healthcare > EXAM > Medical Assistant QUESTION AND ANSWER NEW UPDATE (All)
Medical Assistant QUESTION AND ANSWER NEW UPDATE
Document Content and Description Below
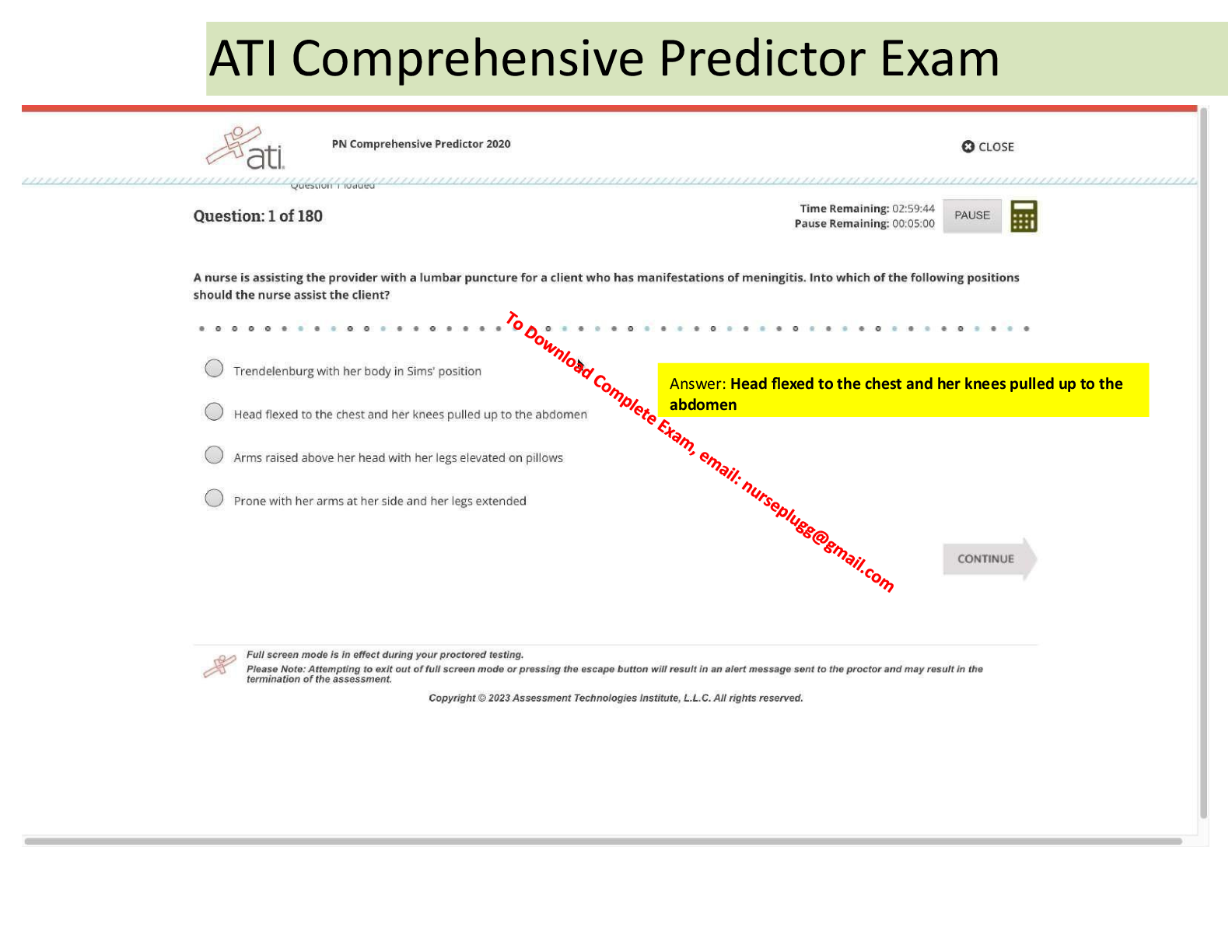
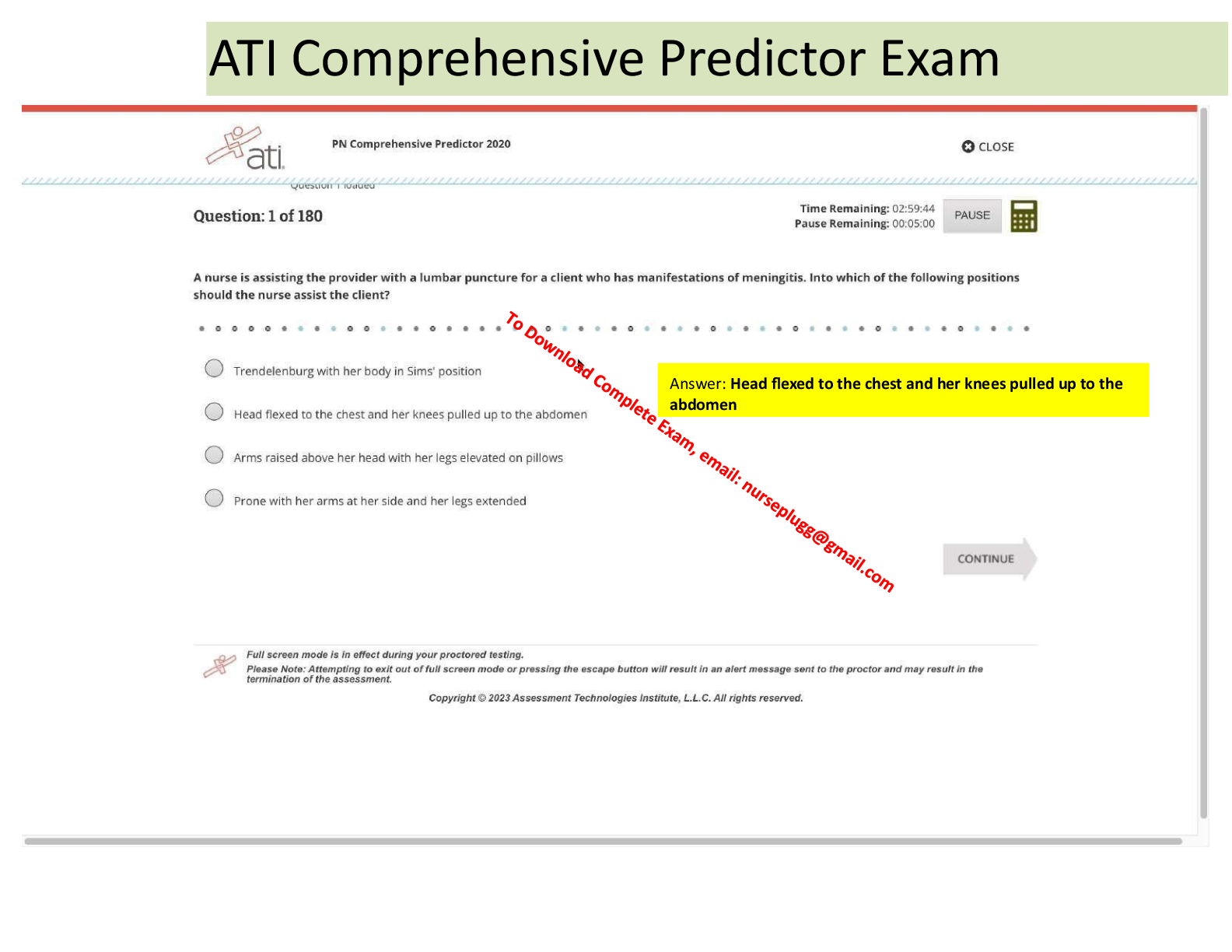
Parts of the medical his- tory include: 1. chief complaint 2. history of present illness (HPI) 3. past, family and social history (PFSH) 4. review of systems (ROS) 2. Define chief compl ... aint what brings the patient in to see the physician 3. Define history of present illness (HPI) 4. Define past medical his- tory explanation of the chief complaint to determine: 1. onset of illness 2. associated symptoms 3. what the patient has done to treat the illness 1. all health problems 2. major illnesses 3. surgeries 4. current medications complete with reasons for taking them 5. allergies 5. Define family history summary of health problems of siblings, parents and other blood relatives 6. Define social history Includes: 1. marital status 2. occupation 3. educational attainment 4. hobbies 5. use of alcohol/tobacco/drugs 6. lifestyles 7. Define review of systems orderly and systematic check of each organ and system of the boy by questions. 8. What are the 3 vital signs that are necessary for life? 9. What are the four vital signs of body function? 1. temperature 2. respiration 3. heart function (blood pressure) 1. temperature 2. pulse 10. What is the normal range of body temperature? 3. respiration 4. blood pressure 96.6-100.6 F 11. Define body temperature the balance between heat production and heat loss 12. Body temperature is reg- ulated by what struc- ture? 13. Site for most accurate body temperature 14. Least accurate site for body temperature the hypothalamus Rectum Axillary 15. 3 types of fever 1. Intermittent 2. Remittent 3. Continuous 16. Define intermittent fever fluctuating fever that returns to or below baseline then rises again 17. Define remittent fever fluctuating fever that remains elevated: it does not return to baseline temperature 18. Define continuous fever a fever that remains constant above the baseline: it does not fluctuate 19. Which is the most com- mon site for tempera- tures 20. In patients who have just finished eating, drinking, or smoking, how long oral 30 minutes should you wait before taking a temperature 21. Patients with heart dis- ease should not have which temperature tak- en? rectal 22. Normal pulse range 60-100 bpm 23. Most accurate pulse apical pulse 24. Normal respiratory range 12 to 20 per minute in adults 25. 3 respiratory rate abnor- malities 1. apnea 2. tachypnea 3. bradypnea 26. Define apnea temporary complete absence of breathing which may be a result of a reduction in the stimuli to the respiratory centers of the brain 27. Define tachypnea respiration rate of greater than 40/minute. It is transient in the newborn and maybe caused by hysteria in the adult 28. Define bradypnea decrease in the number of respirations. This oc- curs during sleep, or certain diseases. 29. Define respiratory rhythm 30. 2 abnormal respiratory rythms 31. Define Cheyenne-Stokes breathing rate 32. Define orthopnea refers to the pattern of breathing. Can vary with age: infants have an irregular rhythm, while adults have regular. 1. Cheyenne-Stokes 2. Orthopnea a regular pattern of irregular breathing rate 33. Patient position when the head is 90 degrees up- right 34. Define depth of respira- tion 35. Name 2 abnormalities in the depth of respiration difficulty or inability to breathe unless in the up- right position high-Fowler's position the amount of air that is inspired and expired during each respiration 1. hypoventilation 2. hyperventilation 36. Define hypoventilation state in which reduced amount of air enters the lungs resulting in decreased oxygen level and increased carbon dioxide level in blood. It can be due to breathing that is too shallow, or too slow, or due to diminished lung function 37. Define hyperpnea abnormal increase in the depth and rate of breathing 38. define hyperventilation state in which there is an increased amount of air entering the lungs 39. Define blood pressure the amount of force exerted by the blood on the peripheral arterial walls 40. How is blood pressure expressed 41. The appropriate width of a cuff is what? 42. The appropriate length of the cuff is what? 43. If the blood pressure cuff is too short or narrow, mm of Hg 40% of the circumference of the limb 80% of the circumference of the limb false high readings how does this effect bp readings? 44. The bp cuff is centered brachial over which artery 45. What is the location of 2.5cm above the bp cuff in relation to the anticubital crease? 46. If the brachial artery is false high far below the heart lev- el, how will this effect the blood pressure 47. If the brachial artery is false low far above heart level, how will this effect the blood pressure reading 48. What is the most com- brachial artery mon artery to use for blood pressure? 49. How high should the bp 30mm Hg cuff be inflated above the palpatory systolic pres- sure 50. What is the rate of re- 2 to 3mm Hg per second lease of pressure when taking a bp? 51. When to you take the the level at which you hear the sounds of at least systolic bp? two consecutive beats 52. When do you take the di- When beats disappear astolic bp? 53. What are the 7 common errors in blood pressure measurements? 54. Define anthropometric measurements 55. Why is length used in anthropometric mea- [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 26 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$22.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 03, 2024
Number of pages
26
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 03, 2024
Downloads
0
Views
106