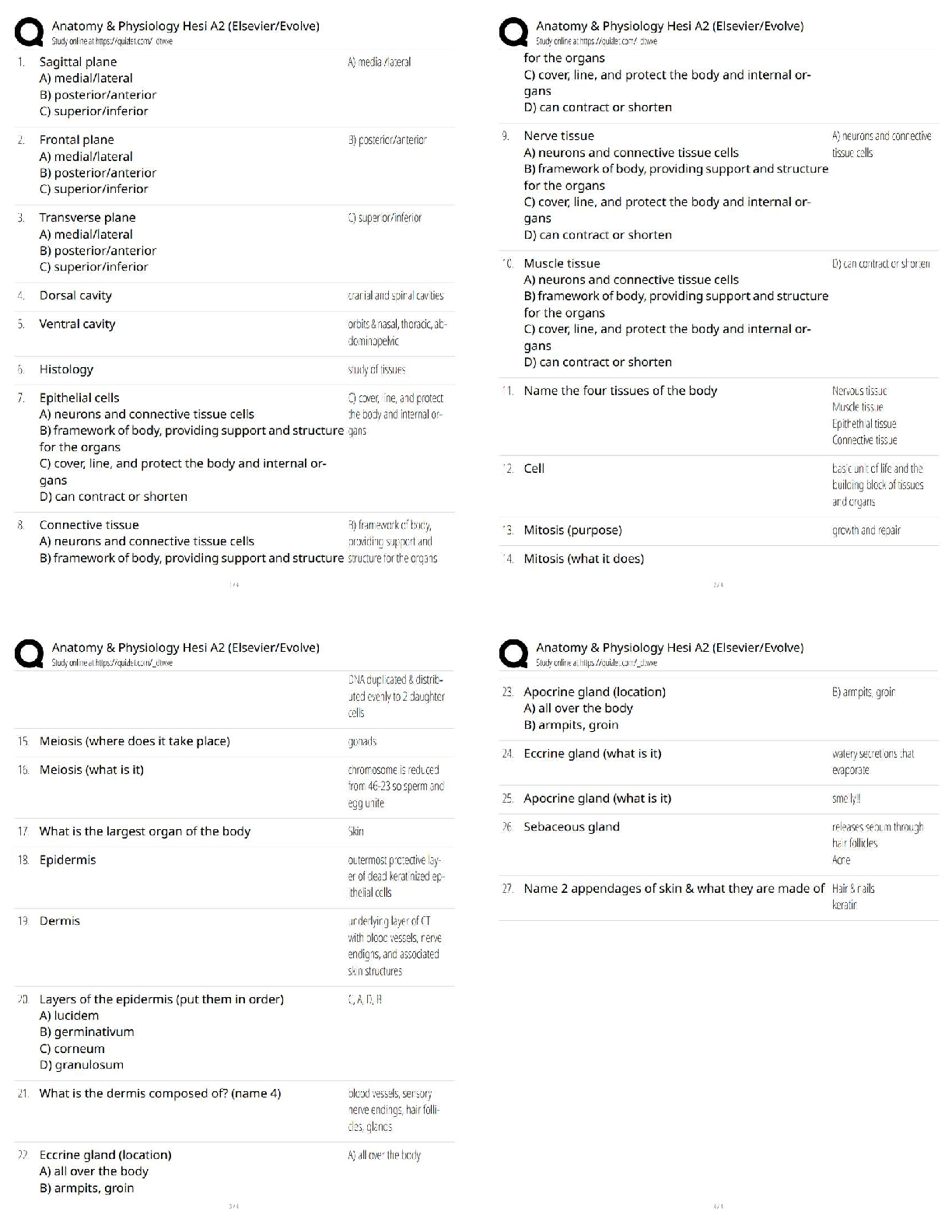
Biochem C785 - WGU - Module 4 - All
Questions
The polysaccharide cellulose is composed of sugar monomers linked through beta linkages, with their
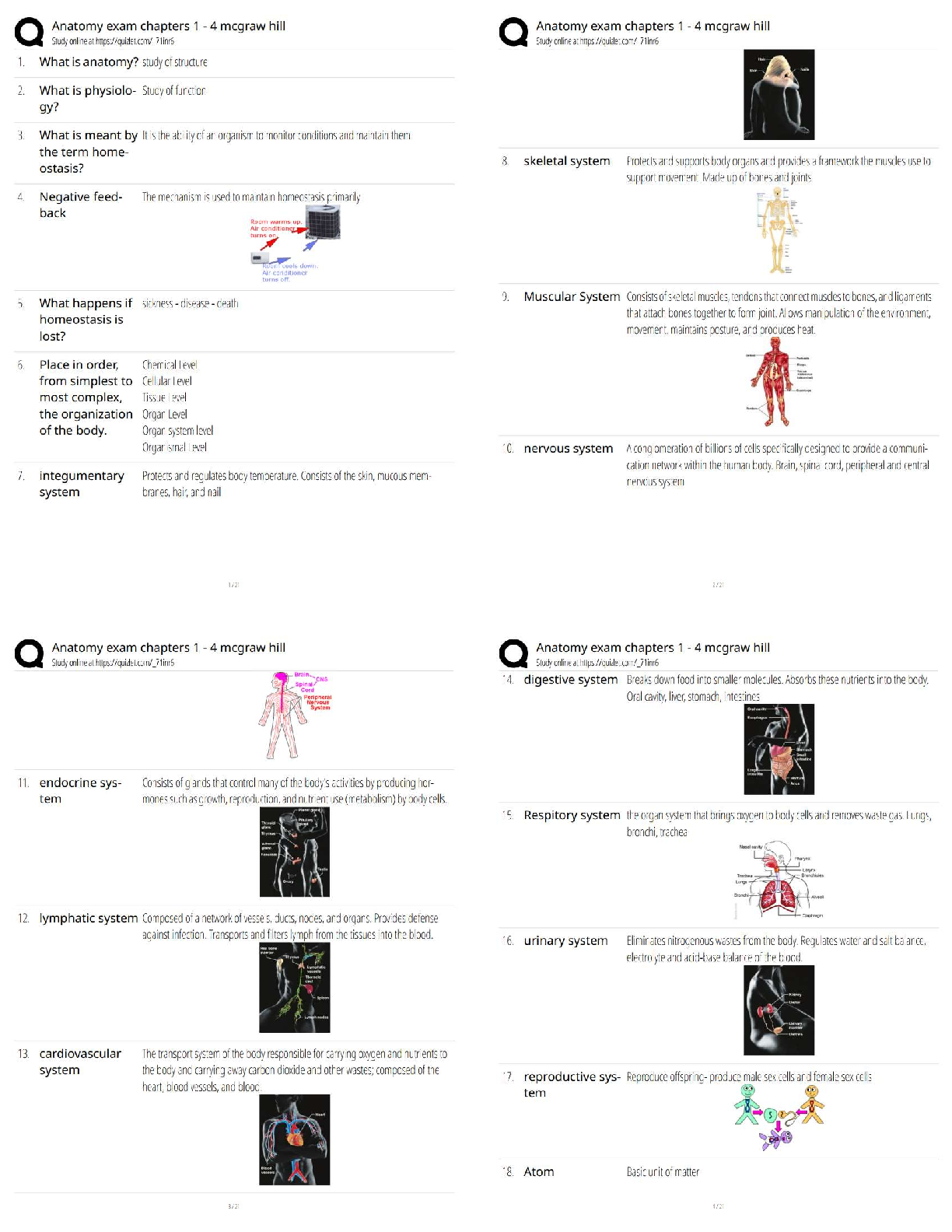
CH2OH groups in opposite direction relative to the neighboring monome
...
Biochem C785 - WGU - Module 4 - All
Questions
The polysaccharide cellulose is composed of sugar monomers linked through beta linkages, with their
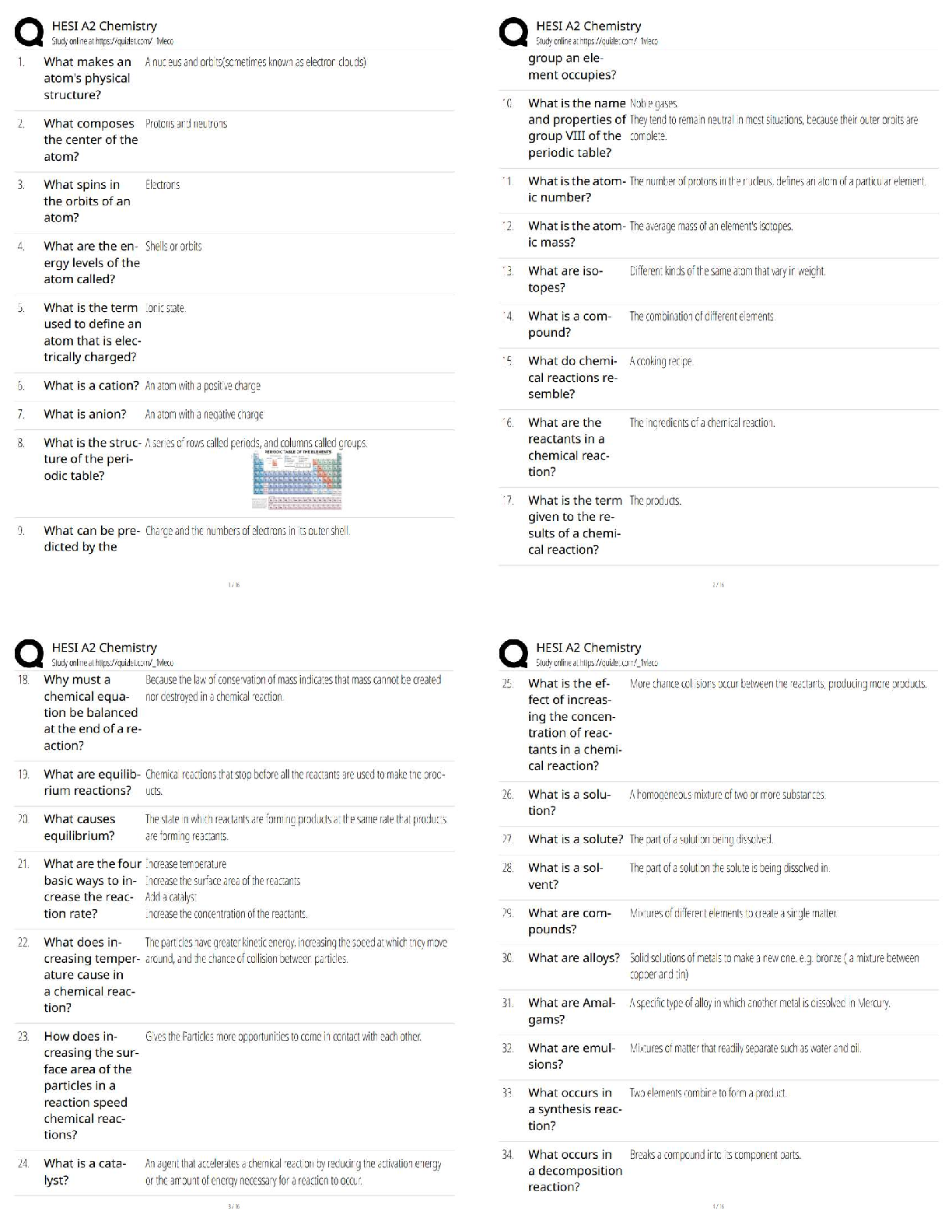
CH2OH groups in opposite direction relative to the neighboring monomer. Correct Answer: True
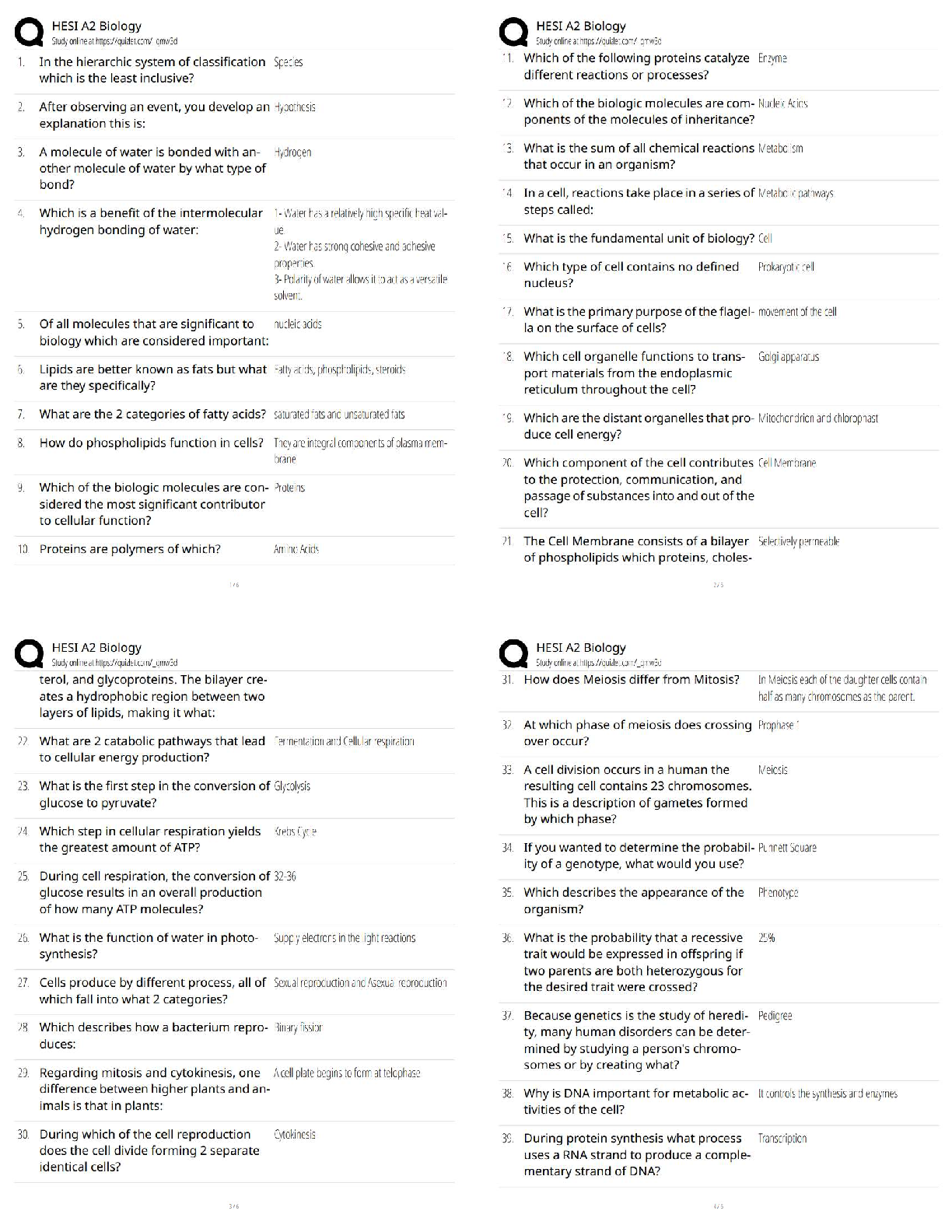
Nutrient that can not be broken down to a substance that can participate in the production of ATP via
aerobic cellular metabolism Correct Answer: Vitamin E
Glycolysis produces 2 ATP molecules, through what process are these ATP molecules made?
Correct Answer: Substrate level phosphorylation
What product of beta oxidation is able to enter the citric acid cycle? Correct Answer: AcetylCoA
What process is shared between anaerobic and aerobic metabolism? Correct Answer: glycolysis
A defect occurs that prevents pyruvate from converting to lactate under anaerobic conditions - what is
a possible consequence? Correct Answer: glycolysis stops because NAD+ levels are too low
What differentiates aerobic from anaerobic cellular metabolism? Correct Answer: utilization of 02 as
an electron acceptor
What takes place in the mitochondria of a cell? Correct Answer: production of FAHD2
production of CO2 in the citric acid cycle
creation of a proton gradient
What does not take place in the mitochondria of a cell? Correct Answer: conversion of pyruvate to
lactic acid
Under aerobic conditions in a human, which molecule is formed in the cytosol by fermentation?
Correct Answer: lactate
A woman is about to begin her ascent of Mount Everest and is preparing for Day 1 of the climb.
Approximately 6 hours before the hike begins, she and her climbing team eat a meal containing 80%
complex carbohydrates. What is the physiological benefit of this approach? Correct Answer:
improving glycogen stores in the liver and muscle
Which process is stimulated when glucagon is released into the bloodstream? Correct Answer:
triglyceride synthesis
Which chemical represents a monosaccharide? Correct Answer: C6H1206
A patient with advanced cancer has not been able to eat a full meal for the past 3 months, and his
intake has gradually diminished over the last month such that his entire intake in the prior 3 days
consists solely of water. What is most likely? Correct Answer: He is likely to have lost adipose tissue
and muscle mass
Which process is stimulated when insulin is released into the bloodstream? Correct Answer:
glycogenesis
What is the largest source of energy storage in the normal human body? Correct Answer:
triglycerides in adipose
What drives glucose from the bloodstream into the cells? Correct Answer: insulin
What chemicals can be produced in dangerous excess in a patient taking metformin because of its
effects of decreasing the liver's participation in the Cori Cycle? Correct Answer: lactic acid
A 2-year old boy found to have an autosomal recessive glycogen storage disease that prevents him
from being able to fully metabolize glucose. On examination, he has an enlarged liver and bulky
appearing muscles. Biopsy of both the liver and the muscles shoes markedly increased amounts of
glycogen compared to normal - What is true? Correct Answer: Since glucose can be partially but not
fully metabolized, there is an increased concentration of the intermediate compounds and this causes
a shift in enzymatic reactions, favoring the production of glycogen
Sucrose is a disaccharide consisting of one molecule of glucose bound to one molecule of fructose.
When you put sucrose in your tea, how is that sucrose utilized by your body for making energy?
(ATP) Correct Answer: sucrose is broken down into its constituent monosaccharides for absorption,
these can then be metabolized via glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
Which of the following directly provides the energy necessary for the conversation of ADP + P to ATP
by ATP synthase? Correct Answer: proton moving down a concentration gradient from the
intermembrane space to the mitochondrial matrix
If a patient is healthy and has a normal oxygen concentration in her blood, approximately how many
ATP are produced for every molecule of glucose that is aerobically metabolized? Correct Answer: 30.
2 ATP are formed in glycolysis via substrate level phosphorylation.
2 ATP are formed in the citric acid cycle via substrate level phosphorylation
26 ATP are formed through oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport chain for a total of
about 30 ATP from one glucose molecule that undergoes aerobic metabolism
What process takes place in the inner membrane of the mitochondria? Correct Answer: electron
transport chain
While barbiturates are potent inhibitors of Complex I in the electron transport chain, they do not
completely block electron transport because: Correct Answer: FADH2 donates electrons to complex II
Where is energy stores in an ATP molecule? Correct Answer: in the bonds between the phosphate
groups
A defect in an enzyme in the citric acid cycle causes the cycle to stop functioning. What are possible
consequences? Correct Answer: decreased levels of ATP
What could result in better outcomes for type 2 diabetes? Correct Answer: an increased number of
GluT4 transports in the cell membrane
Emma was prescribed metformin which is used to control blood glucose levels. One direct effect of
metformin is inhibition of the gluconeogenesis pathway in the liver Correct Answer: True
Emma has an A1C level of 7.0% in her blood. A1C is a form of: Correct Answer: hemoglobin
Catabolism is the breakdown of larger molecules, whereas anabolism is the synthesis of new
molecules. Which of these processes result in the generation of ATP? Correct Answer: catabolism
A molecule that assists an enzyme in driving biochemical reactions is: Correct Answer: coenzyme
Insulin controls both carbohydrates and fat metabolism. What statement describes the effects of
insulin? Correct Answer: 1. stimulates the glucose uptake
2. inhibits the glycogen breakdown
3. stimulates fatty acid production and storage
There are 2 types of diabetes. Type 1, where the insulin is not produced at all or produced in
insufficient amounts. Type 2, where insulin is made in reasonable quantities, but the cells are unable
to respond to the insulin. Thus, not all cases are a result of insufficient amounts of insulin. Correct
Answer: True
The complications of diabetes result from the accumulation of which of the following: Correct Answer:
Advanced Glycation End-products (AGEs)
[Show More]