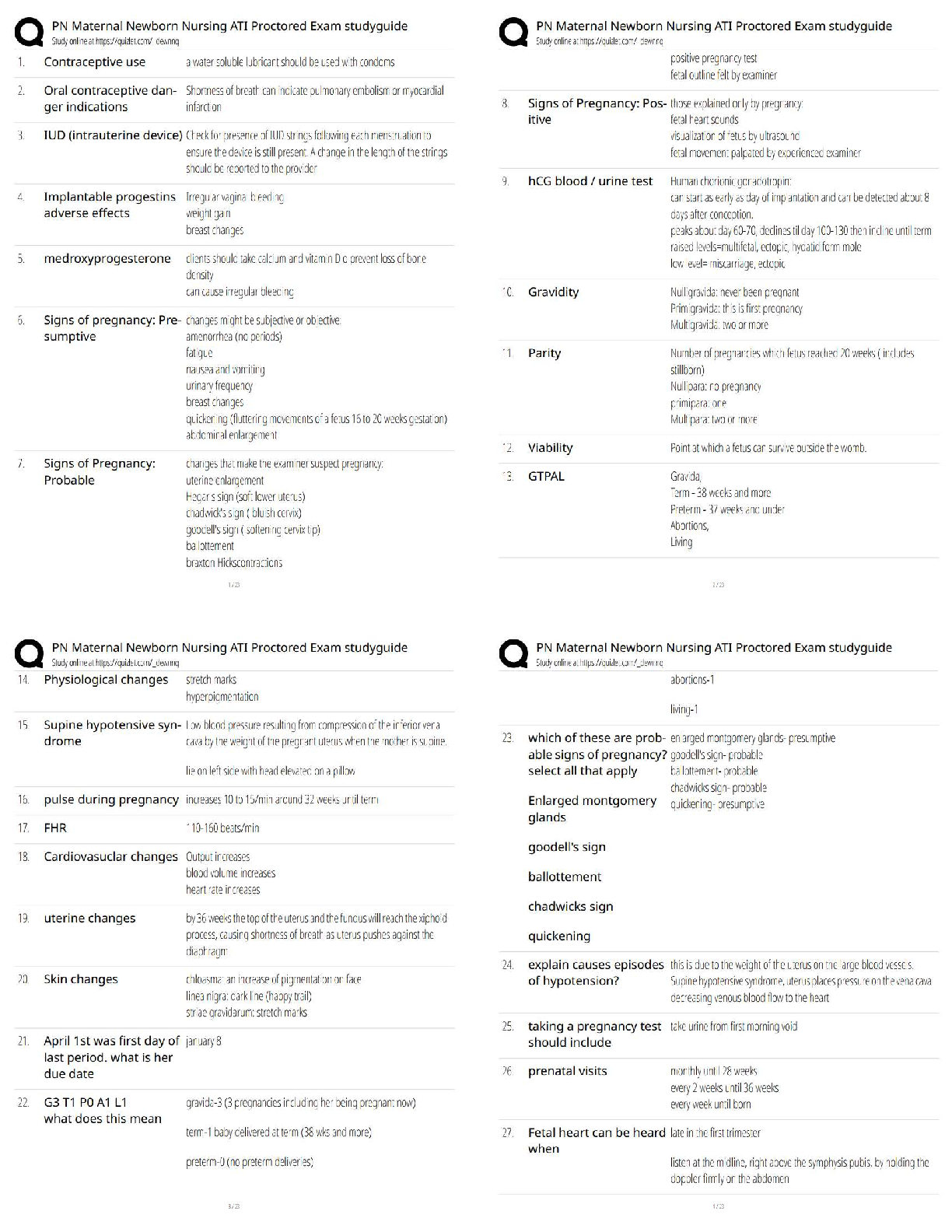
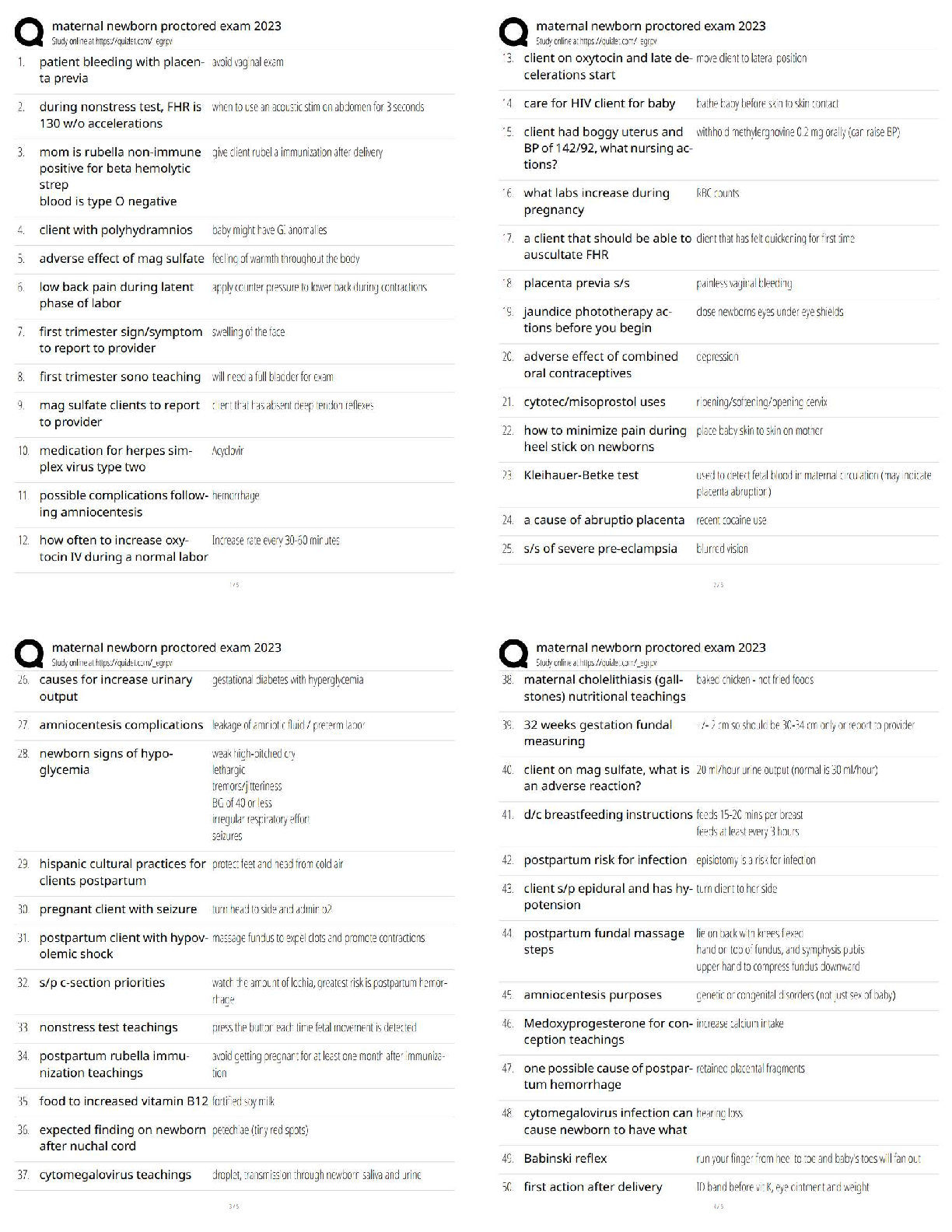
GIS Applications Final Exam 2022 with complete solution The process of assigning new raster values to a current raster value or group of raster values is known as -Answer- reclassification When ... preparing a dataset for kriging interpolation, each sample point is paired with _______ sample points -Answer- all other True or false, before using raster functions, it may be beneficial to clip the raster dataset to only include the subset of information relevant to your goal -Answer- True Pick the situation described below that is NOT fit for suitability modeling: a) Where to site a new housing development b) Where to deploy troops in a military operation c) Where to locate firefighting crews to best fight fires in the dry season d) What method to select for creating interpolated map -Answer- d) what method to select for creating interpolated map The formula for calculating cross-validation error for a sampling point is as follows -Answer- Observed value - predicted value The weighted suitability model applies ----------- to each layer based on their relative importance to the problem being solved a) functions b) ratios c) weights d) equations -Answer- weights True or false, an azimuth of 90 degrees is West direction -Answer- False What among the following is NOT a raster function: a) Surface: Slope b) Surface: Shaded relief c) Surface: Interpolation d) Surface: Hillshade -Answer- Surface: Interpolation True or false, When performing a raster calculation, the NO DATA values are ignored -Answer- True True or false, when running a model, the progress of the model's execution can be visually tracked by finding the tool that has turned green -Answer- false which of the following is not a use of Modelbuilder? a. visualize your workflow sequence as an easy to understand diagram b. run the entire model with no provision for running it in a step by step mode c. build a model by adding geoprocessing tools, map layers, datasets, and other data types and connecting them to a process d. Make your model into a geoprocessing tool that can be shared with others or can be used in Python scripting and other models -Answer- b. run the entire model with no provision for running it in a step by step mode Processing _______ ____________ layer(s) using arithmetic and algebraic operations is termed as map algebra -Answer- multiple, raster True or false, performing pixel by pixel analysis on a raster dataset for two different time periods to determine change in cropped area is an example of neighborhood raster operation -Answer- False __________________ creates a new raster that includes input cell values for each region -Answer- Zonal operation Of the following options, which are TRUE statements in regards to spatial interpolation techniques? A. sample points that are closest to the prediction location are given less weight in the predictions. B. Spatial interpolation may be used to derive a prediction surface that estimates the values of a spatially discrete phenomenon at all other locations in a study area. C. deterministic and geostatistical are the two broad categories spatial interpolation techniques fall under. D. Geostatistical techniques provide more comprehensive measure of error and uncertainty compared to deterministic techniques. -Answer- C. deterministic and geostatistical are the two broad categories spatial interpolation techniques fall under D. Geostatistical techniques provide more comprehensive measure of error and uncertainty compared to deterministic techniques True statements in regards to the principles of geostatistical interpolation A. Local variation in the surface are represented by the spatially autocorrelated random error component. B. The values of local spatial neighbors do not impact the initial prediction for a location made by the deterministic trend component. C. When the deterministic trend component is represented by a constant mean, the spatially autocorrelated random error can be calculated by taking the difference between the mean and measured value of the phenomenon at a given location. D. Spatial autocorrelation is a measure of the degree to which farther away locations are more similar in value than locations that are nearby. -Answer- A. Local variation in the surface are represented by the spatially autocorrelated random error component B. When the deterministic trend component is represented by a constant mean, the spatially autocorrelated random error can be calculated by taking the difference between the mean and measured value of the phenomenon at a given location True or false, When preparing a dataset for kriging interpolation, each sample point is paired with one other sample point. -Answer- False Blue crosses in the semivariogram represent average empirical semivariances -Answer- True True or false, The semivariogram model is a function that represents spatial autocorrelation -Answer- True True or false, kriging involves simulating multiple semivariogram models to account for uncertainty in the empirical model -Answer- False A required assumption for estimating a true semivariogram is that the assumption data has _________ -Answer- stationarity [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 15 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 07, 2022
Number of pages
15
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 07, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
210