Finance > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Financial management - Lecture eight 2023 Update (All)
Financial management - Lecture eight 2023 Update
Document Content and Description Below
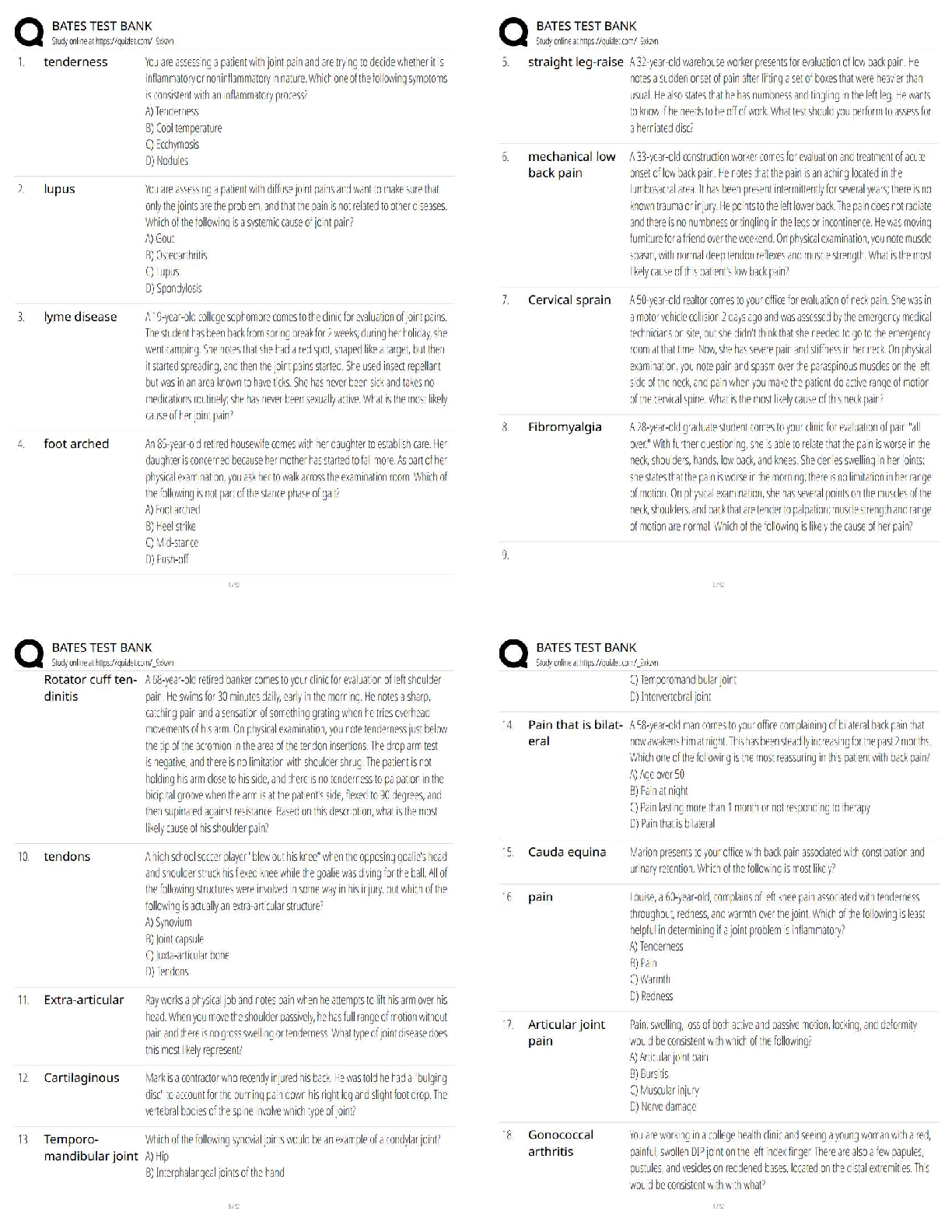
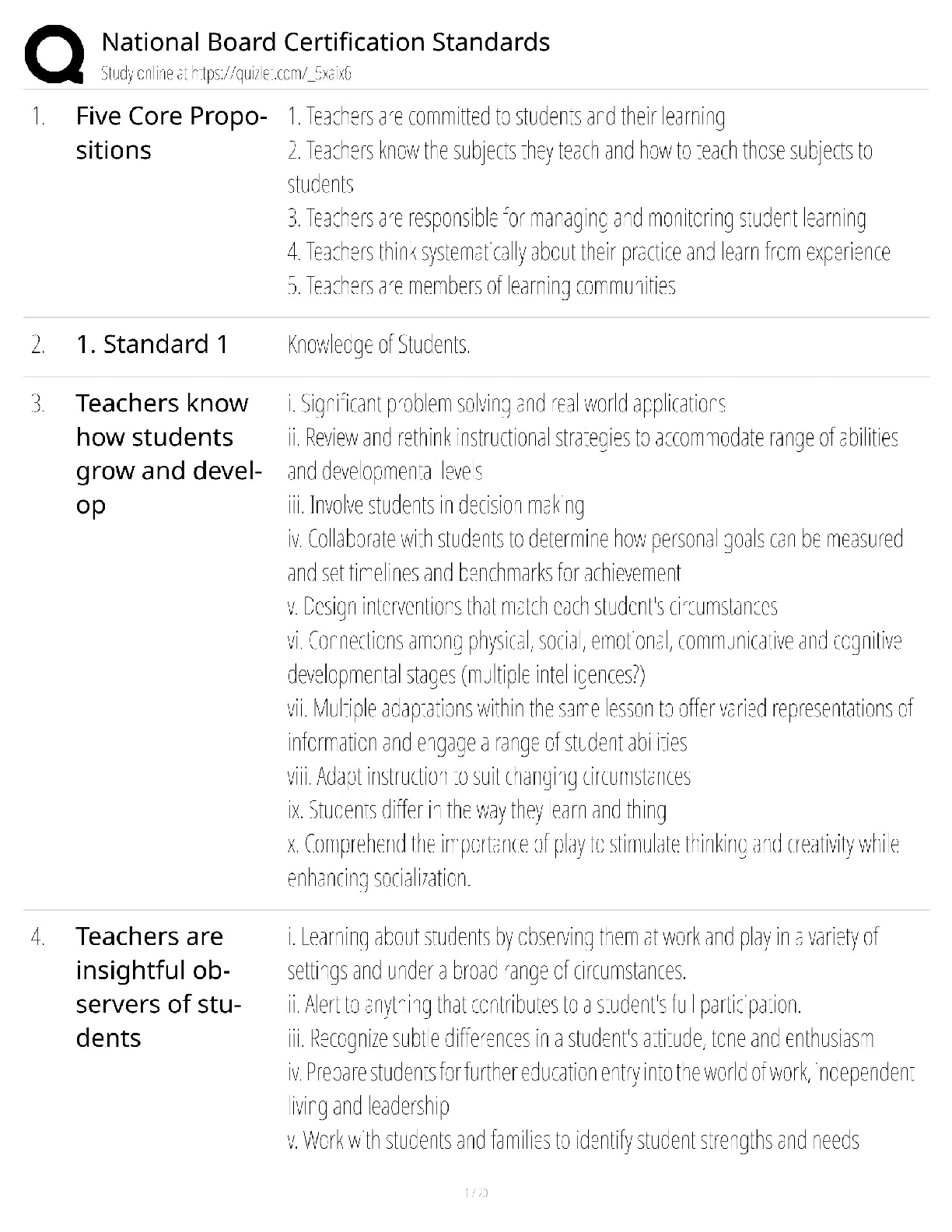
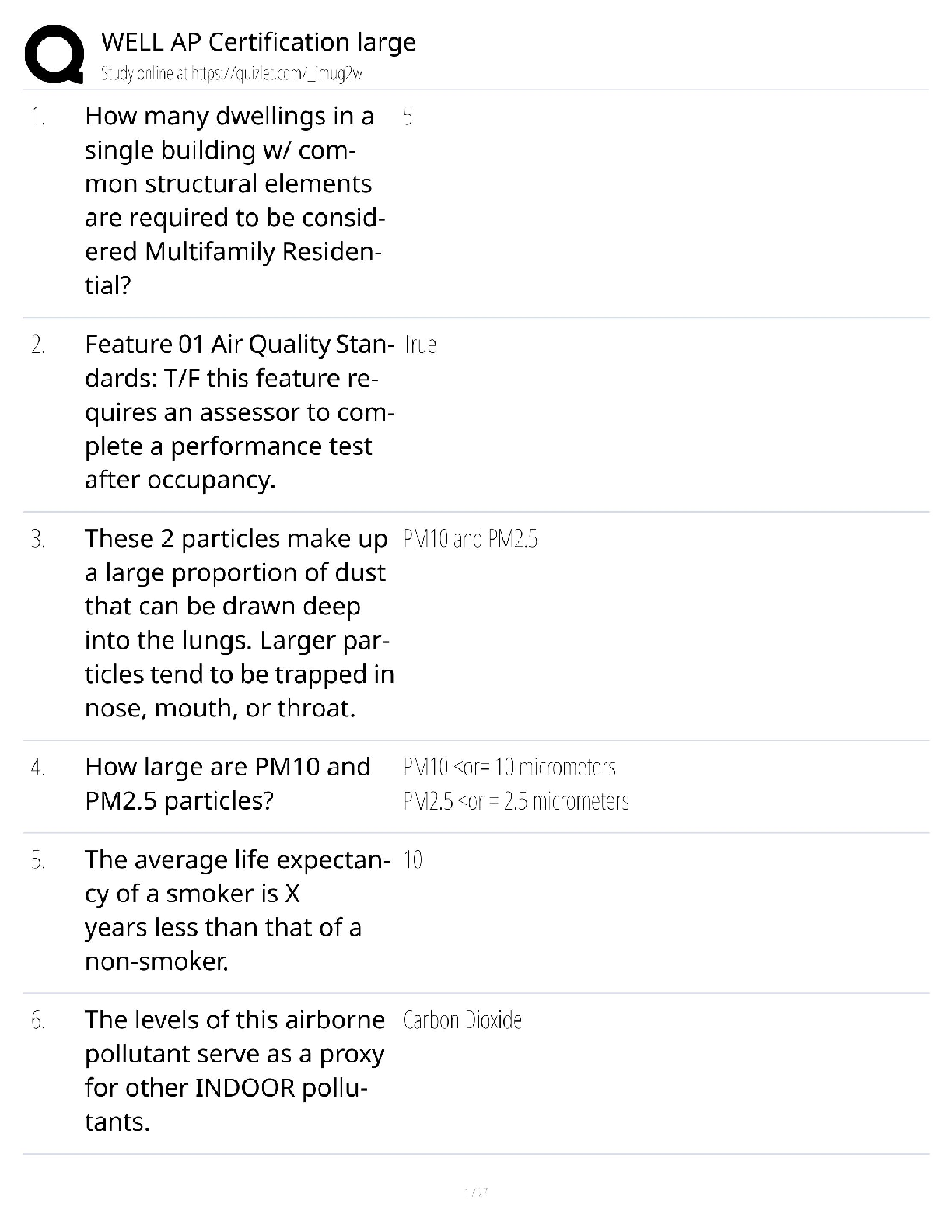
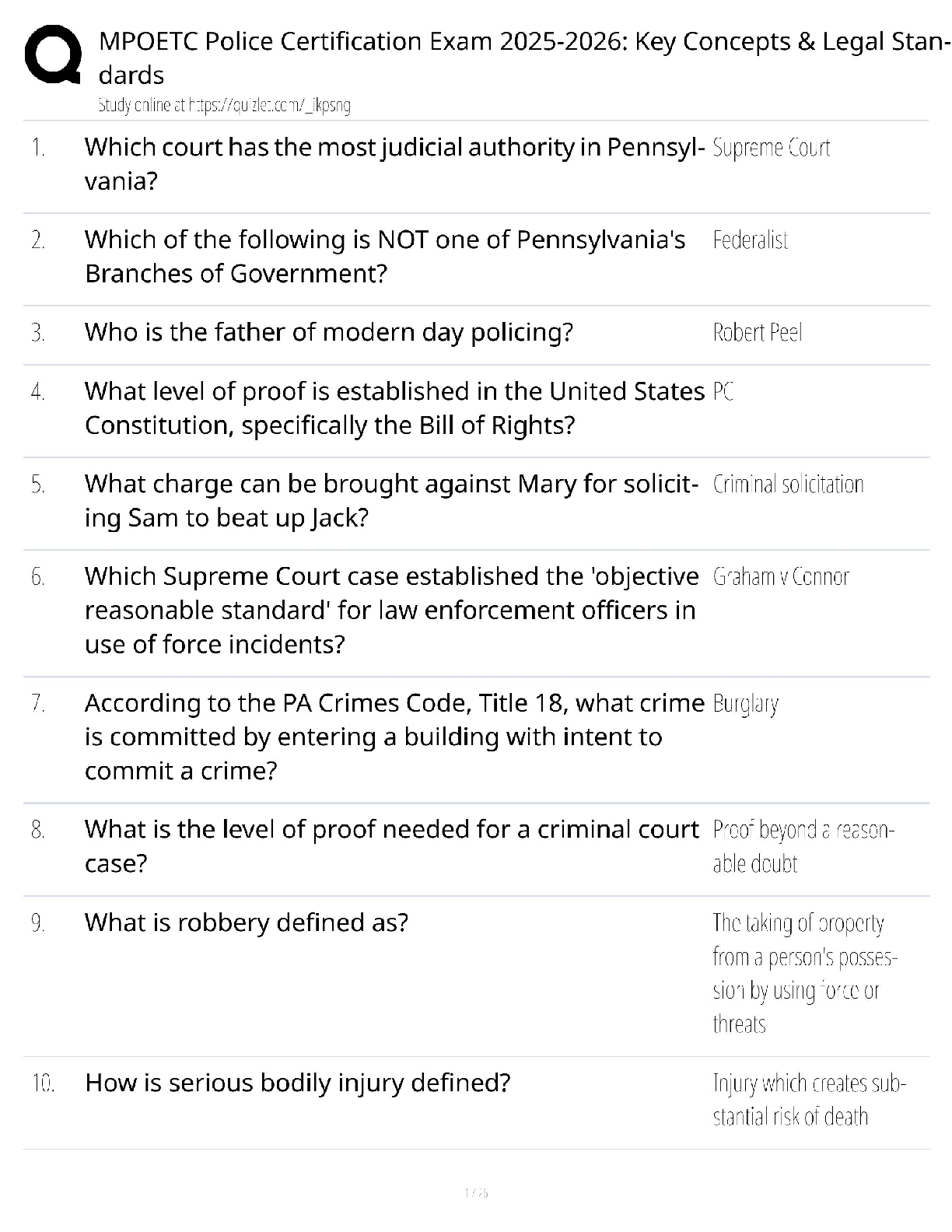
What is an efficient market? - ANS-In an efficient market, security prices adjust rapidly to the arrival of new information, therefore current prices of securities reflect all information about the ... security. An efficient market is a market where information is incorporated into the security's price instantaneously. Investors buying securities in an efficient market should expect to obtain an equilibrium rate of return. Efficient market - Alternative definition - ANS-If a market is efficient, changes in security prices occur randomly - or more technically, there is no systematic correlation between one movement and subsequent ones. -Since stock prices only respond to new information, which by definition arrives randomly, stock prices are said to follow a random walk. -The movements of stock prices from day to day do not reflect any pattern. Condition for efficient markets - ANS--Large number of rational, profit-maximising investors actively participate in the market. -Once information becomes available, market participants analyse it and react quickly and fully to new information. -Competition assures prices reflect information. Efficient market hypothesis (EMH) - ANS-EMH is an empirical hypothesis. EMH is the theory about whether securities' prices reflect the right information under various circumstances. Three levels of efficiency according to the information sets: -Weak-form efficiency (past information) -Semistrong-form efficiency (all publicly available information) -Strong-form efficiency (all relevant information) Weak-form efficiency - ANS--Security prices reflect all past information, including the historical sequence of prices, trading volume data, and other market-generated information. -This implies that past rates of return and other market data should have no relationship with future rates of return. -Technical analysis that attempts to find patterns in stock prices (chartist) to make profits would be of little use. Semi-strong form efficiency - ANS--Security prices reflect all publicly available information, including accounting statements, economic activities, such as change of GDP, interest rate and inflation rate, etc. -Investors cannot act on newly released information to earn abnormal returns, which implies that decisions made on new information after it is public should not lead to above average risk-adjusted profits from those transactions. -Fundamental analysis, which uses economic and accounting information to predict stock prices. Strong-form efficiency - ANS--Security prices reflect all public, as well as private information that is available only to company insiders. -This version of the hypothesis assumes perfect markets. It implies that no group of investors should be able to consistently derive above-average risk-adjusted rates of return. Continues.... [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 21, 2023
Number of pages
5
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 21, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
143