Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Disease
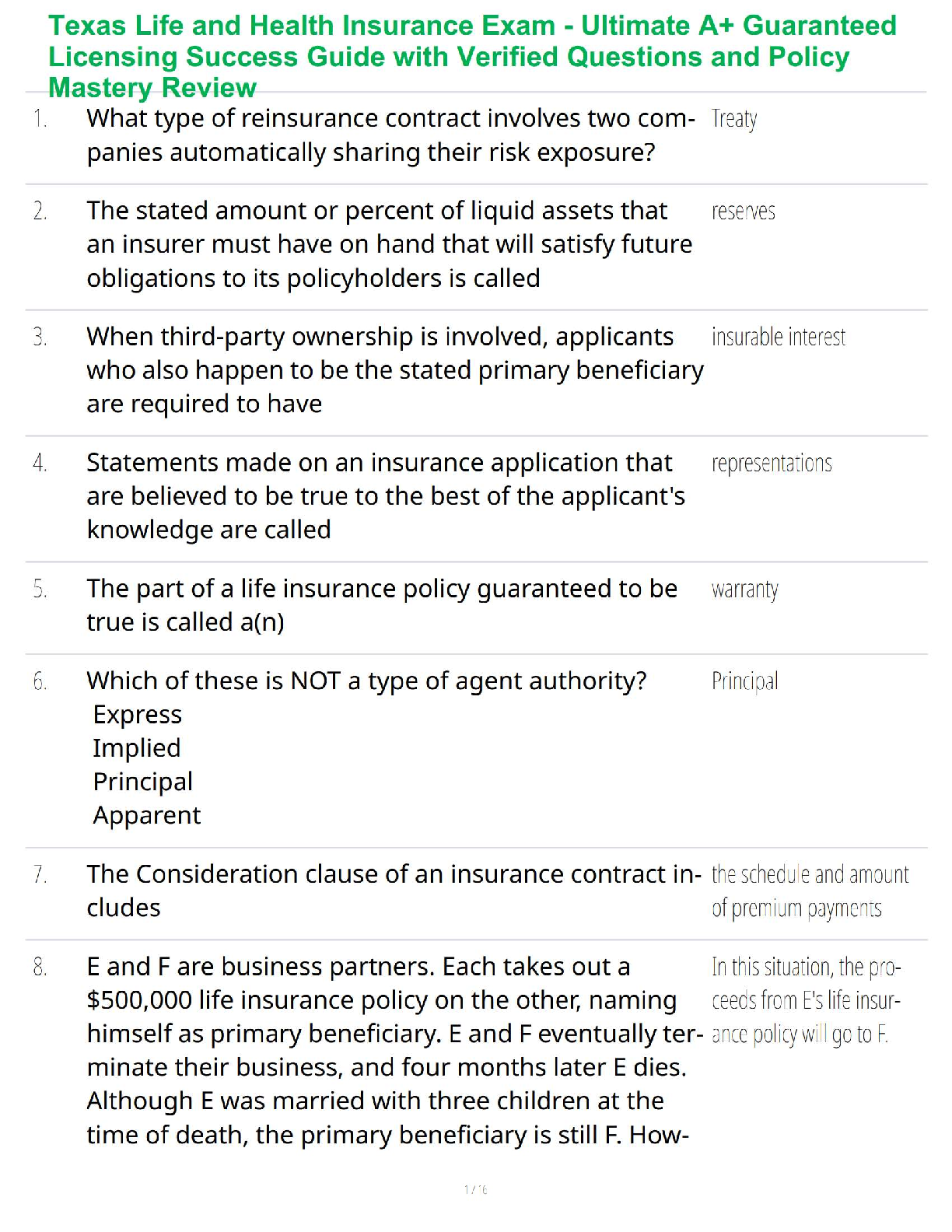
Dyspnea - Subjective sensation of uncomfortable breathing
• a disorder characterized by sudden attacks of respiratory distress that awaken the person, usually after several
...
Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Disease
Dyspnea - Subjective sensation of uncomfortable breathing
• a disorder characterized by sudden attacks of respiratory distress that awaken the person, usually after several hours of sleep in a reclining position
Conditions Caused by Pulmonary Disease or Injury
Hypercapnia - excessive carbon dioxide in the bloodstream, typically caused by inadequate respiration
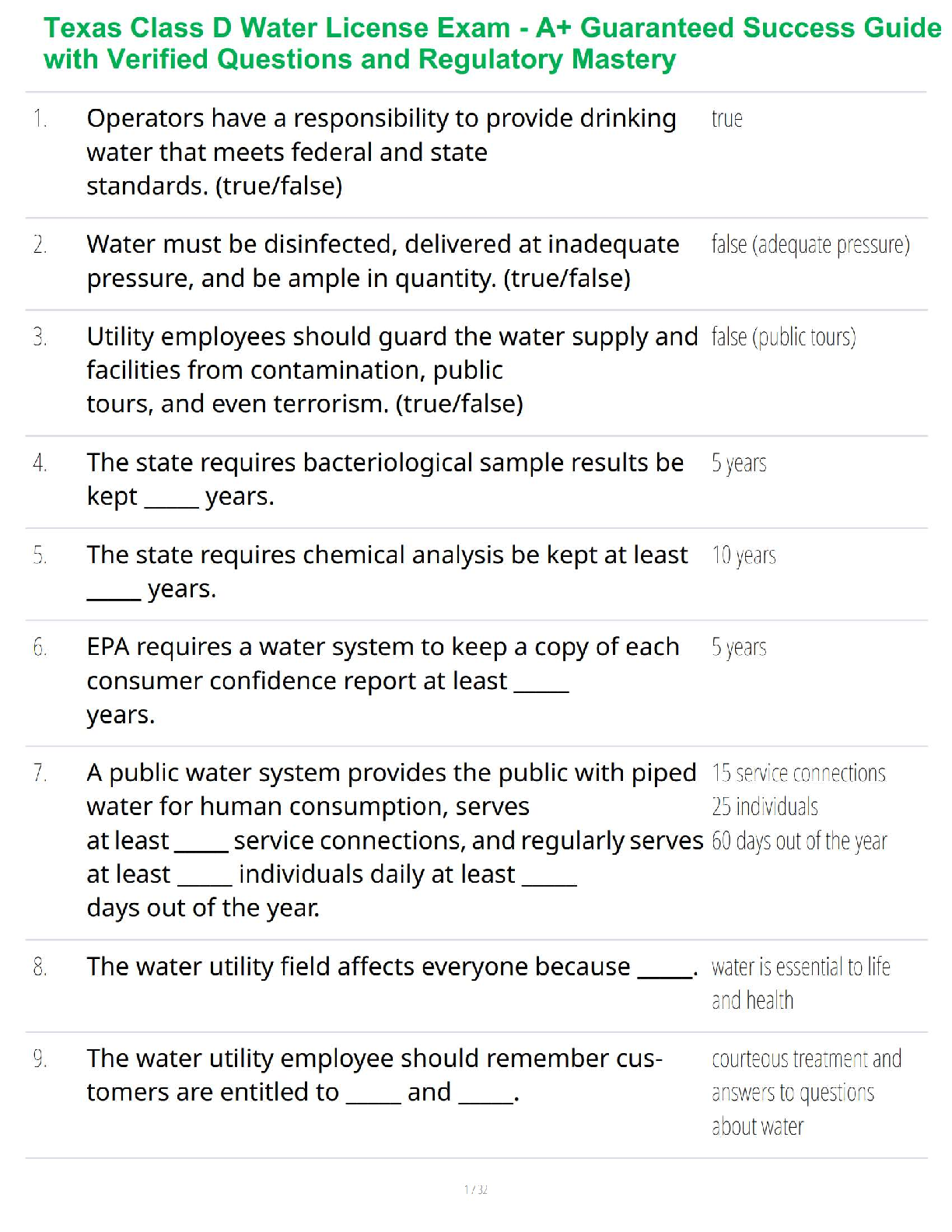
Chest Wall Disorders
Chest wall restriction
- Compromised chest wall = Deformation, immobilization, and/or obesity
Pleural Abnormalities
Pneumothorax - the presence of air or gas in the cavity between the lungs and the chest wall, causing collapse of the lung
Empyema
- Chest pain, which worsens when you breathe in deeply (pleurisy)
- Dry cough
Pulmonary Disorders
Restrictive lung diseases:
Aspiration
• Passage of fluid and solid particles into the lungs
Pulmonary edema - Excess water in the lungs
• Extreme shortness of breath or difficulty breathing (dyspnea) that worsens when lying down
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
• Fulminant form of respiratory failure characterized by acute lung
• Injury to the pulmonary capillary endothelium
- Leading to increased permeability of the alveolar capillary membranes and
Obstructive Lung Diseases:
Airway obstruction that is worse with expiration Asthma
o Chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways
Emphysema
o Abnormal permanent enlargement of the gas-exchange airways accompanied by destruction of alveolar walls without obvious fibrosis
Pneumonia
Inflammation of alveoli and bronchioles
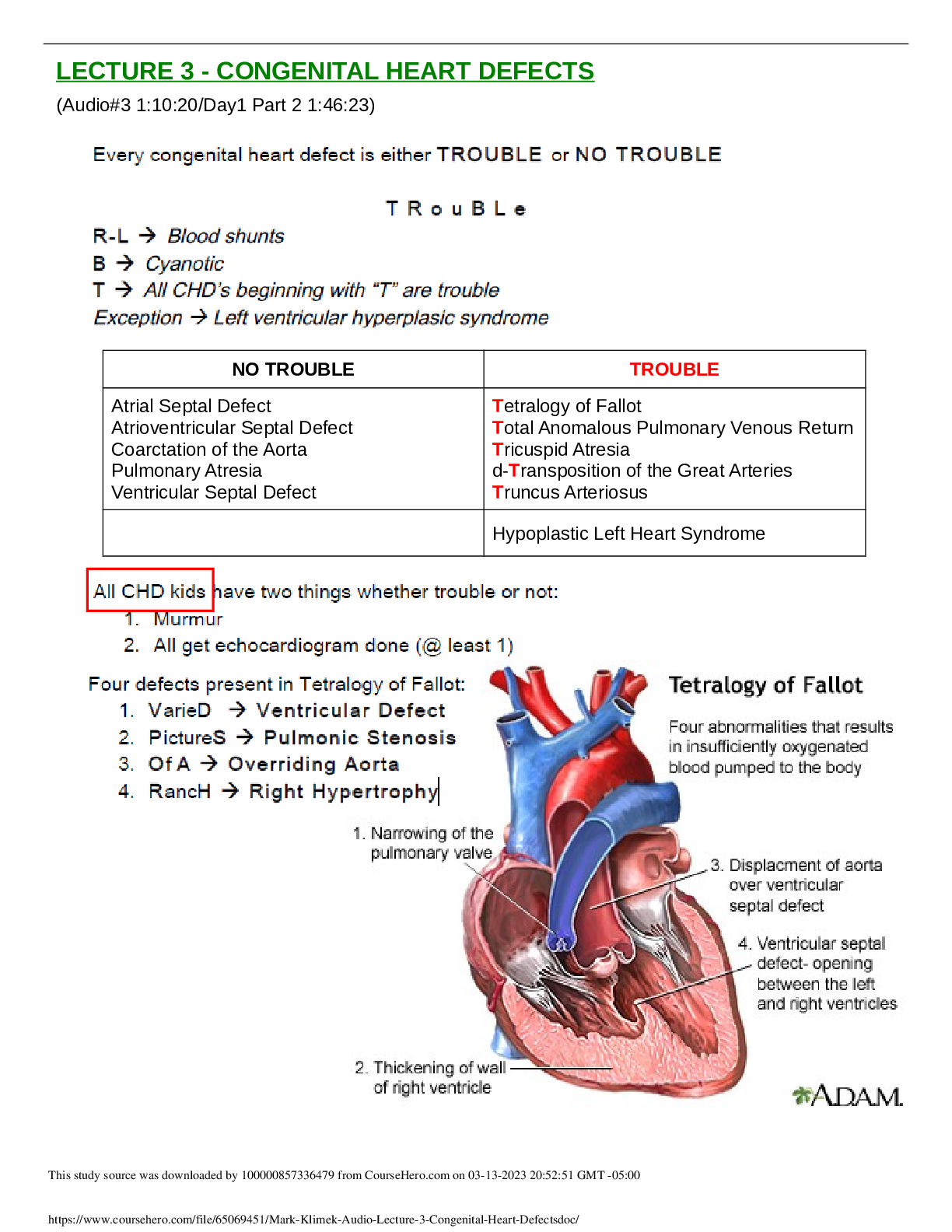
Pressure Ulcers
Pressure ulcers result from any unrelieved pressure on the skin, causing underlying tissue damage
Necrotizing Faciitis
life-threatening, progressive, rapidly spreading, inflammatory infection located in the deep fascia.
Fungal disorders are called mycoses; mycoses caused by dermatophytes are termed tinea
Vascular Disorders
Scleroderma
- Sclerosis of the skin that can progress to the internal organs
Scabies
o contagious disease caused by a mite
o sarcoptes scabiei
Diagnosis:
Definite diagnosis - a definite diagnosis is made by taking skin scrapings from burrows and identifying the mites, their eggs or faeces by microscopy
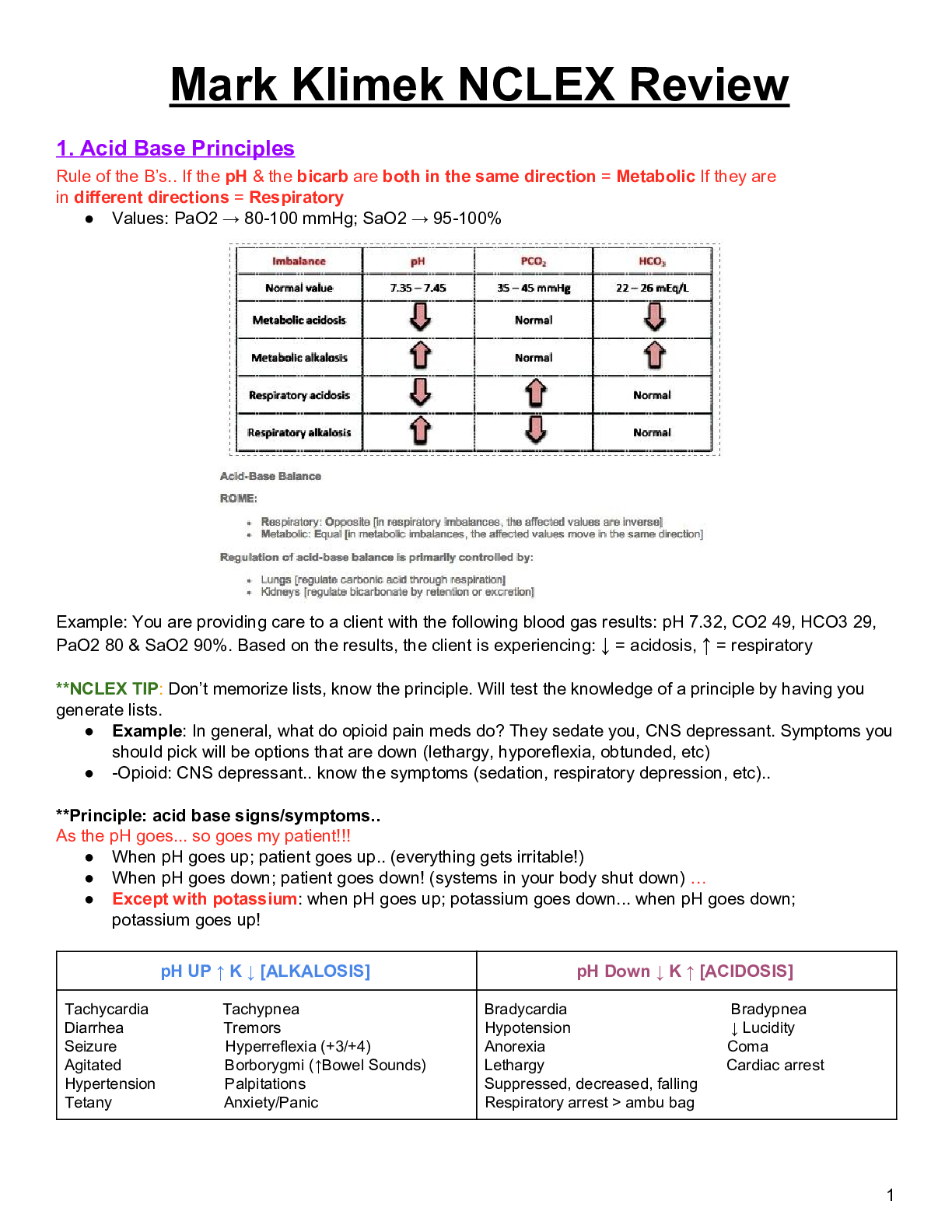
Iron deficiency anemia Alterations of Hematologic Function Hemoglobin Hematocrit Hemoglobin: Considerations by Age & Gender Considerations by Age, Sex, and Other Factors
o Normal ranges do depend on patient populations. Anemia
o Reduction in the total number of erythrocytes in the circulating blood or in the quality or quantity of hemoglobin Macrocytic-Normochromic Anemias
o Also termed megaloblastic anemias Typical anemia symptoms
Neurologic manifestations:
Myeloproliferative RBC Disorders
o Polycythemia
Overproduction of red blood cells
o Relative polycythemia
Quantitative Alterations of Leukocytes Granulocytosis (Neutrophilia) Leukemias
o Malignant disorder of the blood and blood-forming organs
o Excessive accumulation of leukemic cells
Signs and symptoms of leukemia o Acts as a blood filter Lymphadenopathy Malignant Lymphomas
o Malignant transformation Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
o Generic term for a diverse group of lymphomas
Alterations of Platelet Function
o Qualitative alterations in platelet function o Liver disease
Liver disease causes a broad range of hemostasis disorders:
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
o Complex, acquired disorder in which clotting and hemorrhage simultaneously occur
Observed Hematologic Changes
o A decrease in total body water is observed with aging. Blood volume therefore decreases.
o The number of red blood cells (and correspondingly, H&H) are reduced, but not significantly.
o Most of the white Chronic venous insufficiency
o Inadequate venous return over a long period due to varicose veins or valvular incompetence
Deep venous thrombosis
o Obstruction of venous flow leading to increased venous pressure
Hypertension
o Isolated systolic hypertension—becoming prevalent in all age groups
Malignant hypertension Orthostatic (postural) hypotension Thrombus formation Raynaud phenomenon and Raynaud disease
Raynaud phenomenon and Raynaud disease Arteriosclerosis
Chronic disease of the arterial system
Cardiac Output
o CO = Stroke volume X heart rate
Amount of blood ejected from the heart over one minute
Myocardial infarction
Sudden and extended obstruction of the myocardial blood supply causing myocardial cell DEATH (infarction-necrosis-death)
Disorders of The Heart Wall
Disorders of the pericardium:
Pericardial effusion
Acute Rheumatic Fever and Rheumatic Heart Disease
Rheumatic fever
Cardiac Complications of AIDS Dysrhythmias (Arrhythmias) Left heart failure (Congestive heart failure) Types of Shock Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome
Progressive dysfunction of two or more organ systems resulting from an uncontrolled inflammatory response to severe illness or injury
[Show More]
LATEST 2022.png)













.png)