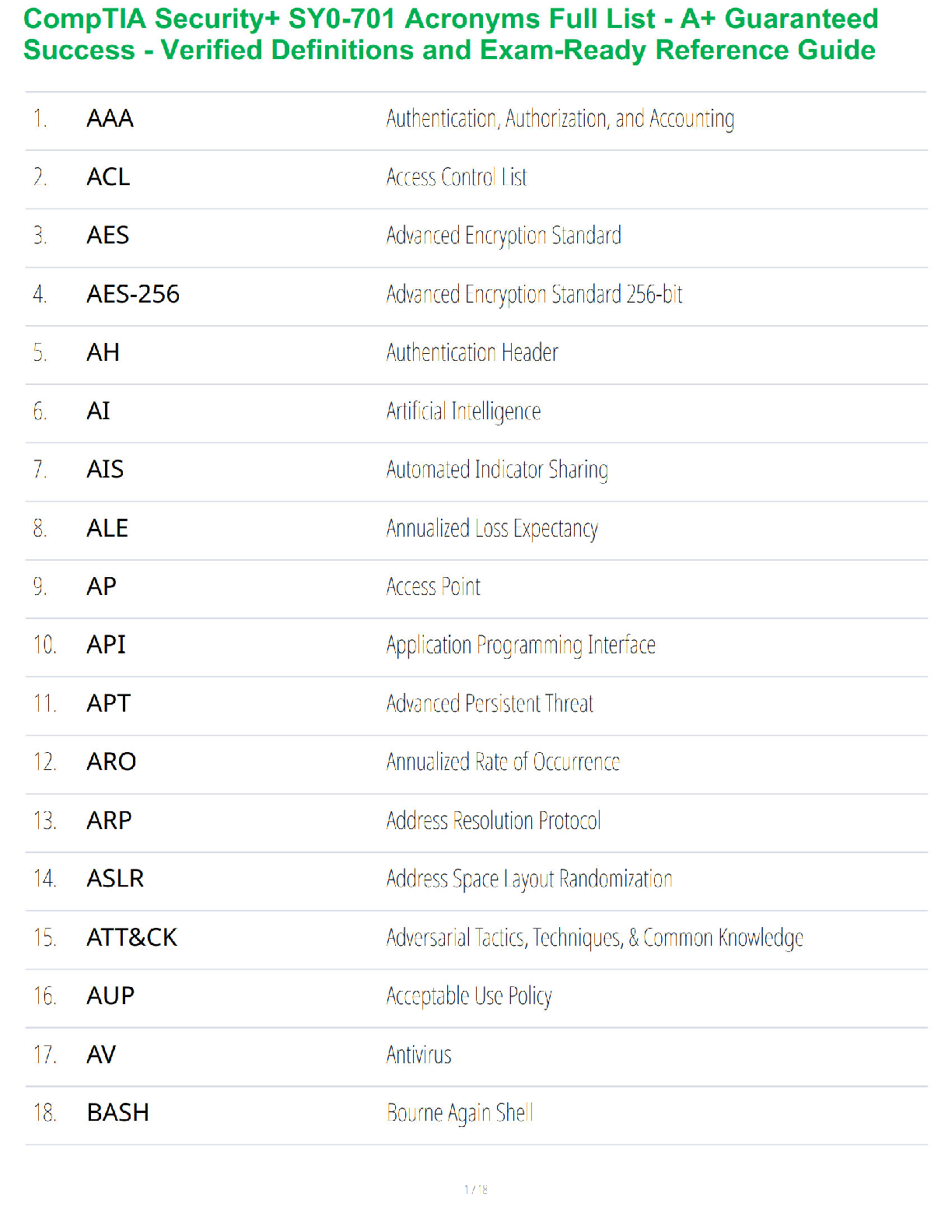
EDC/EDD- Estimated date of confinement/estimated delivery date
Gravid- Pregnant
Parity- Number of pregnancies carried to a point of viability (24 weeks) regardless of outcome
Striae- Stretch marks on abdomen and
...
EDC/EDD- Estimated date of confinement/estimated delivery date
Gravid- Pregnant
Parity- Number of pregnancies carried to a point of viability (24 weeks) regardless of outcome
Striae- Stretch marks on abdomen and thighs
Braxton Hicks Contractions- False, contractions, painless, irregular, and usually relieved by walking
Linea Nigra- Dark line of pigmentation from the umbilicus extending to the public area
Chadwick’s sign- Deepened violet-bluish color of cervix and vaginal mucosa
Amenorrhea- no menstrual flow
STI- Sexually transmitted infections
Hyperemesis gravidarum- persistent vomiting
Leopold’s maneuver- external palpations of the maternal uterus through the abdominal wall to determine number of fetuses; presenting part, lie, and fetal attitude; degree of descent of the presenting part into the pelvis; location of point of maximal impulse (location of fetal heart tones).
Colostrum- secreted during postpartum days 1 to 3. Contains IgA that provides passive immunity to the newborn.
Quickening- Slight fluttering movements of the fetus felt by a woman, usually between 16 and 20 weeks.
Lightening- fetal head descends into the true pelvis about 14 days before labor; “dropped”; easier breathing but more pressure on the bladder causing urinary frequency; more pronounced in patient who are primigravida
Doppler- noninvasive ultrasound to measure the velocity at which RBCs travel in the uterine and fetal vessels
Fetoscope- fiber optic scope used in percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS) or amniocentesis
Amniocentesis- aspiration of amniotic fluid by needle insertion transabdominally into the client’s uterus and amniotic sac after 14 weeks to test for genetic abnormalities
Maternal serum alpha fetal protein (MSAFP)- screening tool used to detect neural tube defects.
hCG- Human chorionic gonadotropin- hormone produced by placenta
LMP- Last menstrual period
Menarche- First menstrual period one year after peak velocity; between 9 and 15 years old
Nagele’s Rule- take the first day of the woman LMP, add seven days, subtract three months, and add one year.
Fundal Height- in cm from pubic symphysis to the top of the uterine fundus after 12 weeks; relates to gestational weeks.
Bishop’s Score- determines maternal readiness for labor by evaluating the cervix: dilation, effacement, consistency (firm, medium, soft), position (posterior, midposition, anterior), and station; all assigned a value between 0-3
Freidman’s curve- rates cervical dilation and fetal descent during active labor
Cervical dilation- most important indicator of progress of labor; part of Bishops score; 1 cm/hr during labor; cervix ripens by dilation; provides uterus with exposure to external environment through vagina
Effacement- cervical thinning and shortening; part of Bishops score
Station- presenting part of Bishops score; measurement of fetal descent in cm with station 0 being at the level of an imaginary line at the level of the ischial spines, minus stations superior to the ischial spines, and plus stations inferior to the ischial spines
Pap smear- at age 21 or 3 years after first sexual intercourse; then every 3 years or new partner
C-Section- surgical removal of baby through incision in the abdomen—cesarean
Progesterone- fluctuating during menstrual cycle
Amniotic fluid- alkaline, clear, odorless fluid that surrounds the fetus
Trimester- first (0-12 weeks), second (13-27), third (28-birth)
Leukorrhea- white or yellow discharge of mucus from vagina; from hyperplasia of the vaginal mucosa and increases mucus production from the endocervial glands
Embryo- less than 8 weeks
Fetus-8+ weeks until birth
Non Stress test- for fetal well-being in third trimester or 28+ weeks; noninvasive; response of fetal heart rate to fetal movement; Doppler used to monitor fetal heart rate, monitor contractions; tracing strips over abdomen then client pushed button when she feels the fetus move; assess fetal status
Contraction stress test- for high-risk pregnancies (gestational diabetes mellitus, postterm pregnancy), used when criteria is not met after non stress test; assess fetal status
Biophysical profile- used when criteria is not met after non stress test; assess fetal status; real-time ultrasounds to visualize physical and physiological characteristics of the fetus and observe for fetal biophysical responses to stimuli
Amniotic fluid index- fetal well-being; part of biophysical profile; amount of amniotic fluid
Vertex- head down
Breech- butt or feet first
Corpusluteum- after ovulation; not fertilized will shrink and disappear; otherwise becomes embryo
Ptyalism- watery mouth before you throw up
Pica- craving unusual food
Fetal Fibronectin- vaginal swab between 24-34 weeks; related to inflammation of the placenta which can lead to preterm birth
Apgar- 1 and 5 minutes after birth to assess for abnormalities and intervene in necessary
Moro reflex- birth to 4 months; strike flat surface baby is laying on, or allowing the head and trunk in a semi sitting position to fall backward to an angle of at least 30 degrees. Arms and legs symmetrically extend and then abduct while fingers spread to form a “C”
Ballard Scale- assesses neuromuscular and physical maturity; six different ranges; each range assigned a value from -1 to 5; totals added to give maturity rating in weeks gestation (a score of 35 indicates 38 weeks of gestation)
Caput- localized swelling of the soft tissue of the scalp caused by pressure on the head during labor
Erythema toxicum- pink rash appearing on the body of a term newborn during the first three weeks. (Newborn rash). No treatment needed
Lanugo- fine downy hair; found on pinna, forehead, and shoulders
Acrocynosis- cyanotic hands and feet
Meconium- within first 24 hours after birth; babies first poop; bad stuff
Gastroschisis- stomach and intestines come out the abdomen but inside the skin
Oomphalacele- stomach and intestines on the outside of skin
Meningocele- contains dura mater and spinal fluid
Myelomeningocele- sac with dura matter, spinal fluid, and portion of spinal cord- spina bifida
Bulb syringe- suck out secretions from baby, such as vomit
VitaminK- prevent hemorrhagic disorders in babies because of lack of vitamin K in the GI; starts to produce about day 8 through formula; 0.5 to 1 mg IM into vastus lateralis within 1 hour of birth.
Erythromycin ophthalmic- prevent neonatorum or gonorrhea or chlamydia can cause blindness
Necrotizing enterocolitis- Inflammatory disease in the GI due to ischemia; results in short gut syndrome; removal of dead small bowels
Necrotizing osteochondritis- resulting from penetration of bone with a lancet during heel stick
FOC- Front occipital circumference- measured daily- across forehead top of the pinna and across the occipital area
Subinvolution- Uterus remains enlarged with continued lochial discharge and may result in postpartum hemorrhage- boggy uterus- higher than normal
Medications
Folic acid- for neurological development and the prevention of fetal neural tube defects. 600 mcg during pregnancy and 500 mcg during lactation. Toxic if mixed with methotrexate.
Foods: leafy green vegetables, dried peas and beans, seeds, and orange juice
Fortified Foods with Folic Acid: Breads, cereals
Zofran or ondansetron- for uncontrollable nausea and vomiting; control anxiety but not pain; cause dry mouth and sedation
Benadryl or diphenhydramine- sedative and antiemetic effect given during early labor; used for allergic responses, such as pruritus; antihistamine blocker
Vitamin B6 or pyridoxine- for hyperemesis gravidarum
Procardia or Nifedipine- for gestational hypertension; calcium channel blocker suppress contraction by blocking calcium from entering smooth muscle
Nursing considerations: monitor for headache, flushing, dizziness, and nausea; orthostatic
hypotension; do not give with magnesium sulfate
Client education: change position slowly; maintain hydration to decrease hypotension
Aldomet or methyldopa- for gestations hypertension
Terbutaline or brethine- Sub Q 0.25 mg; diminish uterine activity; tocolytic; relaxes the uterus prior to the provider’s attempt to replace of the uterus into the uterine cavity and uterus repositioning; no fundal massage; also used to relax uterus prior to D&C if placental expulsion with oxytocics is unsuccessful; for hyper stimulation of uterus;
Magnesium sulfate or lamicel- anticonvulsant; lowers BP and depresses CNS; may feel flush, hot, and sedated; do not give with Procardia; relaxes smooth muscle of uterus and blocks uterine activity by suppressing contractions; D/C if pulmonary edema, chest pain, shortness of breath, respiratory distress, audible wheezing or crackles, and productive cough with blood
Do not give if patient has vaginal bleeding, dilation of cervix greater than 6cm, chorioamnionitis, greater than 34 week of gestation, or acute fetal distress.
Education: report blurred vision, headache, nausea, vomiting, or difficulty breathing
Toxicity: no patellar deep tendon reflexes; urine output less than 30 mL/hr; respirations
less than 12/min; decreased level of consciousness; cardiac dysrhythmias
If suspected: D/C infusion, give calcium gluconate, and prepare for
respiratory or cardiac arrest
Cytotec or misoprostol- prostaglandin E1- used to soften and thin the cervix; can cause hypotension; uterine stimulant; controls postpartum hemorrhage; assess uterine tone and vaginal bleeding
Prostin, prepidil, cervidil or dinoprostone- prostaglandin E1- used to soften and thin cervix
Indocin or indomethacin- NSAID; suppresses preterm labor by blocking the production of prostaglandins; suppresses uterine contractions
Nursing Considerations- D/C if pulmonary edema, chest pain, shortness of breath, respiratory distress, wheezing or crackles, or blood tinged cough; do not give for more than 48 hours; only used in patient less than 32 weeks, check for postpartum hemorrhage related to reduced platelet aggregation; give with food to decrease GI upset; report blurred vision, headache, nausea, vomiting, or difficulty breathing
Methotrexate or Rheumatrex, MTX- used to dissolve pregnancy; inhibits cell division and embryo enlargement; avoid alcohol or vitamins containing folic acid to prevent toxic response
Pitocin or oxytocin- induction of labor; increases intensity and duration of contractions; administer 6-12 hours after prostaglandin; first confirm fetus is in birth canal at station 0; must be “piggyback” infused; use intrauterine pressure catheter to check frequency, duration, and intensity of contraction; assessmaternal BP, pulse, and respirations every 30 minutes; assess fetal heart rate and contraction pattern every 15 minutes; assess fluid intake and urinary output; use Bishop score before starting labor induction protocols; can cause hypertonic uterine contractions; firm contracted uterus prevents excessive bleeding and hemorrhage
Nursing considerations: check for water intoxication (lightheadedness, nausea, vomiting, headache, and malaise) can cause cerebral edema that cause seizures, coma, and death
Demerol or meperidine hydrochloride- opioid, CNS depressant; given IM or IV; IV recommended during labor
Vistaril or hydroxyzine- during labor to decrease nausea and anxiety; IM
Stadol or butorphanol- Opioid, CNS depressant; pain relief without respiratory depression to the mother or fetus; IM or IV
Nubain or nalbuphine- Opioid; CNS depressant; pain relief without respiratory depression to the mother or fetus; IM or IV
Phenergan or promethazine- Phenothiazine; sedation and antiemetic effect; used during labor
Reglan or metoclopramide- control nausea and anxiety; increase gastric emptying; increase breast milk production
Morphinesulfate or Duramorph- used in epidural blocks for local anesthetic
Motrin or ibuprofen- NSAID; for pain and swelling related to engorgement; take before breastfeeding; for fevers above 103.6F
Methergine or Methylergonovine maleate- Oxytocics; controls postpartum hemorrhage; uterine stimulant
Nursingconsiderations: Check uterine tone and vaginal bleeding; do not give if
hypertension; adverse reactions include hypertension, nausea, vomiting, and
headache
Hemabate or carboprosttromethamine- uterine stimulant; controls postpartum hemorrhage
Nursing considerations: assess uterine tone and vaginal bleeding; check for adverse
reactions including fever, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
RhoGAM- immune globulin at 28 weeks for patients who are Rh-Negative; suppresses immune response of clients; give within 72 hours of birth to prevent sensitization in future pregnancies; give extra 15 mL if fetal blood is detected in maternal circulation
Narcan or Nalaxone- reversal for opioid for respiratory depression
Valtrex, Zovirax, acyclovir- antiviral for viral encephalitis or herpes; must be older than 2 years old
Rocephin or ceftriaxone or third cephalosporin- for newborns suspected of sepsis; combined with azithromycin for gonorrhea
Clindamycin or cleocin- bacterial antibiotic; report watery, bloody diarrhea; do not breastfeed
Monistat or clotrimazole- treat candidiasis; OTC; important to get diagnosed first
Digoxin or lanoxin- safe during breastfeeding; improve contractibility and facilitate rate to control atrial fibrillation is present
MMR vaccine- Given between 12-15 months and 4-6 year old; 2 doses
Side effects: local reaction (fever, rash, swollen glands), joint pain for days to weeks,
anaphylaxis, thrombocytopenia
Considerations: pregnant, allergic to gelatin or neomycin, immunosuppression, recent
blood transfusion
Rubella Vaccine- part of MMR; given at 12-15 months and 4-6 years old; German measles
Hep B Vaccine- 3 doses given during childhood at birth, 1-2 months, and 6-18 months of age
EMLA- local anesthetic; applied 45 minutes to 1 hour before biopsy; eutectic mixture; Lidocaine
Dermoplast- spray anesthetic for perineal area for hemorrhoids
Amniotic Fluid
- essential for successful fetal growth and development
- Surrounds the embryo and fetus
- Space between the amnion and the embryo, houses the embryo and yolk sac, except in the area where the developing embryo attaches to the trophoblast via the umbilical cord
- Contained in thin membrane called amniotic sac
- “Bag of waters”
- Barrier of protection from ascending infection
- Constantly changing as fluid moves across the placental membrane
- First appears at 3 weeks about 30 mL then remains stable until pregnancy reaches term
- In late gestation
o Contains fetal urine and fetal lung secretions
o Fetal swallowing and absorption through placenta are primary ways for amniotic fluid
o Fetus swallows 600 mL every 4 hours and up to 400 mL flows from the fetal lungs every 24 hours
- Alkaline and contains antibacterial and other protective substances similar to those found in breast milk
- Contains albumin, uric acid, creatinine, lecithin, sphingomyelin, bilirubin, vernix, leukocytes, epithelial cells, and lanugo
- Decreased amniotic fluid created deformities
- Too much amniotic fluid creates club foot
- Ruptures before labor
- Normally clear and odorless
o Contains white specks (vernix) and fetal hair (lanugo)
- Discoloration means meconium passage or infection
Amniocentesis
- Invasive procedure that involves the removal of amniotic fluid
- Use ultrasound guide needle into maternal abdomen into amniotic sac
- In late pregnancy to determine fetal lung development
o Look for lecithin and sphingomyelin in shake test for ratio of 1:2 by 35 weeks
o Begins at 22 weeks
- Analyzed for chromosomal abnormalities, fetal lung development, infection and presence of bilirubin in Rh-sensitive pregnancies
- Complications
o Rupture of membranes, preterm labor, infection, fetal injury, and fetal death
Amnioscopy
- Visually inspects amniotic fluid though cervix and membranes to detect meconium staining
- Risk for membrane rupture
Breast Examination
- Breast self-examination
o 1 week following menstruation when breast tissue is nontender and smooth
o During menstrual cycle breast are lumpy
o Done monthly to perfect technique and notice changes
o 75% of breast cancers are discovered by women themselves
o Teaching
Inspect for color, contour, shape, and size
• Inspect for dimpling or puckering of the skin
• Inspect for change in nipple direction and redness, rash, or swelling
Repeat with arms slightly raised above head
Inspect and palpate the nipple
• Gently squeeze the nipple and look for discharge
o only a concern if spontaneous
Palpate breast and axillae
• Lay back and place a pillow under each shoulder for the side you are palpating
• Use finger pads of three fingers, use dime sized circular motions and apply three different levels of pressure
Move around the breast in up and down patterns checking the entire breast area until only ribs are left
o Finds tumors when they are the size of a walnut
- Clinical Breast Examinations
o Annually by doctor or at least every 3 years from women 18-39 years old and every year after 40 years old
o Inflammatory breast cancer is rare and aggressive that causes swelling and redness and does not show up on a mammography
- Mammography
o Aid in early diagnosis of breast cancer
o Small dose of ionizing radiation allows for identification of small breast tissue abnormalities
o Digital mammography
Full field digital mammography
Coverts x-rays to electrical signals similar to those found in digital camera
For high risk breast cancer patients
o Computer aided detection (CAD)- highlights areas of increased density, masses, and calcification
Contraceptive methods
- Medication-free
o Natural Family Planning- identify fertile time and avoid intercourse during that time- for Roman Catholic
o Fertility Awareness Method- identify fertile time and use abstinence or other contraceptive forms during this time- can take time to know when you are fertile
o Temperature increases during ovulation by 0.5-1F
o Effectiveness- 75%
- Coitus interruptus
o Withdrawal method- take penis out of vagina before ejaculation of male
o Effectiveness- 71%
- Lactational amenorrhea
o Breastfeeding- used in underdeveloped countries
o Ovulate but not menstruate, cannot menstruate after birth, and infant must be less than 6 months of age
o Effectiveness- 98%
- Abstinence
o No vaginal intercourse- requires commitment and self-control
o 100% effective
- Barrier methods
o Diaphragm
Latex dome shaped barrier with spring rim that resembles ½ tennis ball filled with spermicide
Covers cervix
Must be fitted by doctor
Not best choice for adolescents
Can be in place up to 6 hours, must stay in place for 6 hours after sex, add extra spermicide if 6 hours is not up yet and sex is done again
Replace every 2 years, weight changes, birth, or second term abortion
Side effects
• Allergic reaction, risk for UTI, interfere with emptying the bladder, TSS, Staph infection
Effectiveness- 84%
o Cervical Cap
Thimble shaped latex barrier over cervix and vaginal fornix filled with spermacide
Must be exactly over cervix and checked for placement by doctor after 1 week
Side effects
• Cervical irritation or erosion, not for women with HIV, allergic reaction, high failure rate
Effectiveness
• 74%
o Condoms
Latex, polyurethane or natural membrane
Prevent HIV and STDs
Natural membranes do not offer protection against HIV or STDs because of small pore that permit passage of viruses
Male condoms
• Oldest form
• Over erect penis for vaginal, oral, or anal contact
• Effectiveness- 85%
Female Condoms
• One size fits all/vaginal sheath
o Spermicides
Gels, creams, films, and suppositories inserted into the vagina
Chemical barrier to kills sperm before it enters the cervix
Not for patients with HIV
Films need 15 minutes to become effective
Side effects
• Acute cervicitis, cervical irritation
Effectiveness
• 71%
o Contraceptive sponge
Soft, round, disposable polyurethane device that fits over cervix- one size fits all- permeated with spermicide
One side if concave to fit the cervix and the other side if woven loop to help with removal
Side effects
• Do not leave in for more than 30 hours and this includes the 6 hours waiting period after intercourse due to the risk for TSS
Effectiveness
• 84-87% effective
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Hormonal methods
o Oral Contraceptives
The Pill
Taken until the perimenopausal years
Estrogen- release of follicle stimulating hormone from anterior pituitary
• When kept low the ovarian follicle is unable to form and ovulation is prevented
Progestin- can be used alone or with estrogen
• Block ovulation
• Create thickened cervical mucus to produce a hostile environment for sperm and causes endometrial atrophy
• Block egg implantation and decrease penetration of sperm and ovum transport
Estrogen + progestin = block luteinizing hormone surge required for ovulation
Mono-phasic- same dose of estrogen and progestin for 21 days
Biphasic- same amount of estrogen but increase progestin in last 11 days
Triphasic- mimic natural cycle, provides varied levels of estrogen and progestin
• Reduced breakthrough bleeding
Must be seen by doctor 3 months after medication administration
Used in perimenopausal period for hot flashes and vaginal dryness
Contraindications
• Hypertension, migraines, epilepsy, jaundice, gallbladder disease, sickle cell disease, prolonged immobilization
• Smokers, older than 35, uterine bleeding, diabetes, pulmonary embolisms, ischemic heart, stroke, headaches, breast cancer, liver impairment, pregnancy, cholecystitis
Benefits
• Decreases fibrocystic breast disease, iron anemia, colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer, dysmenorrhea, premenstrual dysphoric syndrome, acute pelvic inflammatory disease, ectopic pregnancy, and osteoporosis
Side effects
• During the first three months
• Scanty periods, breakthrough bleeding, nausea, breast tenderness, headaches, weight gain
Effectiveness- 95%
ACHES- cardiovascular, liver, gallbladder, or thromboembolic events from estrogen
• A- Abdominal pain (problem with liver or gall bladder)
• C- Chest pain or shortness of breath (clot in lungs or heart)
• H- Headaches (hypertension, CVA)
• E- Eye problems (Hypertension, CVA)
• S- Severe leg pain (thromboembolism)
Patient must have 2 regular menstrual cycles before starting
o Low dose progestin only contraceptive pills
Mini pill
No estrogen
Thickens cervical mucus and endometrial atrophy
Can be used in lactating women
Side effects
• Irregular menses, increases number of persistent ovarian follicles
Effectiveness- 92%
o Transdermal Patch
On abdomen, buttock, upper outer arm, or upper torso
Replaced every week for 3 weeks, then left off for withdrawal bleed
Do not put on breast
Low estrogen and progestin
Side effects
• Same warnings as oral combination pill
• Higher concentration of hormones=increased side effects
Effectiveness- 99% for those who weight under 198 pounds
o Vaginal Ring
Estrogen and progestin inserted deep in vaginal by 5th day of menstrual cycle then left in for 3 weeks. 4th week for withdrawal bleeding. Insert ring same day of the following week
Side effects
• Vaginitis, vaginal discomfort, and vaginal infections
• Not for those with cystocele, rectocele, or uterine prolapse
Effectiveness- 98%
o Emergency contraception
Hormonal method
• The morning after pill
• Estrogen and progestin taken within 72 hours after sex, second dose 12 hours after initial dose
• Nausea and vomiting is common; take antiemetic 1 hour before first dose
• 98.9% effective if used correctly
IUD method
• Copper IUD inserted within 5 days of unprotected sex
• No recommended for rapes or STD risks
• Side effects
o Nausea, vomiting, vaginal bleeding
• Effectiveness-99-100%
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Injectable
o Depo-provera, Depo-subQprovera 104
Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate)- progestin only- long term
Last 3 months
IM (Deltoid or gluteal muscle) of 150mg or SubQ (anterior thigh or abdomen) of 104mg
• Never massage
First injection should be within first 5 days of menstruation
Make sure patient is not pregnant
Suppresses ovulation and altering cervical environment, thins endometrium
Ovulation restored after 10 months of D/C medication
Side effects
• Irregular bleeding, spotting during first few months, amenorrhea after 6 months, weight gain, depression, headaches, and breast tenderness
• Reduced bone mineral in IM but not Sub Q
Effectiveness- 98-99%
- Subdermal
o Implanon- single rod implant on inner side of woman’s upper arm
o Contains progestin
o Suppress ovulation and create thickening of cervical mucus
o Antiepileptic agent decrease effectiveness
o Good for 3 years
o Side effects
Irregular bleeding, amenorrhea, emotional lability, weight increase, headache, depression, dysmenorrhea, and acne
o Effectiveness 100%
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Intrauterine
o T-shaped, string hangs out the cervix into the vagina
o Inserted during menses to ensure there is no pregnancy, or after childbirth, or first trimester abortion
o Decrease chances of endometrial cancer
o PAINS
Peroid late= pregnancy
Abdominal pain=infection
Infection=vaginal discharge
Not feeling well, fever, chills= infection
String missing, shorter or longer= IUD expelled
o Mirena
Progestin
Replaced every 5 years
Side effects: amenorrhea, pelvic infections
o Paragard
No hormones, just copper
Replaced every 10 years
Side effects: pelvic infections, heavy bleeding
o Effectiveness: 98-99%
- Sterilization
o Permanent and irreversible
o For males and females
o Females
Bilateral tubal ligation- tying the tubes
Interruption in the patency of the fallopian tubes
During C-section or first 48 hours after vaginal birth or as an outpatient procedure under general anesthesia
Small incision, bring tubes through and cauterize or tie=Minilaparotomy
Clips or tings or destroys a portion of tubes with electrocoagulation=laparoscope
Increased rate for ectopic pregnancy
Microinserts in opening of tubes, allow for scar tissue to form causing blockage= hysteroscopic tubal ligation
• Hysterosalpingram- dye test- after 3 months to detect blockage
• Must use back up birth control until blockage is detected
Side effects
• Infection, hemorrhage, blood vessel injury, damage to adjacent organs, complication from anesthesia
Effectiveness- 96.3%
o
o
o
o
o
o
o Males
Vasectomy
• Small incision in the scrotum, vas deferens is cauterized, clipped, or cut to block sperm from seminal fluid
• Should rest, and apply ice to scrotum, wear tight underwear for support
o Must have semen analyzed weekly until 2 specimen show no sperm and have it checked every few years after
• Side effects
o Infection, hematoma, excessive pain, swelling
• Effectiveness- 99%
Danger Signs of pregnancy
- Gush of fluid from the vagina (rupture of amniotic fluid) prior to 37 weeks of gestation
- Vaginal bleeding (placental problems such as abruption or previa)
- Abdominal pain (premature labor, abruptio placentae, or ectopic pregnancy)
- Changes in fetal activity (decreased fetal movement may indicate fetal distress
- Persistent vomiting (hyperemesis gravidarum)
- Severe headaches (gestational hypertension)
- Elevated temperature (infection)
- Dysuria (urinary tract infection)
- Blurred vision (gestational hypertension)
- Edema of face and hands (gestational hypertension)
- Epigastric pain (gestational hypertension)
- Concurrent occurrence of flushed dry skin, fruity breath, rapid breathing, increased thirst andurination, and headache (hyperglycemia)
- Concurrent occurrence of clammy pale skin, weakness, tremors, irritability, and
- lightheadedness (hypoglycemia)
Discomforts during Pregnancy
- Nausea and vomiting in the first trimester
o Eat crackers or dry toast 30 minutes to 1 hour before rising
o Avoid empty stomach, spicy food, greasy food, or gassy food
o Drink plenty of fluids
- Breast tenderness during first trimester
o Wear a bra for extra support
- Urinary frequency during the first and third trimester
o Empty bladder frequently
o Decrease fluid intake before bed, use pads
o Kegel Exercises
- UTI because of renal changes and vaginal flora becoming alkaline
- Fatigue during first and third trimester
- Heartburn during second and third trimester due to stomach being displaced by growing uterus and slowing the GI mobility and digestion brought about by increasing progesterone levels
o Eat small frequent meals
o Sit up right for 30 minutes after meals
- Constipation during second and third trimester
o Drink lots of fluids and eat fiber and exercise
- Hemorrhoids during second and third trimester
o Warm sitz bath, witch hazel, topical ointments
- Backaches during second and third trimester
o Exercise, pelvic tilts, body mechanics and side-lying position
- Shortness of breath and dyspnea from growing uterus
o Good posture, sleep with extra pillows
- Leg cramps during third trimester from compressed lower extremity nerves and blood vessels
o Keep affected leg straight, dorsiflex foot, apply heat, massage
- Varicose veins and lower leg edema during second and third trimester
o Client should rest, elevate legs, avoid tight clothing, wear TEDs, do not sit or stand for long periods, do not cross legs, sleep on left lateral position
- Gingivitis, nasal stuffiness, epistaxis (Nosebleed) from high estrogen levels causing increased vascularity and proliferation of connective tissue
- Braxton Hicks contractions can start in first trimester and can increase in intensity and frequency into third trimester
o Change position and walk
- Supine hypotension when woman lays on her back and weight of gravid uterus compresses vena cava reducing blood supply to fetus
o Lightheadedness or faint
o Must lay on side of semi-sitting with knees flexed
Dysmenorrhea
- painful menstruation, typically involving abdominal cramps
- Heavy menstrual flow caused by gonorrhea
- Can be alleviated by combined oral contraceptive by decreasing menstrual flow and menstrual cramps
Exercise during pregnancy
- yields positive benefits and should consist of 30 min of moderateexercise (walking or swimming)
Fetal effects of maternal alcohol and drug use
- Neonatal Substance Withdrawal
o From maternal use of alcohol or drugs
Cause neurobehavioral changes, and fetal withdrawal after birth
Substance withdrawal includes drugs, alcohol, tobacco, and prescription drugs
o Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)
Chronic or periodic intake on alcohol during pregnancy
• Feeding problems, CNS dysfunction, hyperactivity, language abnormalities, future substance use, delayed growth and development, poor maternal-newborn bonding
o Assessment
CNS- abstinence syndrome
• Increased wakefulness, highpitched, shrill cry, irritability, tremors, hyperactive with increased Moro reflex, increased deep tendon reflex, increased muscle tone, abrasions, and excoriations on face and knees, and convulsions
• Metabolic, vasomotor, and respiratory findings: nasal congestions with flaring, frequent yawning, skin mottling, tachypnea 60/min+, sweating, and temperature +99F
• GI- poor feeding, regurgitation, diarrhea, uncoordinated and constant sucking
Opiate withdrawal
• Last for 2-3 weeks
• Rapid changes in mood, hypersensitivity to stimuli, dehydration, and poort weight gain
Heroin withdrawal
• Low birth weight, decreased Moro reflex, hypothermia/hyperthermia
Methadone withdrawal
• Seizures, disturbed sleep, high birth weight, risk for SIDS
Marijuana withdrawal
• Preterm birth, meconium staining
Amphetamine withdrawal
• Preterm, drowsy, jittery, disturbed sleep, respiratory distress, frequent infections, poor weight gain, emotional disturbances and delayed growth and development
FAS
• Physical abnormities: eyes with Epicanthal folds, strabismus, ptosis, mouth with poor suck, small teeth, cleft lip or palate
• Deaf
• Abnormal palmar creases and irregular hair
• Vital organ abnormalities: heart defects (atrial ventricular septal defects, tetralogy of Fallot, and patent-ductus arteriosus)
• Developmental delays and neurological abnormalities
• Prenatal and postnatal growth retardation
• Sleep disturbances
Tobacco
• Premature, low birth weight, increased risk for SIDS, increased risk for bronchitis, pneumonia, and developmental delays
Fetal Growth and development
- Pre-embryonic period
o First 2 weeks after conception
o Rapid cellular multiplication, cell differentiation, and embryonic membranes and primary germ layers
o Cephalocaudal, proximal to distal
- Embryonic period
o Critial
o Cleavage of zygote, blastogenesis, and development of nervous system, cardiovascular system, and major internal and external structures
o 2 weeks after LMP
o Third week of fertilization and continues until end of 8th week
Makes organs
- Fetal Period
o Begins 9th week
o Recognizable human being
o Rapid body growth and differentiation of tissues, organs, and systems
o During last 12 weeks: fetal weight triples and body length doubles
Fetal Movement
- Fetal well-being
- Should be recorded daily
o Count fetal activity two/three times a day for 60 minutes
o Less than 3 per hour or movements the cease for 12 hours call the doctor
Can mean fetal distress
- Fetal heartbeat, breathing, and activity
o Tested during nonstress test in third trimester or contraction stress test
- Start between 16 and 20 weeks
Fundal Height
- In cm from the pubic symphysis to the top of the uterine fundus (between 18-32 weeks)
- Used to determine delivery date
o Measurement in relation to gestational weeks equals deliver date
- Decreased one fingerbreadth or 1 cm per day after delivery
- After birth located 1 cm above umbilicus
o Within 24 hours should be 1-2cm lower
o By 6th day should be halfway between pubic symphysis and umbilicus
o By 10th day should not be felt
- Needs to be assessed every 8 hours after birth
GTPAL
- Gravidity
- Term Births (38 weeks or more)
- Preterm Births (from viability up to 37 weeks)
- Abortions/miscarriages (prior to viability)
- Living Children
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
- Ideal blood glucose level during pregnancy should be 70-110
- Can disappear weeks after birth
- 50% of women will have diabetes within 5 years
- Increased risks for
o Spontaneous abortion, infections, hydramnios, ketoacidosis, hypoglycemia, and hyperglycemia
- Risk factors
o Obesity, older than 25 years old, family history, previous delivery was large or stillborn
- Assessments
o Hypoglycemia- nervous, headache, weakness, irritability, hunger, blurred vision, tingling
o Hyperglycemia- thirst, nausea, abdominal pain, frequent urination, flush/dry skin, fruity breath
- Lab test
o Urinalysis with glycosuria
o Glucose tolerance test at 24-28 weeks
o Ketones in urine
- Dx procedures
o Biophysical, amniocentesis, and nonstress test
Hormonal influence during pregnancy
- Can cause nausea and vomiting
- Decreased attention span, poor concentration, memory lapse, difficulty sleeping
- Emotional lability during maternal adaptation
o Mood changes, irritability, tearfulness, anger, joy and cheerfulness
- Can cause postpartum depression after birth from decreased estrogen and progesterone levels
- During 1st trimester, increased progesterone creates increased fatigue and tiredness
- hCG is hormone measured in maternal serum related to the number of viable molar cells
o usually only present if woman is pregnant
- increased glomerular filtration rate and renal plasma flow
- breast tenderness
- increased UTI because of hydoureter, decreased peristalsis, bladder distention, and incomplete emptying
HPV
- papanicolaou (Pap) test to detect
- associated with tattooing and body piercing
- some strains of the virus can cause cervical dysplasia
- Visible wart-like growths in genital area
- Primary risk factor for cervical cancer
- No treatment
- Vaccine (Gardasil) to prevent type from causing cervical cancer, and lesions on the cervix, vulva, and vagina
o For females from 9-26 years old
o Three doses 2nd dose 2 months after first dose 3rd dose 6 months after first dose
o Must have routine cervical screening
- Circumcision=less change of HPV
-
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)
- Growth rate does not meet expected norms
- High-risk pergnancy
- Altered acid-base balance of fetus
- Indication for CST
- Risk for preterm birth with hyperemesis gravidarum
- Common in mothers
o on crack or cocaine
o with rubella
o with herpes
o with significant maternal weight loss
o with decreased fetal oxygen transport from iron-deficiency anemia
o preterm premature rupture of the membranes or placenta previa
o preeclampsia from mild to severe
o with multiple gestations
o pneumonia
o exacerbations that cause hypoxia and decreased uterine blood flow
- In these cases do not use Tocolytics
- Detected with Doppler ultrasounds blood flow studies or Umbilical Velocimetry
-
-
- Detected with biophysical profile
o Score 0- 4/10
o Reduced amniotic fluid
- Can develop hypoglycemia from poor intrauterine nourishment
Levels of prevention
- Primary
o Prevent disease
o Vaccinations
o Handwashing
- Secondary
o Early detection and prompt treatment
o Stop the spread
o Screening and isolating sick children
- Tertiary
o Restore health and highest function state
o Keeping a sick child home, giving fluids, rest, and antibiotics until health is restored
Macrosomia
- causing excessive fetal growth from:
o hyperglycemia
insulin does not cross the placenta
hyperinsulinemia develops and acts as a growth hormone
o mother older than 35
o excessive weight gain by mother
o Obesity (BMI greater than 30 kg/m)
- can cause dysfunctional labor, anaphylactoid syndrome (amniotic fluid embolism), birth trauma
o leading cause of uterine hypotonia
o shoulder dystocia
o cephalopelvic disproportion- unsuccessful vaginal birth because they baby is too big
- detected by increased fundal height
- occurs in 20-25% of diabetic pregnancies
- higher risk for complications
- birth weight is above 90th percentile on growth chart
Maternal serum alpha fetoprotein (MSAFP)
- Screening occurs between 15 to 22 weeks of gestation.
- Used to rule out Down syndrome (low level)
o Chromosomal disorders, gestational trophoblastic disease or hydatidiform mole
- neural tube defects (high level)
o anencephaly, spina bifida, omphalocele
- Protein produced by fetus
- Referred to quad core marker screening, genetic counseling, ultrasound, and amniocentesis for abnormal findings
Nagele’s Rule
- Take the first day of the woman’s last menstrual cycle, subtract 3 months, and then add 7 days and 1 year, adjusting for the year as necessary
- To detect the estimated date of delivery
Placenta Abruption (Abruptio Placenta)
- Premature separation of the placenta from the uterus can be partial or complete detachment
- Occurs at 20 weeks or in the third trimester
- Leading cause of maternal and fetal death
- Coagulation defect, like DIC can cause this as well
- Risk factors
o Maternal hypertension, blunt abdominal trauma, cocaine use, previous cases of abruptio placenta, smoking, premature rupture of membranes, multifetal pregnancy
- Assess
o Subjective
Uterine pain and dark red vaginal bleeding
o Objective
Uterine tenderness, contractions, fetal distress, hypovolemic shock
o Labs
Decreased Hgb and Hct, decreased coagulation factors, clotting defects (DIC), Kleihauer-Betke test (detect fetal blood in maternal circulation)
o Dx Px
Ultrasound for fetal well-being and placental assessment
Biophysical profile
- Patient centered care
o Nursing action
Palpate uterus for tenderness
Assess FHR
Administer IV fluids and possible blood products
• Corticosteroids to promote fetal lung maturity
Administer oxygen 8-10 L/min via face mask
o Client education
Emotional support
Placenta Previa
- Placental abnormally implants in the lower segment of the uterus near or over the uterus instead of the fundus
o Results in bleeding during the third trimester as cervix begins to dilate an efface
- Three categories
o Complete or total- completely covers cervix
o Incomplete or partial- only partial covers cervix
o Marginal or low-lying—placenta is attached in the lower uterine segment but does not touch the cervix
- Risk factors
o Previous cases, uterine scaring (from c-section, curettage, endometritis), mother older than 35-40 years old, multifetal gestation, closely spaced pregnancies, and smoking
- Assessment
o Subjective
Painless, bright red vaginal bleeding during second or third trimester
o Objective
Uterus soft, relaxed and nontender with normal tone
Fundal height greater then expected
Fetus breech, oblique, or transverse
Assess FHR
Assess maternal vital signs
Decrease urinary output better indicator of blood loss
o Lab test
Hgb and Hct, CBC, blood type, Rh factor, coagulation profile, Kleihauer-Betke test
o Dx PX
Transabdominal or transvaginal ultrasound, fetal monitoring
- Patient centered care
o Nursing action
Assess for bleeding, leakage, or contractions
Fundal height
Perform Leopold maneuvers (fetal position and presentation)
Give IV, corticosteroid (Betamethasone- to promote fetal lung maturity for c-sections)
Have oxygen available
Preconception care
- Avoid all OTC, supplements, and prescriptions
- No alcohol, or tobacco
- No substance use
- Educate
o Physical and emotional changes and interventions for relief
o S/S of complications to report
o Birthing options to enhance birthing process
- Maternal adaptation
o Emotional lability- mood changes
o Feelings of ambivalence- normal in early pregnancy and goes away by third trimester
Preeclampsia (Gestational hypertension)
- High blood pressure
- Begins after 20th week of pregnancy
- BP 140/90 mm Hg every 4-6 hours, within 1 week
- Mild
o proteinuria greater than 1+
o Headaches, irritability, possible edema
- Severe
o BP over 160/100 mm Hg
o Proteinuria greater than 3+
o Oliguria, creatinine greater than 1.2 mg/dL, headaches, blurred vision, hyperreflexia, edema, hepatic dysfunction, pain in upper right quadrant, thrombocytopenia
o Eclampsia
Onset of seizures or coma
Headache, severe stomach pain, hyperreflexia, hemoconcentration=convulsions
- HELLP Syndrome
o H- hemolysis causing anemia and jaundice
o EL- elevated liver enzymes causing elevated ALT or AST, gastric pain, and nausea and vomiting
o EP- low platelets (less than 100,000/mm) causing thrombocytopenia, abnormal bleeding and clotting, bleeding gums, petechiae, DIC
- Associated with placental abruption, kidney failure, hepatic rupture, preterm birth, and fetal/maternal death
- Risk factors
o Mother younger than 20 or older than 40 years old
o First pregnancy
o Obese
o Multigestation
o Chronic renal disease, hypertension
o Family Hx of preeclampsia
o Diabetes
o Rh incompatible
o Molar pregnancy, previous Hx of hypertension
- Assessment
o Subjective
Severe headaches, nausea, blurred vision, flashed of lights or dots before the eyes
o Objective
Hypertension, proteinuria, edema, vomiting, oliguria, hyperreflexia, scotoma, stomach pain, RUQ pain, dyspnea, diminished breath sounds, seizures, jaundice
o Labs
Increased liver enzymes (LDH, AST), creatinine, plasma uric acid
Thrombocytopenia, decreased Hgb, hyperbilirubinemia
o Dx PX
Dipstick urine test for proteinuria
24 hr urine collection for protein and creatinine
Non stress test, contraction test, biophysical profile, and serial ultrasounds for fetal status
Doppler blood flow study for fetal status
- Patient centered care
o Nursing care
Assess LOC, oxygen stats, urine output, daily weights, vital signs, lateral positioning, NST and daily kick counts, I&O
o Medications
Antihypertensive
• Methyldopa (Aldomet), Nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia), Hydralazine (Apresoline, Neopresol), Labetalol hydrochloride (Normodyne, Trandate)
• No ACE or ARBS
Anticonvulsant
• Magnesium sulfate for prophylaxis or Tx to lower BP and depress the CNS
Nursing considerations
• IV control device to maintain regular flow
• May feel flush, hot, or sedation with magnesium sulfate
• Check BP, pulse, respirations, and deep-tendon reflex, LOC, output, headache, visual disturbances, stomach pain, uterine contractions, FHR and activity
• Fluid restriction of 100-125 mL/hr
o With output of 30 mL/hr or greater
• Check for magnesium sulfate toxicity
o Absence of patellar reflex, less than 30 mL/hr output, less than 12 respirations/min, decreased LOC, cardiac dysrhythmia
o If suspected
D/C give CALCIUM GLUCONATE
Discharge instructions
• Best rest on side, avoid high sodium foods, no alcohol, no caffeine, drink 8 glasses/day, avoid stimuli to avoid seizures
Nutrition during pregnancy
- Recommended weight gain 11.2-15.9 kg (25-35 lbs)
- Underweight to gain 28-40 pounds
- Overweight to gain 15-25 pounds
- Subjective/objective
o Journal of client’s food habits, eating patterns, and cravings
o Nutrition related questionnaires
o Client’s weight on first prenatal visit and follow-ups
o Hgb and iron levels
- 340 calories/day during 2nd trimester
- 452 calories/day during 3rd trimester
- Increase by 330 calories/day during 1st 6 months
- Increase by 400 calories/day during 2nd 6 months
- Increase protein
o 600 mcg folic acid during pregnancy
o 500 mcg folic acid during lactation
- Increase Iron
o Take with vitamin C
- Increase calcium
o 1000 mg/day for pregnant
- 2-3L fluid of water, fruit juice and milk
- Limit caffeine to 300 mg/day
o Can increase risk for spontaneous abortion or FIUGR
Prenatal Labs
- Blood draw:
o Patient’s blood group, Rh factor, antibody screening, Rapid Plasma Reagent, Venereal disease screen (syphilis), test for hepatitis B, CBC with hemoglobin, hematocrit, CBC with differential, HIV, sickle cells screen, PPD
- Pap Smear
o Test for cervical cancer
Preterm labor
- Pink-stained vaginal discharge, uterine contraction becoming regular, cervical dilation and effacement
Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy
- First trimester
o Spontaneous abortion
Vaginal bleeding, uterine cramping, and partial or complete expulsion of product of conception
o Ectopic pregnancy
Abrupt unilateral lower quadrant abdominal pain without or with vaginal bleeding
- Second trimester
o Gestational trophoblastic disease
Uterine size increasing abnormally fast, abnormally high levels of hCG, nausea and increased emesis, no fetus present on ultrasound, and scant or profuse dark brown or red vaginal bleeding
- Third Trimester
o Placenta previa
Painless vaginal bleeding
o Abruptio placenta
Vaginal bleeding, sharp pain, and tender rigid uterus
- Other causes of bleeding
o Premature dilation of the cervix
Painless bleeding with cervical dilation leading to fetal expulsion
o Preterm Labor
Pink-stained vaginal discharge, uterine contractions becoming regular, cervical dilation and effacement
Medications
NSAIDs
- Indomethacin
o Suppresses preterm labor by blocking the production of prostaglandins
o Blocks uterine contractions
o Nursing Considerations
D/C if signs of pulmonary edema (chest pain, SOB, respiratory distress, audible wheezing, crackles, blood tinged sputum)
Do not use for more than 48 Hr
Only if fetus is more than 32 weeks
Check for hemorrhage causing platelet aggregation
Give with food to decreased GI upset
Report blurred vision, headache, nausea, vomiting, or difficulty breathing
o Given for HSG procedures 30 minutes to 1 hour before
Acetaminophen
- Tylenol
- Nonopioid analgesia
- For pain and discomfort
- Can be given for circumcision
- For fussy newborns or after circumcision for 24-48 hours
- Can interfere with Oral Contraceptives
- Toxic to liver
Aspirin
- Increases bleeding tendencies
- Do not take if taking anticoagulants
- Can cause hyperbilirubinemia
- Acts as an antiplatelet agent and prevents blood from clotting
Pitocin
- Oxytocin
- Induce uterine contractions
- Cannot stop contractions once started
- D/C if
o Fetal Heart rate is less than 110/min for 10 minutes
o Late deceleration of FHR causing maternal hypotension, abruptio placentae, or uterine hyperstimulation
o Variable deceleration of FHR
- Lower dose for cervical ripening
- Indications
o Must be 39 weeks
o Bishop score of greater then 8
o Greater than 10 for nulliparous
- Clinical presentation
o Postterm pregnancy 42 weeks or greater
o Prolonged or difficult labor (dystocia) from inadequate uterine contractions
o Prolonged rupture of membranes
- Preparation for Oxytocin
o Fetus must be engaged in birth canal at minimum of station 0
o Must be given piggyback
o Intrauterine pressure catheter used to monitor frequency, duration, and intensity of contractions
o Assess maternal blood pressure, pulse, and respirations every 30 minutes and with change in dose
o Monitor FHR and contraction pattern every 15 minutes and change in dose
o Bishop score needs to be obtained before starting labor inductions
- Ongoing care
o Increased oxytocin until desired contraction pattern is obtained then maintain the dose if: contraction frequency is 2-3 min, duration is 60-90 seconds, intensity is 40-90 mm Hg, uterine resting tone is 10-15 mm Hg, cervical dilation is 1 cm/hr, and FHR is between 110-160/min
o D/C if: contraction frequency is more than every 2 min, duration is longer than 90 seconds, intensity is greater then 90 mm Hg, uterine resting tone is greater than 20 mm Hg, and no relaxation of uterus between contractions
o Complications
Abnormal baseline less than 110 or greater than 160/min, loss of variability, late or prolonged decelerations
Betamethasone
- Glucocorticoid
- For:
o Administered for 24 hour period before delivery to promote fetal lung development and increase surfactant in attempt to prevent RDA
Two IM injections 24 hours apart between 24-31 weeks gestation to reduce risk of perinatal death, or respiratory distress syndrome
o Usually for anticipated C-section
- Education
o Keep parents informed of care for preterm newborn
o How to recognize signs of pulmonary edema chest pain, SOB, crackles
- Nursing considerations
o Administer into deep gluteal muscle 24 and 48 hours before birth of preterm neonate
o Monitor for pulmonary edema, and hyperglycemia, and heart rate changes
Hemabate or carboprosttromethamine
- Uterine stimulant
- Controls postpartum hemorrhage
- Nursing considerations
o Assess uterine tone and vaginal bleeding
Adverse reactions: fever, chills, headache, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
PRENATAL ASSESSMENT
THERAPEUTIC COMMUNICATION
[Show More]



.png)