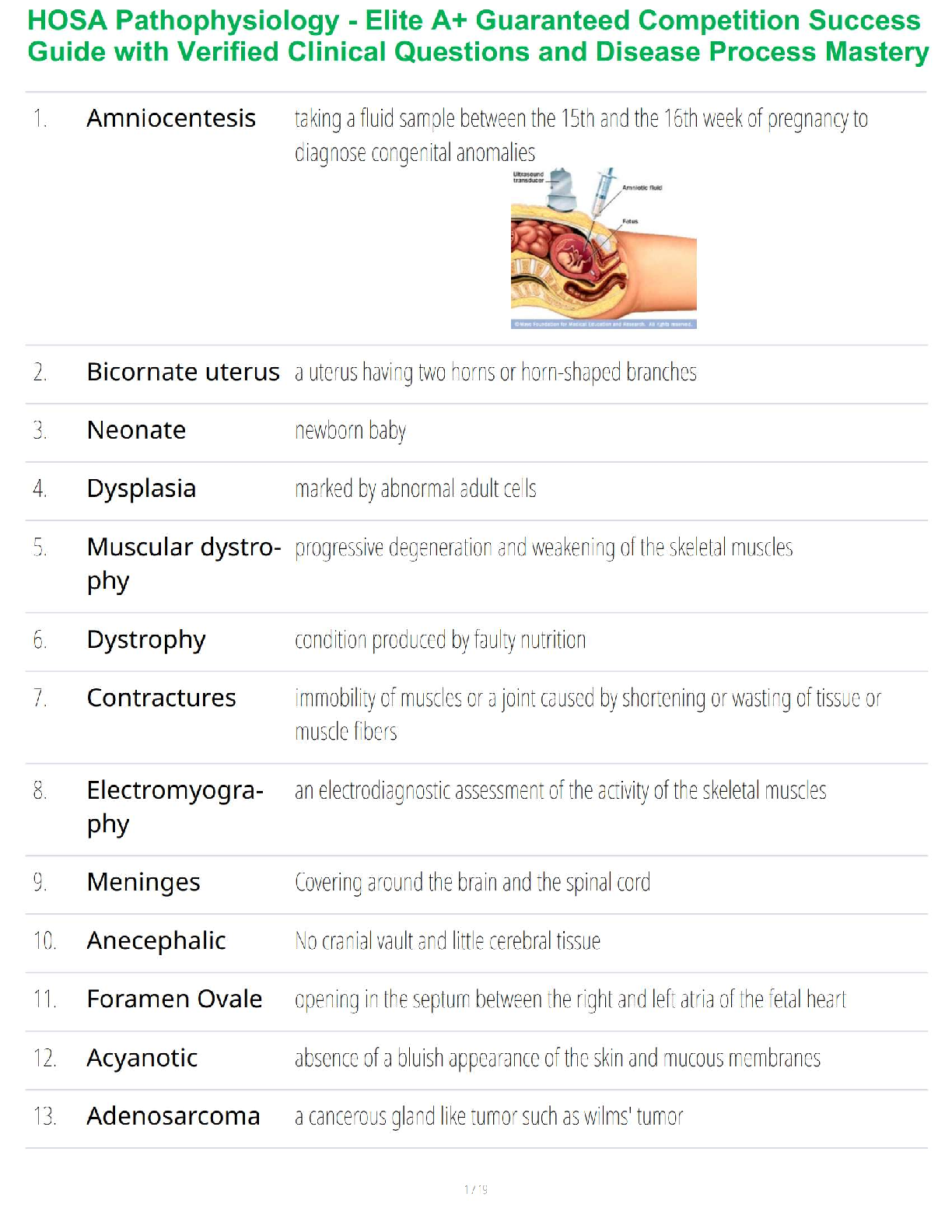
NURSING 1140 Pharm Exam study guide
A patient’s heart rate is found to be 72 beats per minute and regular. The nurse evaluates which
situation in the patient’s peripheral nervous system?
Standard Text: Select all that
...
NURSING 1140 Pharm Exam study guide
A patient’s heart rate is found to be 72 beats per minute and regular. The nurse evaluates which
situation in the patient’s peripheral nervous system?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The sympathetic system is in control.
2. The parasympathetic system is dominating.
3. Both parasympathetic and sympathetic systems are influencing cardiac status.
4. The autonomic nervous system is affecting cardiac status.
5. The somatic nervous system is affecting cardiac status.
Correct Answer: 2,3,4
Rationale 2: Restful cardiac response indicates that the primary input is from the parasympathetic
system.
Rationale 3: These two systems work in tandem to regulate the cardiac response.
Rationale 4: Both the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are part of the autonomic system.
2. A nurse is reading about the development of drugs that inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system.
The nurse would look for articles about which drug classes?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Anticholinergics
2. Parasympathomimetics
3. Parasympatholytics
4. Cholinergics
5. Muscarinic blockers
Correct Answer: 1,3,5
Rationale 1: Anticholinergics inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system.
Rationale 3: Parasympatholytic drugs inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system.
Rationale 5: Muscarinic blockers inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system.Question 3
Type: Hot Spot
Mark the site of the ganglionic synapse on this diagram.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Answer: 3
Rationale: The ganglionic synapse is the gap between the preganglionic neuron and the postganglionic
neuron.
Question 4
Type: MCMA
A patient has been prescribed an oral drug containing atropine. The nurse would hold the drug and
Contact the prescriber if which patient statements are made?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “I would like to wait a few minutes to take this as I just drank some aloe juice.”
2. “Can I take this at the same time as my procainamide?”
3. “I have had a headache this morning.”
4. “I am allergic to penicillin.”5. “My gallbladder surgery is scheduled for next week.”
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Atropine should be used with caution in those who use aloe.
Rationale 2: There is a drug–drug interaction between atropine and procainamide.
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The nurse has completed medication education about pyridostigmine (Mestinon), an indirect cholinergic
drug, for the patient with myasthenia gravis. The nurse determines that learning has occurred when the
patient makes which statement?
1. "My heart may beat slower while I am on this drug."
2. "I will need to increase my fluid intake with this medication."
3. "I must take this medication immediately before eating a full meal."
4. "It is really important to take my medication on time."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 4: Maintaining an optimum blood level of the drug is crucial in promoting muscle functioning,
so it is important for the patient to take his medication on time and as directed.
Question 6
Type: MCSA
The physician has ordered bethanechol (Urecholine), a cholinergic drug, for the patient with urinary
retention. The patient also has an enlarged prostate gland. What is the priority action by the nurse?
1. Hold the drug and prepare to catheterize the patient.
2. Administer the drug and measure urinary output.
3. Administer the drug and push fluids.
4. Hold the drug and contact the physician.
Correct Answer: 4.
Rationale 4: Bethanechol (Urecholine) relaxes the urinary sphincter and increases voiding pressure. It is
contraindicated with any physical obstruction of the urinary tract, such as an enlarged prostate gland.Question 7
Type: MCSA
The preop patient will be receiving glycopyrrolate (Robinul), an anticholinergic drug, and asks the nurse,
"Why do I need to have that shot?" What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "It will decrease your respiratory secretions during surgery."
2. "It will increase your urinary output during surgery."
3. "It will help you breathe better during surgery."
4. "It will help maintain your blood pressure during surgery."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Anticholinergics dry secretions; a decrease in respiratory secretions is indicated prior to
surgery.
Question 8
Type: MCSA
The nurse is preparing to administer medications to a group of patients. One of the medications is
benztropine (Cogentin), an anticholinergic drug. This drug is contraindicated in which patient?
1. The patient with a fractured femur
2. The patient with tachycardia
3. The patient with an irritable colon
4. The patient with diarrhea
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 2: Anticholinergic drugs increase the heart rate; a patient with tachycardia should not receive
benztropine (Cogentin).
Question 9
Type: MCSA
The nurse is preparing to administer medications to a group of patients. One of the medications is
atropine, an anticholinergic drug. This drug is contraindicated in which patient?
1. The patient with glaucoma2. The patient with hyperthyroidism
3. The patient with a hiatal hernia
4. The patient with lung cancer
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Anticholinergic drugs can increase pressure in the eye; they must be avoided in patients
with glaucoma.
Question 10
Type: MCSA
The physician orders dicyclomine (Bentyl), an anticholinergic drug, for a patient. What is the nurse's
priority assessment prior to administering this drug?
1. Does the patient have light sensitivity?
2. Is the patient able to urinate?
3. Does the patient have a history of alcoholism?
4. Is the patient dizzy upon standing?
Correct Answer: 2. Rationale 2: Anticholinergic drugs can cause or increase urinary hesitancy or
retention.
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The patient is quadriplegic and receives oxybutynin (Ditropan), an anticholinergic drug, to increase his
bladder capacity. What is an important assessment of this patient by the nurse?
1. Is he irritable?
2. Is he constipated?
3. Is he gaining weight?
4. Is he lethargic?
Correct Answer: 2. Rationale 2: Anticholinergics slow gastrointestinal (GI) motility and can increase the
risk for constipation.
Question 12Type: MCMA
The nursing instructor teaches the student nurses about the nervous system. The instructor determines
that learning has occurred when the students make which statement(s)?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord."
2. "The peripheral nervous system has mainly sensory functions."
3. "The somatic nervous system gives us voluntary control over our gastrointestinal (GI) tract."
4. "The nervous system helps us react to environmental changes."
5. "The somatic nervous system gives us voluntary control over moving."
Correct Answer: 1,4,5
Rationale 1: The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord.
Rationale 4: The nervous system provides reaction to environmental changes.
Rationale 5: The somatic nervous system provides voluntary control over moving.
Question 13
Type: MCMA
The nursing instructor teaches the student nurses about the autonomic nervous system. The instructor
determines that learning has occurred when the students make which statement(s)?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are not always opposite in their effects."
2. "The parasympathetic nervous system is the "fight-or-flight" response."
3. "Sympathetic stimulation causes dilation of arterioles."
4. "The parasympathetic nervous system causes bronchial constriction."
5. "The sympathetic nervous system is activated under stress."
Correct Answer: 1,4,5
Rationale 1: The sympathetic and parasympathetic systems are not always opposite in their effects.
Rationale 4: The parasympathetic nervous system causes bronchial constriction.Rationale 5: The sympathetic nervous system is activated under stress.
Question 14
Type: MCSA
The student nurse asks the nursing instructor, "Do the medications we are studying actually make more
neurotransmitters?" What is the best response by the nursing instructor?
1. "No, but medications can heal diseases of the autonomic nervous system."
2. "Yes, some of the newer medications are very good at doing this."
3. "Yes, but the newer drugs that do this have some serious side effects."
4. "No, medications can only increase or decrease the action of neurotransmitters."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 4: Medications cannot manufacture new neurotransmitters; they can only increase or
decrease their action.
Question 15
Type: MCSA
The ability of a person to use his arm muscles to lift a weight is primarily regulated by
1. the somatic nervous system.
2. the sympathetic nervous system.
3. the autonomic nervous system.
4. the parasympathetic nervous system.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The somatic nervous system (a division of the peripheral nervous system) controls
voluntary movement such as lifting a weight.
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Which of the following responses are regulated by the sympathetic nervous system?
1. Increased heart rate, bronchial constriction
2. Peripheral artery dilation, reduced peristalsis3. Increased secretions, sex organ stimulation
4. Relaxation of bladder, pupil dilation
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 4: Relaxation of the bladder and pupil dilation is regulated by the sympathetic nervous
system.
Question 17
Type: MCSA
A person who had her adrenergic receptors activated would experience
1. fight-or-flight effects.
2. rest-and-digest effects.
3. increased blood volume.
4. bronchial constriction.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Adrenergic receptors are found within the sympathetic nervous system. Sympathetic
nervous system activation produces the fight-or-flight response.
Question 18
Type: MCSA
Which substance would inhibit the function of the autonomic nervous system?
1. Drugs that bind and then stimulate the postsynaptic neuron
2. Drugs that prohibit neurotransmitter reuptake
3. Drugs that increase neurotransmitter synthesis
4. Drugs that prevent the storage of neurotransmitter in vesicles
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 4: The more neurotransmitter available, the greater the function/stimulation of the
autonomic nervous system.
Question 19
Type: MCSAWhich cholinergic receptor type is found at the ganglionic synapse of both the sympathetic and
parasympathetic nervous systems?
1. Alpha receptors
2. Muscarinic
3. Nicotinic
4. Beta receptors
Correct Answer: 3. Rationale 3: Nicotinic receptors are found at the ganglionic synapse of both
sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems.
Question 20
Type: MCMA
A patient is prescribed an anticholinergic drug. What discharge instructions should the nurse provide?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Wear sunglasses in bright light.
2. Limit fluid intake.
3. Increase fiber intake.
4. Avoid hot showers.
5. Avoid milk and dairy products.
Correct Answer: 1,3,4
Rationale 1: Anticholinergic drugs may cause photosensitivity.
Rationale 3: Use of anticholinergics increases risk for constipation. Fiber intake should be increased.
Rationale 4: Use of anticholinergics reduces ability of patients to sweat and self-regulate temperature.
Hot environments, including hot showers and baths, should be avoided.
Question 21
Type: MCSA
Which statement is accurate regarding exogenous acetylcholine?
1. Acetylcholine has almost no therapeutic effects because it is rapidly destroyed once given.
2. Acetylcholine is broken down rapidly within the body, preventing it from producing adverse effects.3. Acetylcholine will cause the heart rate to increase and blood pressure to drop.
4. When given in small amounts, acetylcholine will produce profound parasympathetic effects.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Exogenous acetylcholine is not generally administered, because it is rapidly destroyed by
the body.
Question 22
Type: MCSA
The nurse explains that atropine (Atropair) increases heart rate in which manner?
1. Blocking the beta receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system.
2. Directly stimulating the sympathetic nervous system.
3. Potentiating the effects of acetylcholine on nicotinic receptors.
4. Blocking the effects of acetylcholine by occupying muscarinic receptors.
Correct Answer: 4 Rationale 4: Atropine is a cholinergic-blocking agent that occupies muscarinic
receptors.
Question 23
Type: MCMA
Which patient situations are considered involuntary responses to autonomic nervous system control?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Sweating when hot
2. Stepping over a chair to prevent falling
3. Complaining of nausea
4. Salivating at the smell of food
5. Breathing deeper when running
Correct Answer: 1,4,5
Rationale 1: Sweating is an involuntary response that is controlled by the sympathetic nervous system.
Rationale 2: Muscle movement is controlled by the somatic nervous system.Rationale 3: Complaining of nausea is a result of sensory neuron input and is not part of the autonomic
system.
Rationale 4: Salivation is involuntary and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
Question 24
Type: MCMA
A patient has sustained a large blood loss. During the assessment, the nurse realizes that which findings
are under the control of the nervous system?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Heart rate
2. Blood pressure
3. Pupil size
4. Bowel sounds
5. Fluid volume
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to
accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as heart rate.
Rationale 2: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to
accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as blood pressure.
Rationale 3: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to
accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as pupil size.
Rationale 4: The brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves act as a smoothly integrated whole to
accomplish minute-to-minute changes in essential functions such as intestinal motility.
Question 25
Type: MCMA
The nurse is caring for a patient with multisystem organ failure. Which patient assessment findings are
under the control of the sympathetic nervous system?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Blood glucose level 210 mg/dL2. Blood pressure 180/90 mmHg
3. Extremities are cool
4. Respiratory rate 14 and regular
5. Hyperactive bowel sounds
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Metabolic effects such as an increase in blood glucose are a sympathetic nervous system
function.
Rationale 2: The constriction and relaxation of arterioles are controlled entirely by the sympathetic
nervous system.
Rationale 3: The sympathetic nervous system controls release of epinephrine and norepinephrine,
which result in peripheral vasoconstriction.
Question 26
Type: MCMA
A student nurse is learning about a medication that affects the autonomic nervous system. When
instructing the student about the effects of this medication, the nurse will begin by explaining the basic
unit of this system. What does this include?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The preganglionic neuron
2. The postganglionic neuron
3. The synaptic cleft
4. Norepinephrine
5. Dopamine
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: The basic unit of the autonomic nervous system is a two-neuron chain. The first neuron,
called the preganglionic neuron, originates in the central nervous system.
Rationale 2: The preganglionic neuron connects with the second nerve in the autonomic nervous system
two-neuron chain through the ganglia, which contains the postganglionic neuron.
Rationale 3: Autonomic messages must cross the synaptic cleft.Question 27
Type: SEQ
The nurse educator is reviewing the process of synaptic transmission following the sympathetic
pathway. In which order will the nurse explain the steps of synaptic transmission?
1. Action potential encounters adrenergic receptors
2. Action potential encounters cholinergic receptors
3. Action potential travels across the preganglionic neuron
4. Action potential travels across the postganglionic neuron
5. Target tissue is reached.
Standard Text: Click and drag the options below to move them up or down.
Correct Answer: 3,2,4,1,5
Question 28
Type: MCMA
A patient is prescribed a medication that will block muscarinic receptors. The nurse realizes that this
medication has implications for which body systems?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Eyes
2. Respiratory
3. Cardiac
4. Endocrine
5. Metabolic
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Medications that block muscarinic receptors are used during ophthalmic procedures.
Rationale 2: Medications that block muscarinic receptors are used in the pharmacologic treatment of
asthma.
Rationale 3: Medications that block muscarinic receptors are used in the pharmacologic treatment of
bradycardia.Question 29
Type: MCMA
A patient has been prescribed scopolamine (Transderm-Scop) for the prevention of motion sickness. The
nurse should teach the patient to immediately report which adverse effects?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Slow heart rate
2. Cardiac palpitations
3. Decreased urinary output
4. Development of tremors
5. Diarrhea
Correct Answer: 2,3,4
Rationale 2: Dysrhythmia is an adverse effect of this drug.
Rationale 3: Decreased urinary output is an adverse effect of this drug.
Rationale 4: Tremors are an adverse effect of this drug.
Question 30
Type: MCMA
A patient who has myasthenia gravis (MG) presents to the emergency department with abrupt onset of
increased muscle weakness and difficulty swallowing. An attempt to distinguish worsening of the MG
symptoms from overdose of the patient’s prescribed anticholinergic is planned. What medications
should the nurse obtain for use in this procedure?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Donepezil (Aricept)
2. Pyridostigmine (Mestinon)
3. Neostigmine (Prostigmin)
4. Edrophonium (Edrophonium Injectable)
5. Atropine (Atropine Injectable)
Correct Answer: 4,5Rationale 4: Edrophonium (Edrophonium Injectable) is given as a test dose. If muscular symptoms
improve, the patient is having a myasthenic crisis.
Rationale 5: Atropine (Atropine Injectable) is given if the test results in a cholinergic crisis.
Chapter 13:
Question 1
Type: MCSA
The patient receives methyldopa (Aldomet), an adrenergic drug. The nurse determines that the patient
is having side effects when the patient makes which statement?
1. "Will you check my pupils? I can't see very well at all."
2. "I am so thirsty; will you please bring me another pitcher of water?"
3. "I am so anxious; I really need to walk around the room."
4. "I feel so sleepy that I don't think I can eat my dinner."
Correct Answer: 3.Rationale 3: Adrenergic drugs mimic the effect of the sympathetic nervous system
(SNS). This can result in anxiety and restlessness.
Question 2
Type: MCSA
The patient receives metaproterenol (Alupent), an adrenergic drug. A consulting physician orders
carteolol (Cartrol), a beta blocker. What best describes the nurse's assessment?
1. The patient is at risk for a hypertensive crisis.
2. The effects of metaproterenol (Alupent) will be decreased.
3. The drugs are compatible; there will not be any adverse effects.
4. The effects of metaproterenol (Alupent) will be increased.
Correct Answer: 2.Rationale 2: Beta-adrenergic blockers block the receptors that are stimulated by
adrenergic drugs; the effects of metaproterenol (Alupent) would be decreased.
Question 3
Type: MCSA
The nurse has been doing medication education for the patient receiving atenolol (Tenormin), a beta
blocker. The nurse determines that learning has occurred when the patient makes which statement?1. "I need to take my pulse every day."
2. "If I have any side effects, I will stop the medication."
3. "I cannot take this drug if I develop glaucoma."
4. "I cannot continue to have my morning cup of coffee."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Beta blockers slow the heart rate; therefore, the patient must monitor his pulse every day.
Question 4
Type: MCSA
The physician ordered prazosin (Minipress), an alpha-adrenergic blocker, for the patient. The nurse
plans to do medication education. What will the best plan of the nurse include?
1. Instruct the patient to not take OTC herbal preparations containing saw palmetto.
2. Instruct the patient to not take tub baths.
3. Instruct the patient to decrease his intake of sodium.
4. Instruct the patient to wear sunglasses when outdoors.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: A hypotensive response may occur when saw palmetto is taken concurrently
Question 5
A patient has been prescribed an alpha1 adrenergic agonist drug. The nurse would plan to monitor for
effects from which organs?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Kidneys
2. Eyes
3. Heart
4. Bowels
5. LungsCorrect Answer: 1,2,4,5
Rationale 1: Alpha1 receptors have potential to affect the renal system.
Rationale 2: Alpha1 receptors result in dilation of the pupils.
Rationale 4: Alpha1 receptors have potential to affect receptors in the gastrointestinal tract.
Rationale 5: Alpha1 receptors have potential to affect receptors in the respiratory system.
Question 6
A patient is prescribed a drug that activates alpha2 receptors. The nurse would plan care based on which
physiological response?
1. Inhibition of norepinephrine release
2. Absence of monoamine oxidase
3. Increased lipolysis
4. Destruction of presynaptic nerve terminals
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The action of alpha2 receptors is to inhibit release of norepinephrine.
Question 7
A nurse is reviewing medical records for usage of drugs that are beta2 agonists. The nurse should start
with the medical records of patients with which conditions?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Heart failure
2. Asthma
3. COPD
4. Overactive bladder
5. Nasal congestion
Correct Answer: 2,3
Rationale 2: Beta2 agonists are useful in the treatment of asthma.Rationale 3: Beta2 agonists are useful in the treatment of COPD.
Question 9
A patient who is in heart failure is administered a beta1 agonist. The nurse would evaluate that the drug
is effective if which changes occur?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Heart rate increases
2. Pulse becomes stronger
3. Pupils dilate
4. Dysrhythmias dissipate
5. Blood pressure drops
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: One of the effects of beta1 agonists is to increase the heart rate.
Rationale 2: One of the effects of beta1 agonists is to increase force of cardiac contraction, which would
be felt as a stronger pulse.
Question 10
A patient has been prescribed isoproterenol (Isuprel). The nurse plans care based on the drug’s
stimulation of which receptors?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Alpha1
2. Alpha2
3. Beta1
4. Beta2
5. Beta3
Correct Answer: 3,4
Rationale 3: Isoproterenol (Isuprel) is a nonselective drug that stimulates beta1 receptors.Rationale 4: Isoproterenol (Isuprel) is a nonselective drug that stimulates beta2 receptors.
Question 11
Type: Hot Spot
The nurse is providing discharge medication instruction to the family of a child who is severely allergic to
peanuts. Mark the spot where the family or patient should inject epinephrine from an EpiPen should an
allergic response occur.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Answer: 4.Rationale: This drug should be injected into the thigh only.
Question 12
A nurse is providing discharge medication instruction regarding use of injectable epinephrine (EpiPen).
What information should the nurse include?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. If you need to use this pen, seek medical advice as follow-up.
2. You can dispose of a used EpiPen in your regular trash.
3. Keep an extra EpiPen on hand.
4. Store this device in your refrigerator.
5. Carry an EpiPen in your car’s glovebox.
Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: If it is necessary to use the EpiPen, it is important to seek immediate follow-up by calling
911 or the provider.
Rationale 3: It is recommended that the patient have an extra EpiPen on hand in case of emergency or
failure of the original unit.
Question 13
A patient has been prescribed phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) spray for nasal congestion. What
information about adverse effects should the nurse provide in discharge teaching?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “This drug may cause some stinging or burning in your nose.”
2. “You may notice that your nasal secretions take on a slightly orange tint.”
3. “You may feel like your blood pressure is low for the first few times you use this spray.”
4. “One of the major adverse effects of this drug is rebound congestion if it is used more than a few
days.”
5. “Do not drink herbal teas while taking this medication.”
Correct Answer: 1,4
Rationale 3: Intranasal medications, if used properly, should have little or no effect on blood pressure.
Rationale 4: Rebound congestion is likely to occur if the drug is used for over 3–5 days.
Question 14
Type: MCMAThe nurse is preparing to administer an adrenergic drug intravenously. What nursing actions should be
planned?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Give the drug as rapidly as possible by intravenous push.
2. Dilute the drug before administration.
3. Use an infusion pump to control rate of administration.
4. Monitor for blanching at the infusion site.
5. Advise the patient that a sweet taste may occur as the drug is being given.
Correct Answer: 2,3,4
Rationale 2: These drugs should be diluted prior to administration.
Rationale 3: Infusion of these drugs should be controlled via an infusion pump.
Rationale 4: Blanching at the infusion site indicates probable extravasation. The drip should be stopped.
Question 15
Type: MCMA
A patient has been prescribed phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine). Prior to administering this drug the
nurse would review the patient’s medication history for presence of which drugs?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. MAO inhibitors
2. Tricyclic antidepressants
3. Iron supplements
4. Digoxin
5. Aspirin
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4Rationale 1: Concurrent use with MAO inhibitors may result in hypertensive crisis.
Rationale 2: Tricyclic antidepressants can potentiate the effects of phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine).
Rationale 3: Iron supplements are incompatible with phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine).
Rationale 4: Dysrhythmias may occur when phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) and digoxin are used
concurrently.
Question 16
A patient who was recently prescribed an adrenergic drug says, “I am so nervous and I cannot sleep.”
The nurse would ask which questions?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “How much coffee do you drink?”
2. “Have you recently increased your intake of dairy products?”
3. “Do you eat chocolate?”
4. “When was the last time you ate pickled foods or aged cheese?”
5. “How much wine or other alcoholic beverages do you drink?”
Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: The caffeine in coffee may cause excessive nervousness, insomnia, and tremors.
Rationale 3: The caffeine in chocolate may cause excessive nervousness, insomnia, and tremors.
Question 17
Type: MCMA
A patient who has used an adrenergic nasal spray for 2 weeks complains that, “I am more stuffed up
now than I was when I was sick.” What advise should the nurse provide?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “You are having an allergic reaction to the nasal spray. Stop using it immediately.”
2. “You probably have developed a secondary infection.”
3. “Try increasing the amount of fluids you are drinking.”4. “Switch to a saline-based nasal spray.”
5. “Continue to use your current nasal spray until the congestion goes away.”
Correct Answer: 3,4
Rationale 3: Increased oral fluids may help to thin secretions, making them easier to remove.
Rationale 4: The patient is probably experiencing rebound congestion. Switching from the adrenergic
spray to a saline spray will keep the mucosa moist and more comfortable until the effects of the
adrenergic spray abate.
Question 18
An older adult patient received an adrenergic eye drop to dilate the pupils for a retinal exam. What
information should the nurse provide when discharging this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “Do not drive until the effects of the eye drops have worn off.”
2. “Wear sunglasses when in bright light.”
3. “You may be more comfortable in a darkened room.”
4. “You may experience burning in your eyes for a couple of days.”
5. “Do not eat or drink anything for at least an hour after discharge.”
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Older adults may notice blurring of vision after receiving drops to dilate the eyes. The
patient should not drive until vision is clear.
Rationale 2: Photosensitivity is a common effect, and protective eyewear should be worn.
Rationale 3: Photosensitivity is a common effect, and the patient may be more comfortable in a
darkened room or with a soft cloth covering the eyes.
Question 19
A patient has been prescribed an adrenergic nasal spray. What medication instruction should the nurse
provide?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.1. “Do not share this spray with anyone.”
2. “Sit upright while using this spray.”
3. “Only use this spray for 3–5 days.”
4. “Do not shake the bottle before using this spray.”
5. “Keep this spray refrigerated.”
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Sharing nasal sprays may spread infection.
Rationale 2: The patient should sit upright to use this medication so that it is delivered appropriately,
avoiding overdosage.
Rationale 3: Adrenergic nasal sprays may cause rebound congestion if used more that 3–5 days.
Question 20
Type: MCSA
Which statement is accurate concerning drugs classified as adrenergic antagonists?
1. They are also known as anticholinergics.
2. Their actions will block the neurotransmitter acetylcholine.
3. Their actions are the opposite of those of sympathomimetics.
4. They will stimulate the sympathetic nervous system.
Correct Answer: 3.Rationale 3: Adrenergic antagonists inhibit the actions of the sympathetic nervous
system.
Question 21
During assessment a patient says, “I took my blood pressure at home and it was high. I have been taking
my husband’s propranolol (Inderal) for the last week.” The nurse is especially concerned about this
action when it is noted that the patient has which preexisting conditions?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Obesity2. Diabetes mellitus
3. COPD
4. Asthma
5. Rheumatoid arthritis
Correct Answer: 2,3,4
Rationale 2: Beta blockers may cause hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and may mask the symptoms of
hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes.
Rationale 3: Beta blockers may cause significant bronchial constriction.
Rationale 4: Beta blockers may cause significant bronchial constriction.
Question 22
A patient states, “I stopped taking that beta blocker last week. It made me so tired, I just couldn’t go on
taking it.” What are the priority nursing assessments?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Blood pressure
2. Heart rhythm
3. Urinary output
4. Presence of chest pain
5. Presence of respiratory crackles
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Abruptly discontinuing beta blockers may result in acute resurgence of symptoms such as
hypertension.
Rationale 2: Abruptly discontinuing beta blockers may result in acute resurgence of symptoms such as
dysrhythmia.
Rationale 4: Abruptly discontinuing beta blockers may result in chest pain.
Question 23
A patient has been prescribed prazosin (Minipress). What information should the nurse provide?Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “Stay out of the sun until you determine if you become sun-sensitive.”
2. “Take this medication just before you go to bed.”
3. “This medication may make you dizzy.”
4. “This medication may slow your heart rate noticeably.”
5. “Do not take this medication with milk.”
Correct Answer: 2,3
Rationale 2: This medication should be taken just before bedtime as it may cause drowsiness or lightheadedness.
Rationale 3: Dizziness is a common adverse effect of this drug.
Question 24
A patient who was administered prazosin (Minipress) became unconscious 30 minutes after the first
dose. What medications should the nurse prepare for resuscitation?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Normal saline
2. Dobutamine
3. Atenolol (Tenormin)
4. Carvedilol (Coreg)
5. Propranolol (Inderal)
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Unconsciousness after the first dose of prazosin (Minipress) is typically due to severe
hypotension. Normal saline can be used as a volume expander.
Rationale 2: Unconsciousness after the first dose of prazosin (Minipress) is typically due to severe
hypotension. Treatment with a vasopressor such as dobutamine may be indicated.
Question 25Type: MCMA
A patient has been prescribed an adrenergic-blocker for treatment of hypertension. What information
should the nurse provide?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “Rise from a sitting position slowly.”
2. “Sit on the side of the bed a few moments before you stand.”
3. “If you feel dizzy, add more salt to your diet.”
4. “If you feel dizzy, sit or lie down until the dizziness passes.”
5. “Try to continue daily activities even if dizziness occurs.”
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Patients who are starting on adrenergic-blocking drugs should move slowly from the sitting
position.
Rationale 2: Sitting on the side of the bed will help blood pressure normalize before standing.
Rationale 4: If the patient feels dizzy, sitting down or lying down will help to prevent falls.
Question 26
A patient returns to the clinic for follow-up after taking an adrenergic blocking medication for benign
prostatic hypertrophy (BPH.) What assessment questions should the nurse ask?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “What color is your urine?”
2. “Do you have any difficulty starting to urinate?”
3. “Do you have the feeling that your bladder is full?”
4. “When was your last bowel movement?”
5. “Have you noticed being more hungry than usual?”
Correct Answer: 2,3
Rationale 2: Adrenergic blockers may result in hesitancy.Rationale 3: Adrenergic blockers may result in retention of urine.
Question 27
The nurse would classify which sympathomimetics as binding to and activating adrenergic receptors?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Epinephrine
2. Dopamine
3. Amphetamine
4. Cocaine
5. Ephedrine
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: Epinephrine is an endogenous catecholamine that acts directly by binding to and activating
adrenergic receptors.
Rationale 2: Dopamine is an endogenous catecholamine that acts directly by binding to and activating
adrenergic receptors.
Rationale 5: Ephedrine acts both directly and indirectly.
Question 28
A patient is being assessed for the presence of pheochromocytoma. The nurse would prepare for which
interventions?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Monitoring blood pressure
2. Monitoring bowel sounds
3. Administration of phentolamine (Regitine)
4. Rapid administration of normal saline
5. Urinary catheterization to bypass prostatic enlargement
Correct Answer: 1,3Rationale 1: Pheochromocytoma affects blood pressure, so continuous monitoring is necessary.
Rationale 3: Sudden and marked reduction of blood pressure results when a patient with
pheochromocytoma is administered phentolamine (Regitine) parenterally.
Question 29
Due to an administration error, a patient may have received too much phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine).
Which findings would support the nurse’s concerns about overdosage? Standard Text: Select all that
apply.
1. The patient’s heart rate has increased from 72 bpm to 114 bpm.
2. The patient reports feeling anxious.
3. The patient’s blood pressure has increased from 140/86 mmHg to 180/98 mmHg.
4. The patient’s stools are dark and tarry.
5. The patient reports burning at the injection site.
Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: An overdose of phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) will result in tachycardia.
Rationale 3: Overdosage of phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) will result in hypertension.
Question 30
A 48-year-old male patient tells the nurse, “I have stopped taking my prazosin (Minipress). I don’t like its
effect on me.” The nurse should ask further assessment questions about which possible effects?
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Impotence
2. Nasal congestion
3. Somnolence
4. Nervousness
5. Slow heart rate
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Some alpha blockers result in impotence or inhibition of ejaculation.
Rationale 2: Nasal congestion is a common adverse effect of alpha blockade.Rationale 3: Drowsiness may occur with alpha blockers.
Chapter 14:
Question 1
Type: MCSA
The patient tells the nurse he worries about everything all day, feels confused, restless, and just can't
stop worrying. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "You have generalized anxiety; I will teach you some relaxation techniques."
2. "This sounds like social anxiety. You need to calm down and you'll be fine."
3. "You have posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and it is time for your therapy session."
4. "This is called panic disorder; I'll get your medication for you."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive anxiety but not to panic levels.
Other symptoms include restlessness, muscle tension, and loss of focus and ability to concentrate.
Relaxation techniques are effective in reducing anxiety.
Rationale 2: Social anxiety disorder is characterized by "performance anxiety," (i.e., extreme fear when
a patient is in a social situation); there is no information to support that this is what the patient is
experiencing. Also, telling the patient to "calm down" is non-therapeutic.
Rationale 3: Posttraumatic stress disorder is situational anxiety that develops in response to reexperiencing a previous traumatic life event; there is no information that the patient has experienced a
trauma.
Rationale 4: Panic disorder is characterized by intense feelings of apprehension, terror, and impending
doom and increased autonomic nervous system anxiety; the patient does not have these symptoms.
Global Rationale: Generalized anxiety disorder is characterized by excessive anxiety but not to panic
levels. Other symptoms include restlessness, muscle tension, and loss of focus and ability to
concentrate. Relaxation techniques are effective in reducing anxiety. Panic disorder is characterized by
intense feelings of apprehension, terror, and impending doom and increased autonomic nervous system
anxiety; the patient does not have these symptoms. Posttraumatic stress disorder is situational anxiety
that develops in response to re-experiencing a previous traumatic life event; there is no information that
the patient has experienced a trauma. Social anxiety disorder is characterized by "performance anxiety,"
(i.e., extreme fear when a patient is in a social situation); there is no information to support that this is
what the patient is experiencing. Also, telling the patient to "calm down" is non-therapeutic.Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-1 Identify the major types of anxiety disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 162
Question 2
Type: MCMA
The nurse has completed group education for patients with anxiety disorders. The education is
evaluated as successful when the patients make which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Relaxation techniques will often decrease anxiety."
2. "Antianxiety medicine should be used until anxiety is gone."
3. "Antianxiety medicine should not be used indefinitely."
4. "Therapy may help identify where this anxiety comes from."
5. "Different medications are required for treating anxiety than for treating difficulty sleeping."
Correct Answer: 1,3,4Rationale 1: Nonpharmacological techniques such as relaxation techniques are effective in reducing
some levels of anxiety.
Rationale 2: Absence of anxiety is an unrealistic goal because all individuals will have some level of
anxiety during their lifetime.
Rationale 3: For most patients, anti-anxiety medication is intended for short-term use.
Rationale 4: Patients with anxiety disorders should be encouraged to uncover the cause of the anxiety
through cognitive-behavioral therapy or other counseling techniques.
Rationale 5: Often, the same medication can be used for anxiety as well as insomnia.
Global Rationale: Patients with anxiety disorders should be encouraged to uncover the cause of the
anxiety through cognitive-behavioral therapy or other counseling techniques. Nonpharmacological
techniques such as relaxation techniques are effective in reducing some levels of anxiety. For most
patients, anti-anxiety medication is intended for short-term use. Absence of anxiety is an unrealistic goal
because all individuals will have some level of anxiety during their lifetime. Often, the same medication
can be used for anxiety as well as insomnia.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 14-3 Discuss factors contributing to anxiety and explain some nonpharmacologic
therapies used to cope with this disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 164Question 3
Type: MCSA
The patient tells the nurse that she is interested in the human brain and questions which parts of the
brain control anxiety and insomnia. What is the best reply by the nurse?
1. "The limbic system and reticular activating system control anxiety and insomnia."
2. "The frontal lobes and limbic system control anxiety and insomnia."
3. "The thalamus and reticular activating system control anxiety and insomnia."
4. "The limbic system and hypothalamus control anxiety and insomnia."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Neural systems associated with anxiety and restlessness include the limbic system and the
reticular activating system. The reticular activating system is responsible for sleeping and wakefulness
and performs an alerting function for the entire cerebral cortex.
Rationale 2: The frontal lobes are not responsible for anxiety and sleep.
Rationale 3: The thalamus is not responsible for anxiety and sleep.
Rationale 4: The hypothalamus is not responsible for anxiety and sleep.
Global Rationale: Neural systems associated with anxiety and restlessness include the limbic system and
the reticular activating system. The reticular activating system is responsible for sleeping and
wakefulness and performs an alerting function for the entire cerebral cortex. The limbic system and the
reticular activating system, not the hypothalamus, are responsible for anxiety and sleep. The limbic
system and the reticular activating system, not the frontal lobes, are responsible for anxiety and sleep.
The limbic system and the reticular activating system, not the thalamus, are responsible for anxiety and
sleep.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.2 Synthesize theories and concepts from liberal education to build an
understanding of the human experience.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-2 Identify the regions of the brain associated with anxiety, sleep, and
wakefulness.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 162
Question 4
Type: MCMA
The patient tells the nurse, "I am really confused after talking to my doctor. He said I would be taking
different kinds of medications for my anxiety and insomnia. Will you please explain it?" What is the best
response by the nurse?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "You will be taking medications known as sedative-hypnotics."
2. "You will be taking medications known as antidepressants."
3. "You will be taking a medication known as paraldehyde."
4. "You will be taking medications known as barbiturates."
5. "You will be taking medications known as benzodiazepines."
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: The three categories of medications used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders include the
sedative-hypnotics.
Rationale 2: The three categories of medications used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders include the
antidepressants.
Rationale 3: Paraldehyde is no longer used for anxiety or insomnia because of significant side effects
and the availability of more effective medications.
Rationale 4: Barbiturates are no longer used for anxiety or insomnia because of significant side effects
and the availability of more effective medications.Rationale 5: The three categories of medications used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders include the
benzodiazepines.
Global Rationale: The three categories of medications used to treat anxiety and sleep disorders include
the benzodiazepines, antidepressants, and sedative-hypnotics. Barbiturates are no longer used for
anxiety or insomnia because of significant side effects and the availability of more effective medications.
Paraldehyde is no longer used for anxiety or insomnia because of significant side effects and the
availability of more effective medications.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-4 Identify the three classes of medications used to treat anxiety and sleep
disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.2 Compare the classes of medication used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 167
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The patient has generalized anxiety disorder. He asks the nurse, "Will I need medication for this? My
neighbor is very nervous and he takes medication." What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Medications are a way of life for patients with anxiety disorders."
2. "Medication is necessary initially; later we will try therapy."
3. "Probably not, but you shouldn't compare yourself to your neighbor."4. "Medication is necessary when anxiety interferes with your quality of life."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Medications are not considered "a way of life" for patients with anxiety disorders; many
patients can manage anxiety without medications.
Rationale 2: Medication combined with therapy is considered the best approach for treatment of
anxiety disorders.
Rationale 3: The nurse does not have enough information to tell the patient that medications will
probably not be necessary.
Rationale 4: It is more productive to identify and treat the cause of anxiety than to use medications.
When anxiety becomes severe enough to significantly interfere with the patient's quality of life,
pharmacotherapy is indicated.
Global Rationale: It is more productive to identify and treat the cause of anxiety than to use
medications. When anxiety becomes severe enough to significantly interfere with the patient's quality of
life, pharmacotherapy is indicated. Medications are not considered "a way of life" for patients with
anxiety disorders; many patients can manage anxiety without medications. The nurse does not have
enough information to tell the patient that medications will probably not be necessary. Medication
combined with therapy is considered the best approach for treatment of anxiety disorders.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-5 Explain the pharmacologic management of anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 164Question 6
Type: MCSA
The patient has been treated by the same physician for 2 years and has had insomnia the entire time.
Many different medications have been tried with limited success. What should be the nurse's primary
assessment at this time?
1. Assess for a primary sleep disorder such as sleep apnea.
2. Assess if the patient has been selling his medications to addicts.
3. Assess if the patient has an addictive personality disorder.
4. Assess the patient for a primary personality disorder.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: If the patient has a primary sleep disorder such as sleep apnea, this must be treated to
relieve the insomnia. Also, medications such as benzodiazepines depress respiratory drive and would
aggravate the sleep apnea.
Rationale 2: While it is remotely possible that the patient is selling his medication, it is not likely for a
patient with an anxiety disorder to do this.
Rationale 3: There is no information that the patient might have an addictive personality disorder. If he
did, the nurse would know this after 2 years of treatment.
Rationale 4: There is no information that the patient might have a personality disorder. If he did, the
nurse would most likely recognize this after 2 years of treatment.
Global Rationale: If the patient has a primary sleep disorder such as sleep apnea, this must be treated to
relieve the insomnia. Also, medications such as benzodiazepines depress respiratory drive and would
aggravate the sleep apnea. There is no information that the patient might have a personality disorder. If
he did, the nurse would most likely recognize this after 2 years of treatment. While it is remotely
possible that the patient is selling his medication; it is not likely for a patient with an anxiety disorder to
do this. There is no information that the patient might have an addictive personality disorder. If he did,
the nurse would know this after 2 years of treatment.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.2 Demonstrate an understanding of the basic elements of the
research process and models or applying evidence to clinical practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-7 Identify normal sleep patterns and explain how these might be affected by
anxiety and stress.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 165
Question 7
Type: MCSA
The patient is scheduled to have an EEG to confirm the presence of a sleep disorder. The patient asks
the nurse to describe NREM stage 3 sleep. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "This is the lightest stage of sleep and is profoundly affected by anxiety."
2. "Dreaming occurs here; without dreams you will be irritable and paranoid."
3. "This is the deepest stage of sleep; without it you will be tired and depressed."
4. "This is the also called paradoxical sleep."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: NREM stage 3 sleep is the deepest stage of sleep. Patients who are deprived of it
experience depression and a feeling of apathy and fatigue.
Rationale 2: Dreaming occurs in REM sleep, not NREM sleep.
Rationale 3: NREM stage 3 is not the lightest stage of sleep.
Rationale 4: REM sleep is often called paradoxical sleep.Global Rationale: NREM stage 3 sleep is the deepest stage of sleep. Patients who are deprived of it
experience depression and feelings of apathy and fatigue. Dreaming occurs in REM sleep, not NREM
sleep. NREM stage 3 is not the lightest stage of sleep. REM sleep is often called paradoxical sleep.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.2 Demonstrate an understanding of the basic elements of the
research process and models or applying evidence to clinical practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-7 Identify normal sleep patterns and explain how these might be affected by
anxiety and stress.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 166
Question 8
Type: MCSA
The patient has been taking lorazepam (Ativan) for 2 years. The patient stopped this medication after a
neighbor said the drug manufacturer's plant was contaminated with rat droppings. What best describes
the nurse's assessment of the patient when seen 3 days after stopping his medication?
1. Increased heart rate, fever, and muscle cramps
2. Nothing different; it is safe to abruptly stop lorazepam (Ativan)
3. Pinpoint pupils, constipation, and urinary retention4. A sense of calmness and lack of anxiety
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Many central nervous system (CNS) depressants can cause physical and psychological
dependence. The withdrawal syndrome for some central nervous system (CNS) depressants can include
fever, seizures, increased pulse, anorexia, muscle cramps, disorientation, etc.
Rationale 2: It is not safe to abruptly stop lorazepam (Ativan); withdrawal symptoms will occur.
Rationale 3: Pinpoint pupils, constipation, and urinary retention are signs of opioid use.
Rationale 4: The patient would be anxious, not calm, during benzodiazepine withdrawal.
Global Rationale: Many central nervous system (CNS) depressants can cause physical and psychological
dependence. The withdrawal syndrome for some central nervous system (CNS) depressants can include
fever, seizures, increased pulse, anorexia, muscle cramps, disorientation, etc. It is not safe to abruptly
stop lorazepam (Ativan); withdrawal symptoms will occur. Pinpoint pupils, constipation, and urinary
retention are signs of opioid use. The patient would be anxious, not calm, during benzodiazepine
withdrawal.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-5 Explain the pharmacologic management of anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 167Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient comes to the emergency department after an overdose of lorazepam (Ativan). The nurse
will plan to administer which medication?
1. Pralidoxime (Protopam)
2. Naloxone (Narcan)
3. Flumazenil (Romazicon)
4. Nalmefene (Revex)
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Pralidoxime (Protopam) is indicated for treatment of organophosphate poisoning.
Rationale 2: Naloxone (Narcan) is indicated for treatment of opiate overdose.
Rationale 3: Should an overdose of benzodiazepines occur, flumazenil (Romazicon) is a specific
benzodiazepine receptor antagonist that can be administered to reverse central nervous system (CNS)
depression.
Rationale 4: Nalmefene (Revex) is indicated for treatment of opiate overdose.
Global Rationale: Should an overdose of benzodiazepines occur, flumazenil (Romazicon) is a specific
benzodiazepine receptor antagonist that can be administered to reverse central nervous system (CNS)
depression. Naloxone (Narcan) is indicated for treatment of opiate overdose. Nalmefene (Revex) is
indicated for treatment of opiate overdose. Pralidoxime (Protopam) is indicated for treatment of
organophosphate poisoning.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 14-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drugs and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4. 2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacological
management.
Page Number: 171
Question 10
Type: MCSA
The nurse works with a physician who frequently prescribes benzodiazepines. The use of
benzodiazepines in which patient would cause the nurse the most concern?
1. An 87-year-old patient who uses a cane for ambulation
2. A 9-year-old child with panic attacks
3. A 42-year-old businessman who travels internationally
4. A 32-year-old mother of two preschool children
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Benzodiazepines should be used with caution in older adults due to their adverse effects of
drowsiness and sedation. This puts older adults at risk of falls.
Rationale 2: Benzodiazepines must be used with caution in children, but these patients are not at as
high risk as older adults.
Rationale 3: There is minimal concern with benzodiazepine use in a 42-year-old patient.
Rationale 4: There is minimal concern with benzodiazepine use in a 32-year-old patient.
Global Rationale: Benzodiazepines should be used with caution in older adults due to their adverse
effects of drowsiness and sedation. This puts older adults at risk for falls. There have been few studies of
benzodiazepine use in the pediatric population; benzodiazepines must be used with caution, but these
patients are not at as high risk as the elderly population. There is minimal concern with benzodiazepine
use in a 32-year-old patient. There is minimal concern with benzodiazepine use in a 42-year-old patient.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition of care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-6 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of anxiety and
insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 171
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The nurse has completed medication education for the anxious patient who is receiving buspirone
(BuSpar). The nurse determines that the patient needs additional instruction when the patient makes
which statement?
1. "Side effects I might experience include dizziness, headache, and drowsiness."
2. "I can take this medication when I feel anxious and it will relax me."
3. "I have to take this medicine on a regular basis for it to help me."
4. "I don't need to worry about becoming dependent on this medication."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Side effects of buspirone (BuSpar) include dizziness, headache, and drowsiness.Rationale 2: Buspirone (BuSpar) works by altering levels of neurotransmitters and takes a few weeks to
achieve optimal anxiety reduction. It cannot be used as an "as needed" (prn) medication.
Rationale 3: Buspirone (BuSpar) works by altering levels of neurotransmitters and takes a few weeks to
achieve optimal anxiety reduction. The drug must be taken consistently for this to occur.
Rationale 4: Dependence and withdrawal are less of a concern with buspirone (BuSpar) than with some
other antianxiety drugs.
Global Rationale: Buspirone (BuSpar) works by altering levels of neurotransmitters and takes a few
weeks to achieve optimal anxiety reduction. It cannot be used as an "as needed" (prn) medication. Side
effects of buspirone (BuSpar) include dizziness, headache, and drowsiness. Dependence and withdrawal
are less of a concern with buspirone (BuSpar) than with some other antianxiety drugs. Buspirone
(BuSpar) works by altering levels of neurotransmitters and takes a few weeks to achieve optimal anxiety
reduction. The drug must be taken consistently for this to occur.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition of care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 14-6 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of anxiety and
insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 172
Question 12
Type: MCSAThe patient is receiving zolpidem (Ambien) for treatment of short-term insomnia. What is the primary
safety concern of the nurse when the patient takes this medication?
1. Dizziness and daytime sedation
2. Nausea
3. Diarrhea
4. Sleepwalking
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Dizziness and daytime sedation are common side effects of zolpidem (Ambien) and usually
subside after a few days on the medication.
Rationale 2: Nausea is a common side effect of zolpidem (Ambien) and usually subsides after a few days
on the medication.
Rationale 3: Diarrhea is a common side effect of zolpidem (Ambien) and usually subsides after a few
days on the medication.
Rationale 4: During sleepwalking, a patient may leave the home and cause injury to self.
Global Rationale: During sleepwalking, a patient may leave the home and cause injury to self. Nausea
and gastrointestinal (GI) distress are common side effects of zolpidem (Ambien) and usually subside
after a few days on the medication. Dizziness and daytime sedation are common side effects of
zolpidem (Ambien) and usually subside after a few days on the medication. Nausea and diarrhea are
common side effects of zolpidem (Ambien) and usually subside after a few days on the medication.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drugs and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4. 2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacological
management.
Page Number: 174
Question 13
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving escitalopram (Lexapro) for treatment of generalized anxiety disorder. The
patient asks the nurse, "I am just nervous, not depressed. Why am I taking an antidepressant medicine?"
What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "The same brain chemicals are involved with anxiety as well as depression.”
2. "You are really depressed; it is just manifested as anxiety. These medications are safer than
benzodiazepines."
3. "Your doctor thinks that this is the best treatment for your anxiety, and these medications are safer
than benzodiazepines."
4. "The two disorders go together, and if you treat depression, the anxiety goes away."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Antidepressants are frequently used to treat symptoms of anxiety. They reduce anxiety by
altering levels of norepinephrine and serotonin. These neurotransmitters are also involved in
depression.
Rationale 2: The patient is being treated for generalized anxiety; this is different from depression.
Rationale 3: Telling the patient that the doctor knows best is a condescending reply and does not
answer the patient's question.
Rationale 4: Depression and anxiety are two separate disorders.
Global Rationale: Antidepressants are frequently used to treat symptoms of anxiety. They reduce
anxiety by altering levels of norepinephrine and serotonin. These neurotransmitters are also involved in
depression. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are safer than benzodiazepines, but
depression and anxiety are two separate disorders. The patient is being treated for generalized anxiety;this is different from depression. Telling the patient that the doctor knows best is a condescending reply
and does not answer the patient's question.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drugs and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4. 2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacological
management.
Page Number: 169
Question 14
Type: MCSA
The patient has been receiving escitalopram (Lexapro) for treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Unknown to the nurse, the patient has also been self-medicating with St. John's wort. The patient comes
to the office with symptoms of hyperthermia and diaphoresis. Which statement best describes the
result of the nurse's assessment?
1. The patient is experiencing symptoms of St. John's wort toxicity, as the medication was most likely
outdated.
2. The patient has contracted a viral infection. Escitalopram (Lexapro) and St. John's wort are safe to
take together.3. The patient has not been taking escitalopram (Lexapro) and is experiencing withdrawal.
4. The patient has combined two antidepressant medications and is experiencing serotonin syndrome.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: The patient's symptoms are consistent with a different syndrome, and there is no evidence
that the patient's St. John's wort is outdated.
Rationale 2: It is not considered safe to combine escitalopram (Lexapro) and St. John's wort.
Rationale 3: There is no evidence that the patient has not been taking the escitalopram (Lexapro).
Rationale 4: Use caution with herbal supplements such as St. John's wort, which may increase the
effects of escitalopram (Lexapro) and cause serotonin syndrome. The patient's symptoms are consistent
with serotonin syndrome.
Global Rationale: Use caution with herbal supplements such as St. John's wort, which may increase the
effects of escitalopram (Lexapro) and cause serotonin syndrome. The patient's symptoms are consistent
with serotonin syndrome, and there is no evidence that the patient has not been taking the
escitalopram (Lexapro). The patient's symptoms are consistent with serotonin syndrome, and there is no
evidence that the patient's St. John's wort is outdated. The patient's symptoms are consistent with
serotonin syndrome. It is not considered safe to combine escitalopram (Lexapro) and St. John's wort.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drugs and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4. 2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacological
management.
Page Number: 169
Question 15
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving the benzodiazepine clonazepam (Klonopin) for the treatment of panic attacks.
What is an important medication outcome for this patient as it relates to safety?
1. The patient will verbalize the signs of developing Stevens-Johnson rash.
2. The patient will verbalize the importance of diet restrictions related to this drug.
3. The patient will verbalize the importance of having routine blood work done.
4. The patient will verbalize the consequences of stopping the drug abruptly.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Stevens-Johnson rash is not a side effect of benzodiazepines.
Rationale 2: There aren't any diet restrictions with the use of benzodiazepines.
Rationale 3: Routine blood work is not required with the use of benzodiazepines.
Rationale 4: Abrupt discontinuation of benzodiazepines like clonazepam (Klonopin) can result in serious
withdrawal symptoms.
Global Rationale: Abrupt discontinuation of benzodiazepines like clonazepam (Klonopin) can result in
serious withdrawal symptoms. There aren't any diet restrictions with the use of benzodiazepines.
Routine blood work is not required with the use of benzodiazepines. Stevens-Johnson rash is not a side
effect of benzodiazepines.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 14-8 Categorize drugs used for anxiety and insomnia based on their classification
and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.2 Compare the classes of medication used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 170
Question 16
Type: MCSA
An individual who has difficulty sleeping due to two final examinations scheduled for the same day later
in the week most likely would be suffering from
1. situational anxiety.
2. social anxiety.
3. obsessive-compulsive disorder.
4. performance anxiety.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The final examination is a temporary event that is the cause of the anxiety. Once the
examination is over, it is likely that the situational anxiety will end.
Rationale 2: Social anxiety is a fear of crowds.
Rationale 3: Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) involves recurrent, intrusive thoughts or repetitive
behaviors that interfere with normal activities or relationships.
Rationale 4: Although the situation presented required the student to perform on the exam, it is best
defined as situational anxiety.
Global Rationale: The final examination is a temporary event that is the cause of the anxiety. Once the
examination is over, it is likely that the situational anxiety will end. Social anxiety is a fear of crowds.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) involves recurrent, intrusive thoughts or repetitive behaviors thatinterfere with normal activities or relationships. Although the situation presented required the student
to perform on the exam, it is best defined as situational anxiety.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-1 Identify the major types of anxiety disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 162
Question 17
Type: MCSA
The most productive way of managing stress would be to
1. use a combined approach (drug use and nonpharmacological strategies).
2. use anxiolytics.
3. practice meditation.
4. determine the cause and address it accordingly.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: A combined approach is the second best approach.
Rationale 2: Use of medications alone is not the best approach.
Rationale 3: Meditation may or may not be useful for specific individuals.Rationale 4: Stress is generally a symptom of an underlying disorder. It is more productive to uncover
and address the cause than to treat the symptoms.
Global Rationale: Stress is generally a symptom of an underlying disorder. It is more productive to
uncover and address the cause than to treat the symptoms. A combined approach is the second best
approach. Use of medications alone is not the best approach. Meditation may or may not be useful for
specific individuals.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 14-3 Discuss factors contributing to anxiety and explain some nonpharmacologic
therapies used to cope with this disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 164
Question 18
Type: MCSA
Which area of the brain is primarily responsible for maintaining sleep and wakefulness?
1. Reticular activating system
2. Cerebral cortex
3. Limbic system
4. CerebellumCorrect Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The reticular activating system is responsible for sleeping and wakefulness.
Rationale 2: The primary functions of the cerebral cortex do not include sleep and wakefulness.
Rationale 3: The limbic system is responsible for emotional expression, learning, and memory.
Rationale 4: The primary functions of the cerebellum do not include sleep and wakefulness.
Global Rationale: The reticular activating system is responsible for sleeping and wakefulness. The limbic
system is responsible for emotional expression, learning, and memory. The primary functions of the
cerebral cortex and cerebellum do not include sleep and wakefulness.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-3 Discuss factors contributing to anxiety and explain some nonpharmacologic
therapies used to cope with this disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 163
Question 19
Type: MCSA
Which drug category can be used for treating anxiety?
1. Antitussives2. Anticoagulants
3. Seizure drugs
4. Antibiotics
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Antitussives are used as cough suppressants.
Rationale 2: Anticoagulants are used to prevent blood clots from forming.
Rationale 3: In addition to antidepressants, several other drug classes are used to treat anxiety,
including seizure drugs.
Rationale 4: Antibiotics are used primarily for bacterial infections.
Global Rationale: In addition to antidepressants, several other drug classes are used to treat anxiety,
including seizure drugs. Antibiotics are used primarily for bacterial infections. Antitussives are used as
cough suppressants. Anticoagulants are used to prevent blood clots from forming.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 14-5 Explain the pharmacologic management of anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.2 Compare the classes of medication used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 172
Question 20Type: MCSA
Benzodiazepines are often the drug of choice for managing anxiety and insomnia. Which statement best
explains why?
1. Benzodiazepines are the most effective.
2. Benzodiazepines have the lowest risk of dependency and tolerance.
3. Benzodiazepines are most likely to be covered under insurance premiums.
4. Benzodiazepines are the most affordable.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Benzodiazepines are not necessarily more effective than other drugs.
Rationale 2: Benzodiazepines have a lower risk of dependency and tolerance than do other drugs used
for anxiety and insomnia (such as the barbiturates).
Rationale 3: Benzodiazepines are not necessarily more likely to be covered under insurance premiums.
Although economics is an important factor in pharmacology, drug safety is essential for widespread use.
Rationale 4: Benzodiazepines are not necessarily more affordable. Although economics is an important
factor in pharmacology, drug safety is essential for widespread use.
Global Rationale: Benzodiazepines have a lower risk of dependency and tolerance than do other drugs
used for anxiety and insomnia (such as the barbiturates). They are not necessarily more effective,
affordable, or likely to be covered under insurance premiums. Although economics is an important
factor in pharmacology, drug safety is essential for widespread use.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: PlanningLearning Outcome: 14-5 Explain the pharmacologic management of anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.2 Compare the classes of medication used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 170
Question 21
Type: MCSA
Which common adverse effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) would be stressed by
the nurse during patient discharge?
1. Drowsiness and coma
2. Weight gain and sexual dysfunction
3. Headache and nausea
4. Dry mouth and urine retention
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Drowsiness or coma is not a common adverse effect.
Rationale 2: Weight gain or sexual dysfunction are common adverse effects and may result in poor
medication adherence.
Rationale 3: Headache is not a common adverse effect.
Rationale 4: Although anticholinergic effects such as dry mouth and urine retention could occur, they
are not as common as another set of adverse effects.
Global Rationale: Although anticholinergic effects such as dry mouth and urine retention could occur,
they are not as common as weight gain or sexual dysfunction. Headache is not a common adverse
effect, and neither is drowsiness or coma. Overdoses will cause anxiety and restlessness (not
drowsiness).
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-5 Explain the pharmacologic management of anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.2 Compare the classes of medication used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 169
Question 22
Type: MCSA
A patient taking which of the following medications should avoid foods high in tyramine?
1. MAOIs
2. SSRIs
3. Beta blockers
4. Benzodiazepines
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: MAOIs and foods high in tyramine can produce a hypertensive crisis, and therefore should
not be taken together.
Rationale 2: There is no associated between SSRIs and avoidance of tyramine.
Rationale 3: MAOIs and foods high in tyramine can produce a hypertensive crisis, and therefore should
not be taken together. There is no associated between beta blockers and avoidance of tyramine.
Rationale 4: MAOIs and foods high in tyramine can produce a hypertensive crisis, and therefore should
not be taken together. There is no associated between benzodiazepines and avoidance of tyramine.
Global Rationale: MAOIs and foods high in tyramine can produce a hypertensive crisis, and therefore
should not be taken together. There is no associated between SSRIs, beta blockers, or benzodiazepines
and avoidance of tyramine.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 14-5 Explain the pharmacologic management of anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 170
Question 23
Type: MCSA
Which statement regarding the use of zolpidem (Ambien) for insomnia is accurate?
1. Patients using Ambien should avoid foods that contain tyramine.
2. Ambien will take longer to produce an effect when taken with food.
3. Ambien is contraindicated during pregnancy but can be taken by breastfeeding mothers.
4. Ambien is classified as a benzodiazepine.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Patients using MAOIs (not Ambien) should avoid foods high in tyramine.
Rationale 2: The absorption of Ambien is slowed when taken with food.
Rationale 3: It is classified as pregnancy category B and should be avoided by breastfeeding mothers.
Patients using MAOIs (not Ambien) should avoid foods high in tyramine.Rationale 4: It is classified as a nonbenzodiazepine CNS depressant.
Global Rationale: The absorption of Ambien is slowed when taken with food. It is classified as a
nonbenzodiazepine CNS depressant. It is classified as pregnancy category B and should be avoided by
breastfeeding mothers. Patients using MAOIs (not Ambien) should avoid foods high in tyramine.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 14-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drugs and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4. 2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacological
management.
Page Number: 10
Question 24
Type: MCSA
Which explanation best indicates why barbiturates are rarely used to treat anxiety and insomnia?
1. They have a greater associated cost.
2. They have a high risk of producing an allergic response.
3. They are seldom effective.4. They produce many serious adverse effects.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Barbiturates are not necessarily more expensive.
Rationale 2: Allergic reactions can occur, but are rare, and are not a primary reason they are no longer
used for anxiety and/or insomnia.
Rationale 3: Barbiturates can be effective.
Rationale 4: Barbiturates were the drug of choice for anxiety and insomnia prior to the discovery of
safer drug alternatives.
Global Rationale: Barbiturates were the drug of choice for anxiety and insomnia prior to the discovery
of safer drug alternatives. They can be effective and are not necessarily more expensive. Allergic
reactions can occur, but are rare, and are not a primary reason they are no longer used for anxiety
and/or insomnia.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 14-4 Identify the three classes of medications used to treat anxiety and sleep
disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.2 Compare the classes of medication used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 171
Question 25
Type: MCMAIt is important for the nurse to obtain a thorough history from a patient who is experiencing anxiety.
This history will help to distinguish
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. the best method of pharmacotherapy.
2. whether the patient might benefit from individual or group therapy.
3. the category of anxiety disorder.
4. the region of the brain that is causing the anxiety disorder.
5. substances that might worsen anxiety.
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: The health care provider must accurately diagnose the anxiety disorder, because treatment
differs among the various types of anxiety disorders. Some anxiety disorders are debilitating and require
effective pharmacotherapy.
Rationale 2: Some patients benefit from individual or group psychotherapy, which can help them
identify and overcome the root causes of their worry and fear.
Rationale 3: A thorough health history is not used to determine the category of anxiety disorder.
Rationale 4: A thorough health history is not used to determine the region of the brain that is causing
the anxiety disorder.
Rationale 5: When obtaining a comprehensive medication history during the initial patient assessment,
the nurse should observe any substances the patient is taking that might worsen or cause anxiety
symptoms. Sometimes discontinuing or substituting an alternate drug for these "anxiety-promoting"
medications can lessen patient symptoms.
Global Rationale: The health care provider must accurately diagnose the anxiety disorder, because
treatment differs among the various types of anxiety disorders. Some anxiety disorders are debilitating
and require effective pharmacotherapy. Some patients benefit from individual or group psychotherapy,
which can help them identify and overcome the root causes of their worry and fear. When obtaining a
comprehensive medication history during the initial patient assessment, the nurse should observe any
substances the patient is taking that might worsen or cause anxiety symptoms. Sometimes discontinuing
or substituting an alternate drug for these "anxiety-promoting" medications can lessen patient
symptoms. A thorough health history is not used to determine the category of anxiety disorder or the
region of the brain that is causing the anxiety disorder.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 174
Question 26
Type: MCMA
The patient is diagnosed with post-traumatic stress disorder. What will the nurse assess in this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Tachycardia
2. Extreme nervousness or panic attacks
3. Inability to focus
4. A fear of exposure to germs
5. Hallucinations, nightmares, or flashbacks
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,5Rationale 1: PTSD is a type of extreme situational anxiety. Tachycardia is a symptom of anxiety.
Rationale 2: PTSD is a type of extreme situational anxiety. Extreme nervousness or panic attacks are
symptoms of anxiety.
Rationale 3: PTSD is a type of extreme situational anxiety. Symptoms of anxiety include inability to
focus.
Rationale 4: A fear of exposure to germs is typical of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Rationale 5: In post-traumatic stress disorder the person re-experiences traumatic events, which can
take the form of nightmares, hallucinations, or flashbacks.
Global Rationale: PTSD is a type of extreme situational anxiety. Tachycardia, inability to focus, and
extreme nervousness is a symptom of this anxiety. In post-traumatic stress disorder the person reexperiences traumatic events, which can take the form of nightmares, hallucinations, or flashbacks. A
fear of exposure to germs is typical of obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 14-3 Discuss factors contributing to anxiety and explain some nonpharmacologic
therapies used to cope with this disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 162
Question 27Type: MCMA
A patient has been in the intensive care unit for a week receiving various procedures throughout the day
and night. Currently the patient, though physiologically stable, is irritable and paranoid and complains of
vivid dreams when dozing off to sleep. What are the best actions for the nurse to take at this time?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Check the patient's oxygen status.
2. Request an order for sleep medication.
3. Assess the patient's vital signs.
4. Turn down the lights at night and reduce noise to a minimum.
5. Schedule all tests and procedures before 9 p.m. or after 7 a.m.
Correct Answer: 2,4,5
Rationale 1: The patient is physiologically stable.
Rationale 2: Since it is important for the patient to get rest, an order for sleep medication would be
appropriate.
Rationale 3: It is not necessary to assess the patient's vital signs, since the patient is physiologically
stable.
Rationale 4: Turning down the lights and reducing noises will help support sleep.
Rationale 5: Scheduling tests and procedures so as to not disturb the patient's sleep is indicated.
Global Rationale: Since it is important for the patient to get rest, an order for sleep medication would
be appropriate. When deprived of REM sleep, people experience a sleep debt and become frightened,
irritable, paranoid, and even emotionally disturbed. It is speculated that to make up for their lack of
dreaming, these persons experience far more daydreaming and fantasizing throughout the day. It is
important to institute measures that promote restful sleep. Turning down the lights and reducing noises
will help support sleep. It is not necessary to assess the patient's vital signs or oxygenation status, since
the patient is physiologically stable.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Psychosocial IntegrityClient Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 166
Question 28
Type: MCMA
A patient whose spouse recently died is having difficulty falling asleep and does not want to take any
prescription medications to induce sleep. How should the nurse respond?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Make certain your bedroom is nice and warm."
2. "There are alternative methods to treat insomnia, such as yoga, meditation, and massage therapy."
3. "Eating a large meal at bedtime will help induce sleep."
4. "Avoid caffeinated beverages, nicotine, and alcohol immediately prior to bedtime."
5. "Count sheep after lying down in order to enhance sleep."
Correct Answer: 2,4Rationale 1: Sleep disturbances may be related to sleeping in a room that is too warm.
Rationale 2: Acupuncture, aromatherapy, yoga, prayer, massage, meditation, biofeedback therapy,
hypnosis, guided imagery, and music therapy are alternative treatments for anxiety and insomnia.
Rationale 3: Eating a large meal prior to bedtime is a secondary cause of insomnia.
Rationale 4: Amphetamines, cocaine, caffeinated beverages, corticosteroids, sympathomimetics,
antidepressants, alcohol use, nicotine, and tobacco use are secondary causes of insomnia.
Rationale 5: There is no evidence that counting sheep at bedtime helps to induce sleep.
Global Rationale: Acupuncture, aromatherapy, yoga, prayer, massage, meditation, biofeedback therapy,
hypnosis, guided imagery, and music therapy are alternative treatments for anxiety and insomnia.
Amphetamines, cocaine, caffeinated beverages, corticosteroids, sympathomimetics, antidepressants,
alcohol use, nicotine, and tobacco use are secondary causes of insomnia. Sleep disturbances may be
related to sleeping in a room that is too warm. Eating a large meal prior to bedtime is a secondary cause
of insomnia. There is no evidence that counting sheep at bedtime helps to induce sleep.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.2 Demonstrate an understanding of the basic elements of the
research process and models or applying evidence to clinical practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-7 Identify normal sleep patterns and explain how these might be affected by
anxiety and stress.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.1 Examine the etiology, pathophysiology and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 165
Question 29Type: MCMA
A patient who has recently experienced the loss of a spouse asks the nurse if there are any over-thecounter herbs or nonprescription medications that can be used to improve insomnia. How should the
nurse respond to this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Ginger root is commonly taken to improve sleep."
2. "Ginkgo is an herb commonly taken to improve sleep."
3. "Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and doxylamine are over-the-counter meds sometimes taken to
produce drowsiness."
4. "Valerian and melatonin are herbs commonly taken to improve sleep."
5. "Kava is an herb taken to improve sleep."
Correct Answer: 3,4
Rationale 1: Ginger root is not used to improve sleep.
Rationale 2: Ginkgo is not used to improve sleep.
Rationale 3: Diphenhydramine and doxylamine are two antihistamines frequently used to produce
drowsiness.
Rationale 4: An herbal product with demonstrated efficacy in promoting relaxation is valerian root.
Supplemental melatonin at bedtime is alleged to decrease the time required to fall asleep and to
produce a deep and restful sleep.
Rationale 5: High doses of kava can damage the liver and should not be used unless recommended by a
health care provider.
Global Rationale: Diphenhydramine and doxylamine are two antihistamines frequently used to produce
drowsiness. An herbal product with demonstrated efficacy in promoting relaxation is valerian root.
Supplemental melatonin at bedtime is alleged to decrease the time required to fall asleep and to
produce a deep and restful sleep. Ginger root is not used to improve sleep. Ginkgo is not used to
improve sleep. High doses of kava can damage the liver and should not be used unless recommended by
a health care provider.
Cognitive Level: ApplyingClient Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 14-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
anxiety and insomnia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.4.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 165 and 177
Question 30
Type: MCMA
A patient who is complaining of anxiety and difficulty sleeping has asked what prescription medications
would assist in getting to sleep. What would be appropriate responses?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
2. Valerian root
3. Ramelteon (Rozerem)
4. Flurazepam (Dalmane)
5. Zolpidem (Ambien)
Correct Answer: 3,4,5Rationale 1: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) can be obtained over the counter and does not need a
prescription to obtain. It does promote getting to sleep.
Rationale 2: Valerian is an herbal product that does not need a prescription to obtain. It does promote
getting to sleep.
Rationale 3: Rozerem is a newer, nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic approved to treat chronic insomnia in
people who have problems falling asleep.
Rationale 4: Benzodiazepines are drugs of choice for generalized anxiety disorder and the short-term
therapy of insomnia. Flurazepam (Dalmane) should be taken at bedtime because it quickly produces
significant drowsiness.
Rationale 5: Ambien is a sedative-hypnotic approved for short-term treatment of insomnia.
Chapter 15:
Question 1
Type: MCSA
The patient says to the nurse, "My doctor said I have epilepsy and need to take medicine for those
seizures I had. Do I really need medicine?" What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Having epilepsy is the same as having a mental illness; the medications are very similar."
2. "You will need medicine for a little while to cure the seizures."
3. "You might not need medicine; you may be controlled by a ketogenic diet."
4. "Yes, you need to take medication on a continual basis to control the seizures."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Epilepsy is not a mental illness, although some of the same medications are used to control
symptoms of both disorders.
Rationale 2: Epilepsy and associated seizures are not curable with medications.
Rationale 3: The ketogenic diet is used when seizures cannot be controlled through pharmacotherapy or
when there are unacceptable side effects to the medications.
Rationale 4: Epilepsy is a disease where seizures occur on a chronic basis. Once seizures are controlled,
patients are continued indefinitely on the antiseizure drug.
Global Rationale: Epilepsy is a disease where seizures occur on a chronic basis. Once seizures are
controlled, patients are continued indefinitely on the antiseizure drug. Epilepsy and associated seizures
are not curable with medications. The ketogenic diet is used when seizures cannot be controlledthrough pharmacotherapy or when there are unacceptable side effects to the medications. Epilepsy is
not a mental illness, although some of the same medications are used to control symptoms of both
disorders.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-2 Recognize possible causes of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 181
Question 2
Type: MCMA
The nurse is teaching a class for patients who have been recently diagnosed with epilepsy. The nurse
determines that learning has occurred when the patients make which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Excessive stress levels cause disruptions in how the brain receives oxygen, leading to epilepsy."
2. "Epilepsy may be caused by a head injury."
3. "Eating disorders, like anorexia nervosa, increase the risk for developing epilepsy."
4. "A stroke, or brain attack, could increase the risk for developing epilepsy."5. "With some cases of epilepsy, the cause is never determined."
Correct Answer: 2,4,5
Rationale 1: Excessive levels of stress cannot disrupt cerebral oxygen to the extent that epilepsy would
occur.
Rationale 2: Head trauma is a known cause of seizures.
Rationale 3: There is no known correlation with anorexia nervosa and the development of epilepsy.
Rationale 4: Changes in cerebral perfusion such as hypotension; strokes, or brain attacks; and shock may
be causes of seizures.
Rationale 5: In some cases, the exact etiology may not be identified.
Global Rationale: Epilepsy is a disorder where seizures occur on a chronic basis. Head trauma is a known
cause of seizures. In some cases, the exact etiology may not be identified. Changes in cerebral perfusion
such as hypotension; strokes, or brain attacks; and shock may be causes of seizures. There is no known
correlation with anorexia nervosa and the development of epilepsy. Excessive levels of stress cannot
disrupt cerebral oxygen to the extent that epilepsy would occur.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 15-2 Recognize possible causes of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 181
Question 3Type: MCSA
A parent says to the nurse, "The doctor prescribed ethosuximide (Zarontin) for my child, who has
absence seizures. What does this mean?" What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Absence seizures are basically the same kind of seizures as grand mal, but they are less frequent."
2. "Your daughter's seizures manifest as a staring into space for a few seconds. Ethosuximide (Zarontin)
is a good medication for this type of seizure."
3. "Explaining the types of seizure activity is complicated. Have you spoken to your doctor about it?"
4. "Are you sure your doctor prescribed ethosuximide (Zarontin)? Phenobarbital (Luminal) is used much
more frequently with children."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Grand mal, or tonic-clonic, seizures are different from absence or petit mal seizures; they
are different forms of epilepsy.
Rationale 2: It is the responsibility of the RN to educate the patient, not just refer questions to the
physician.
Rationale 3: Ethosuximide (Zarontin), not phenobarbital (Luminal), is the drug of choice for absence
seizures.
Rationale 4: Absence seizures, formerly known as petit mal, last a few seconds and are seen most often
in children. Ethosuximide (Zarontin) is a drug of choice for this type of seizure disorder.
Global Rationale: Absence seizures, formerly known as petit mal, last a few seconds and are seen most
often in children. Ethosuximide (Zarontin) is a drug of choice for this type of seizure disorder. Grand mal,
or tonic-clonic, seizures are different from absence or petit mal seizures; they are different forms of
epilepsy. Ethosuximide (Zarontin), not phenobarbital (Luminal), is the drug of choice for absence
seizures. It is the responsibility of the RN to educate the patient, not just refer questions to the
physician.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-3 Relate signs and symptoms to specific types of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 183
Question 4
Type: MCSA
The patient has epilepsy and receives phenytoin (Dilantin). The patient has been seizure-free, and asks
the nurse why he still needs blood tests when he is not having seizures. What is the best response by the
nurse?
1. "Because phenytoin (Dilantin) has a very narrow range between a therapeutic dose and a toxic dose."
2. "Because phenytoin (Dilantin) can cause blood-thinning in some patients."
3. "Because phenytoin (Dilantin) can cause Stevens-Johnson syndrome, which will show up in the blood
tests."
4. "Because phenytoin (Dilantin) can deplete your system of potassium."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Phenytoin (Dilantin) has a very narrow range between a therapeutic dose and a toxic dose;
blood levels must be monitored to ensure a therapeutic level and to prevent toxicity.
Rationale 2: Phenytoin (Dilantin) is not an anticoagulant and does not cause thinning of the blood.
Rationale 3: Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a severe skin reaction that can be an adverse outcome with
phenytoin (Dilantin), but it is monitored by skin assessment, not blood tests.
Rationale 4: There isn't any evidence to support that phenytoin (Dilantin) causes potassium depletion.
Global Rationale: Phenytoin (Dilantin) has a very narrow range between a therapeutic dose and a toxic
dose; blood levels must be monitored to ensure a therapeutic level and to prevent toxicity. There isn'tany evidence to support that phenytoin (Dilantin) causes potassium depletion. Stevens-Johnson
syndrome is a severe skin reaction that can be an adverse outcome with phenytoin (Dilantin), but it is
monitored by skin assessment, not blood tests. Phenytoin (Dilantin) is not an anticoagulant and does not
cause thinning of the blood.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.5 Use evidence-based practices to guide health teaching, health
counseling, screening, outreach, disease and outbreak investigation, referral and follow-up throughout
the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-5 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 183
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The nurse has been conducting medication education for a patient with epilepsy. What is the best
outcome for this patient?
1. The patient will recognize that the antiseizure medication must be continued indefinitely.
2. The patient will recognize the need to be on a tyramine-free diet while on antiseizure medications.
3. The patient will recognize the need to be on a ketogenic diet in combination with antiseizure
medications.
4. The patient will recognize the need to be on antiseizure medication for 1 year after the last seizure.
Correct Answer: 1Rationale 1: Once seizures have been controlled, patients are continued indefinitely on the antiseizure
drug.
Rationale 2: A tyramine-free diet is indicated for patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor
medications.
Rationale 3: A ketogenic diet is indicated when seizures cannot be controlled through pharmacotherapy
or when there are unacceptable side effects to the medications.
Rationale 4: It is unknown how long antiseizure drugs will be necessary, but many patients require a lifetime regimen.
Global Rationale: Once seizures have been controlled, patients are continued indefinitely on the
antiseizure drug. A ketogenic diet is indicated when seizures cannot be controlled through
pharmacotherapy or when there are unacceptable side effects to the medications. A tyramine-free diet
is indicated for patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitor medications. It is unknown how long
antiseizure drugs will be necessary, but many patients require a life-time regimen.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.5 Use evidence-based practices to guide health teaching, health
counseling, screening, outreach, disease and outbreak investigation, referral and follow-up throughout
the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 15-5 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 184
Question 6
Type: MCSAThe physician has ordered intravenous (IV) diazepam (Valium) for the patient in status epilepticus.
During administration, which assessment by the nurse is most important?
1. Assessing respirations
2. Assessing level of consciousness
3. Assessing pulse for bradycardia
4. Assessing blood pressure for hypertension
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Respiratory depression is common when diazepam is given intravenously (IV). Respiratory
assessment is the priority.
Rationale 2: A different assessment has higher priority than assessing the level of consciousness.
Rationale 3: Although tachycardia is an effect of intravenous diazepam (Valium), it is not the top
priority.
Rationale 4: Although hypotension is an effect of intravenous diazepam (Valium), it is not the top
priority.
Global Rationale: Respiratory depression is common when diazepam is given intravenously (IV).
Respiratory assessment is the priority. Although hypotension is an effect of intravenous diazepam
(Valium), it is not the top priority. Although tachycardia is an effect of intravenous diazepam (Valium), it
is not the top priority. Assessing respirations is a higher priority than assessing the level of
consciousness.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: AssessmentLearning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 190
Question 7
Type: MCSA
The physician has ordered intravenous (IV) phenytoin (Dilantin). The nurse does not read the drug label
and administers the medication intramuscularly (IM). What is the most likely response in the patient?
1. Local tissue damage following extravasation will most likely occur.
2. A phenomenon known as purple gluteus syndrome will most likely occur.
3. A marked decrease in serum glucose levels will most likely occur.
4. Nothing adverse, the medication may be administered intravenously (IV) or intramuscularly (IM).
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Phenytoin (Dilantin) injectable is a soft-tissue irritant that causes local tissue damage
following extravasation.
Rationale 2: There isn't any such thing as purple gluteus syndrome; purple glove syndrome occurs when
phenytoin (Dilantin) is administered in a hand vein and causes a serious local vasoconstrictive response.
Rationale 3: Phenytoin (Dilantin) causes an increase in serum glucose.
Rationale 4: It should not be administered intramuscularly but should be given intravenously into a large
vein or via a central catheter.
Global Rationale: Phenytoin (Dilantin) injectable is a soft-tissue irritant that causes local tissue damage
following extravasation. It should not be administered intramuscularly but should be given intravenously
into a large vein or via a central catheter. There isn't any such thing as purple gluteus syndrome; purple
glove syndrome occurs when phenytoin (Dilantin) is administered in a hand vein and causes a serious
local vasoconstrictive response. Phenytoin (Dilantin) causes an increase in serum glucose.Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 191
Question 8
Type: MCMA
The physician has ordered intravenous phenytoin (Dilantin). The patient is also receiving 5% dextrose in
water (D5W) intravenously (IV). What will the nurse plan to do before administering this medication?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Use a large vein for the infusion.
2. Use an intravenous (IV) line with a filter.
3. Flush the intravenous (IV) line with saline.
4. Monitor the patient for hypertension.
5. Monitor the patient for Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3Rationale 1: Phenytoin (Dilantin) is a soft-tissue irritant that will cause local tissue damage if
extravasation occurs, so a large vein must be used for infusion.
Rationale 2: An intravenous filter will trap any precipitate that occurs.
Rationale 3: Intravenous lines of 5% dextrose in water (D5W) must be flushed with saline, as traces of
dextrose can cause microscopic precipitate formations that become emboli, if infused.
Rationale 4: Patients receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) are at risk for hypotension, not hypertension.
Rationale 5: Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a side effect of phenytoin (Dilantin), but it takes days to
occur.
Global Rationale: Intravenous lines of 5% dextrose in water (D5W) must be flushed with saline, as traces
of dextrose can cause microscopic precipitate formations that become emboli, if infused. An intravenous
filter will trap any precipitate that occurs. Phenytoin (Dilantin) is a soft-tissue irritant that will cause local
tissue damage if extravasation occurs, so a large vein must be used for infusion. Patients receiving
phenytoin (Dilantin) are at risk for hypotension, not hypertension. Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a side
effect of phenytoin (Dilantin), but it takes days to occur.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 191Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving valproic acid (Depakene) for treatment of seizures. The patient has also been
taking a daily 81 mg aspirin tablet prophylactically for a cardiac condition. What would the nurse be
most likely to observe?
1. An increase in seizure activity
2. Stevens-Johnson syndrome
3. Migraine headaches and generalized irritability
4. Bleeding from the gums and bruising of the skin
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Increased seizure activity is not associated with valproic acid (Depakene) and aspirin use.
Rationale 2: Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a side effect of valproic acid (Depakene); its occurrence is not
increased with concomitant aspirin use.
Rationale 3: Migraine headaches and generalized irritability do not result from valproic acid (Depakene)
and aspirin use.
Rationale 4: Valproic acid (Depakene) can prolong bleeding time; concomitant aspirin use can cause
severe bleeding.
Global Rationale: Valproic acid (Depakene) can prolong bleeding time; concomitant aspirin use can
cause severe bleeding. Increased seizure activity is not associated with valproic acid (Depakene) and
aspirin use. Stevens-Johnson syndrome is a side effect of valproic acid (Depakene); its occurrence is not
increased with concomitant aspirin use. Migraine headaches and generalized irritability do not result
from valproic acid (Depakene) and aspirin use.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medicalmanagement, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 192
Question 10
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving Phenobarbital (Luminal) for control of seizures. The patient tells the nurse she
plans to become pregnant. What is the best response of the nurse?
1. "Your medication dose will need to be decreased during your pregnancy."
2. "Please talk to your doctor; this drug is contraindicated in pregnancy."
3. "Your medication dose will need to be increased during your pregnancy."
4. "Please talk to your doctor; you will need a safer drug like valproic acid (Depakene)."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: The medication does not need to be decreased; it might need to be stopped.
Rationale 2: Phenobarbital (Luminal) falls under Pregnancy Category D and is contraindicated in
pregnancy.
Rationale 3: The medication does not need to be increased; it might need to be stopped.
Rationale 4: Valproic acid (Depakene) is also a Pregnancy Category D drug and is contraindicated during
pregnancy.
Global Rationale: Phenobarbital (Luminal) falls under Pregnancy Category D and is contraindicated in
pregnancy. The medication does not need to be increased; it might need to be stopped. The medicationdoes not need to be decreased; it might need to be stopped. Valproic acid (Depakene) is also a
Pregnancy Category D drug and is contraindicated during pregnancy.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 189
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The patient tells the nurse that she has been taking phenytoin (Dilantin) for 2 years now and is still
having too many side effects. She wants to stop taking it. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Please do not stop the medication abruptly, as you will have withdrawal seizures."
2. "Side effects are a problem, but they are not as bad as the seizures you were having."
3. "This is the best medication for you; we can add another medication to decrease side effects."
4. "You have probably been on the medication long enough; I'll let your doctor know you are stopping
it."
Correct Answer: 1Rationale 1: Seizures are likely to occur with abrupt withdrawal of antiseizure medication. The
medication must be withdrawn over a period of 6 to 12 weeks.
Rationale 2: Telling a patient that medication side effects are not as bad as seizures is an inappropriate
and non-therapeutic response that does not address the patient's concerns.
Rationale 3: There is no other medication that can be added to decrease the side effects associated with
phenytoin (Dilantin).
Rationale 4: The nurse does not know if the patient has been on the medication long enough, and the
patient must be informed of the consequences of abruptly stopping the medication.
Global Rationale: Seizures are likely to occur with abrupt withdrawal of antiseizure medication. The
medication must be withdrawn over a period of 6 to 12 weeks. There is no other medication that can be
added to decrease the side effects associated with phenytoin (Dilantin). The nurse does not know if the
patient has been on the medication long enough, and the patient must be informed of the
consequences of abruptly stopping the medication. Telling a patient that medication side effects are not
as bad as seizures is an inappropriate and non-therapeutic response that does not address the patient's
concerns.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.5 Use evidence-based practices to guide health teaching, health
counseling, screening, outreach, disease and outbreak investigation, referral and follow-up throughout
the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-5 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 184Question 12
Type: MCSA
The physician has prescribed phenytoin (Dilantin) for a patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus. What does
the nurse include in the plan of care for this patient?
1. Plan to discuss with the physician the need to decrease the patient's insulin based on serum glucose
levels.
2. Plan to discuss with the physician the need to increase the patient's insulin based on serum glucose
levels.
3. Plan to assess the patient for petechiae, epistaxis, and hematuria.
4. Plan to institute safety precautions, as the patient is at risk for dizziness and ataxia.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Phenytoin (Dilantin) can increase serum glucose levels, not decrease them.
Rationale 2: Phenytoin (Dilantin) can increase serum glucose levels, and the patient may need additional
insulin.
Rationale 3: All patients receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) are at risk for petechiae, epistaxis, and
hematuria; this is not specific to the patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Rationale 4: All patients receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) are at risk for dizziness and ataxia; this is not
specific to the patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Global Rationale: Phenytoin (Dilantin) can increase serum glucose levels, and the patient may need
additional insulin. All patients receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) are at risk for dizziness and ataxia; this is
not specific to the patient with type 1 diabetes mellitus. All patients receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) are at
risk for petechiae, epistaxis, and hematuria; this is not specific to the patient with type 1 diabetes
mellitus. Phenytoin (Dilantin) can increase serum glucose levels, not decrease them.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 15-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of seizures of an
acute nature and epilepsy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 191
Question 13
Type: MCSA
The young child has absence seizures. The physician has prescribed valproic acid (Depakene) syrup. The
nurse has completed medication education with the child's mother and determines that learning has
occurred when the mother makes which statement?
1. "I should not mix this with carbonated beverages."
2. "If my child gets a headache from this, I can administer a baby aspirin."
3. "I can still give the clonazepam (Klonopin) prescribed by the psychiatrist for sleep."
4. "I can give this on a full stomach or an empty stomach."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Mixing valproic acid (Depakene) syrup with carbonated beverages will trigger immediate
release of the drug, which causes severe mouth and throat irritation.
Rationale 2: Aspirin can increase valproic acid (Depakene) toxicity, and aspirin should not be given to
children because of Reye syndrome.
Rationale 3: Clonazepam (Klonopin) given with valproic acid (Depakene) can induce absence seizures.
Rationale 4: Valproic acid (Depakene) is a gastrointestinal (GI) irritant and should be given with food.
Global Rationale: Mixing valproic acid (Depakene) syrup with carbonated beverages will trigger
immediate release of the drug, which causes severe mouth and throat irritation. Valproic acid
(Depakene) is a gastrointestinal (GI) irritant and should be given with food. Aspirin can increase valproic
acid (Depakene) toxicity, and aspirin should not be given to children because of Reye syndrome.
Clonazepam (Klonopin) given with valproic acid (Depakene) can induce absence seizures.Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 192
Question 14
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving phenobarbital (Luminal) for seizure control. The patient asks the nurse how this
little pill can stop his seizures. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Phenobarbital (Luminal) stops your seizures by decreasing the calcium in your brain, which is
responsible for the seizures."
2. "Phenobarbital (Luminal) stops your seizures by increasing a chemical called glutamate that calms
down the excitability in your brain."
3. "Phenobarbital (Luminal) stops your seizures by decreasing the sodium in your brain, which is
responsible for the seizures."
4. "Phenobarbital (Luminal) stops your seizures by increasing a chemical called GABA that calms down
the excitability in your brain."Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Succinimides, not phenobarbital (Luminal), suppress calcium influx.
Rationale 2: Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain; enhancing this
neurotransmitter will increase the likelihood of seizures.
Rationale 3: Hydantoins and phenytoin-like drugs, not phenobarbital (Luminal), suppress sodium influx.
Rationale 4: Phenobarbital (Luminal) acts biochemically in the brain by enhancing the action of the
neurotransmitter GABA, which is responsible for suppressing abnormal neuronal discharges that can
cause epilepsy.
Global Rationale: Phenobarbital (Luminal) acts biochemically in the brain by enhancing the action of the
neurotransmitter GABA, which is responsible for suppressing abnormal neuronal discharges that can
cause epilepsy. Glutamate is the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain; enhancing this
neurotransmitter will increase the likelihood of seizures. Hydantoins and phenytoin-like drugs, not
phenobarbital (Luminal), suppress sodium influx. Succinimides, not phenobarbital (Luminal), suppress
calcium influx.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-7 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of seizures based on their classification
and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 181
Question 15Type: MCSA
An older adult patient is taking phenobarbital (Luminal) for seizure control. What is most important for
the nurse to assess in the patient?
1. Fluid intake
2. Electrolyte balance
3. Respiratory function
4. Nutritional status
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Fluid intake is often decreased in older adults but is not a side effect of barbiturates.
Rationale 2: Barbiturates do not affect electrolyte balance.
Rationale 3: Older adults are at risk for cumulative effects of barbiturates due to diminished hepatic and
renal function. Central nervous system (CNS) depression can lead to suppression of respiratory function.
Rationale 4: Nutritional status is important with older adult patients but is not the primary concern.
Global Rationale: Older adults are at risk for cumulative effects of barbiturates due to diminished
hepatic and renal function. Central nervous system (CNS) depression can lead to suppression of
respiratory function. Nutritional status is important with older adults but is not the primary concern.
Fluid intake is often decreased in older adults but is not a side effect of barbiturates. Barbiturates do not
affect electrolyte balance.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 15-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of seizures of an
acute nature and epilepsy.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 189
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Identify the correct statement regarding seizures.
1. Convulsions are a symptom of the underlying seizure disorder.
2. Seizures can be caused by bacterial infections of the nervous system.
3. Epilepsy is an acute disorder characterized by non-convulsive seizures.
4. All seizures are convulsions, but not all convulsions are seizures.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Convulsions are a type of seizure, and seizures are a symptom of an underlying disorder.
Rationale 2: Several things, including bacterial infections, can cause seizures.
Rationale 3: Epilepsy is generally chronic and can present with convulsive seizures.
Rationale 4: All convulsions are seizures, but not all seizures are convulsions.
Global Rationale: Several things, including bacterial infections, can cause seizures. All convulsions are
seizures, but not all seizures are convulsions. Convulsions are a type of seizure, and seizures are a
symptom of an underlying disorder. Epilepsy is generally chronic and can present with convulsive
seizures.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 15-1 Compare and contrast the terms seizures, convulsion, and epilepsy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 181
Question 17
Type: MCSA
A person who stops talking mid-sentence and has a blank stare for 5 seconds would most likely be
experiencing
1. a simple partial seizure.
2. status epilepticus.
3. a petit mal seizure.
4. a drop attack.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Simple partial seizures manifest in olfactory, auditory, or visual hallucinations; intense
emotions; or twitching of arms, legs, and face.
Rationale 2: Status epilepticus is continuous seizure activity, which can lead to coma or death.
Rationale 3: The symptoms presented indicate a general (absence) or petit mal seizure.
Rationale 4: Drop attacks are manifested by falling or stumbling for no reason. These attacks typically
last a few seconds.
Global Rationale: The symptoms presented indicate a general (absence) or petit mal seizure. Simple
partial seizures manifest in olfactory, auditory, or visual hallucinations; intense emotions; or twitching of
arms, legs, and face. Status epilepticus is continuous seizure activity, which can lead to coma or death.
Drop attacks are manifested by falling or stumbling for no reason. These attacks typically last a few
seconds.
Cognitive Level: ApplyingClient Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 15-3 Relate signs and symptoms to specific types of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 183
Question 18
Type: MCMA
A parent states, “The doctors all say that my son’s problem is epilepsy, but I don’t think that is correct. I
have never seen him jerk or thrash.” What nursing response is indicated?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “The episodes of jerking and thrashing are called convulsions.”
2. “Seizures take many forms.”
3. “Your son may have seizures, but not epilepsy.”
4. “Seizures can be a sign that epilepsy is present.”
5. “If there is no physical movement, epilepsy is ruled out.”
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Convulsions are the involuntary, violent spasms of the large skeletal muscles of the face,
neck, arms, and legs. It is important to provide this parent with correct terminology.Rationale 2: There are many types of seizures.
Rationale 3: It is inappropriate to lead the parent to believe that the diagnosis is incorrect. The nurse
does not have all the necessary information.
Rationale 4: Epilepsy is any disorder that is characterized by recurrent seizures.
Rationale 5: Many seizures do not include physical movement, yet the patient still is diagnosed with
epilepsy.
Global Rationale: Convulsions are the involuntary, violent spasms of the large skeletal muscles of the
face, neck, arms, and legs. It is important to provide this parent with correct terminology. There are
many types of seizures. Epilepsy is any disorder that is characterized by recurrent seizures. It is
inappropriate to lead the parent to believe that the diagnosis is incorrect. The nurse does not have all
the necessary information. Many seizures do not include physical movement, yet the patient still is
diagnosed with epilepsy.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 15-1 Compare and contrast the terms seizures, convulsion, and epilepsy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 181
Question 19
Type: MCSAA low-income patient without insurance has been prescribed several different medications over several
months for seizure control without any improvement. The patient indicates she has not experienced any
adverse effects. At this point the nurse should
1. recommend nontypical drug use.
2. inform the patient that it might take years for the medications to work.
3. assess for medication compliance.
4. advise the patient to double the current dose.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Another drug might be indicated, but compliance should be assessed first.
Rationale 2: It generally doesn't take years for seizure medications to work.
Rationale 3: Due to the financial situation presented and absence of any side effects, it is possible the
patient is not in compliance. The nurse should assess for this possibility at this point.
Rationale 4: Changing the prescribed dose of a medication is not within the scope of practice of the
nurse.
Global Rationale: Due to the financial situation presented and absence of any side effects, it is possible
the patient is not in compliance. The nurse should assess for this possibility at this point. Another drug
might be indicated, but compliance should be assessed first. It generally doesn't take years for seizure
medications to work. Changing the prescribed dose of a medication is not within the scope of practice of
the nurse.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.5 Use evidence-based practices to guide health teaching, health
counseling, screening, outreach, disease and outbreak investigation, referral and follow-up throughout
the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: AssessmentLearning Outcome: 15-5 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 195
Question 20
Type: MCSA
Which of the following adverse effects would most likely be associated with the use of phenytoin
(Dilantin)?
1. Vitamin B deficiency
2. Leg edema
3. Bleeding
4. Hypoglycemia
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Dilantin affects the metabolism of vitamin K, which can lead to blood dyscrasias.
Hyperglycemia is more common than hypoglycemia, and leg edema is not generally experienced as an
adverse effect. Vitamin B deficiency is not the most common complication.
Rationale 2: Leg edema is not generally experienced as an adverse effect.
Rationale 3: Dilantin affects the metabolism of vitamin K, which can lead to blood dyscrasias.
Rationale 4: Hyperglycemia is more common than hypoglycemia.
Global Rationale: Dilantin affects the metabolism of vitamin K, which can lead to blood dyscrasias.
Hyperglycemia is more common than hypoglycemia, and leg edema is not generally experienced as an
adverse effect. Vitamin B deficiency is not the most common complication.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 15-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 191
Question 21
Type: MCSA
A drug that is used to treat petit mal seizures but not tonic-clonic seizures and works by decreasing
neuronal activity in the motor cortex is
1. diazepam (Valium).
2. valproic acid (Depakote).
3. phenytoin (Dilantin).
4. ethosuximide (Zarontin).
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Valium can be effective for tonic-clonic seizures.
Rationale 2: Succinimides like Zarontin are indicated for petit mal seizures but not for tonic-clonic
seizures. Depakote can be effective for tonic-clonic seizures.
Rationale 3: Dilantin can be effective for tonic-clonic seizures.
Rationale 4: Succinimides like Zarontin are indicated for petit mal seizures but not for tonic-clonic
seizures.
Global Rationale: Succinimides like Zarontin are indicated for petit mal seizures but not for tonic-clonic
seizures. Depakote, Valium, and Dilantin can be effective for tonic-clonic seizures.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 15-7 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of seizures based on their classification
and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 193
Question 22
Type: MCSA
The nurse would be especially cautious to avoid extravasation of which drug that is commonly
administered intravenously?
1. Phenobarbital (Luminal)
2. Phenytoin (Dilantin)
3. Ethosuximide (Zarontin)
4. Clonazepam (Klonopin)
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Phenobarbital would be more likely to be administered orally and is infrequently given
intravenously.
Rationale 2: Dilantin is frequently administered IV due to slow and variable absorption rates when given
orally. If Dilantin extravasates, serious soft tissue damage can result.Rationale 3: Zarontin is an oral medication.
Rationale 4: Klonopin is an oral medication.
Global Rationale: Dilantin is frequently administered IV due to slow and variable absorption rates when
given orally. If Dilantin extravasates, serious soft tissue damage can result. Phenobarbital would be more
likely to be administered orally and is infrequently given intravenously. Zarontin and Klonopin are oral
medications.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 15-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of seizures of an
acute nature and epilepsy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 191
Question 23
Type: MCMA
A patient had a tonic-clonic seizure. Which findings does the nurse evaluate as indicating the patient is
in a postictal state?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.1. The patient is incontinent of urine.
2. The patient is in a deep sleep.
3. The patient is confused as to place and time.
4. The patient reports an odd taste in his mouth.
5. The patient is attempting to remove his hospital gown.
Correct Answer: 2,3
Rationale 1: Incontinence of bowel or bladder is common during a tonic-clonic seizure but is not
indicative of a postictal state.
Rationale 2: Deep sleep after the seizure is a finding associated with the postictal state.
Rationale 3: Patients who are in the postictal state may be confused and disoriented.
Rationale 4: An odd taste, specific odor or noise, or other sensory change often heralds a seizure. This is
called an aura.
Rationale 5: During complex partial seizures, patients sometimes fumble with or attempt to remove
clothing.
Global Rationale: Deep sleep after the seizure is a finding associated with the postictal state. Patients
who are in the postictal state may be confused and disoriented. Incontinence of bowel or bladder is
common during a tonic-clonic seizure but is not indicative of a postictal state. An odd taste, specific odor
or noise, or other sensory change often heralds a seizure. This is called an aura. During complex partial
seizures, patients sometimes fumble with or attempt to remove clothing.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 15-3 Relate signs and symptoms to specific types of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 183
Question 24
Type: MCMA
The nurse has completed education to the parents of a child newly diagnosed with tonic-clonic seizures.
Which comments made by the parents would the nurse evaluate as indicating need for further
education?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Some of the times when I thought he was ignoring me may have actually been seizure activity."
2. "He just needs to focus more to prevent these attacks."
3. "I know he will outgrow these seizures with time."
4. "I hope we can help our son identify his seizure aura."
5. "We will watch for the development of status epilepticus."
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Behavior that manifests as the child ignoring outside stimuli is most likely absence seizure,
which is different from tonic-clonic seizure.
Rationale 2: The patient who suffers seizure disorder cannot prevent seizure occurrence by focusing
harder.
Rationale 3: The patient with tonic-clonic seizure disorder is less likely to outgrow them than the patient
with absence seizure disorder.
Rationale 4: Many patients experience an aura prior to the tonic-clonic phase. Identifying the aura can
provide time for the patient to move to a safe area, notify another person of the impending seizure, and
to prepare.Rationale 5: Status epilepticus is a medical emergency that may occur in the patient who suffers with
tonic-clonic seizure disorder.
Global Rationale: Behavior that manifests as the child ignoring outside stimuli is most likely absence
seizure, which is different from tonic-clonic seizure. The patient who suffers seizure disorder cannot
prevent seizure occurrence by focusing harder. The patient with tonic-clonic seizure disorder is less
likely to outgrow them than the patient with absence seizure disorder. Many patients experience an
aura prior to the tonic-clonic phase. Identifying the aura can provide time for the patient to move to a
safe area, notify another person of the impending seizure, and to prepare. Status epilepticus is a medical
emergency that may occur in the patient who suffers with tonic-clonic seizure disorder.
Cognitive Level: Evaluating
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 15-3 Relate signs and symptoms to specific types of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 183
Question 25
Type: MCMA
The patient who is prescribed valproic acid (Depakene) for seizure control would like to have a baby.
Which statements should the nurse include in a discussion with this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.1. "Since your epilepsy may flare up during pregnancy, your doctor will likely have you take a second
antiepileptic medication."
2. "Thankfully, most modern antiepileptic medications will not interfere with you getting pregnant."
3. "Your current antiepileptic medication should not be used when you are pregnant."
4. "Folic acid supplementation is important for you."
5. "You should consider adopting a baby instead since there are so many problems associated with
epilepsy and pregnancy."
Correct Answer: 3,4
Rationale 1: Since there are many side effects to antiepileptic medications, single drug therapy is the
goal for pregnant patients.
Rationale 2: Women who have epilepsy have a reduced fertility rate, and some do not ovulate.
Rationale 3: Valproic acid (Depakene) is Pregnancy Category D.
Rationale 4: Folic acid supplementation is important for all women who are, or wish to become,
pregnant. This is especially true of women who are epileptic because many antiepileptic medications
cause folic acid deficiency.
Rationale 5: Women who are epileptic can and do conceive and deliver healthy babies. The nurse should
not discourage this patient but should provide information to the patient and then support the patient's
choice.
Global Rationale: Valproic acid (Depakene) is Pregnancy Category D. Folic acid supplementation is
important for all women who are, or wish to become, pregnant. This is especially true of women who
are epileptic because many antiepileptic medications cause folic acid deficiency. Since there are many
side effects to antiepileptic medications, single drug therapy is the goal for pregnant patients. Women
who have epilepsy have a reduced fertility rate, and some do not ovulate. Women who are epileptic can
and do conceive and deliver healthy babies. The nurse should not discourage this patient but should
provide information to the patient and then support the patient's choice.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-8 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 196
Question 26
Type: MCMA
The nurse is planning education sessions for a patient regarding use of a newly prescribed antiepileptic
drug (AED). Which topics should be included in this session?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The patient should take the medication at the same time every day.
2. If the patient forgets a dose of medication, wait until the next dose is due and take both doses
together.
3. The patient should take an additional dose of medication upon experiencing a seizure aura.
4. If the patient experiences side effects of the medication, the patient should skip the next dose to see
if the side effects lessen.
5. The patient should avoid using dietary supplements containing kava when on this medication.
Correct Answer: 1,5
Rationale 1: Stable blood levels of medication are important in the control of seizure activity. In order to
achieve this stability, the medication should be taken at the same time every day.Rationale 2: The patient should take the dose as soon as it is remembered but should not take two
doses at the same time or close together.
Rationale 3: Oral medications are not delivered rapidly to the system, so taking an additional dose of
medication when an aura occurs is not effective in controlling the impending seizure.
Rationale 4: The patient should never abruptly discontinue taking these medications and should not skip
doses.
Rationale 5: Kava interferes with many AEDs, often adding to their sedative effects.
Global Rationale: Stable blood levels of medication are important in the control of seizure activity. In
order to achieve this stability, the medication should be taken at the same time every day. Kava
interferes with many AEDs, often adding to their sedative effects. The patient should take the dose as
soon as it is remembered but should not take two doses at the same time or close together. Oral
medications are not delivered rapidly to the system, so taking an additional dose of medication when an
aura occurs is not effective in controlling the impending seizure. The patient should never abruptly
discontinue taking these medications and should not skip doses.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-8 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 196Question 27
Type: MCMA
A mother phones the clinic and tells the nurse, "My 5-year-old son had a febrile seizure this morning."
She adds that this is the child's first seizure experience. The nurse responds by asking the mother to
bring the child in to be seen today. What other information should the nurse offer?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Febrile seizures are uncommon in boys."
2. "High temperatures generally induce seizures."
3. "Five-year-olds are too old for febrile seizures."
4. "Febrile seizures occur in up to 2% of children."
5. "Seizure medications are usually not necessary for febrile seizures."
Correct Answer: 4,5
Rationale 1: Febrile seizures occur in both genders.
Rationale 2: Many children experience high temperatures without experiencing seizures.
Rationale 3: Febrile seizures are most common in childhood.
Rationale 4: Up to 2% of children experience seizure activity related to temperature elevation.
Rationale 5: The best course of action for febrile seizures is prevention by using acetaminophen to
prevent onset of fever.
Global Rationale: Up to 2% of children experience seizure activity related to temperature elevation. The
best course of action for febrile seizures is prevention by using acetaminophen to prevent onset of
fever. Febrile seizures occur in both genders. Many children experience high temperatures without
experiencing seizures. Febrile seizures are most common in childhood.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Reduction of Risk PotentialQSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-2 Recognize possible causes of seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 181
Question 28
Type: MCMA
The nurse is talking with a patient who was just prescribed ethosuximide (Zarontin). Which patient
statement should the nurse immediately discuss with the patient's health care provider?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Did I mention that I used to take phenobarbital for my seizures?"
2. "I forgot to tell the doctor that I am allergic to penicillin."
3. "I take ginkgo to help improve my memory."
4. "My husband and I plan to have a baby in a couple of years."
5. "My husband and I are leading a 20-mile bicycle tour next weekend for the company we have just
started."
Correct Answer: 3,5
Rationale 1: There is no indication that previous phenobarbital use is problematic with the use of
ethosuximide (Zarontin).
Rationale 2: There is no indication of cross sensitivity with penicillin.
Rationale 3: Ginkgo may reduce the therapeutic effects of ethosuximide (Zarontin).Rationale 4: Ethosuximide (Zarontin) is Pregnancy Category C.
Rationale 5: The most common adverse effects of ethosuximide (Zarontin) include dizziness, ataxia, and
fatigue. These effects may be problematic for the owner of a company that promotes bicycle touring.
Global Rationale: Ginkgo may reduce the therapeutic effects of ethosuximide (Zarontin). The most
common adverse effects of ethosuximide (Zarontin) include dizziness, ataxia, and fatigue. These effects
may be problematic for the owner of a company that promotes bicycle touring. There is no indication
that previous phenobarbital use is problematic with the use of ethosuximide (Zarontin). There is no
indication of cross sensitivity with penicillin. Ethosuximide (Zarontin) is Pregnancy Category C.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management, and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 15-8 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 193
Question 29
Type: MCMA
A patient has been prescribed to follow a ketogenic diet to supplement pharmacotherapy for a seizure
disorder. The nurse would support the inclusion of which types of food in menu selection?Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Foods high in fat
2. Salty foods
3. Foods high in vitamin K
4. Low protein foods
5. Low carbohydrate foods
Correct Answer: 1,4,5
Rationale 1: The ketogenic diet is high in fat.
Rationale 2: The presence of salt is not a determining factor in inclusion of foods in a ketogenic diet.
Rationale 3: The presence of high amounts of vitamin K is not a determining factor in inclusion of foods
in a ketogenic diet.
Rationale 4: The ketogenic diet is low in protein.
Rationale 5: The ketogenic diet is low in carbohydrates.
Global Rationale: The ketogenic diet is high in fat and low in protein and carbohydrates. The presence of
salt or vitamin K is not a determining factor in inclusion of foods in a ketogenic diet.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.5 Use evidence-based practices to guide health teaching, health
counseling, screening, outreach, disease and outbreak investigation, referral and follow-up throughout
the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Context and Environment: Chronic disease management.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: ImplementationLearning Outcome: 15-5 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
epilepsy and seizures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.5.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 185
Question 30
Type: MCMA
The parents of an infant with recurrent seizures are interested in starting amino acid therapy for their
child. The father says, “After all, amino acids are natural; it couldn’t hurt to give this a try.” The nurse
should consider which complications of this therapy when formulating a response?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Allergic reactions to the product
2. Cardiac changes such as palpitations
3. Neurological effects such as dizziness and lack of coordination
4. Gastrointestinal effects such as decreased weight gain
5. Failure to thrive.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Allergic reactions to amino acids are not uncommon.
Rationale 2: Irregular heartbeat may occur in response to this therapy.
Rationale 3: Neurological effects of amino acid therapy include drowsiness, dizziness, and problems with
coordination.
Rationale 4: Decreased weight gain may occur but is not likely to be a direct result of amino acid
therapy.
Rationale 5: There is no evidence that amino acid therapy results in failure to thrive.
Chapter 16:
Question 1Type: MCSA
The patient tells the nurse, "I thought I was just depressed, but my doctor says I have bipolar disorder.
What is that?" What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Bipolar disorder is just another type of depression, except your depression occurs in cycles."
2. "Bipolar disorder is a type of depression that includes attention deficit disorder symptoms."
3. "Bipolar disorder just means that your mood alternates with the seasons, and it becomes worse in the
winter."
4. "Bipolar disorder means you have cycles of depression as well as hyperactivity, or mania."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Bipolar disorder must include either mania or hypomania, not just depression.
Rationale 2: Bipolar disorder must include depression with either mania or hypomania, not attentiondeficit hyperactivity disorder.
Rationale 3: A mood change that becomes worse in the winter is called seasonal affective disorder.
Rationale 4: Patients with bipolar disorder may shift from emotions of extreme depression to extreme
rage and agitation. Mania may include grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, pressured speech, racing
thoughts, buying sprees, and sexual indiscretions.
Global Rationale: Patients with bipolar disorder may shift from emotions of extreme depression to
extreme rage and agitation. Mania may include grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, pressured speech,
racing thoughts, buying sprees, and sexual indiscretions. Bipolar disorder must include either mania or
hypomania, not just depression. Bipolar disorder must include depression with either mania or
hypomania, not attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. A mood change that becomes worse in the
winter is called seasonal affective disorder.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-1 Identify the two major categories of mood disorders and their symptoms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 210
Question 2
Type: MCSA
The mother of a 7-year-old child says to the nurse, "My child is distractible in school, cannot complete
assignments on time, and interrupts other children while they are speaking. What do you think?" What
is the best response by the nurse?
1. "This sounds like your child is depressed; depression looks different in children and is very serious."
2. "This sounds like bipolar disorder; you might want to have your child tested by a child psychiatrist."
3. "This could be attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD); you might want to have your child
tested."
4. "This sounds like typical 7-year-old behaviors to me; if they do not resolve, have your child tested."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Depression does look different in children, but these symptoms are not symptoms of
depression.
Rationale 2: Being distractible, unable to complete assignments, and interrupting other children are not
symptoms of bipolar disorder.
Rationale 3: Symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) include difficulty in paying
attention and focusing on tasks, hyperactivity, distractibility, impulsivity, and talking excessively.
Rationale 4: Being distractible, unable to complete assignments, and interrupting other children are not
typical 7-year-old behaviors.
Global Rationale: Symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) include difficulty in
paying attention and focusing on tasks, hyperactivity, distractibility, impulsivity, and talking excessively.
Being distractible, unable to complete assignments, and interrupting other children are not typical 7-year-old behaviors. Depression does look different in children, but these symptoms are clearly
symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Being distractible, unable to complete
assignments, and interrupting other children are symptoms of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
(ADHD), not bipolar disorder.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-2 Identify the symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.3 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage ADHD.
Page Number: 211
Question 3
Type: MCMA
The nurse is conducting a group education session for patients who have been diagnosed with
depression. The nurse evaluates the education as effective when a patient makes which comments
about the cause of depression?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Depression has many causes; they could include environmental as well as brain-based disorders."
2. "Depression includes impaired relationships and is also an inherited illness."
3. "We really don't know what causes depression; it has not been studied very much."4. "Depression results from unresolved conflicts in your childhood."
5. "Depression results from parents who are cold and distant and don't really care about their children."
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Depression has many causes; it is a brain-based disorder that is exacerbated by
environmental influences.
Rationale 2: Depression runs in families, supporting a genetic link, and will include impaired
relationships.
Rationale 3: Depression has been studied extensively.
Rationale 4: Environmental influences are only one of the causes of depression; this answer does not
include the biological basis for depression.
Rationale 5: Depression could result from cold and distant parents, but this answer does not include the
biological basis for depression.
Global Rationale: Depression has many causes; it is a brain-based disorder that is exacerbated by
environmental influences. Depression runs in families, supporting a genetic link, and will include
impaired relationships. Environmental influences are only one of the causes of depression; this answer
does not include the biological basis for depression. Depression could result from cold and distant
parents, but this answer does not include the biological basis for depression. Depression has been
studied extensively.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 16-3 Explain the etiology of major depressive disorder.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 201
Question 4
Type: MCSA
The patient receives imipramine (Tofranil) as treatment for depression. He is admitted to the emergency
department following an intentional overdose of this medication. What will the priority assessment by
the nurse include?
1. The patient's cardiac status
2. The patient's liver function
3. The patient's renal status
4. The patient's neurological function
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Tricyclic antidepressants are cardiotoxic. An overdose could result in a fatal dysrhythmia.
Cardiac status is the primary assessment.
Rationale 2: Liver function is not the priority assessment.
Rationale 3: Renal function is not the priority assessment.
Rationale 4: Neurologic function may be affected but is not the primary assessment.
Global Rationale: Tricyclic antidepressants are cardiotoxic. An overdose could result in a fatal
dysrhythmia. Cardiac status is the primary assessment, not the patient's renal status. Cardiac status is
the primary assessment, not the patient's liver function. Cardiac status is the primary assessment, not
the patient's neurological function.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-5 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 189
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The patient has been receiving amitriptyline (Elavil) for 2 weeks. He tells the nurse he doesn't think this
medicine is working, as he is still depressed. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "It is working, but it can take several weeks to have an effect."
2. "You might still feel depressed, but you are looking much better."
3. "This may not be the best medicine for you; I'll call your doctor."
4. "It is working, but it can take several months to have an effect."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The therapeutic effects of tricyclic antidepressants may take 2 to 6 weeks to occur.
Rationale 2: Telling a depressed patient he looks better negates the patient's feelings and is
inappropriate.
Rationale 3: It is inappropriate for the nurse to call the physician at this point.
Rationale 4: The time frame for efficacy is several weeks, not several months.Global Rationale: The therapeutic effects of tricyclic antidepressants may take 2 to 6 weeks to occur. It
is inappropriate for the nurse to call the physician; tricyclic antidepressants need time to work. Telling a
depressed patient he looks better negates the patient's feelings and is inappropriate. The time frame for
efficacy is several weeks, not several months.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 16-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of patients with
depression, bipolar disorder, or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.3 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage ADHD.
Page Number: 212
Question 6
Type: MCSA
The physician has prescribed sertraline (Zoloft) for the patient who is anxious and depressed. The
patient calls the nurse to report that he has experienced delayed ejaculation since being on this
medication. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "I will let your doctor know, and he will most likely change your medication."
2. "This does happen, but treating your depression is a bigger priority."
3. "I am concerned that you will become suicidal if you stop the medication."
4. "Keep taking the medicine, as this usually goes away after a few months."
Correct Answer: 1Rationale 1: One of the most common side effects of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
relates to sexual dysfunction; up to 70% or men and women can experience this. In men, delayed
ejaculation and impotence may occur.
Rationale 2: It is inappropriate to tell a patient that his depression is a higher priority; sexual functioning
is important to patients.
Rationale 3: The patient could become suicidal if he stops the medication, but this response does not
address the patient's concern, and he will most likely stop the medicine anyway.
Rationale 4: It is inappropriate to tell a patient that the sexual dysfunction usually subsides because it
does not usually subside.
Global Rationale: One of the most common side effects of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
(SSRIs) relates to sexual dysfunction; up to 70% or men and women can experience this. In men, delayed
ejaculation and impotence may occur. It is inappropriate to tell a patient that his depression is a higher
priority; sexual functioning is important to patients. It is inappropriate to tell a patient that the sexual
dysfunction usually subsides because it does not usually subside. The patient could become suicidal if he
stops the medication, but this response does not address the patient's concern, and he will most likely
stop the medicine anyway.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 16-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of patients with
depression, bipolar disorder, or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 203Question 7
Type: MCSA
The patient has been depressed, and the physician plans to begin treatment with an antidepressant
medication. In performing the initial assessment, what is the most important question for the nurse to
ask?
1. "How much alcohol do you consume during the week?"
2. "Are you allergic to any medications?"
3. "How long have you been depressed?"
4. "Have you had any thoughts about killing yourself?"
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Assessing for alcohol intake is important but is not the priority safety issue.
Rationale 2: Asking about allergies is a good safety question, but is not the priority with a depressed
patient, and there are very few allergies to antidepressant medication. This question can be asked later.
Rationale 3: The length of the patient's depression is important but is not a safety issue.
Rationale 4: The nurse should always assess for suicidal ideation in any depressed patient who is about
to begin antidepressant treatment. The medication takes several weeks before the full benefit is
obtained. This is a safety issue.
Global Rationale: The nurse should always assess for suicidal ideation in any depressed patient who is
about to begin antidepressant treatment. The medication takes several weeks before the full benefit is
obtained. This is a safety issue. The length of the patient's depression is important but is not a safety
issue. Assessing for alcohol intake is important but is not a safety issue. Asking about allergies is a good
safety question, but is not the priority with a depressed patient, and there are very few allergies to
antidepressant medication. This question can be asked later.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of patients with
depression, bipolar disorder, or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 212
Question 8
Type: MCMA
The nurse has completed medication education for a patient prior to the patient receiving phenelzine
(Nardil). The nurse evaluates the education as effective when the patient makes which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "I am really going to miss my morning coffee and sweet roll."
2. "I'll have to give up my beer at the football games."
3. "I can't eat fried chicken and gravy."
4. "I am not supposed to have processed meats or cheese."
5. "I really shouldn't eat at a restaurant; too many foods are on my restricted list."
Correct Answer: 2,4
Rationale 1: Coffee and a sweet roll are not high in tyramine and are considered safe.
Rationale 2: Beer is high in tyramine. Combining tyramine-rich foods with a monoamine oxidase
inhibitor can result in a hypertensive crisis.
Rationale 3: Fried chicken and gravy are not high in tyramine and are considered safe.Rationale 4: Processed meats and cheese are high in tyramine. Combining tyramine-rich foods with a
monoamine oxidase inhibitor can result in a hypertensive crisis.
Rationale 5: There are many foods that are safe to eat; the patient can safely eat at a restaurant.
Global Rationale: Beer and processed meats and cheese are high in tyramine. Combining tyramine-rich
foods with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor can result in a hypertensive crisis. Fried chicken and gravy are
not high in tyramine and are considered safe. There are many foods that are safe to eat; the patient can
safely eat at a restaurant. Coffee and a sweet roll are not high in tyramine and are considered safe.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 16-5 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 209
Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient has bipolar disorder and is in a manic phase. The physician prescribes lithium (Eskalith). The
patient's current lithium level is 0.4. What will the nurse expect to assess in this patient?1. A return to baseline behavior, calm and rational
2. Hyperactivity and pressured speech
3. Signs and symptoms of depression
4. A decrease in manic behavior
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: The patient will not return to baseline behavior but will continue in the manic phase until
the lithium level is within a therapeutic range.
Rationale 2: A therapeutic lithium level is 0.6 to 1.5. Since this patient's level is low, behaviors will
indicate mania (i.e., hyperactivity and pressured speech).
Rationale 3: The patient will not exhibit signs and symptoms of depression but will continue in the
manic phase until the lithium level is within a therapeutic range. The patient will not return to baseline
behavior but will continue in the manic phase until the lithium level is within a therapeutic range.
Rationale 4: There will be no decrease in manic behavior because the lithium level is not within range.
Global Rationale: A therapeutic lithium level is 0.6 to 1.5. Since this patient's level is low, behaviors will
indicate mania (i.e., hyperactivity and pressured speech). There will be no decrease in manic behavior
because the lithium level is too low. The patient will not exhibit signs and symptoms of depression but
will continue in the manic phase until the lithium level is within a therapeutic range. The patient will not
return to baseline behavior but will continue in the manic phase until the lithium level is within a
therapeutic range.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: AssessmentLearning Outcome: 16-5 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 189
Question 10
Type: MCSA
The nurse has completed medication education with the patient who is receiving lithium (Eskalith).
What is the priority patient outcome?
1. The patient will be able to work a normal work schedule and will receive adequate sleep.
2. The patient will identify signs of lithium (Eskalith) toxicity and verbalize measures to avoid it.
3. The patient will engage in activities of daily living and report enjoyment with them.
4. The patient will report stabilization of mood, including absence of mania or depression.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Working a normal work schedule and receiving adequate sleep are important but are not
the priority outcome.
Rationale 2: Lithium (Eskalith) has a narrow therapeutic range. In order to avoid toxicity, patients must
understand the signs of toxicity and measures to avoid it.
Rationale 3: Engaging in activities of life and enjoying them are important but are not the priority
outcome.
Rationale 4: Stabilization of mood is important but is not the priority outcome.
Global Rationale: Lithium (Eskalith) has a narrow therapeutic range. In order to avoid toxicity, patients
must understand the signs of toxicity and measures to avoid it. Stabilization of mood is important, but
with medication education about lithium (Eskalith), the focus must be on identifying and avoiding signs
of toxicity. Working a normal work schedule and receiving adequate sleep are important, but with
medication education about lithium (Eskalith), the focus must be on identifying and avoiding signs of
toxicity. Engaging in activities of life and enjoying them are important, but with medication education
about lithium (Eskalith), the focus must be on identifying and avoiding signs of toxicity.Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 16-5 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 210
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The patient asks the nurse why she needs to continue using table salt because her prescribed lithium
(Eskalith) is a salt. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "You must continue to use salt to avoid lithium (Eskalith) toxicity. If you use sea salt, you don't need
as much."
2. "You must use table salt or your kidneys will retain lithium (Eskalith), and you will become toxic."
3. "The amount is not important; just increase your table salt if you notice signs of lithium (Eskalith)
toxicity."
4. "Salt is very important to avoid lithium (Eskalith) toxicity, but not as important as drinking 1 to 1.5 L of
water per day."
Correct Answer: 2Rationale 1: There is no evidence to support the claim that sea salt is more effective than any other kind
of salt.
Rationale 2: The kidneys are responsible for maintaining normal sodium levels. If there is sodium
depletion, the kidneys will conserve any salt, in this case lithium (Eskalith). This will lead to lithium
(Eskalith) toxicity.
Rationale 3: Instructing a patient to increase salt if toxicity occurs is inappropriate because the patient
must try to avoid toxicity, not treat it after it occurs.
Rationale 4: Drinking 1 to 1.5 L of water per day is important but does not substitute for adequate
sodium chloride.
Global Rationale: The kidneys are responsible for maintaining normal sodium levels. If there is sodium
depletion, the kidneys will conserve any salt, in this case lithium (Eskalith). This will lead to lithium
(Eskalith) toxicity. Instructing a patient to increase salt if toxicity occurs is inappropriate because the
patient must try to avoid toxicity, not treat it after it occurs. There is no evidence to support the claim
that sea salt is more effective than any other kind of salt. Drinking 1 to 1.5 L of water per day is
important but does not substitute for adequate sodium chloride.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 16-7 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.Page Number: 213
Question 12
Type: MCSA
What is the priority outcome for a 6-year-old patient who had been started on methylphenidate
(Ritalin)?
1. The patient will avoid altercations with peers.
2. The patient will be able to complete age-appropriate chores at home.
3. The patient will use age-appropriate play with peers.
4. The patient will maintain weight within norms for this age group.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Avoiding altercations with peers does not address a decrease in ADHD-related behaviors.
Rationale 2: Completing age-appropriate chores at home does not address the interaction and play with
peers, which is crucial during this developmental stage.
Rationale 3: Children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder have difficulty engaging in play with
peers due to their distractibility, impulsiveness, and hyperactivity. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) increases
their focus and decreases their distractibility, impulsiveness, and hyperactivity. Age-appropriate play
with peers is fundamental to healthy development with school-age children.
Rationale 4: Maintaining weight does not address the interaction and play with peers, which is crucial
during this developmental stage.
Global Rationale: Children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder have difficulty engaging in play
with peers due to their distractibility, impulsiveness, and hyperactivity. Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
increases their focus and decreases their distractibility, impulsiveness, and hyperactivity. Ageappropriate play with peers is fundamental to healthy development with school-age children. Avoiding
altercations with peers does not address a decrease in ADHD-related behaviors. Completing ageappropriate chores at home does not address the interaction and play with peers, which is crucial during
this developmental stage. Maintaining weight does not address the interaction and play with peers,
which is crucial during this developmental stage.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological IntegrityClient Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 16-7 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 211
Question 13
Type: MCSA
The 8-year-old patient is receiving methylphenidate (Ritalin). The patient's mother tells the nurse that
he won't eat while on his medication. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "It sounds like he is becoming depressed. I will speak to the doctor about starting an antidepressant
medication."
2. "Give the medication after meals and encourage him to have supplements between meals."
3. "You are right to be concerned. I will speak to the doctor about starting an appetite stimulant
medication."
4. "This is a very serious concern; it would be best for him to see a nutritionist for counseling."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: There isn't any evidence to support that the patient is becoming depressed.
Rationale 2: Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is an appetite suppressant. The best approach is to have the
patient take the medication after meals and consume nutritious supplements between meals.Rationale 3: It is premature to start an appetite stimulant medication without trying other strategies
first.
Rationale 4: Seeing a nutritionist is premature at this time.
Global Rationale: Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is an appetite suppressant. The best approach is to have the
patient take the medication after meals and consume nutritious supplements between meals. Seeing a
nutritionist is premature at this time. There isn't any evidence to support that the patient is becoming
depressed. It is premature to start an appetite stimulant medication without trying other strategies first.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-5 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 218
Question 14
Type: MCSA
A patient was prescribed sertraline (Zoloft) for the treatment of depression and anxiety. The patient’s
spouse calls the clinic and reports the patient is increasingly moody and seems “disconnected with life.”
What is the best response by the nurse?1. "Try giving him some diphenhydramine (Benadryl) to see if that helps him relax."
2. "Bring him to the clinic for assessment today.."
3. "Hold his medication today and see if his mood improves."
4. " “Double the daily dose of sertraline (Zoloft) and call us back in three days.”
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) is not indicated.Rationale 2: Sertraline (Zoloft) increases the
risk of suicidal thinking and behavior. The patient must be assessed. Rationale 3: Holding the
medication is not a sufficient intervention.Rationale 4: Doubling the dose is not indicated and
assessment should occur before next week.
Global Rationale: Sertraline (Zoloft) increases the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior. The patient
must be assessed. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) is not indicated. Holding the medication is not a
sufficient intervention. Doubling the dose is not indicated and assessment should occur before next
week.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Psychological Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-7 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 206Question 15
Type: MCSA
Which symptoms experienced over 1 month would be most helpful to diagnose bipolar disorder?
1. Difficulty sleeping, obsession with death, hallucinations
2. Delusions, unkempt appearance, fatigue
3. Abnormal eating patterns, feelings of despair, flight of ideas
4. Increased goal-directed behavior and talkativeness, distractibility
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Difficulty sleeping, obsession with death, and hallucinations are symptoms of depression.
Rationale 2: Delusions, unkempt appearance, and fatigue are symptoms of depression.
Rationale 3: Bipolar disorder involves periods of mania and depression. Abnormal eating patterns and
feelings of despair are symptoms of depression, whereas flight of ideas is a symptom of mania.
Rationale 4: Increased goal-directed behavior, talkativeness, and distractibility are symptoms of mania.
Global Rationale: Bipolar disorder involves periods of mania and depression. Abnormal eating patterns
and feelings of despair are symptoms of depression, whereas flight of ideas is a symptom of mania.
Increased goal-directed behavior, talkativeness, and distractibility are symptoms of mania. Difficulty
sleeping, obsession with death, hallucinations, delusions, unkempt appearance, and fatigue are
symptoms of depression.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-1 Identify the two major categories of mood disorders and their symptoms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 210
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Which statement is accurate regarding attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
1. ADHD is characterized by periods of mania and periods of depression.
2. Anxiety and social withdrawal are more frequently seen in girls than in boys.
3. Diagnosis is higher in girls than in boys.
4. ADHD is generally diagnosed later in life.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Periods of mania and periods of depression are more characteristic with bipolar disorder,
not ADHD.
Rationale 2: Girls show less aggression but more social withdrawal and anxiety.
Rationale 3: ADHD is generally in boys more frequently than in girls.
Rationale 4: ADHD is generally diagnosed in childhood.
Global Rationale: ADHD is generally diagnosed in childhood and in boys more frequently than in girls.
Boys have more overt activity levels, where girls show less aggression but more social withdrawal and
anxiety. Periods of mania and periods of depression are more characteristic with bipolar disorder, not
ADHD.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 16-2 Identify the symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.3 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage ADHD.
Page Number: 211
Question 17
Type: MCSA
Depression that occurs during cold winter months would be classified as
1. baby blues.
2. bipolar disorder.
3. seasonal affective disorder.
4. obsessive-compulsive disorder.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Baby blues are associated with mothers who have recently had a baby.
Rationale 2: Bipolar disorder involves periods of mania and periods of depression.
Rationale 3: Seasonal affective disorder is frequently experienced during the winter months.
Rationale 4: Obsessive-compulsive disorder involves doing certain tasks repetitively.
Global Rationale: Seasonal affective disorder is frequently experienced during the winter months.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder involves doing certain tasks repetitively. Baby blues are associated with
mothers who have recently had a baby. Bipolar disorder involves periods of mania and periods of
depression.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-3 Explain the etiology of major depressive disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 201
Question 18
Type: MCSA
Which drug type used to treat depression works by preventing enzymatic destruction of the
neurotransmitter norepinephrine?
1. Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
2. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
3. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
4. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: SNRIs inhibit the reabsorption of serotonin and norepinephrine and elevate mood.
Rationale 2: SSRIs slow the reuptake of serotonin.
Rationale 3: TCAs inhibit neurotransmitter reuptake.Rationale 4: MAOIs limit the breakdown of norepinephrine by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine
oxidase.
Global Rationale: MAOIs limit the breakdown of norepinephrine by inhibiting the enzyme monoamine
oxidase. TCAs inhibit neurotransmitter reuptake, while SSRIs slow the reuptake of serotonin. SNRIs
inhibit the reabsorption of serotonin and norepinephrine and elevate mood.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-6 Categorize drugs used for mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders based on
their classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 207
Question 19
Type: MCSA
Which drug type is often used as a first-line treatment for depression due to its side effect profile?
1. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
2. Beta-adrenergic blockers
3. Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)
4. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: MAOIs have a low safety margin.
Rationale 2: Currently beta blockers are more commonly used for treatment of hypertension.
Rationale 3: TCAs have some unpleasant and serious side effects.
Rationale 4: Of the drugs available for depression, the SSRIs have the most favorable side effect profile.
Global Rationale: Of the drugs available for depression, the SSRIs have the most favorable side effect
profile. MAOIs have a low safety margin. Currently beta blockers are more commonly used for
treatment of hypertension. TCAs have some unpleasant and serious side effects.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-6 Categorize drugs used for mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders based on
their classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 203
Question 20
Type: MCSA
Which food items should the nurse advise a patient taking a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) to
avoid?1. Orange juice, cottage cheese, and turkey
2. Spring water, ice cream, and salmon
3. Chocolate, wine, and fava beans
4. Spinach, rice, and venison
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Orange juice, cottage cheese, and turkey are not contraindicated.
Rationale 2: Spring water, ice cream, and salmon are not contraindicated.
Rationale 3: Chocolate, wine, and fava beans are high in tyramine, which can cause severe hypertension
in patients taking MAOIs.
Rationale 4: Spinach, rice, and venison are not contraindicated.
Global Rationale: Chocolate, wine, and fava beans are high in tyramine, which can cause severe
hypertension in patients taking MAOIs.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of patients with
depression, bipolar disorder, or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.3 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage ADHD.
Page Number: 210Question 21
Type: MCSA
The traditionally prescribed drug types used to treat attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
include
1. CNS depressants.
2. parasympathomimetics.
3. CNS stimulants.
4. sympathomimetics.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: CNS depressants have not traditionally been the drug of choice for treating ADHD.
Rationale 2: Parasympathomimetics have not traditionally been the drug of choice for treating ADHD.
Rationale 3: CNS stimulants have traditionally been the drug of choice for treating ADHD.
Rationale 4: Sympathomimetics have not traditionally been the drug of choice for treating ADHD.
Global Rationale: CNS stimulants have traditionally been the drug of choice for treating ADHD. CNS
depressants, parasympathomimetics, and sympathomimetics have not traditionally been the drug of
choice for treating ADHD.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-6 Categorize drugs used for mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders based on
their classification and drug action.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 215
Question 22
Type: MCSA
Which statement best explains drugs like methylphenidate help a patient with attention-deficit
hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)?
1. Neurotransmitters are blocked, limiting the effects they can produce within the PNS.
2. Activation of certain areas of the brain causes increased attention and ability to focus.
3. Neurotransmitter levels are reduced, which produces a calming effect within the CNS.
4. Certain areas of the brain are deactivated, resulting in a calming effect.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Neurotransmitters such as epinephrine and serotonin are released, not blocked.
Rationale 2: At first, it might seem confusing to use a CNS stimulant to treat a hyperactivity disorder.
However, CNS stimulants activate the reticular activating system, causing higher levels of attention and
ability to focus.
Rationale 3: Neurotransmitters such as epinephrine and serotonin are released, not reduced.
Rationale 4: Areas of the brain are not deactivated.
Global Rationale: At first, it might seem confusing to use a CNS stimulant to treat a hyperactivity
disorder. However, CNS stimulants activate the reticular activating system, causing higher levels of
attention and ability to focus. Neurotransmitters such as epinephrine and serotonin are released, not
blocked or reduced. Areas of the brain are not deactivated.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-6 Categorize drugs used for mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders based on
their classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 215
Question 23
Type: MCSA
A 40-year-old patient experiencing periods of mania and periods of depression would most likely benefit
from which of the following?
1. Atomoxetine (Strattera)
2. Amitriptyline (Elavil)
3. Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
4. Carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Atomoxetine is indicated for ADHD. Amitriptyline is indicated for depression.
Rationale 2: Amitriptyline is indicated for depression.
Rationale 3: Methylphenidate is indicated for ADHD. Amitriptyline is indicated for depression.
Rationale 4: Antiseizure drugs such as carbamazepine (Tegretol) are often used in the treatment of
bipolar disorder.
Global Rationale: Antiseizure drugs such as carbamazepine (Tegretol) are often used in the treatment of
bipolar disorder. Methylphenidate and atomoxetine are indicated for ADHD. Amitriptyline is indicated
for depression.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-6 Categorize drugs used for mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders based on
their classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.2 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage bipolar
disorder.
Page Number: 211
Question 24
Type: MCMA
The nurse is concerned that a patient is moving into the manic phase of bipolar disorder when what is
assessed?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Not sleeping
2. Losing weight
3. Sluggish activity
4. Complaints of muscle pain
5. Constant talking
Correct Answer: 1,2,5Rationale 1: Decreased need for sleep is a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Rationale 2: Decreased need for food is a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Rationale 3: Sluggish activity is not a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Rationale 4: Complaints of muscle pain are not a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Rationale 5: Increased talkativeness is a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Global Rationale: Decreased need for sleep and food are symptoms of the manic phase of bipolar
disorder. Increased talkativeness is a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder. Sluggish activity is
not a symptom of the manic phase of bipolar disorder. Complaints of muscle pain are not a symptom of
the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-2 Identify the symptoms of attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.3 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage ADHD.
Page Number: 210
Question 25
Type: MCMA
The nurse is instructing a patient on the cause of bipolar disorder. What neurotransmitters will the
nurse describe as contributing to the manic phase of this disorder?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Excessive glutamate
2. Excessive norepinephrine
3. Deficiency of gamma-aminobutyric acid
4. Deficiency of dopamine
5. Excessive serotonin
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Mania may involve an excess of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate.
Rationale 2: Mania may involve an excess of excitatory neurotransmitters such as norepinephrine.
Rationale 3: Mania may involve a deficiency of inhibitory neurotransmitters such as gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA).
Rationale 4: Dopamine is not associated with the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Rationale 5: Serotonin is not associated with the manic phase of bipolar disorder.
Global Rationale: Mania may involve an excess of excitatory neurotransmitters such as glutamate and
norepinephrine. Mania may involve a deficiency of inhibitory neurotransmitters such as gammaaminobutyric acid (GABA). Dopamine and serotonin are not associated with the manic phase of bipolar
disorder.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-3 Explain the etiology of major depressive disorder.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.1 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage
depression.
Page Number: 210
Question 26
Type: MCMA
During a health history, the nurse wants to include an assessment of depression with an older patient.
What statements will the nurse use to make this assessment?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "How often do you go out to socialize with friends?"
2. "Explain your self-care activities."
3. "How much alcohol do you consume every day?"
4. "How is living with your oldest daughter and her family working out for you?"
5. "Are you feeling depressed?"
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: This question would assess if the patient is reluctant to leave the home, which can indicate
depression in the older adult.
Rationale 2: Depression may cause the patient to lack interest in personal appearance. Information
about this feeling may be elicited by asking about self-care activities.
Rationale 3: In some cases, the older patient may overuse alcohol or combine it with other medications
that are depressants, which can further impact depression.
Rationale 4: Factors that contribute to depression in the older patient include the need to move in with
other family members because of health status or finances.
Rationale 5: Depression is greatly underdiagnosed among older patients. One reason is the reluctance
to admit depression because it can be seen as a sign of weakness or an inability to care for oneself.
Asking patients directly if they feel depressed is not likely to elicit the desired information.
Global Rationale: Asking about socialization would assess if the patient is reluctant to leave the home,
which can indicate depression in the older adult. Depression may cause the patient to lack interest inpersonal appearance. Information about this feeling may be elicited by asking about self-care activities.
In some cases, the older patient may overuse alcohol or combine it with other medications that are
depressants, which can further impact depression. Factors that contribute to depression in the older
patient include the need to move in with other family members because of health status or finances.
Depression is greatly underdiagnosed among older patients. One reason is the reluctance to admit
depression because it can be seen as a sign of weakness or an inability to care for oneself. Asking
patients directly if they feel depressed is not likely to elicit the desired information.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-7 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 202
Question 27
Type: MCMA
During a health history, the nurse is concerned that a patient with depression is at risk for suicide when
the patient
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. states that "suicide is always an option."
2. describes a previous unsuccessful attempt at suicide by aspirin overdose.
3. states that the prescribed medication is not working and that feelings of depression are worse.
4. requests prescriptions for pain medication and a sleeping aid.
5. expresses interest in meeting with friends more often.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: If a person verbalizes about committing suicide, the talk must be taken seriously.
Rationale 2: A patient who has had a previous suicide attempt is at higher risk for suicide and must be
monitored carefully.
Rationale 3: Worsening symptoms of depression must be reported immediately because these may
indicate that the drug is not working or that the patient is not compliant with pharmacotherapy.
Rationale 4: All prescription drugs must be monitored because suicidal patients often take overdoses.
Therapy with multiple central nervous system depressants is discouraged because these agents produce
additive sedation.
Rationale 5: This information would not indicate a worsening of depression or the risk for suicide.
Global Rationale: If a person verbalizes about committing suicide, the talk must be taken seriously. A
patient who has had a previous suicide attempt is at higher risk for suicide and must be monitored
carefully. Worsening symptoms of depression must be reported immediately because these may
indicate that the drug is not working or that the patient is not compliant with pharmacotherapy. All
prescription drugs must be monitored because suicidal patients often take overdoses. Therapy with
multiple central nervous system depressants is discouraged because these agents produce additive
sedation. Interest in meeting friends more often does not indicate a worsening of depression or the risk
for suicide.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 16-7 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 212
Question 28
Type: MCMA
A patient who has been taking antidepressant medication for several months and is demonstrating an
improvement in symptoms tells the nurse that counseling sessions might be helpful. Which types of
therapies will the nurse review with the patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Behavioral therapy
2. Interpersonal therapy
3. Cognitive-behavioral therapy
4. Psychodynamic therapy
5. Crisis therapy
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: Behavioral therapies help patients unlearn the behavioral patterns that contribute to or
result from their depression.Rationale 2: Interpersonal therapy focuses on a patient's disturbed personal relationships that both
cause and exacerbate depression.
Rationale 3: Cognitive-behavioral therapies help patients change negative styles of thought and
behavior that are often associated with depression.
Rationale 4: Psychodynamic therapies focus on resolving the patient's internal conflicts by looking at the
influence of past experiences on current behavior and how behavior is influenced by emotional factors.
Rationale 5: Crisis therapy is not a type of therapy for depression.
Global Rationale: Behavioral therapies help patients unlearn the behavioral patterns that contribute to
or result from their depression. Interpersonal therapy focuses on a patient's disturbed personal
relationships that both cause and exacerbate depression. Cognitive-behavioral therapies help patients
change negative styles of thought and behavior that are often associated with depression.
Psychodynamic therapies focus on resolving the patient's internal conflicts by looking at the influence of
past experiences on current behavior and how behavior is influenced by emotional factors.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 16-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of patients with
depression, bipolar disorder, or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.3 Examine characteristics of and classes of drugs used to manage ADHD.
Page Number: 202
Question 29
Type: MCMAA patient with depression does not want to take prescribed medication because of the side effects.
What can the nurse suggest to help with medication adherence?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Use ice chips to help alleviate dry mouth.
2. Chew gum or use hard candy to help alleviate dry mouth.
3. Avoid alcohol-based mouthwash to help alleviate dry mouth.
4. Use "dry eye" drops to help with eye dryness.
5. Ask the pharmacist to fill the prescription with the same drug from a different manufacturer.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: Using ice chips helps to alleviate dry mouth associated with these medications.
Rationale 2: Chewing gum or sucking on hard candy helps to alleviate dry mouth associated with these
medications.
Rationale 3: Alcohol-based mouthwash can increase the feeling of dry mouth associated with these
medications.
Rationale 4: "Dry eye" drops help alleviate eye dryness associated with these medications.
Rationale 5: The patient should use the same manufacturer’s brand each time the prescription is filled.
Global Rationale: Using ice chips helps to alleviate dry mouth associated with these medications.
Chewing gum or sucking on hard candy helps to alleviate dry mouth associated with these medications.
Alcohol-based mouthwash can increase the feeling of dry mouth associated with these medications.
"Dry eye" drops help alleviate eye dryness associated with these medications. The patient should use
the same manufacturer’s brand each time the prescription is filled.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 16-7 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
mood, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.1.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 214
Question 30
Type: MCMA
The parent of a child being treated for ADHD says a neighbor child with the same diagnosis is on a “drug
holiday.” How should the nurse explain this treatment option?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “Drug holidays may be used to reduce dependence on medications or to assess symptoms.”
2. “If you feel like the medication is sedating your child too much, you can hold doses for 3 or 4 days
which is known as a drug holiday.”
3. “Drug holidays are times when dosage is increased to assess the patient’s tolerance to medications.”
4. “You should not consider using a drug holiday until you have discussed that option with your
provider.”
5. “Drug holidays require careful scheduling.”
Correct Answer: 1,4,5Rationale 1: Some medications used for treatment of ADHD may result in dependence. Drug holidays
are used to reduce risk of dependence and to assess for level of symptoms without medications.
Rationale 2: Drug holidays are not initiated by the parent without guidance.
Rationale 3: Dosage increases are not a part of drug holidays.
Rationale 4: Drug holidays should be undertaken only after careful consideration and discussion with
the provider.
Rationale 5: Drug holidays should be scheduled around times that increased symptoms of ADHD will not
interfere with school or other important activities.
Chapter 17:
Question 1
Type: MCMA
The patient has been admitted to the hospital for the treatment of schizophrenia. The patient's mother
says to the nurse, "This is all so confusing. How did he get this? Did I do something?" Which nursing
responses are indicated?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Schizophrenia is a biological brain disorder."
2. "Schizophrenia is linked to drinking alcohol during pregnancy."
3. "Research indicates that a very stressful environment causes schizophrenia."
4. "Research indicates that schizophrenia is a genetic disorder."
5. "Schizophrenia is due to too much dopamine in certain parts of the brain."
Correct Answer: 1,4,5
Rationale 1: Theories explaining the cause of schizophrenia include imbalances in neurotransmitters in
specific areas of the brain.
Rationale 2: There isn't any evidence to support that schizophrenia is linked to alcohol consumption
during pregnancy.
Rationale 3: A stressful environment will exacerbate the symptoms of schizophrenia but does not cause
the illness.
Rationale 4: Theories explaining the cause of schizophrenia include a genetic component.Rationale 5: Theories explaining the cause of schizophrenia include overactive dopaminergic pathways
in the basal nuclei.
Global Rationale: Theories explaining the cause of schizophrenia include a genetic component,
imbalances in neurotransmitters in specific areas of the brain, and overactive dopaminergic pathways in
the basal nuclei. There isn't any evidence to support that schizophrenia is linked to alcohol consumption
during pregnancy. A stressful environment will exacerbate the symptoms of schizophrenia but does not
cause the illness.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-1 Explain theories for the etiology of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 225
Question 2
Type: MCSA
The patient with schizophrenia is sitting quietly in a chair. The patient does not respond much to what is
happening and has a lack of interest in the environment. How does the nurse interpret this assessment?
1. The patient is most likely very depressed.
2. The patient is most likely hearing voices.
3. The patient is experiencing positive symptoms.
4. The patient is experiencing negative symptoms.Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: There isn't any evidence to support that the patient is very depressed.
Rationale 2: There isn't any evidence to support that the patient is hearing voices.
Rationale 3: Positive symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, and a disorganized thought or speech
pattern.
Rationale 4: Negative symptoms are those that subtract from normal behavior. These symptoms include
a lack of interest, motivation, responsiveness, or pleasure in daily activities.
Global Rationale: Negative symptoms are those that subtract from normal behavior. These symptoms
include a lack of interest, motivation, responsiveness, or pleasure in daily activities. Positive symptoms
include hallucinations, delusions, and a disorganized thought or speech pattern. There isn't any evidence
to support that the patient is hearing voices. There isn't any evidence to support that the patient is very
depressed.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-2 Compare and contrast the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 224
Question 3
Type: MCSAThe physician has prescribed haloperidol (Haldol) for the patient with schizophrenia. What is the priority
patient outcome?
1. The patient will consume adequate fluids and a high-fiber diet.
2. The patient will be compliant with taking the medication as prescribed.
3. The patient will report a decrease in auditory hallucinations.
4. The patient will report symptoms of restlessness.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Adequate fluids and fiber will decrease the side effect of constipation, but this is not the
priority outcome.
Rationale 2: Medication compliance is a priority for patients with schizophrenia. Relapse of symptoms
will occur without the medications.
Rationale 3: A decrease in auditory hallucinations is an expected effect of haloperidol (Haldol), but this
is not the priority outcome.
Rationale 4: The symptom of restlessness is known as akathisia. This would be important to report but is
not the priority outcome.
Global Rationale: Medication compliance is a priority for patients with schizophrenia. Relapse of
symptoms will occur without the medications. The symptom of restlessness is known as akathisia. This
would be important to report but is not the priority outcome. Adequate fluids and fiber will decrease
the side effect of constipation, but this is not the priority outcome. A decrease in auditory hallucinations
is an expected effect of haloperidol (Haldol), but this is not the priority outcome.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 230
Question 4
Type: MCSA
The nurse is managing the care of a group of patients with schizophrenia. The patients are receiving
conventional antipsychotic medications. When assessing for anticholinergic side effects, which would
the nurse immediately report to the physician?
1. Acute dystonia
2. Complaint of a severe headache
3. Hypertension
4. Urinary retention
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Acute dystonia must be reported immediately to the physician, but this is not an
anticholinergic side effect.
Rationale 2: Headaches are not anticholinergic side effects.
Rationale 3: Hypotension, not hypertension, is a cardiac side effect, not an anticholinergic side effect.
Rationale 4: Urinary retention is an anticholinergic side effect of conventional antipsychotics. This must
be reported immediately to the physician.
Global Rationale: Urinary retention is an anticholinergic side effect of conventional antipsychotics. This
must be reported immediately to the physician. Hypotension, not hypertension, is a cardiac side effect,
not an anticholinergic side effect. Headaches are not anticholinergic side effects. Acute dystonia must be
reported immediately to the physician, but this is not an anticholinergic side effect.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 233
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The patient has been receiving chlorpromazine (Thorazine) for the treatment of schizophrenia. The
nurse assesses that the patient has tardive dyskinesia. What findings support this conclusion?
1. Tremor, muscle rigidity, and a shuffling gait
2. Severe muscle spasms of the back, neck, and tongue
3. An inability to rest or relax, and restlessness
4. Unusual facial movements and lip smacking
Correct Answer: 4Rationale 1: Tremor, muscle rigidity, and a shuffling gait are known as parkinsonism, not tardive
dyskinesia.
Rationale 2: Severe muscle spasms of the back, neck, and tongue are known as acute dystonia, not
tardive dyskinesia.
Rationale 3: An inability to rest or relax and restlessness are known as akathisia, not tardive dyskinesia.
Rationale 4: Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by unusual tongue and face movements, such as lip
smacking, and wormlike motions of the tongue.
Global Rationale: Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by unusual tongue and face movements, such as lip
smacking, and wormlike motions of the tongue. Severe muscle spasms of the back, neck, and tongue are
known as acute dystonia, not tardive dyskinesia. An inability to rest or relax and restlessness are known
as akathisia, not tardive dyskinesia. Tremor, muscle rigidity, and a shuffling gait are known as
parkinsonism, not tardive dyskinesia.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-6 Explain the symptoms associated with extrapyramidal symptoms of
antipsychotic drugs.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 229Question 6
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving risperidone (Risperdal). During morning assessment, the nurse notes that the
patient has a temperature of 102 degrees F. What is the priority nursing intervention?
1. Contact the physician, as this could be a symptom of neuroleptic malignant syndrome.
2. Contact the physician, as this could be a symptom of an acute urinary infection.
3. Contact the physician, as this could be a symptom of a bacterial pneumonia.
4. Contact the physician, as this could be a symptom of extrapyramidal side effects.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome includes symptoms of elevated temperature, unstable
blood pressure, profuse sweating, dyspnea, muscle rigidity, and incontinence.
Rationale 2: Patients with acute urinary infections do run elevated temperatures; however, when the
patient is receiving an antipsychotic drug and runs an elevated temperature, a different condition must
be considered first.
Rationale 3: Patients with bacterial pneumonias do run elevated temperatures; however, when the
patient is receiving an antipsychotic drug and runs an elevated temperature, a different condition must
be considered first.
Rationale 4: An elevated temperature is not an extrapyramidal side effect.
Global Rationale: Neuroleptic malignant syndrome includes symptoms of elevated temperature,
unstable blood pressure, profuse sweating, dyspnea, muscle rigidity, and incontinence. Patients with
acute urinary infections do run elevated temperatures; however, when the patient is receiving an
antipsychotic drug and runs an elevated temperature, neuroleptic malignant syndrome must always be
suspected. Patients with bacterial pneumonias do run elevated temperatures; however, when the
patient is receiving an antipsychotic drug and runs an elevated temperature, neuroleptic malignant
syndrome must always be suspected. An elevated temperature is not an extrapyramidal side effect.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-6 Explain the symptoms associated with extrapyramidal symptoms of
antipsychotic drugs.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 227
Question 7
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving clozapine (Clozaril) for the treatment of schizophrenia. The nurse evaluates that
this medication has been effective when the patient makes which statement?
1. "I will start going to group therapy."
2. "I think I am ready for discharge, as I feel better."
3. "I am not hearing the voices anymore."
4. "I promise not to skip breakfast anymore."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: A patient stating he will go to group therapy does not indicate the remission of any
psychotic symptoms.
Rationale 2: A patient stating he feels better and is ready for discharge does not indicate the remission
of any psychotic symptoms.
Rationale 3: Therapeutic effects of clozapine (Clozaril) include remission of a range of psychotic
symptoms to include delusions, paranoia, auditory hallucinations, and irrational behavior.
Rationale 4: A patient stating he will not skip breakfast does not indicate the remission of any psychotic
symptoms.Global Rationale: Therapeutic effects of clozapine (Clozaril) include remission of a range of psychotic
symptoms to include delusions, paranoia, auditory hallucinations, and irrational behavior. A patient
stating he feels better and is ready for discharge does not indicate the remission of any psychotic
symptoms. A patient stating he will go to group therapy does not indicate the remission of any psychotic
symptoms. A patient stating he will not skip breakfast does not indicate the remission of any psychotic
symptoms.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 17-5 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 230
Question 8
Type: MCSA
The nurse has completed medication education with the patient who is receiving risperidone
(Risperdal). The nurse evaluates that the education has been effective when the patient makes which
statement?
1. "I must call my doctor if I start to have a lot of nightmares."
2. "I must have my blood work done while taking this medication."
3. "I must call my doctor if I start to lose a lot of weight."4. "I must call my doctor if I notice any a metallic taste in my mouth."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Nightmares are not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Rationale 2: Agranulocytosis can be a life-threatening side effect of risperidone (Risperdal), which may
also suppress bone marrow and lower infection-fighting ability. It is very important, therefore, that the
patient have regular blood work done while on this medication.
Rationale 3: Weight gain, not weight loss, is a serious side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Rationale 4: A metallic taste is not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Global Rationale: Agranulocytosis can be a life-threatening side effect of risperidone (Risperdal), which
may also suppress bone marrow and lower infection-fighting ability. It is very important, therefore, that
the patient have regular blood work done while on this medication. A metallic taste is not a side effect
of risperidone (Risperdal). Weight gain, not weight loss, is a serious side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Nightmares are not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 17-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 235Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving risperidone (Risperdal). What is a priority outcome for this patient?
1. The patient reports any narrowing of the field of vision.
2. The patient reports any joint pain or swelling.
3. The patient reports any signs of a sore throat or an infection.
4. The patient reports any yellowish halos around lights.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Narrowing of the field of vision is not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Rationale 2: Joint pain or swelling is not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Rationale 3: Signs of a sore throat or an infection could indicate agranulocytosis, which is a lifethreatening side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Rationale 4: Yellowish halos around lights are not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Global Rationale: Signs of a sore throat or an infection could indicate agranulocytosis, which is a lifethreatening side effect of risperidone (Risperdal). Yellowish halos around lights are not a side effect of
risperidone (Risperdal). Joint pain or swelling is not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal). Narrowing of
the field of vision is not a side effect of risperidone (Risperdal).
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: PlanningLearning Outcome: 17-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 235
Question 10
Type: MCMA
A patient has been well controlled on an oral liquid medication for schizophrenia. Today the patient’s
caregiver reports return to both positive and negative symptoms over the last week. Which nursing
assessment questions are indicated?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “Have you changed the fluid you are using to mix with the medication?”
2. “Have you changed pharmacies?”
3. “What was the patient’s last fasting blood glucose measurement?”
4. “Has the patient started smoking again?”
5. “Is the patient drinking more milk than usual?”
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Mixing the liquid medication in cola, tea, or caffeine-containing liquids may change
effectiveness.
Rationale 2: The patient should not switch brands of medication.
Rationale 3: Blood glucose management is important but would not cause these symptoms.
Rationale 4: Smoking may decrease effectiveness of some medications.
Rationale 5: Drinking more milk is not an issue with these medications.Global Rationale: Mixing the liquid medication in cola, tea, or caffeine-containing liquids may change
effectiveness. The patient should not switch brands of medication. Smoking may decrease effectiveness
of some medications. Blood glucose management is important but would not cause these symptoms.
Drinking more milk is not an issue with these medications.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 234
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The nurse has completed diet education for a group of patients who are receiving antipsychotic
medications. If the medication education has been effective, patients will eliminate what choice from
their menu selection?
1. Meats with a high-fat content2. Beverages with caffeine
3. Refined breads and desserts
4. Shellfish and peanuts
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Although unhealthy, high-fat meats do not affect the action of antipsychotic medications.
Rationale 2: The use of caffeine-containing substances will decrease the effect of antipsychotic
medications.
Rationale 3: Although unhealthy, refined breads and desserts do not affect the action of antipsychotic
medications.
Rationale 4: Many individuals are allergic to shellfish and peanuts, but they do not affect the action of
antipsychotic medications.
Global Rationale: The use of caffeine-containing substances will decrease the effect of antipsychotic
medications. Although unhealthy, high-fat meats do not affect the action of antipsychotic medications.
Although unhealthy, refined breads and desserts do not affect the action of antipsychotic medications.
Many individuals are allergic to shellfish and peanuts, but they do not affect the action of antipsychotic
medications.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 17-4 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.Page Number: 234
Question 12
Type: MCSA
The patient is receiving antipsychotic medications and tells the nurse he has not had a bowel movement
for 2 days. What is the best initial action of the nurse?
1. Hold the medication until the patient has a bowel movement.
2. Have the patient drink prune juice and additional fluids.
3. Contact the physician for an order for a Fleet Enema.
4. Contact the physician for an order for a stool softener.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Antipsychotic medications should not be held because of constipation.
Rationale 2: Constipation is a common side effect of antipsychotic medications. The best approach is to
have the patient increase dietary fiber and fluids and to exercise to prevent constipation.
Rationale 3: Contacting the physician for an order for a Fleet Enema is premature.
Rationale 4: Contacting the physician for an order for a stool softener is premature.
Global Rationale: Constipation is a common side effect of antipsychotic medications. The best approach
is to have the patient increase dietary fiber and fluids and to exercise to prevent constipation.
Contacting the physician for an order for a Fleet Enema is premature; the patient should initially
increase dietary fiber, fluids, and exercise to prevent constipation. Contacting the physician for an order
for a stool softener is premature; the patient should initially increase dietary fiber, fluids, and exercise to
prevent constipation. Antipsychotic medications should not be held because of constipation.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 233
Question 13
Type: MCSA
The patient who is receiving antipsychotic medication complains of having a dry mouth. The patient
refused the morning dose of the medication. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Why are you refusing the medicine?"
2. "I can give you benztropine (Cogentin) for your dry mouth."
3. "I will let your doctor know about your dry mouth."
4. "A dry mouth is common, but drinking more water will help."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Asking the patient why he is refusing his medication is an inappropriate question, as the
nurse knows the patient has been complaining of a dry mouth.
Rationale 2: Benztropine (Cogentin) is indicated for extrapyramidal side effects, not for a dry mouth.
Rationale 3: Dry mouth is a common side effect treated by nursing interventions, not physician's orders.
Rationale 4: The symptom of dry mouth is very common with antipsychotic medications. The best
approach is to have the patient suck on sugarless candy, chew gum, or have frequent drinks of water.Global Rationale: The symptom of dry mouth is very common with antipsychotic medications. The best
approach is to have the patient suck on sugarless candy, chew gum, or have frequent drinks of water.
Benztropine (Cogentin) is indicated for extrapyramidal side effects, not for a dry mouth. Asking the
patient why he is refusing his medication is an inappropriate question, as the nurse knows the patient
has been complaining of a dry mouth. Dry mouth is a common side effect treated by nursing
interventions, not physician's orders.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 233
Question 14
Type: MCSA
The patient receives quetiapine (Seroquel) and asks the nurse how the medication works. What is the
best response by the nurse?
1. "Quetiapine (Seroquel) decreases norepinephrine in your brain, and that decreases your auditory
hallucinations."2. "Quetiapine (Seroquel) increases norepinephrine in your brain, and that decreases your feelings of
depression."
3. "Quetiapine (Seroquel) decreases dopamine in your brain, and that decreases your symptoms."
4. "Quetiapine (Seroquel) increases dopamine in your brain, and that helps you to think more clearly."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Quetiapine (Seroquel) does not decrease norepinephrine in the brain.
Rationale 2: Quetiapine (Seroquel) does not increase norepinephrine in the brain.
Rationale 3: Quetiapine (Seroquel) acts by interfering with the binding of dopamine to its receptors in
the brain.
Rationale 4: Quetiapine (Seroquel) does not increase dopamine in the brain.
Global Rationale: Quetiapine (Seroquel) acts by interfering with the binding of dopamine to its
receptors in the brain. Quetiapine (Seroquel) does not increase dopamine in the brain. Quetiapine
(Seroquel) does not decrease norepinephrine in the brain. Quetiapine (Seroquel) does not increase
norepinephrine in the brain.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-8 Categorize drugs used for psychoses based on their classification and drug
action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 231Question 15
Type: MCSA
Symptoms of schizophrenia are thought to be associated with which receptor sites?
1. Dopamine type 2
2. Adrenergic
3. Beta 2
4. Cholinergic
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Although other receptor sites can be involved, it appears that dopamine type 2 receptors
are the most responsible.
Rationale 2: There is another site thought to be more responsible for these effects.
Rationale 3: There is another site thought to be more responsible for these effects.
Rationale 4: There is another site thought to be more responsible for these effects.
Global Rationale: Although other receptor sites can be involved, it appears that dopamine type 2
receptors are the most responsible.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-1 Explain theories for the etiology of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.Page Number: 225
Question 16
Type: MCSA
A patient with a psychiatric history is communicating using made-up words and indicates he doesn’t
care about anything. This patient would most likely be
1. demonstrating symptoms of depression.
2. demonstrating positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
3. demonstrating negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
4. demonstrating symptoms of bipolar disorder.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: These are not symptoms of depression.
Rationale 2: The use of made-up words and detachment from life most likely indicate he is
demonstrating the positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Rationale 3: These are not negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
Rationale 4: These are not symptoms of bipolar disorder.
Global Rationale: The use of made-up words and detachment from life most likely indicate he is
demonstrating the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. These are not negative symptoms. These are
not symptoms of depression or bipolar disorder.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-2 Compare and contrast the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 224
Question 17
Type: MCSA
Which drug would be indicated for a schizophrenic who needs management of both positive and
negative symptoms?
1. Thioridazine HCL (Mellaril)
2. Haloperidol (Haldol)
3. Clozapine (Clozaril)
4. Chlorpromazine (Thorazine)
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Conventional antipsychotic agents like thioridazine HCL (Mellaril) are indicated for positive
symptoms.
Rationale 2: Conventional antipsychotic agents like haloperidol (Haldol) are indicated for positive
symptoms.
Rationale 3: Clozaril is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for positive and negative symptoms of
schizophrenia.
Rationale 4: Conventional antipsychotic agents like chlorpromazine (Thorazine) are indicated for
positive symptoms.
Global Rationale: Clozaril is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for positive and negative symptoms of
schizophrenia. Conventional antipsychotic agents (phenothiazines and phenothiazine-like drugs) are
indicated for positive symptoms.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological IntegrityClient Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 17-3 Discuss the rationale for selecting a specific antipsychotic drug for the
treatment of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 237
Question 18
Type: MCSA
The relapse rate for psychotic patients who are not compliant and discontinue their medications is
1. 60–80%.
2. 50–70%.
3. 30–40%.
4. 20–50%.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The relapse rate for psychotic patients who are not compliant and discontinue their
medications is 60 to 80%.
Rationale 2: This is not the relapse rate for this situation.
Rationale 3: This is not the relapse rate for this situation.
Rationale 4: This is not the relapse rate for this situation.Global Rationale: The relapse rate for psychotic patients who are not compliant and discontinue their
medications is 60 to 80%.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe patient care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-4 Explain the importance of patient drug compliance in the pharmacotherapy of
schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 226
Question 19
Type: MCSA
An older female patient with psychosis has been taking haloperidol (Haldol) for 1 week. The patient has
been making wormlike movements with her tongue. How would the nurse evaluate this finding?
1. An adverse effect likely caused by the medication, known as tardive dyskinesia
2. A normal reaction to the medication that will likely go away in a week or two
3. A desired sign that the patient has not been taking the medication
4. A sign of the patient's underlying psychosis, indicating that the medication is not effective
Correct Answer: 1Rationale 1: Older female patients on Haldol have a higher incidence of tardive dyskinesia (an adverse
effect). Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by wormlike movements of the tongue.
Rationale 2: This reaction is common but will not go away in a week or two.
Rationale 3: While this effect does indicate the patient is taking the medication, it is not desirable.
Rationale 4: This is not an effect of the underlying disease.
Global Rationale: Older female patients on Haldol have a higher incidence of tardive dyskinesia (an
adverse effect). Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by wormlike movements of the tongue. This reaction
is common but will not go away in a week or two. While this effect does indicate the patient is taking the
medication, it is not desirable. This is not an effect of the underlying disease.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-6 Explain the symptoms associated with extrapyramidal symptoms of
antipsychotic drugs.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 229
Question 20
Type: MCSAA patient experiencing an extrapyramidal adverse effect is not able to relax. How would the nurse
record this information in the medical record?
1. As dystonia
2. As tardive dyskinesia
3. As akathisia
4. As secondary parkinsonism
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Dystonia involves severe muscle spasms, particularly of the back, neck, tongue, and face.
Rationale 2: Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by unusual tongue and face movements such as lip
smacking.
Rationale 3: The inability to relax is akathisia.
Rationale 4: Secondary parkinsonism includes tremor, muscle rigidity, stooped posture, and a shuffling
gait.
Global Rationale: The inability to relax is akathisia. Dystonia involves severe muscle spasms, particularly
of the back, neck, tongue, and face. Tardive dyskinesia is characterized by unusual tongue and face
movements such as lip smacking. Secondary parkinsonism includes tremor, muscle rigidity, stooped
posture, and a shuffling gait.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: ImplementationLearning Outcome: 17-6 Explain the symptoms associated with extrapyramidal symptoms of
antipsychotic drugs.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 229
Question 21
Type: MCSA
A patient overdosed on risperidone (Risperdal) 20 minutes ago. The nurse should prepare to take which
action?
1. Administer a CNS depressant
2. Administer an anticholinergic
3. Administer activated charcoal
4. Symptom management since there is no other treatment
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: CNS depressants likely will worsen symptoms.
Rationale 2: Anticholinergic agents likely will worsen symptoms.
Rationale 3: Activated charcoal will bind the Risperdal that has not been absorbed and prevent
absorption into the bloodstream.
Rationale 4: symptom management might be warranted, but given that the overdose occurred only 20
minutes ago, there is a different effective treatment.
Global Rationale: Activated charcoal will bind the Risperdal that has not been absorbed and prevent
absorption into the bloodstream. Symptom management might be warranted, but given that the
overdose occurred only 20 minutes ago, charcoal likely will be effective and should be used.
Anticholinergic agents and CNS depressants likely will worsen symptoms.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral TherapiesQSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 235
Question 22
Type: MCSA
A patient who has been treated with antipsychotic agents for schizophrenia has an elevated blood
pressure, dyspnea, and an extremely high temperature. The nurse prepares to treat which disorder?
1. Akathisia
2. Extrapyramidal side effects
3. Acute dystonias
4. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Akathisia is an inability to rest or relax.
Rationale 2: Extrapyramidal side effects include dystonia, akathisia, secondary parkinsonism, and tardive
dyskinesia.
Rationale 3: Acute dystonias involve severe muscle spasms, particularly of the back, neck, tongue, and
face.
Rationale 4: The condition that causes an elevated blood pressure, dyspnea, and high temperature is
neuroleptic malignant syndrome.Global Rationale: The condition that causes an elevated blood pressure, dyspnea, and high temperature
is neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Akathisia is an inability to rest or relax. Extrapyramidal side effects
include dystonia, akathisia, secondary parkinsonism, and tardive dyskinesia. Acute dystonias involve
severe muscle spasms, particularly of the back, neck, tongue, and face.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 17-5 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 229
Question 23
Type: MCMA
The nurse suspects a patient is demonstrating negative symptoms of schizophrenia and will be a
challenge to treat because of which barriers?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The patient feels that the symptoms are normal.
2. Family members feel the patient is going through a period of depression.
3. The patient is suspicious of the motives of the health care provider.4. Family members have labeled the patient as lazy.
5. The patient is indifferent to obtaining help.
Correct Answer: 2,4,5
Rationale 1: Patients with a psychosis rather than the negative symptoms of schizophrenia are often
unaware that their bizarre behavior is not normal.
Rationale 2: Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are often mistaken for depression.
Rationale 3: Suspicion that someone is trying to do harm is characteristic of delusions.
Rationale 4: Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are often mistaken for laziness.
Rationale 5: Negative symptoms are characteristic of the indifferent personality typical of many patients
with schizophrenia.
Global Rationale: Negative symptoms of schizophrenia are often mistaken for depression or laziness.
They are characteristic of the indifferent personality typical of many patients with schizophrenia.
Patients with a psychosis rather than the negative symptoms of schizophrenia are often unaware that
their bizarre behavior is not normal. Suspicion that someone is trying to do harm is characteristic of
delusions.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 17-2 Compare and contrast the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 224Question 24
Type: MCMA
The nurse is performing the initial assessment on a patient admitted to the psychiatric unit. The patient
hears voices saying to cut the patient's arms with razor blades until they bleed. The nurse should assess
for which findings?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Family history of first-degree relative with schizophrenia
2. Use of illegal substances
3. Recent episodes of anxiety
4. Family history of heart disease
5. History of a dysfunctional family
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: A person has a 5–10 times greater risk of getting schizophrenia if a first-degree relative has
the disorder.
Rationale 2: Use of drugs such as cocaine can produce hallucinations or paranoia.
Rationale 3: A history of anxiety has no connection to the development of schizophrenia.
Rationale 4: A family history of heart disease has no connection to the development of schizophrenia.
Rationale 5: Family dynamics can affect coping skills, which can influence the onset of schizophrenia.
Global Rationale: A person has a 5–10 times greater risk of getting schizophrenia if a first-degree
relative has the disorder. Use of drugs such as cocaine can produce hallucinations or paranoia. Family
dynamics can affect coping skills, which can influence the onset of schizophrenia. A history of anxiety
has no connection to the development of schizophrenia. A family history of heart disease has no
connection to the development of schizophrenia.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 232
Question 25
Type: MCMA
A patient with a history of suicidal behavior with schizophrenia stopped taking clozapine (Clozaril) after
4 weeks of therapy. The patient is currently experiencing a return of hallucinations. What might the
nurse assess when determining the reason the patient stopped taking the medication?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Feeling sedated all the time
2. Significant weight gain
3. Agitation
4. Fatigue and headache
5. Uncontrollable sexual urges
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: Patients do not like the side effect of being sedated all the time.Rationale 2: Substantial weight gain has been reported in some patients taking this medication. This is a
reason some stop taking the medication.
Rationale 3: Agitation may be an extrapyramidal symptom of treatment with this medication and is an
unwanted adverse effect.
Rationale 4: Fatigue and headache are possible side effects of this medication.
Rationale 5: Side effects include loss of libido, not uncontrollable sexual urges.
Global Rationale: Patients do not like the side effect of being sedated all the time. Substantial weight
gain has been reported in some patients taking this medication. This is a reason some stop taking the
medication. Agitation may be an extrapyramidal symptom of treatment with this medication and is an
unwanted adverse effect. Fatigue and headache are possible side effects of this medication. Side effects
include loss of libido, not uncontrollable sexual urges.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-5 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 231
Question 26
Type: MCMAThe nurse is assessing a female patient who has been taking chlorpromazine for schizophrenia. What
should the nurse include in this assessment?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Ask the patient if she is compliant with the use of St. John’s wort as an adjunctive medication.
2. Draw blood to check a lipid profile.
3. Ask the patient questions regarding amount of alcohol intake.
4. Determine the date of her last menstrual period.
5. Draw blood to check thyroid function.
Correct Answer: 2,3,4
Rationale 1: St. John’s wort may result in an increase in the risk and severity of dystonia.
Rationale 2: Antipsychotic drugs have cardiometabolic effects. A lipid profile should be drawn at each
visit.
Rationale 3: It is important to assess for alcohol use as this could cause excessive drowsiness.
Rationale 4: It is important to assess for pregnancy as this drug is Pregnancy Category C.
Rationale 5: There is no indication that antipsychotics affect thyroid function, and nothing in the
scenario indicates the need to check thyroid function.
Global Rationale: It is important to assess for alcohol use as this could cause excessive drowsiness. It is
important to assess for pregnancy as this drug is Pregnancy Category C. St. John’s wort may result in an
increase in the risk and severity of dystonia. Antipsychotic drugs have cardiometabolic effects. A lipid
profile should be drawn at each visit. There is no indication that antipsychotics affect thyroid function,
and nothing in the scenario indicates the need to check thyroid function.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-9 Use the nursing process to care for patient receiving pharmacotherapy for
psychoses.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 228
Question 27
Type: MCMA
A patient taking risperidone (Risperdal) for schizophrenia is experiencing signs of hypotension with
certain activities since starting this medication. What should the nurse teach the patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Avoid being outside in the heat of the day.
2. Avoid hot baths or hot showers.
3. Avoid vitamin C-containing preparations.
4. Change positions slowly, especially from lying or sitting to standing.
5. Take frequent naps during the day.
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: The patient should avoid any situation that might cause overheating, especially in hot
weather, to reduce the risk of hypotension.
Rationale 2: Hot baths and hot showers should be avoided to decrease the chance of hypotension.
Rationale 3: There is no association between vitamin C-containing products and hypotension.Rationale 4: Changing positions slowly will help reduce orthostatic hypotension.
Rationale 5: Frequent naps will not affect the symptoms of hypotension.
Global Rationale: The patient should avoid any situation that might cause overheating, especially in hot
weather, to reduce the risk of hypotension. Hot baths and hot showers should be avoided to decrease
the chance of hypotension. Changing positions slowly will help reduce orthostatic hypotension. There is
no association between vitamin C-containing products and hypotension. Frequent naps will not affect
the symptoms of hypotension.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge and science and quality
and safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 17-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 235
Question 28
Type: MCMA
During an assessment, the nurse determines a patient is demonstrating symptoms of a psychosis. What
did the nurse assess in this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The patient says, "The servants need to be disciplined."
2. The patient says, "The voice told me to cut myself."
3. The patient laughs when asked about the health of a family member hospitalized for cancer
treatment.
4. The patient asks to close the room door so "that man can't get to me."
5. The patient says, "I have not been able to get any sleep for months."
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: This statement is an example of a grandiose delusion.
Rationale 2: This statement is an example of an auditory hallucination.
Rationale 3: During a psychotic episode, the patient's mood and affect may vary widely and be
inappropriate, such as laughing at sad events.
Rationale 4: This statement is an example of a delusion in which someone is trying to harm the patient.
Rationale 5: The lack of sleep is not a symptom of psychosis.
Global Rationale: Grandiose delusions, auditory hallucinations, and delusions are symptoms of
psychosis. During a psychotic episode, the patient's mood and affect may vary widely and be
inappropriate, such as laughing at sad events. The lack of sleep is not a symptom of psychosis.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-2 Compare and contrast the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 224
Question 29
Type: MCMA
While conducting a health history, the nurse notes that the patient is demonstrating positive signs of
schizophrenia. What did the nurse assess in this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Disorganized sentence structure
2. Kicking the nurse
3. Not responding to questions
4. Difficulty following instructions
5. Stating that God wants the patient to go home
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: Disorganized speech is a positive symptom of schizophrenia.
Rationale 2: Combativeness is a positive symptom of schizophrenia.
Rationale 3: Lack of responsiveness is a negative symptom of schizophrenia.
Rationale 4: Difficulty following instructions is not a positive symptom of schizophrenia.
Rationale 5: A delusion is a positive symptom of schizophrenia.
Global Rationale: Disorganized speech, combativeness, and delusions are positive symptoms of
schizophrenia. Lack of responsiveness is a negative symptom of schizophrenia. Difficulty following
instructions is not a positive symptom of schizophrenia.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychosocial Integrity
Client Need Sub:QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 17-2 Compare and contrast the positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.2.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, and clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 224
Question 30
Type: MCMA
A patient who exhibits both positive and negative signs of schizophrenia has tried a number of
medications without success due to intolerable side effects. How would the nurse categorize the next
logical drug choice for this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. As a dopamine-serotonin system stabilizer
2. As an atypical drug
3. As a conventional drug
4. As a third generation drug
5. As a second generation drug
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Dopamine-serotonin system stabilizers were developed due to side effects of previously
developed drugs.
Rationale 2: The drug of choice will control both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia;
therefore, it is an atypical drug.Rationale 3: Conventional drugs treat only the positive signs of schizophrenia.
Rationale 4: Third generation antipsychotics are used when drugs from a lower generation are
ineffective.
Rationale 5: Second class antipsychotics do not have the properties needed by this patient.
Chapter 18:
Question 1
Type: MCMA
The nurse teaches patients about nonpharmacological techniques for pain management. The nurse
determines learning has occurred when the patients make which statement(s)?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Nonpharmacological techniques are a good adjunct to pharmacotherapy."
2. "Nonpharmacological techniques have not reached mainstream yet."
3. "Nonpharmacological techniques may be used in place of drugs."
4. "Nonpharmacological techniques include an aerobic exercise."
5. "Nonpharmacological techniques are not usually valued by nurses."
Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: Nonpharmacological techniques may be used as an adjunct to pharmacotherapy.
Rationale 2: Nonpharmacological techniques have reached mainstream and are commonly used.
Rationale 3: Nonpharmacological techniques may be used in place of drugs.
Rationale 4: An aerobic exercise is not considered a nonpharmacological technique for relief of pain.
Rationale 5: Nonpharmacological techniques are valued and used by most nurses.
Global Rationale: Nonpharmacological techniques may be used in place of drugs or as an adjunct to
pharmacotherapy. An aerobic exercise is not considered a nonpharmacological technique for relief of
pain. Nonpharmacological techniques have reached mainstream and are commonly used.
Nonpharmacological techniques are valued and used by most nurses.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Basic Care and Comfort
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 18-4 Describe the role of complementary and alternative therapies in pain
management.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 240
Question 2
Type: MCSA
The nursing instructor teaches the nursing students about neural mechanisms of pain. What does the
nursing instructor teach about substance P?
1. Substance P modifies sensory information in the spinal cord.
2. Substance P is also known as an endogenous opioid.
3. Substance P stimulates pain receptors in the spinal cord.
4. Substance P controls which pain signals reach the brain.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Endogenous opioids, not substance P, modify sensory information at the level of the spinal
cord.
Rationale 2: Substance P is not an endogenous opioid.Rationale 3: Substance P does not stimulate pain receptors in the spinal cord.
Rationale 4: Spinal substance P is critical because it controls whether pain signals will continue to the
brain.
Global Rationale: Spinal substance P is critical because it controls whether pain signals will continue to
the brain. Endogenous opioids, not substance P, modify sensory information at the level of the spinal
cord. Substance P does not stimulate pain receptors in the spinal cord. Substance P is not an
endogenous opioid.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-2 Explain the neural mechanisms at the level of the spinal cord responsible for
pain.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.1 Differentiate the types of pain and the effect each can have on a client.
Page Number: 241
Question 3
Type: MCSA
A patient, addicted to heroin, is being treated for opioid dependence. He has been prescribed
methadone (Dolophine). The patient asks how this will help because methadone (Dolophine) is another
opioid. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Methadone (Dolophine) will make you really sick if you use heroin."
2. "Methadone (Dolophine) does not cause euphoria like heroin does."3. "Methadone (Dolophine) cures your addiction to heroin."
4. "Methadone (Dolophine) causes you to have an allergy to heroin."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Methadone (Dolophine) will not cause a person to become sick if they use heroin.
Rationale 2: Methadone (Dolophine) does not cause the euphoria of heroin. It is a substitute drug that
allows the patient to be productive.
Rationale 3: Methadone (Dolophine) does not cure heroin addiction.
Rationale 4: Methadone (Dolophine) does not cause an allergy to heroin.
Global Rationale: Methadone (Dolophine) does not cause the euphoria of heroin or cure the
dependence. It is a substitute drug that allows the patient to be productive. Methadone (Dolophine)
does not cure heroin addiction. Methadone (Dolophine) does not cause an allergy to heroin. Methadone
(Dolophine) will not cause a person to become sick if they use heroin.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Base individualized care plan on patient values, clinical expertise and
evidence.
AACN Essentials Competencies: VII.4 Use behavioral change techniques to promote health and manage
illness.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-7 Describe the long-term treatment of opioid dependence.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 246Question 4
Type: MCMA
A nurse is providing community education on the increase in heroin use. Which information would be
included?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Heroin is an opioid drug.
2. Heroin is a narcotic drug.
3. Heroin causes CNS agitation.
4. Heroin is the same drug as morphine.
5. Heroin is not as dangerous as oxycodone.
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Heroin is classified as an opioid.
Rationale 2: Heroin is an illegal drug. Narcotic is the term often used to describe such drugs.
Rationale 3: Heroin causes CNS depression, not agitation.
Rationale 4: Morphine and heroin are in the same class but are different drugs.
Rationale 5: Heroin is addictive and dangerous—as dangerous, if not more dangerous, as oxycodone.
Global Rationale: Heroin is classified as an opioid. Heroin is an illegal drug. Narcotic is the term often
used to describe such drugs. Heroin causes CNS depression, not agitation. Morphine and heroin are in
the same class but are different drugs. Heroin is addictive and dangerous—as dangerous, if not more
dangerous, as oxycodone.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral TherapiesQSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-10 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of pain based on their classification
and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 243
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The patient receives morphine for pain. He asks the nurse how it works to relieve pain. What is the best
response by the nurse?
1. "It inhibits the primary pain neurotransmitters in your brain."
2. "It stimulates the receptors that secrete endorphins in your brain."
3. "It interacts with receptors in your body that produce analgesia."
4. "It promotes the primary pleasure neurotransmitters in your brain."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Opioids do not inhibit neurotransmitters responsible for pain.
Rationale 2: Opioids do not promote secretion of endorphins.
Rationale 3: Opioids exert their actions by interacting with the mu and kappa receptors in the brain.
Drugs that stimulate these receptors are opioid agonists.
Rationale 4: Opioids do not promote release of the pleasurable neurotransmitters. Opioids do not
promote secretion of endorphins.
Global Rationale: Opioids exert their actions by interacting with the mu and kappa receptors in the
brain. Drugs that stimulate these receptors are opioid agonists. Opioids do not promote release of thepleasurable neurotransmitters. Opioids do not promote secretion of endorphins. Opioids do not inhibit
neurotransmitters responsible for pain.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-5 Compare and contrast the types of opioid receptors and their importance in
effective management of pain.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 240
Question 6
Type: MCSA
The patient has a patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump following surgery. The nurse keeps naloxone
(Narcan) in the patient's room as per protocol. What does the nurse recognize as the rationale for this
protocol?
1. Naloxone (Narcan) enhances the effect of the opioid in the patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump
and increases analgesia.
2. Naloxone (Narcan) is the antidote if an anaphylactic reaction to the opioid in the patient-controlled
analgesia (PCA) pump occurs.
3. Naloxone (Narcan) is available to treat any systemic side effects, like constipation, of the opioid in the
patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump.4. Naloxone (Narcan) will reverse the effects of the narcotic in the patient-controlled analgesia (PCA)
pump if an overdose occurs.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Naloxone (Narcan) does not enhance the effects of opioids.
Rationale 2: Naloxone (Narcan) is not used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
Rationale 3: Naloxone (Narcan) is not used to treat opioid-related constipation.
Rationale 4: Naloxone (Narcan) is an opioid antagonist and will reverse the effects of the narcotic in the
pump if an overdose occurs.
Global Rationale: Naloxone (Narcan) is an opioid antagonist and will reverse the effects of the narcotic
in the pump if an overdose occurs. Naloxone (Narcan) does not enhance the effects of opioids. Naloxone
(Narcan) is not used to treat anaphylactic reactions. Naloxone (Narcan) is not used to treat opioidrelated constipation.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 18-6 Explain the role of opioid antagonists in the diagnosis and treatment of acute
opioid toxicity.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 245Question 7
Type: MCSA
What is a priority assessment question to ask a postsurgical patient prior to administration of an opioid
analgesic?
1. "Have you ever been addicted to prescription pain medications?"
2. "Why do you want to receive this pain medication?"
3. "Would you like me to help you change your position for comfort?"
4. "Would you please rate your pain on a scale of 1 to 10?"
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Administration of pain medication postsurgery is a priority; this is not the time to assess if
the patient has an addiction.
Rationale 2: Asking a postsurgical patient why a pain medication is requested does not make a lot of
sense.
Rationale 3: Offering to help a postsurgical patient change positions is appropriate but should be done
after the patient receives the pain medication.
Rationale 4: The nurse should always assess the patient's level of pain prior to the administration of an
analgesic.
Global Rationale: The nurse should always assess the patient's level of pain prior to the administration
of an analgesic. Asking a postsurgical patient why a pain medication is requested does not make a lot of
sense. Administration of pain medication postsurgery is a priority; this is not the time to assess if the
patient has an addiction. Offering to help a postsurgical patient change positions is appropriate but
should be done after the patient receives the pain medication.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Basic Care and Comfort
QSEN Competencies: I.B.4 Assess presence and extent of pain and suffering.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-1 Relate the importance of pain assessment to effective pharmacotherapy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 247
Question 8
Type: MCSA
The postsurgical patient has an order for morphine 2 mg IV push every 2 hours and propoxyphene 100
(Darvon 100) every 3 hours. He received the morphine 2 hours ago and is complaining of pain again.
What will the best plan of the nurse include?
1. Plan to administer the morphine again.
2. Plan to administer the propoxyphene 100 (Darvon 100).
3. Plan to have the patient do some distraction techniques.
4. Plan to assess the patient's level of pain.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: A different intervention should be done prior to administration of additional morphine.
Rationale 2: A different intervention should be done prior to administration of propoxyphene (Darvon)
100.
Rationale 3: Distraction techniques are appropriate but should not take the place of other interventions.
Rationale 4: The patient's level of pain should be assessed prior to the administration of any analgesic.
Global Rationale: The patient's level of pain should be assessed prior to the administration of any
analgesic. The patient's level of pain should be assessed prior to administration of propoxyphene
(Darvon) 100. The patient's level of pain should be assessed prior to administration of additional
morphine. Distraction techniques are appropriate but should not take the place of a pain assessment
and administration of an analgesic.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Basic Care and Comfort
QSEN Competencies: I.B.4 Assess presence and extent of pain and suffering.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-1 Relate the importance of pain assessment to effective pharmacotherapy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 240
Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient comes to the emergency department with a head injury, broken ribs, and internal bleeding.
Opioid analgesics are contraindicated. What does the nurse recognize as the primary rationale for this?
1. The use of opioid analgesics will depress the patient's blood pressure.
2. The patient may not be able to communicate his level of pain.
3. Opioids will not effectively relieve pain in the patient's periphery.
4. Opioids can mask changes in the patient's level of consciousness.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Depression of blood pressure could occur, but this is not as critical as a different effect.
Rationale 2: The patient may not be able to determine his level of pain, but this is not as critical as a
different effect.Rationale 3: Opioids do not effectively relieve pain in the patient's periphery, but this is not as critical as
a different effect.
Rationale 4: Opioids are central nervous system (CNS) depressants and can mask the patient's level of
consciousness; this is dangerous when the patient has a head injury.
Global Rationale: Opioids are central nervous system (CNS) depressants and can mask the patient's level
of consciousness; this is dangerous when the patient has a head injury. Depression of blood pressure
could occur, but this is not as critical as level of consciousness. The patient may not be able to determine
his level of pain, but this is not as critical as level of consciousness. Opioids do not effectively relieve pain
in the patient's periphery, but this is not as critical as level of consciousness.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 18-11 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
pain and for migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 243
Question 10
Type: MCSAThe patient receives morphine for pain. Which comment by the patient does the nurse assess to be a
side effect of morphine?
1. "My ears are constantly ringing."
2. "My heart feels like it is skipping beats."
3. "I feel like I am going to throw up."
4. "I feel cold shivers all over."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Ringing ears are not associated with morphine.
Rationale 2: Heart palpitations are not associated with morphine.
Rationale 3: Nausea is a common side effect of morphine.
Rationale 4: Feeling cold shivers is not associated with morphine.
Global Rationale: Nausea is a common side effect of morphine. Feeling cold shivers is not associated
with morphine. Ringing ears are not associated with morphine. Heart palpitations are not associated
with morphine.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain the mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 246
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The patient receives aspirin. The nurse assesses an adverse effect to this drug when the patient makes
which response?
1. "My stools have been dark in color."
2. "My nose is stuffed up."
3. "Bright lights give me a headache."
4. "I have to get up a lot at night to urinate."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Aspirin may result in ulceration and bleeding, which would result in darker than normal
stools.
Rationale 2: There isn't any relationship between aspirin and nasal congestion.
Rationale 3: Aspirin does not cause photophobia.
Rationale 4: There isn't any relationship between aspirin and nocturnal renal output.
Global Rationale: Aspirin may result in ulceration and bleeding, which would result in darker than
normal stools. Aspirin does not cause photophobia or nasal congestion. There isn't any relationship
between aspirin and nocturnal renal output.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medicalmanagement and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain the mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 251
Question 12
Type: MCSA
The nurse provides care for several patients. For which patient would the nurse assess acetaminophen
(Tylenol) to be contraindicated?
1. A 2-year-old with a high fever due to the flu
2. A 65-year-old with osteoarthritis
3. A 19-year-old with a bladder infection
4. A 55-year old who drinks alcohol
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) would be the drug of choice for a child with the flu.
Rationale 2: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) would not be contraindicated with osteoarthritis, but aspirin
would be more effective.
Rationale 3: There isn't any association between the use of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and a bladder
infection.
Rationale 4: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is hepatotoxic and may cause problems in patients who consume
alcohol.
Global Rationale: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) is hepatotoxic and may cause problems in patients who
consume alcohol. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) would be the drug of choice for a child with the flu.Acetaminophen (Tylenol) would not be contraindicated with osteoarthritis, but aspirin would be more
effective. There isn't any association between the use of acetaminophen (Tylenol) and a bladder
infection.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 18-10 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of pain based on their classification
and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 251
Question 13
Type: MCSA
What is an important instruction for the nurse to give to the patient who is taking acetaminophen
(Tylenol)?
1. "Check your gums for bleeding when taking acetaminophen (Tylenol)."
2. "Do not take any narcotics with acetaminophen (Tylenol)."
3. "You may experience diarrhea while taking acetaminophen (Tylenol)."
4. "Acetaminophen (Tylenol) can cause drowsiness."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Bleeding in the gums is an effect of aspirin, not acetaminophen (Tylenol).Rationale 2: There is no contraindication between acetaminophen (Tylenol) and narcotics; they are
often combined for more effective pain relief.
Rationale 3: Constipation is a more common effect of acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Rationale 4: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) can cause drowsiness in some patients.
Global Rationale: Acetaminophen (Tylenol) can cause drowsiness in some patients. There is no
contraindication between acetaminophen (Tylenol) and narcotics; they are often combined for more
effective pain relief. Bleeding in the gums is an effect of aspirin, not acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Constipation is a more common effect of acetaminophen (Tylenol).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 18-10 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of pain based on their classification
and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 251
Question 14
Type: MCMA
The patient is to start on sumatriptan (Imitrex) for migraine headaches. What will the best plan of the
nurse include as it relates to this medication?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.1. Plan to teach the patient not to drive until the effects of the medication are known.
2. Plan to teach the patient to avoid pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) with this medication.
3. Plan to teach the patient the importance of taking the medication with protein.
4. Plan to instruct the patient to take the medication with food to avoid ulcers.
5. Plan to teach the patient to increase fluid intake with this medication.
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Drowsiness and dizziness can occur with sumatriptan (Imitrex).
Rationale 2: Pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) is a vasoconstrictor as is sumatriptan (Imitrex). The
combination could dramatically increase the patient's blood pressure.
Rationale 3: There isn't any relationship between sumatriptan (Imitrex) and ulcers.
Rationale 4: Sumatriptan (Imitrex) does not need to be taken with protein.
Rationale 5: There is no need to increase fluid intake with sumatriptan (Imitrex).
Global Rationale: Drowsiness and dizziness can occur with sumatriptan (Imitrex). Pseudoephedrine
(Sudafed) is a vasoconstrictor as is sumatriptan (Imitrex). The combination could dramatically increase
the patient's blood pressure. There isn't any relationship between sumatriptan (Imitrex) and ulcers.
Sumatriptan (Imitrex) does not need to be taken with protein. There is no need to increase fluid intake
with sumatriptan (Imitrex).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.7 Provide appropriate patient teaching that reflects developmental
stage, age, culture, spirituality, patient preferences, and health literacy considerations to foster patient
engagement in their care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: PlanningLearning Outcome: 18-8 Compare the pharmacotherapeutic approaches of preventing migraines with
those of aborting migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 256
Question 15
Type: MCSA
A patient complains of dull, aching pain in the lower back. The nurse plans to provide relief from which
kind of pain?
1. Acute pain
2. Somatic pain
3. Neuropathic pain
4. Visceral pain
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: There is not enough information provided to determine if this pain is acute.
Rationale 2: Somatic pain is sharp and localized.
Rationale 3: The nurse cannot determine if this pain is neuropathic in origin.
Rationale 4: Visceral pain is defined as a dull, throbbing, or aching pain.
Global Rationale: Visceral pain is defined as a dull, throbbing, or aching pain. There is not enough
information provided to determine if this pain is acute. Somatic pain is sharp and localized. The nurse
cannot determine if this pain is neuropathic in origin.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Basic Care and Comfort
QSEN Competencies: I.B.4 Assess presence and extent of pain and suffering.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-1 Relate the importance of pain assessment to effective pharmacotherapy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 240
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Identify the correct statement regarding the neural mechanism of pain.
1. Once the pain impulse reaches the spinal cord, neurotransmitters inhibit the signal.
2. Alpha fibers are wrapped in myelin; C fibers are not.
3. When tissues are damaged, pain impulses go directly to the brain via alpha and beta fibers.
4. Myelin is a substance that slows nerve transmission.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Once the impulse reaches the spinal cord, neurotransmitters pass the message along to the
next neuron.
Rationale 2: The alpha fibers are wrapped in myelin; the C fibers are not.
Rationale 3: A pain impulse travels to the spinal cord via alpha and C fibers.
Rationale 4: Myelin is a lipid substance that speeds nerve transmission.
Global Rationale: A pain impulse travels to the spinal cord via alpha and C fibers. The alpha fibers are
wrapped in myelin (a lipid substance that speeds nerve transmission); the C fibers are not. Once the
impulse reaches the spinal cord, neurotransmitters pass the message along to the next neuron.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 18-2 Explain the neural mechanisms at the level of the spinal cord responsible for
pain.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.1 Differentiate the types of pain and the effect each can have on a client.
Page Number: 241
Question 17
Type: SEQ
The nurse educator is reviewing the process of pain transmission. Students should place these steps in
which sequence?
1. Substance P continues pain message.
2. A and C fibers transmit the pain signal.
3. Nociceptors are stimulated.
4. Pain impulses reach the spinal cord.5. Pain impulses reach the brain.
Standard Text: Click and drag the options below to move them up or down.
Correct Answer: 3,2,4,1,5
Global Rationale: The order of pain transmission is stimulation of the nociceptors, transmission of pain
signal by A and C fibers to the spinal cord, continuation of the pain message by substance P, and pain
impulses reach the brain.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-2 Explain the neural mechanisms at the level of the spinal cord responsible for
pain.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.1 Differentiate the types of pain and the effect each can have on a client.
Page Number: 241
Question 18
Type: MCSAIdentify the correct statement regarding opioid receptors.
1. The sigma and kappa receptors are of greatest concern from a pharmacologic standpoint.
2. Drugs that block opioid receptors inhibit the pain impulse.
3. Opioid agonists will activate mu and kappa receptors, producing analgesia.
4. Opioids exert their actions by interacting with a total of three receptors.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: The mu and kappa receptors are of greatest concern from a pharmacologic standpoint.
Rationale 2: Drugs that block opioid receptors are called opioid antagonists and do not inhibit the pain
impulse.
Rationale 3: Opioid agonists stimulate mu and kappa receptors, resulting in a variety of effects,
including analgesia.
Rationale 4: There are four major types of receptors.
Global Rationale: Opioid agonists stimulate mu and kappa receptors, resulting in a variety of effects,
including analgesia. There are four major types of receptors. The mu and kappa receptors are of greatest
concern from a pharmacologic standpoint. Drugs that block opioid receptors are called opioid
antagonists and do not inhibit the pain impulse.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-5 Compare and contrast the types of opioid receptors and their importance in
effective management of pain.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 242
Question 19
Type: MCSA
A patient brought to the emergency department for oxycodone overdose has a respiratory rate of 8 and
is difficult to arouse. What is the priority nursing intervention?
1. Administering activated charcoal
2. Administering an opioid agonist
3. Administering an opioid antagonist
4. Preparing for intubation and mechanical ventilation
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Administering activated charcoal is not indicated when the patient is nonresponsive.
Rationale 2: Opioid agonists are used to relieve pain. Additional medications would worsen the
situation.
Rationale 3: Opioid antagonists such as naloxone (Narcan) block opioid activity.
Rationale 4: Intubation and mechanical ventilation may be necessary, but another intervention takes
priority.
Global Rationale: Opioid antagonists such as naloxone (Narcan) block opioid activity. Administering
activated charcoal is not indicated when the patient is nonresponsive. Opioid agonists are used to
relieve pain. Additional medications would worsen the situation. Intubation and mechanical ventilation
may be necessary, but another intervention takes priority.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 18-6 Explain the role of opioid antagonists in the diagnosis and treatment of acute
opioid toxicity.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 245
Question 20
Type: MCSA
Which finding is an adverse effect associated with morphine and would be the priority if present?
1. The patient is very restless and cannot lie still.
2. The patient has not had a bowel movement in 3 days.
3. The patient’s respiratory effort is slow and shallow.
4. The patient says, “I can’t live without my morphine patches.”
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Restlessness may occur but is not of highest priority.
Rationale 2: Constipation may occur but is not of highest priority.
Rationale 3: Respiratory depression may result in death and is the highest priority assessment finding.
Rationale 4: Psychological dependence may occur but is not of highest priority.
Global Rationale: Respiratory depression may result in death and is the highest priority assessment
finding. Restlessness, constipation, and psychological dependence may occur but are not of highest
priority.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain the mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 246
Question 21
Type: MCSA
Which patient would be at greatest risk for developing opioid dependence?
1. 24-year-old with sickle-cell anemia
2. 33-year-old with diabetes
3. 17-year-old with a broken arm
4. 75-year-old with congestive heart failure
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Sickle-cell anemia is a chronic and painful disorder and is often treated with opioids.
Rationale 2: Diabetes is a chronic disorder but is not typically managed with opioids.Rationale 3: Broken bones are painful, and opioids may be used. However, broken bones and the
associated pain are acute events.
Rationale 4: Congestive heart failure is a chronic disorder but is not typically managed with opioids.
Global Rationale: Sickle-cell anemia is a chronic and painful disorder and is often treated with opioids.
Diabetes and congestive heart failure are chronic disorders but are not typically managed with opioids.
Broken bones are painful, and opioids may be used. However, broken bones and the associated pain are
acute events.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: I.I Integrate theories and concepts from liberal education into nursing
practice.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-3 Explain how pain can be controlled by inhibiting the release of spinal
neurotransmitters.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 242
Question 22
Type: MCSA
Which statement is accurate concerning the management of migraine headaches?
1. Acute treatment and prevention are achieved via the same medications.
2. There are no pharmacologic agents available to prevent migraine headaches.
3. NSAIDs are used to prevent migraine development.4. Vasoconstriction of cranial arteries helps reduce acute headache pain.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Migraine termination and migraine prevention are treated with different drugs.
Rationale 2: Medications to treat migraines exist.
Rationale 3: NSAIDs are the initial drug administered to terminate a migraine.
Rationale 4: Migraine headaches are thought to occur from an initial vasoconstrictive episode.
Global Rationale: Migraine headaches are thought to occur from an initial vasoconstrictive episode.
Migraine termination and migraine prevention are treated with different drugs. Two different types of
medications are used to treat migraines. Medications to treat migraines exist. NSAIDs are the initial drug
administered to terminate a migraine.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.7 Provide appropriate patient teaching that reflects developmental
stage, age, culture, spirituality, patient preferences, and health literacy considerations to foster patient
engagement in their care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 18-8 Compare the pharmacotherapeutic approaches of preventing migraines with
those of aborting migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 254
Question 23
Type: MCSAFor which patient suffering a migraine headache would sumatriptan (Imitrex) be indicated?
1. 73-year-old with angina pectoris
2. 36-year-old female with preeclampsia
3. 45-year-old diabetic male
4. 27-year-old asthmatic male
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Sumatriptan is contraindicated in patients with angina.
Rationale 2: Sumatriptan is a Pregnancy Category C drug.
Rationale 3: Sumatriptan is contraindicated in patients with diabetes.
Rationale 4: Sumatriptan would be useful for a client with asthma.
Global Rationale: Sumatriptan would be useful for a client with asthma. It is contraindicated in patients
with hypertension, angina, and diabetes. It also is a Pregnancy Category C drug.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 18-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain the mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.Page Number: 256
Question 24
Type: MCSA
Which statement is accurate concerning the use of aspirin (ASA) to treat pain?
1. High doses are necessary (1 gram) to achieve anticoagulant effects.
2. Enteric-coated capsules are available to reduce GI side effects.
3. Increase consumption of herbs such as garlic and ginger to potentiate the anti-inflammatory effects.
4. In low doses (325 mg), it significantly reduces inflammation.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Aspirin can cause bleeding in low doses.
Rationale 2: Enteric-coated capsules can help prevent bleeding.
Rationale 3: Avoiding certain herbs such as ginger and garlic should be advised.
Rationale 4: The anti-inflammatory effects of aspirin occur in high doses.
Global Rationale: Aspirin can cause bleeding in low doses. Enteric-coated capsules can help prevent
bleeding, and avoiding certain herbs such as ginger and garlic should be advised. The anti-inflammatory
effects of aspirin occur in high doses.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain the mechanism of drug action, primary actions, and important adverse
effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.2 Compare the classes of medications used to treat pain.
Page Number: 252
Question 25
Type: MCMA
How should the nurse plan to manage caring for patients in pain?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Treat all patients alike.
2. Listen carefully to the patient's comments about pain.
3. Show respect for the patient's preferences.
4. Ask questions about the patient's beliefs and customs regarding pain management.
5. Watch how other nurses provide care to their patients.
Correct Answer: 2,3,4
Rationale 1: Not all patients respond identically to interventions.
Rationale 2: Careful listening is an important step in providing care.
Rationale 3: Showing respect is important in providing care in all areas, including pain management.
Rationale 4: The nurse cannot practice what the nurse does not know. Asking questions is the method
used to gain information to facilitate sensitive care.
Rationale 5: Other nurses may not be providing the care needed for this nurse's patients.
Global Rationale: Careful listening is an important step in providing care. Showing respect is important
in providing care in all areas, including pain management. The nurse cannot practice what the nursedoes not know. Asking questions is the method used to gain information to facilitate sensitive care.
Other nurses may not be providing the care needed for this nurse's patients. Not all patients respond
identically to interventions.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Basic Care and Comfort
QSEN Competencies: I.B.4 Assess presence and extent of pain and suffering.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.1 Conduct comprehensive and focused physical, behavioral,
psychological, spiritual, socioeconomic, and environmental assessments of health and illness parameters
in patients, using developmentally and culturally appropriate approaches.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-1 Relate the importance of pain assessment to effective pharmacotherapy.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 240
Question 26
Type: MCMA
The patient has advanced cancer and is experiencing pain. How should the nurse plan to manage this
pain?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Monitor for subtle signs of pain.
2. Set up a dosing schedule that provides for around-the-clock doses.
3. Encourage the patient to wait 10 minutes after pain medication is required to ask for a dose.4. Augment the patient's regimen with other pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical pain relief
measures for breakthrough pain.
5. Counsel the patient that it is not possible to eliminate all the pain of cancer and that some must be
tolerated.
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Subtle signs of pain such as hesitancy to move and grimacing may occur and should be
recognized.
Rationale 2: Often the problem in controlling pain of any type is that the patient "gets behind" the pain
rather than medicating for it before it gets severe. Around-the-clock dosing helps to prevent "playing
catch-up" to the pain.
Rationale 3: This plan would allow the pain to worsen before medication is given and would result in the
patient getting "behind" the pain.
Rationale 4: Breakthrough pain is expected and may require additional pharmaceutical or
nonpharmaceutical measures.
Rationale 5: While it is true that some cancer patients develop intractable pain, many are able to control
pain to a level that is very tolerable.
Global Rationale: Subtle signs of pain such as hesitancy to move and grimacing may occur and should be
recognized. Often the problem in controlling pain of any type is that the patient "gets behind" the pain
rather than medicating for it before it gets severe. Around-the-clock dosing helps to prevent "playing
catch-up" to the pain. Breakthrough pain is expected and may require additional pharmaceutical or
nonpharmaceutical measures. While it is true that some cancer patients develop intractable pain, many
are able to control pain to a level that is very tolerable.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 18-11 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
pain and for migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 247
Question 27
Type: MCMA
During report on a newly assigned patient, the nurse learns that buccal fentanyl has been ordered. What
can the nurse learn from this information?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The patient is already on fentanyl.
2. The patient has breakthrough pain.
3. The patient is opioid naïve.
4. The patient has migraine headaches.
5. The patient is a child under 16 years of age.
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Buccal fentanyl is used only for patients who are already receiving fentanyl.
Rationale 2: Buccal fentanyl is used for breakthrough cancer pain.
Rationale 3: The opioid naïve patient would not be started on buccal fentanyl.
Rationale 4: Buccal fentanyl is not used for migraine headaches.
Rationale 5: Buccal fentanyl is only used for adult patients.Global Rationale: Buccal fentanyl is used only for adult patients who are already receiving fentanyl and
who have breakthrough cancer pain. The opioid naïve patient would not be started on buccal fentanyl.
Buccal fentanyl is not used for migraine headaches.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 18-11 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
pain and for migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 245
Question 28
Type: MCMA
What medication teaching would the nurse provide for a patient who is newly prescribed a nasal
medication for migraine headache?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Use the medication at the first sign of migraine.
2. Overusing this medication may result in rebound headaches.
3. Instill the spray into one nostril only.
4. Increase dietary intake of tyramine-containing foods.
5. Pain relief will not begin for up to an hour after administration.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: In order to be most effective, these medications should be used at the first sign of migraine.
Rationale 2: Overuse of these medications may result in rebound headache.
Rationale 3: Proper administration of nasal medications includes instillation into one nostril only.
Rationale 4: The patient should avoid tyramine-containing foods.
Rationale 5: Pain relief should begin within several minutes of use.
Global Rationale: In order to be most effective, these medications should be used at the first sign of
migraine. Overuse of these medications may result in rebound headache. Proper administration of nasal
medications includes instillation into one nostril only. The patient should avoid tyramine-containing
foods. Pain relief should begin within several minutes of use.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 18-11 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
pain and for migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 254
Question 29
Type: MCMA
The patient has been started on morphine sulfate (MS Contin) for chronic back pain resulting from
inoperable disk degeneration. What nursing actions are indicated?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Use the prn order of MiraLax routinely every night.
2. Ask the dietary department to add bran cereal to the patient's breakfast trays.
3. Ask the health care provider to write an order for an indwelling urinary catheter.
4. Review the trending of the patient's daily weights.
5. Check the medical record for a prn order for an antiemetic.
Correct Answer: 1,2,4,5
Rationale 1: One of the adverse effects of morphine therapy is constipation. The nurse should be
proactive by giving the MiraLax every night.
Rationale 2: Intake of additional fiber, as long as sufficient fluid is taken, is useful in preventing the
constipation that is common with the use of morphine.
Rationale 3: While morphine may promote urinary retention, other methods of controlling this adverse
effect should be used initially.
Rationale 4: Morphine should not be administered to those who are hypovolemic due to the risk of
hypotension. Daily weight is a good way to monitor hydration status.Rationale 5: Nausea and vomiting are adverse effects of the use of morphine. Until the patient becomes
tolerant of this effect, an antiemetic may be necessary.
Global Rationale: One of the adverse effects of morphine therapy is constipation. The nurse should be
proactive by giving the MiraLax every night. Intake of additional fiber, as long as sufficient fluid is taken,
is useful in preventing the constipation that is common with the use of morphine. Morphine should not
be administered to those who are hypovolemic due to the risk of hypotension. Nausea and vomiting are
adverse effects of the use of morphine. Until the patient becomes tolerant of this effect, an antiemetic
may be necessary. While morphine may promote urinary retention, other methods of controlling this
adverse effect should be used initially.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.7 Initiate effective treatments to relieve pain and suffering in light of patient
values, preference and expressed needs.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 18-11 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
pain and for migraines.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.7.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 248
Question 30
Type: MCMAThe patient has been keeping a "headache diary" of her migraines. Upon review of this diary, the nurse
notes that the headaches are described as mild and have happened four times in the last 3 months. The
patient reports that she "generally just lies down until they pass" but that her new job will not allow that
time. She is requesting information about pain medication. What medications would the nurse expect to
be prescribed?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Ibuprofen
2. Acetaminophen
3. Sumatriptan (Imitrex)
4. Ergotamine (Ergostat)
5. Amitriptyline (Elavil)
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: NSAIDs are often effective for the mild migraines this patient experiences.
Rationale 2: Acetaminophen is used for treatment of mild migraines.
Rationale 3: Sumatriptan is a serotonin receptor agonist and is usually used only for moderate to severe
migraines.
Rationale 4: Ergotamine is an ergot alkaloid that is a serotonin receptor agonist. This drug is used only
with moderate to severe migraines.
Rationale 5: Amitriptyline is used to prevent migraines, not to reduce pain once they occur.
Chapter 19:
Question 1
Type: MCMA
The nursing instructor teaches the nursing students about the advantages of local anesthetics, such as
lidocaine (Xylocaine). What will the best plan of the nursing instructor include?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Amides have fewer side effects than esters.2. Amides block potassium entry into the cell.
3. Amides are similar in structure to cocaine.
4. Amides tend to last longer than esters.
5. Amides block calcium entry into the cell.
Correct Answer: 1,4
Rationale 1: Amides have largely replaced esters because they produce fewer side effects.
Rationale 2: Amides block sodium, not potassium, entry into the cell.
Rationale 3: Cocaine is a natural ester, not an amide.
Rationale 4: Amides have largely replaced esters because they generally have a longer duration of
action.
Rationale 5: Amides block sodium, not calcium, entry into the cell.
Global Rationale: Amides have largely replaced esters because they produce fewer side effects and
generally have a longer duration of action. Amides block sodium, not potassium, entry into the cell.
Cocaine is a natural ester, not an amide. Amides block sodium, not calcium, entry into the cell.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 19-2 Describe differences between the two major chemical classes of local
anesthetics.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 265Question 2
Type: MCSA
The patient has entered Stage 3 of general anesthesia, known as surgical anesthesia. What will the best
assessment of the nurse reveal?
1. Heart rate and breathing become irregular.
2. General sensation is lost, but the patient remains conscious.
3. The medulla region of the brain is paralyzed.
4. Relaxation, stable respiration, and slow eye movements
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Heart rate and breathing become irregular in Stage 2, not Stage 3.
Rationale 2: Loss of general sensation while still conscious occurs in Stage 1, not Stage 3.
Rationale 3: The medulla region of the brain is paralyzed in Stage 4, not Stage 3.
Rationale 4: In surgical anesthesia, skeletal muscles become relaxed, cardiovascular and breathing
activities stabilize, and eye movements are slow.
Global Rationale: In surgical anesthesia, skeletal muscles become relaxed, cardiovascular and breathing
activities stabilize, and eye movements are slow. Heart rate and breathing become irregular in Stage 2,
not Stage 3. The medulla region of the brain is paralyzed in Stage 4, not Stage 3. Loss of general
sensation while still conscious occurs in Stage 1, not Stage 3.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: AssessmentLearning Outcome: 19-6 Identify the four stages of general anesthesia.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 3
Type: MCMA
The nurse teaches the patient about the correct use of a topical anesthetic for a skin condition. The
nurse determines that learning has occurred when the patient makes which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "This lotion should only be used on small areas of skin."
2. "I must wear gloves when I apply the lotion."
3. "This lotion works well on cuts too."
4. "I must wash my hands before touching my eyes."
5. "It's all right to use a lotion after the expiration date."
Correct Answer: 1,4
Rationale 1: Injury could result if topical anesthetics are applied to large areas of skin.
Rationale 2: The nurse, not the patient, must wear gloves when applying topical anesthetics.
Rationale 3: Topical anesthetics should be applied to intact skin only, not on cuts.
Rationale 4: Topical anesthetics must be kept away from the eyes unless they are ophthalmic
preparations.
Rationale 5: Drugs, including lotions, should not be used past the expiration date.
Global Rationale: Topical anesthetics must be kept away from the eyes unless they are ophthalmic
preparations, and injury could result if topical anesthetics are applied to large areas of skin. Topical
anesthetics should be applied to intact skin only, not on cuts. Drugs, including lotions, should not be
used past the expiration date. The nurse, not the patient, must wear gloves when applying topical
anesthetics.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.7 Provide appropriate patient teaching that reflects developmental
stage, age, culture, spirituality, patient preferences, and health literacy considerations to foster patient
engagement in their care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 19-1 Compare and contrast the five major clinical techniques for administering local
anesthetics.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 269
Question 4
Type: MCSA
What does the nurse recognize as the most dangerous adverse effect of volatile liquid inhalation
anesthesia?
1. Hypertension
2. Ventricular tachycardia
3. Malignant hyperthermia
4. Increased intracranial pressure
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Hypotension is more likely to occur than hypertension.
Rationale 2: Ventricular tachycardia is serious but can be treated.
Rationale 3: Malignant hyperthermia is rare, but it is fatal if not treated immediately.Rationale 4: Increased intracranial pressure is not a common adverse effect but can be treated.
Global Rationale: Malignant hyperthermia is rare, but it is fatal if not treated immediately. Ventricular
tachycardia is serious but can be treated. Increased intracranial pressure is not a common adverse effect
but can be treated. Hypotension is more likely to occur than hypertension.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-4 Identify the actions of general anesthetics on the central nervous system.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 272
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The patient receives succinylcholine (Anectine). What will be a priority assessment by the nurse?
1. Spontaneous bleeding
2. Respiratory paralysis
3. Anaphylactic shock
4. Delirium
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Spontaneous bleeding is not related to this drug.Rationale 2: Succinylcholine (Anectine) is a neuromuscular blocker that paralyzes muscles, including
those of respiration.
Rationale 3: Allergic reactions, like anaphylactic shock, are uncommon with this drug.
Rationale 4: Delirium is not related to this drug.
Global Rationale: Succinylcholine (Anectine) is a neuromuscular blocker that paralyzes muscles,
including those of respiration. Spontaneous bleeding is not related to this drug. Delirium is not related
to this drug. Allergic reactions, like anaphylactic shock, are uncommon with this drug.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 19-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 277
Question 6
Type: MCSA
The student nurse does an operating room rotation and notes that many patients receive
succinylcholine (Anectine). The student nurse asks the nursing instructor how the drug works. What is
the best response by the nursing instructor?1. "It causes the patient to rapidly lose consciousness."
2. "It increases cardiac output by raising the heart rate."
3. "It interferes with impulse transmission, resulting in total anesthesia from the pain of surgery."
4. "It reduces the amount of general anesthetic needed for procedures."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: The patient does not lose consciousness and is wide awake.
Rationale 2: Heart rate is not increased.
Rationale 3: The changes to impulse transmission do not result in pain control or anesthesia.
Rationale 4: Succinylcholine (Anectine) does decrease the amount of general anesthetic needed.
Global Rationale: Succinylcholine (Anectine) does decrease the amount of general anesthetic needed.
The patient does not lose consciousness and is wide awake. Heart rate is not increased. The changes to
impulse transmission do not result in pain control or anesthesia.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 277Question 7
Type: MCSA
The patient has a serious laceration to the arm. The patient receives a local anesthetic mixed with
epinephrine prior to suturing. What does the nurse recognize as the rationale for the epinephrine?
1. Constricted blood vessels will extend the duration of action of the drug.
2. Constricted blood vessels will decrease the amount of pain experienced.
3. Constricted blood vessels will promote relaxation of the patient.
4. Constricted blood vessels will result in decreased bleeding.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Epinephrine is often added to local anesthetics to constrict blood vessels and extend the
duration of action of the drug.
Rationale 2: Vasoconstriction does not decrease pain.
Rationale 3: Vasoconstriction will not promote relaxation in the patient.
Rationale 4: The amount of vasoconstriction will not significantly decrease bleeding.
Global Rationale: Epinephrine is often added to local anesthetics to constrict blood vessels and extend
the duration of action of the drug. The amount of vasoconstriction will not significantly decrease
bleeding. Vasoconstriction does not decrease pain. Vasoconstriction will not promote relaxation in the
patient.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 19-3 Explain why epinephrine and sodium bicarbonate are sometimes included in
local anesthetic cartridges.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 264
Question 8
Type: MCSA
Which patient is most likely to experience an adverse reaction to inhalation anesthesia?
1. A 15-year-old with diabetes mellitus
2. A 6-year-old with no chronic health problems
3. A 79-year-old with arteriosclerosis
4. A 55-year-old with a serious neck injury
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Adolescents are similar to adults in risk factors associated with inhalation anesthesia; they
are not at high risk for an adverse reaction.
Rationale 2: Children are more sensitive to inhalation anesthesia than adults, but this 6 year-old child is
healthy and so should not be at high risk for an adverse reaction.
Rationale 3: Older adults are more sensitive to the effects of inhalation anesthesia, and arteriosclerosis
indicates that other organs may not be healthy.
Rationale 4: Adults are usually considered safe for inhalation anesthesia, and the neck injury is not a
contraindication to anesthesia.
Global Rationale: Older adults are more sensitive to the effects of inhalation anesthesia, and
arteriosclerosis indicates that other organs may not be healthy. Adolescents are similar to adults in risk
factors associated with inhalation anesthesia; they are not at high risk for an adverse reaction. Children
are more sensitive to inhalation anesthesia than adults, but this 6 year-old child is healthy and so should
not be at high risk for an adverse reaction. Adults are usually considered safe for inhalation anesthesia,
and the neck injury is not a contraindication to anesthesia.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-9 Use the nursing process to care for patients who are receiving
pharmacotherapy with anesthetic agents.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 275
Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient is in Stage 2 of general anesthesia. What are the priority nursing interventions at this time?
1. Assist the anesthesiologist in repositioning the patient.
2. Complete the surgical scrub.
3. Keep the environment quiet and calm.
4. Insert the indwelling urinary catheter.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: It is not appropriate to reposition the patient during Stage 2 of anesthesia.
Rationale 2: It is not appropriate to complete the surgical scrub during Stage 2 of anesthesia.Rationale 3: The patient is hyperexcitable in Stage 2 of anesthesia so the environment must be kept
quiet to minimize stimulation.
Rationale 4: It is not appropriate to insert an indwelling urinary catheter during Stage 2 of anesthesia.
Global Rationale: The patient is hyperexcitable in Stage 2 of anesthesia so the environment must be
kept quiet to minimize stimulation. It is not appropriate to reposition the patient during Stage 2 of
anesthesia. It is not appropriate to insert an indwelling urinary catheter during Stage 2 of anesthesia. It
is not appropriate to complete the surgical scrub during Stage 2 of anesthesia.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-6 Identify the four stages of general anesthesia.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 10
Type: MCSA
A pregnant woman has a malignant melanoma on her leg and will need surgery. She is concerned about
anesthesia. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "You will probably have an epidural, and this won't harm your baby."
2. "There are newer general anesthetics available that are safe for your baby."
3. "You will most likely have local anesthesia; this will not affect your baby."
4. "Inhalation anesthetics are safe because they remain in your lungs."Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Epidural anesthesia is not indicated in this situation.
Rationale 2: There are not any general anesthetics that are considered safe, and this patient will most
likely have local anesthesia.
Rationale 3: Local anesthetics are most commonly used to remove lesions. They stay in the treatment
area and do not impact the baby.
Rationale 4: Inhalation anesthesia is not indicated in this situation, and even though it remains primarily
in the lungs, it can affect the baby.
Global Rationale: Local anesthetics are most commonly used to remove lesions. They stay in the
treatment area and do not impact the baby. There are not any general anesthetics that are considered
safe, and this patient will most likely have local anesthesia. Epidural anesthesia is not indicated in this
situation. Inhalation anesthesia is not indicated in this situation, and even though it remains primarily in
the lungs, it can affect the baby.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-7 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary actions, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 267Question 11
Type: MCSA
The patient is scheduled for a surgical procedure. The nurse plans to teach the patient about anesthesia.
Which statement would be included in the best plan of the nurse?
1. "An inhaled agent needs to be followed by an intravenous (IV) agent if it is ineffective."
2. "An inhaled agent is used to induce sleep, followed by an intravenous (IV) agent for relaxation."
3. "An intravenous (IV) agent to induce sleep is usually all that is required."
4. "An intravenous (IV) agent will be used first to induce sleep; then, an inhaled agent will be used."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Inhaled agents are given after intravenous (IV) agents to maintain anesthesia, not if the
intravenous (IV) agent is ineffective.
Rationale 2: An intravenous (IV) agent, not an inhaled agent, is used to induce sleep.
Rationale 3: Patients require more anesthesia than just intravenous (IV) anesthesia.
Rationale 4: Intravenous agents are usually administered first because they act within a few seconds.
After the patient loses consciousness, inhaled agents are used to maintain the anesthesia.
Global Rationale: Intravenous agents are usually administered first because they act within a few
seconds. After the patient loses consciousness, inhaled agents are used to maintain the anesthesia.
Patients require more anesthesia than just intravenous (IV) anesthesia. An intravenous (IV) agent, not an
inhaled agent, is used to induce sleep. Inhaled agents are given after intravenous (IV) agents to maintain
anesthesia, not if the intravenous (IV) agent is ineffective.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: ImplementationLearning Outcome: 19-5 Compare and contrast the two primary ways that general anesthesia may be
induced.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 12
Type: MCSA
The 2-year-old child comes to the emergency department with a laceration to the lower leg. The
physician plans to use a local anesthetic, but the child screams at the sight of the needle. What is the
best action by the nurse?
1. Wrap the child in a blanket to restrain him and ensure safety during suturing.
2. Rub a local anesthetic cream on the skin so the child will not feel the needle.
3. Administer a small dose of a medication such as lorazepam (Ativan).
4. Ask the parents to leave the room so the child will quiet down.
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Restraining the child will terrify him and is not indicated at this time.
Rationale 2: The child will be more cooperative if there isn't any pain from an injection.
Rationale 3: There isn't any indication to administer lorazepam (Ativan).
Rationale 4: The presence of parents usually decreases a child's anxiety and increases cooperation.
Global Rationale: The child will be more cooperative if there isn't any pain from an injection. There isn't
any indication to administer lorazepam (Ativan). Restraining the child will terrify him and is not indicated
at this time. The presence of parents usually decreases a child's anxiety and increases cooperation.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-8 Categorize drugs used before, during, and after anesthesia based on their
classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 267
Question 13
Type: MCSA
The patient has gastroesophageal reflux disease and receives lidocaine viscous prior to an endoscopy.
What will be the nurse’s priority assessment immediately after the procedure?
1. Assess for a return of the gag reflex.
2. Assess for nausea and vomiting.
3. Assess for any damage to the teeth or gums.
4. Assess for a headache.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The gag reflex must be assessed before giving the patient anything to eat or drink.
Rationale 2: Nausea and vomiting are not common after an endoscopy.
Rationale 3: Damage to the teeth or gums is rare following an endoscopy.
Rationale 4: Headaches are not common after an endoscopy.
Global Rationale: The gag reflex must be assessed before giving the patient anything to eat or drink.
Damage to the teeth or gums is rare following an endoscopy. Nausea and vomiting are not common
after an endoscopy. Headaches are not common after an endoscopy.
Cognitive Level: AnalyzingClient Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-9 Use the nursing process to care for patients who are receiving
pharmacotherapy with anesthetic agents.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 269
Question 14
Type: MCSA
Which clinical technique for administering anesthesia is common for pregnant women during labor and
delivery?
1. Nerve block
2. Topical
3. Infiltration
4. Epidural
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Nerve block is not a form of anesthesia commonly used for women during labor and
delivery.
Rationale 2: Topical is not a form of anesthesia commonly used for women during labor and delivery.Rationale 3: Anesthesia via the epidural route is the most common for women during labor and
delivery. Infiltration is not a form of anesthesia commonly used for women during labor and delivery.
Rationale 4: Anesthesia via the epidural route is the most common for women during labor and
delivery.
Global Rationale: Anesthesia via the epidural route is the most common for women during labor and
delivery.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 19-1 Compare and contrast the five major clinical techniques for administering local
anesthetics.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 264
Question 15
Type: MCSA
Local anesthetics work by
1. enhancing the influx of calcium into the cell.
2. occupying potassium receptors.
3. increasing nerve impulse transmission.
4. blocking sodium channels.Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Enhancing calcium into the cell is not the mechanism of action for local anesthetics.
Rationale 2: Occupying potassium receptors is not the mechanism of action for local anesthetics.
Rationale 3: Local anesthetics block sodium channels, resulting in diminished motor and sensory
impulse transmission. Increasing nerve impulse transmission is not the mechanism of action for local
anesthetics.
Rationale 4: Local anesthetics block sodium channels, resulting in diminished motor and sensory
impulse transmission.
Global Rationale: Local anesthetics block sodium channels, resulting in diminished motor and sensory
impulse transmission. Enhancing calcium into the cell, occupying potassium receptors, and increasing
nerve impulse transmission are not the mechanism of action for local anesthetics.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 19-8 Categorize drugs used before, during, and after anesthesia based on their
classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 264
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Which local anesthetic agent would be considered for use first due to its lower rate of adverse effects?1. Tetracaine (Pontocaine)
2. Procaine (Novocain)
3. Lidocaine (Xylocaine)
4. Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine)
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Tetracaine (Pontocaine) is classified as an ester, which has more side effects than an amide.
Rationale 2: Procaine (Novocain) is classified as an ester, which has more side effects than an amide.
Rationale 3: Lidocaine is classified as an amide, and amides produce fewer side effects than do esters.
Rationale 4: Chloroprocaine (Nesacaine) is classified as an ester, which has more side effects than an
amide.
Global Rationale: All except lidocaine are classified as esters. Lidocaine is classified as an amide, and
amides produce fewer side effects than do esters.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 19-2 Describe differences between the two major chemical classes of local
anesthetics.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 265
Question 17Type: MCSA
A patient with severe cardiac disorder requires closure of a deep laceration. The nurse would advocate
for which plan for analgesia?
1. Plain epinephrine
2. Laceration repair without anesthesia
3. Topical application of lidocaine gel
4. Injected lidocaine without epinephrine
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Epinephrine is not an analgesic.
Rationale 2: Laceration repair is painful and should not be done without anesthesia.
Rationale 3: Topical application would not be sufficient analgesia for repair of a deep laceration.
Rationale 4: Epinephrine extends the time anesthesia is present because it causes vasoconstriction
which slows the rate of distribution. It is not necessary for effective anesthesia and is contraindicated in
those with severe cardiovascular disorders.
Global Rationale:. Epinephrine extends the time anesthesia is present because it causes
vasoconstriction which slows the rate of distribution. It is not necessary for effective anesthesia and is
contraindicated in those with severe cardiovascular disorders. Epinephrine is not an analgesic.
Laceration repair is painful and should not be done without anesthesia. Topical application would not be
sufficient analgesia for repair of a deep laceration.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: PlanningLearning Outcome: 19-3 Explain why epinephrine and sodium bicarbonate are sometimes included in
local anesthetic cartridges.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 266
Question 18
Type: MCSA
Which statement correctly identifies a sign of general anesthesia?
1. A sleeping state that can be awakened easily
2. An unconscious state, without analgesia
3. A total loss of body movements
4. A conscious but sleepy state of being
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Easy awakening is not a condition of general anesthesia.
Rationale 2: General anesthesia involves total analgesia.
Rationale 3: General anesthesia involves total analgesia and loss of consciousness, memory, and body
movements.
Rationale 4: General anesthesia involves loss of consciousness.
Global Rationale: General anesthesia involves total analgesia and loss of consciousness, memory, and
body movements.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-4 Identify the actions of general anesthetics on the central nervous system.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 266
Question 19
Type: MCSA
Which statement correctly identifies the initial use for an IV in a patient undergoing a lengthy abdominal
surgery that requires general anesthesia?
1. To administer agents that will produce rapid unconsciousness
2. To administer reversal agents or other medications used to treat the adverse effects associated with
general anesthesia
3. To administer large amounts of colloid solutions following surgical blood loss
4. To administer a volatile liquid that will keep the patient asleep
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: IV lines are started prior to surgical procedures requiring general anesthesia to administer
agents that will cause rapid loss of consciousness.
Rationale 2: The IV may be used to treat adverse effects but this is not an initial use.
Rationale 3: The IV may be used to administer replacement fluids, but this is not an initial use.
Rationale 4: Volatile liquids are inhaled gases.
Global Rationale: IV lines are started prior to surgical procedures requiring general anesthesia to
administer agents that will cause rapid loss of consciousness. The IV also may be used to treat adverse
effects and administer replacement fluids, but these would not be initial uses. Volatile liquids are
inhaled gases.
Cognitive Level: UnderstandingClient Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-5 Compare and contrast the two primary ways that general anesthesia may be
induced.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 20
Type: MCSA
Which description correctly identifies a state of general anesthesia desirable for surgery?
1. The patient is unconscious, with arm and leg movement.
2. The patient is not responsive to pain, and has no spontaneous breathing.
3. The patient is unconscious with slow eye movements.
4. The patient loses sensation, but is awake.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Surgical anesthesia involves loss of voluntary movement.
Rationale 2: Stage 4 includes paralysis of the medulla with loss of respiratory drive.
Rationale 3: Surgical anesthesia occurs at Stage 3, where the patient is not conscious and is relaxed, eye
movement has slowed, and vital signs have stabilized.
Rationale 4: Surgical anesthesia includes loss of consciousness.
Global Rationale: Surgical anesthesia occurs at Stage 3, where the patient is not conscious and is
relaxed, eye movement has slowed, and vital signs have stabilized. It includes loss of voluntarymovement and loss of consciousness. Stage 4 includes paralysis of the medulla with loss of respiratory
drive.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-6 Identify the four stages of general anesthesia.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 21
Type: MCSA
A patient undergoing surgery is receiving general anesthesia as well as a neuromuscular blocking agent.
Which statement best indicates the primary reason for the neuromuscular blocking agent?
1. To potentiate analgesic effects
2. To prevent adverse effects associated with inhaled gases
3. To cause total skeletal muscle relaxation
4. To induce unconsciousness
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: They do allow for lower amounts of anesthetics to be used, which can reduce adverse
effects, but this is not the primary reason.
Rationale 2: Neuromuscular blocking agents do not potentiate analgesia.Rationale 3: The primary purpose of administering neuromuscular blocking agents is to cause total
skeletal muscle relaxation.
Rationale 4: Neuromuscular blocking agents do not induce unconsciousness.
Global Rationale: The primary purpose of administering neuromuscular blocking agents is to cause total
skeletal muscle relaxation. Neuromuscular blocking agents do not potentiate analgesia or induce
unconsciousness. They do allow for lower amounts of anesthetics to be used, which can reduce adverse
effects, but this is not the primary reason.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-8 Categorize drugs used before, during, and after anesthesia based on their
classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 276
Question 22
Type: MCMA
Midazolam (Versed) may be administered as part of surgical anesthesia. This drug is recognized as
having which effects?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Producing effects consistent with those observed in administering other benzodiazepines2. Reducing anxiety and stress associated with surgery
3. Producing central nervous system depression and skeletal muscle relaxation
4. Maintaining stable cardiac and respiratory activity
5. Preventing cardiac dysrhythmias
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Midazolam (Versed) can produce serious cardiovascular side effects, including hypotension,
tachycardia, and cardiovascular collapse. Midazolam (Versed) can produce laryngospasm. These are the
same effects that can be observed when other benzodiazepines are administered.
Rationale 2: Midazolam (Versed) reduces anxiety and stress associated with surgery.
Rationale 3: Midazolam (Versed) produces central nervous system depression and skeletal muscle
relaxation.
Rationale 4: Midazolam (Versed) is not associated with maintaining stable cardiac and respiratory
activity.
Rationale 5: Midazolam (Versed) does not prevent cardiac dysrhythmias.
Global Rationale: Midazolam (Versed) can produce serious cardiovascular side effects, including
hypotension, tachycardia, and cardiovascular collapse. Midazolam (Versed) can produce laryngospasm.
Midazolam (Versed) reduces anxiety and stress associated with surgery and produces central nervous
system depression and skeletal muscle relaxation. It is not associated with maintaining stable cardiac
and respiratory activity and does not prevent cardiac dysrhythmias.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: ImplementationLearning Outcome: 19-8 Categorize drugs used before, during, and after anesthesia based on their
classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 276
Question 23
Type: MCMA
Balanced anesthesia is the use of a combination of medications to produce general anesthesia. Which
drugs may be used in combination?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Benzodiazepines
2. Neuromuscular blockers
3. Inhaled anesthetics
4. Proton-pump inhibitors
5. Intravenous anesthetics
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,5
Rationale 1: Benzodiazepines reduce anxiety, produce central nervous system depression, and relax
skeletal muscle.
Rationale 2: Neuromuscular blockers provide skeletal muscle relaxation, which is an important
component of general anesthesia.
Rationale 3: Inhaled agents are used to maintain an anesthetized state.
Rationale 4: Proton-pump inhibitors are not used in balanced anesthesia.
Rationale 5: Intravenous anesthetics relax muscles, diminish pain, and produce sleep.
Global Rationale: Benzodiazepines reduce anxiety, produce central nervous system depression, and
relax skeletal muscle. Neuromuscular blockers provide skeletal muscle relaxation, which is an important
component of general anesthesia. Inhaled agents are used to maintain an anesthetized state.
Intravenous anesthetics relax muscles, diminish pain, and produce sleep. Proton-pump inhibitors are not
used in balanced anesthesia.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-8 Categorize drugs used before, during, and after anesthesia based on their
classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 24
Type: MCMA
Preoperative adjunct medications are used for which reasons?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. To reduce anxiety and facilitate sedation
2. To facilitate a faster recovery
3. To reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia
4. To reduce the risk of a postoperative ileus
5. To manage pain
Correct Answer: 1,3,5
Rationale 1: Benzodiazepines or short-acting barbiturates are used to reduce anxiety and facilitate
sedation.Rationale 2: Preoperative adjuncts are not associated with a faster recovery.
Rationale 3: Preoperative adjunct medications such as histamine-2 receptor agonists or anticholinergics
are used to reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia.
Rationale 4: Preoperative adjuncts are not associated with a reduced risk of a postoperative ileus.
Rationale 5: Preoperative adjuncts help to reduce pain that will be felt after surgery.
Global Rationale: Benzodiazepines or short-acting barbiturates are used to reduce anxiety and facilitate
sedation. Preoperative adjunct medications such as histamine-2 receptor agonists or anticholinergics are
used to reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia. Preoperative adjuncts help to reduce pain that will be
felt after surgery. Preoperative adjuncts are not associated with a faster recovery. Preoperative adjuncts
are not associated with a reduced risk of a postoperative ileus.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 19-8 Categorize drugs used before, during, and after anesthesia based on their
classification and drug action.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 276
Question 25
Type: Hot SpotThe nurse explaining epidural anesthesia to a patient would indicate which area as the placement for
this type of anesthesia?
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
Answer: 4
Rationale: An epidural is administered “above the dura.”
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.7 Provide appropriate patient teaching that reflects developmental
stage, age, culture, spirituality, patient preferences, and health literacy considerations to foster patient
engagement in their care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: ImplementationLearning Outcome: 19-1 Compare and contrast the five major clinical techniques for administering local
anesthetics.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 263
Question 26
Type: MCMA
A patient who has history of severe arteriosclerosis has sustained a laceration on the forearm that will
be repaired in the emergency department. The nurse would plan to obtain a local anesthetic with which
properties?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. With no epinephrine
2. With sodium bicarbonate
3. Without lidocaine
4. With a volatile liquid
5. With proparacaine (Alcaine)
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Local anesthetics with epinephrine are not typically used for patients with cardiac diseases.
Rationale 2: Sodium bicarbonate is often used to retard bacterial growth.
Rationale 3: There is no reason to avoid lidocaine in this patient.
Rationale 4: Volatile liquids are used for inhalation anesthesia.
Rationale 5: Proparacaine (Alcaine) is used for ocular procedures.Global Rationale: Local anesthetics with epinephrine are not typically used for patients with cardiac
diseases. Sodium bicarbonate is often used to retard bacterial growth. There is no reason to avoid
lidocaine in this patient. Volatile liquids are used for inhalation anesthesia. Proparacaine (Alcaine) is
used for ocular procedures.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 19-3 Explain why epinephrine and sodium bicarbonate are sometimes included in
local anesthetic cartridges.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 265
Question 27
Type: MCMA
A novice nurse says, "We want to keep our patients in Stage 4 anesthesia during their surgery." How
should the supervising nurse interpret this statement?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The novice nurse has made an error in this statement.
2. Stage 4 anesthesia is avoided.
3. This is a good description of the goal of anesthesia.4. The novice nurse should have said Stage 3 anesthesia.
5. A more accurate statement would be that the patient is maintained in anxiolysis anesthesia.
Correct Answer: 1,2,4
Rationale 1: Stage 4 is not the goal for anesthesia.
Rationale 2: In Stage 4, the medulla is paralyzed and breathing and circulation could stop. This stage is
avoided.
Rationale 3: This is not the goal of anesthesia.
Rationale 4: The goal of anesthesia is rapid induction through Stages 1 and 2 with the patient remaining
in Stage 3 until the end of the procedure.
Rationale 5: Anxiolysis is a term used to describe minimal sedation, not general anesthesia.
Global Rationale: Stage 4 is not the goal for anesthesia. In Stage 4, the medulla is paralyzed and
breathing and circulation could stop. This stage is avoided. The goal of anesthesia is rapid induction
through Stages 1 and 2 with the patient remaining in Stage 3 until the end of the procedure. Anxiolysis is
a term used to describe minimal sedation, not general anesthesia.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice and research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 19-6 Identify the four stages of general anesthesia.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 270
Question 28Type: MCMA
A patient has multiple lacerations following a motor vehicle accident. The nurse will be certain that
lidocaine without epinephrine is used for local anesthesia when lacerations of which areas are repaired?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Laceration to the cheek
2. Laceration to the earlobe
3. Laceration to the end of the nose
4. Laceration on the top of the foot
5. Laceration on the fingertip
Correct Answer: 2,3,5
Rationale 1: There is no reason to avoid epinephrine when repairing a laceration to the cheek.
Rationale 2: Epinephrine should not be used in repair of areas with decreased blood flow, such as the
earlobe.
Rationale 3: Epinephrine should not be used in repair of areas with decreased blood flow, such as the
end of the nose.
Rationale 4: There is no reason to avoid epinephrine when repairing a laceration to the top of the foot.
Rationale 5: Epinephrine should not be used in repair of areas with decreased blood flow, such as the
fingertip.
Global Rationale: Epinephrine should not be used in repair of areas with decreased blood flow, such as
the earlobe, end of the nose, or fingertips. There is no reason to avoid epinephrine when repairing a
laceration to the cheek or top of the foot.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral TherapiesQSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-9 Use the nursing process to care for patients who are receiving
pharmacotherapy with anesthetic agents.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 269
Question 29
Type: MCMA
A patient has inadvertently received two doses of propofol (Diprivan) within 2 minutes of one another.
What nursing actions are indicated?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Increase intravenous fluid rate.
2. Monitor the patient closely for development of an allergic skin reaction.
3. Monitor the patient closely for respiratory depression.
4. Have serum calcium levels drawn immediately.
5. Administer a benzodiazepine.
Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: One of the treatment recommendations for overdose is increasing intravenous fluid rate.
Rationale 2: An allergic skin reaction is not likely and is not a priority.Rationale 3: Propofol (Diprivan) causes respiratory depression. Close monitoring is indicated.
Rationale 4: There is no reason to have an immediate calcium level drawn.
Rationale 5: Administering a benzodiazepine would complicate the patient’s care.
Global Rationale: One of the treatment recommendations for overdose is increasing intravenous fluid
rate. Propofol (Diprivan) causes respiratory depression. Close monitoring is indicated. An allergic skin
reaction is not likely and is not a priority. . There is no reason to have an immediate calcium level drawn.
Administering a benzodiazepine would complicate the patient’s care.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 19-9 Use the nursing process to care for patients who are receiving
pharmacotherapy with anesthetic agents.
MNL Learning Outcome:
Page Number: 271
Question 30
Type: MCMAA patient is scheduled for an operative procedure in which isoflurane (Forane) will be used as the
anesthetic agent. The nurse would immediately collaborate with the anesthesiologist if the patient
makes which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “I stopped taking my vitamin C supplement last week because it upset my stomach.”
2. “I have been so depressed about having this surgery. I don’t think my St. John’s wort is helping at all.”
3. “I have not eaten anything since before my CT scan yesterday.”
4. “My brother ran a high fever and had seizures after his surgery.”
5. “My last dose of levodopa was yesterday.”
Correct Answer: 2,4
Rationale 1: There is no contraindication between vitamin C therapy and use of isoflurane (Forane).
Rationale 2: St. John’s wort should be discontinues 2 to 3 weeks prior to administration of isoflurane
(Forane) due to possible risk of hypotension.
Chapter 20:
Question 1
Type: MCMA
Several senior citizens have asked the nurse to do a presentation on degenerative diseases. What does
the nurse plan to teach as the most common degenerative diseases?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
2. Multiple sclerosis
3. Alzheimer's disease
4. Huntington's chorea
5. Parkinson's disease
Correct Answer: 3,5Rationale 1: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is not as common as other diseases.
Rationale 2: Multiple sclerosis is not as common as other diseases.
Rationale 3: Alzheimer's disease is one of the most common diseases of the central nervous system.
Rationale 4: Huntington's chorea is not as common as other diseases.
Rationale 5: Parkinson's disease is one of the most common diseases of the central nervous system.
Global Rationale: Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease are the two most common diseases of the
central nervous system. Multiple sclerosis is not as common as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's
disease. Huntington's chorea is not as common as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is not as common as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.7 Provide appropriate patient teaching that reflects developmental
stage, age, culture, spirituality, patient preferences, and health literacy considerations to foster patient
engagement in their care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-1 Identify the most common degenerative diseases of the central nervous
system.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 282
Question 2
Type: MCSAThe patient is diagnosed with Parkinson's disease. The patient's wife asks the nurse how taking medicine
will help her husband. What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "The medications will help prevent muscle wasting in your husband."
2. "The medications will boost your husband's appetite and energy."
3. "The medications will balance serotonin and acetylcholine in your husband's brain."
4. "The medications will help your husband to eat and walk."
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Medications do not prevent muscle wasting.
Rationale 2: Medications do not boost appetite or energy.
Rationale 3: The medications help restore balance between dopamine, not serotonin, and acetylcholine.
Rationale 4: The goal of pharmacotherapy for Parkinson's disease is to increase the ability of the patient
to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) such as walking, eating, dressing, and bathing.
Global Rationale: The goal of pharmacotherapy for Parkinson's disease is to increase the ability of the
patient to perform activities of daily living (ADLs) such as walking, eating, dressing, and bathing.
Medications do not prevent muscle wasting. Medications do not boost appetite or energy. The
medications help restore balance between dopamine, not serotonin, and acetylcholine.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 20-3 Explain the neurochemical basis for Parkinson’s disease, focusing on the roles
of dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 283
Question 3
Type: MCMA
The nurse plans to teach a class about Alzheimer's disease to a caregiver's support group. What will the
best plan by the nurse include?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Depression and aggressive behavior are common with the disease.
2. Alzheimer's disease accounts for about 50% of all dementias.
3. Glutamergic inhibitors are the most common class of drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease.
4. Chronic inflammation of the brain may be a cause of the disease.
5. Memory difficulties are an early symptom of the disease.
Correct Answer: 1,4,5
Rationale 1: Depression and aggressive behavior are common symptoms of the disease.
Rationale 2: Alzheimer's disease accounts for about 70% of all dementias.
Rationale 3: The acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, not the glutamergic inhibitors, are the most widely
used class of drugs for treating the disease.
Rationale 4: It is suspected that chronic inflammation and excess free radicals may cause neuron
damage and contribute to the disease.
Rationale 5: Memory difficulties are an early symptom of Alzheimer's disease.
Global Rationale: Memory difficulties are an early symptom of Alzheimer's disease. It is suspected that
chronic inflammation and excess free radicals may cause neuron damage and contribute to the disease.
Depression and aggressive behavior are common symptoms of the disease. Alzheimer's disease
accounts for about 70% of all dementias. The acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, not the glutamergic
inhibitors, are the most widely used class of drugs for treating the disease.Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-5 Describe symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and explain theories about why
these symptoms develop.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 287
Question 4
Type: MCSA
The nurse plans care for a patient with Parkinson's disease. What will the best plan by the nurse
include?
1. Monitor the patient for the ability to chew and swallow.
2. Check peripheral circulation for thrombophlebitis.
3. Monitor the patient for psychotic symptoms.
4. Limit exercise to decrease the possibility of fractures.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: In Parkinson's disease, muscle function is lost, and the patient's ability to chew and swallow
to prevent aspiration becomes a safety issue.
Rationale 2: Thrombophlebitis is not related to Parkinson's disease.
Rationale 3: Psychosis is possible; however, this is not the primary concern.Rationale 4: Activity is important to maintain as much muscle tone as possible and should not be
limited.
Global Rationale: In Parkinson's disease, muscle function is lost, and the patient's ability to chew and
swallow to prevent aspiration becomes a safety issue. Psychosis is possible; however, this is not the
primary concern. Activity is important to maintain as much muscle tone as possible and should not be
limited. Thrombophlebitis is not related to Parkinson's disease.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-2 Describe symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 282
Question 5
Type: MCSA
The patient receives levodopa-carbidopa (Sinemet). The nurse has completed medication education and
determines that learning has occurred when the patient makes which statement?
1. "I need to increase my daily intake of protein."
2. "I must increase the fiber in my diet."
3. "I need to check my pulse before taking the medication."
4. "I must avoid carbohydrates in my diet."Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: There isn't any need to increase the daily intake of protein, and a high protein diet may
interfere with absorption.
Rationale 2: Fiber will help prevent constipation, which is a side effect of levodopa-carbidopa (Sinemet).
Rationale 3 There isn't any need to check the pulse prior to the medication.
Rationale 4: There isn't any need to avoid carbohydrates.
Global Rationale: Fiber will help prevent constipation, which is a side effect of levodopa-carbidopa
(Sinemet). There isn't any need to check the pulse prior to the medication. There isn't any need to avoid
carbohydrates. There isn't any need to increase the daily intake of protein.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 20-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of Parkinson’s
disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 284
Question 6
Type: MCSA
The nurse prepares to administer benztropine (Cogentin) to the patient. The nurse holds the dose and
notifies the physician based on which assessment finding?1. A respiratory rate of 14
2. A pulse of 112
3. Blood pressure of 88/60 mmHg
4. A temperature of 100.2°F
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: A respiratory rate of 14 is a normal finding.
Rationale 2: Benztropine (Cogentin) can cause tachycardia.
Rationale 3: Initial hypotension may occur, but this is uncommon.
Rationale 4: An elevated temperature is not related to benztropine (Cogentin).
Global Rationale: Benztropine (Cogentin) can cause tachycardia. Initial hypotension may occur, but this
is uncommon. An elevated temperature is not related to benztropine (Cogentin). A respiratory rate of 14
is a normal finding.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 288Question 7
Type: MCSA
The patient receives aspirin, a multivitamin, and an antihistamine every day. What is the best instruction
by the nurse prior to administering levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo)?
1. "You should not take the aspirin with your levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo)."
2. "You should not take the antihistamine with your levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo)."
3. "You should not take the multivitamin with your levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo)."
4. "These medications are safe to take with levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo)."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: There isn't any contraindication to the use of aspirin and levodopa, carbidopa, and
entacapone (Stalevo).
Rationale 2: There isn't any contraindication to the use of an antihistamine and levodopa, carbidopa.
and entacapone (Stalevo).
Rationale 3: Vitamin B6 will decrease the effects of levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo), so
the patient should not take a multivitamin while receiving levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone
(Stalevo).
Rationale 4: One of these medications will decrease the effects of levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone
(Stalevo).
Global Rationale: Vitamin B6 will decrease the effects of levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo),
so the patient should not take a multivitamin while receiving levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone
(Stalevo). There isn't any contraindication to the use of aspirin and levodopa, carbidopa, and
entacapone (Stalevo). There isn't any contraindication to the use of an antihistamine and levodopa,
carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 20-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 286
Question 8
Type: MCSA
An older adult receives levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo). The nurse is primarily concerned
about which problem with this patient?
1. Hypertension
2. Diarrhea
3. Muscle twitching
4. Dark urine
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Hypotension, not hypertension, is possible with levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone
(Stalevo).
Rationale 2: Constipation, not diarrhea, is a side effect of levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone
(Stalevo).
Rationale 3: Muscle twitching may indicate toxicity.
Rationale 4: Dark urine is a normal finding associated with this medication.Global Rationale: Muscle twitching may indicate toxicity. Constipation, not diarrhea, is a side effect of
levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone (Stalevo). Dark urine is a normal finding associated with this
medication. Hypotension, not hypertension, is possible with levodopa, carbidopa, and entacapone
(Stalevo).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 286
Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient receives levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet). What will the best teaching by the nurse include
as relates to this medication?
1. Avoid drinking caffeinated beverages.
2. Take the medication with meals.3. Take the medication on an empty stomach.
4. Take the medication with a protein food.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: There isn't any significant relationship between caffeine and Levodopa and carbidopa
(Sinemet).
Rationale 2: Levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) should not be taken with meals; this will decrease
absorption.
Rationale 3: Levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) should be taken on an empty stomach for better
absorption.
Rationale 4: Levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) should not be taken with a protein food; this will
decrease absorption.
Global Rationale: Levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) should be taken on an empty stomach for better
absorption. Levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) should not be taken with meals; this will decrease
absorption. Levodopa and carbidopa (Sinemet) should not be taken with a protein food; this will
decrease absorption. There isn't any significant relationship between caffeine and Levodopa and
carbidopa (Sinemet).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 20-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
degenerative diseases of the central nervous system.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 295
Question 10
Type: MCSA
The patient has been diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. What is the best medication education the
nurse gives to the patient's husband?
1. "The medication may help her symptoms for a little while."
2. "The medication has serious side effects if used for a long time."
3. "Her symptoms will improve as long as she takes the medication."
4. "Her symptoms should begin improving in a few days."
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Medications will only slow the progression of the disease.
Rationale 2: The medications are usually not used over a long period of time.
Rationale 3: Improvement with medication usually only lasts a matter of months.
Rationale 4: It takes a minimum of 1 to 4 weeks to begin to see improvement.
Global Rationale: Medications will only slow the progression of the disease. Improvement with
medication usually lasts only a matter of months. It takes a minimum of 1 to 4 weeks to begin to see
improvement. The medications do not have serious side effects and are usually not used over a long
period of time.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 20-5 Describe symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease and explain theories about why
these symptoms develop.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 289
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The nurse is teaching a class for caregivers of patients with Alzheimer's disease. The nurse determines
that learning has occurred when the caregivers make which statement?
1. “Antianxiety drugs are not effective when the patient’s anxiety is due to Alzheimer’s disease."
2. "No new drugs are being developed for Alzheimer’s disease.”
3. "Some health care providers think vitamin E and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications may
help control Alzheimer’s symptoms."
4. "All of the drugs used for Alzheimer’s disease are from the same drug class.."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: There are antianxiety drugs that will treat anxiety associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Rationale 2: New drugs are being used and are in development.
Rationale 3: Vitamin E and NSAIDS may be effective in slowing progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Rationale 4: Drugs to treat Alzheimer’s disease come from different classes.
Global Rationale: Vitamin E and NSAIDS may be effective in slowing progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
There are antianxiety drugs that will treat anxiety associated with Alzheimer’s disease. New drugs are
being used and are in development. Drugs to treat Alzheimer’s disease come from different classes.
Cognitive Level: AnalyzingClient Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 20-6 Explain the goals of pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease and the efficacy
of existing medication.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 288
Question 12
Type: MCSA
The patient has multiple sclerosis and develops depression. What is the best education the nurse can
give the patient's family?
1. "Anytime someone has a brain disease, depression will result."
2. "Depression is very easy to treat with medications we have available."
3. "This is a common problem with chronic debilitating diseases but requires close monitoring."
4. "This is a result of the medications taken for control of symptoms."
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Patients with a neurological illness do not always develop depression.
Rationale 2: Depression is treatable with medications, but this does not help the family to understand
what is happening with the patient.Rationale 3: Depression is common with any chronic, debilitating disease, but may also be associated
with medications. Close monitoring is required.
Rationale 4: The medications are not the cause of the depression.
Global Rationale: Depression is common with any chronic, debilitating disease, but may also be
associated with medications. Close monitoring is required.. The medications are not the cause of the
depression. Patients with a neurological illness do not always develop depression. Depression is
treatable with medications, but this does not help the family to understand what is happening with the
patient.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Psychological Integrity
Client Need Sub:
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
degenerative diseases of the central nervous system.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 295
Question 13
Type: MCSAThe patient receives trihexyphenidyl (Artane) for Parkinson's disease. Which assessment data will the
nurse report to the physician?
1. Dry mouth
2. Anorexia
3. Hypertension
4. Urinary retention
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Dry mouth is a common side effect of trihexyphenidyl (Artane) that does not need
reporting.
Rationale 2: Anorexia is not a side effect of trihexyphenidyl (Artane).
Rationale 3: Hypertension is not a side effect of trihexyphenidyl (Artane).
Rationale 4: Urinary retention is a serious side effect that must be reported to the physician.
Global Rationale: Urinary retention is a serious side effect that must be reported to the physician. Dry
mouth is a common side effect of trihexyphenidyl (Artane) that does not need reporting. Hypertension
is not a side effect of trihexyphenidyl (Artane). Anorexia is not a side effect of trihexyphenidyl (Artane).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of Parkinson’s
disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.Page Number: 287
Question 14
Type: MCSA
The patient receives donepezil (Aricept) as treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Which laboratory test(s)
will the nurse primarily assess?
1. Serum amylase levels
2. Complete blood count
3. Pulmonary function tests
4. Liver function tests
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Donepezil (Aricept) does not affect pancreatic function; so monitoring of serum amylase
levels is not required.
Rationale 2: Donepezil (Aricept) does not affect blood counts; so monitoring of complete blood counts
(CBC) is not required.
Rationale 3: Donepezil (Aricept) does not affect pulmonary function; so monitoring of pulmonary
function tests is not required.
Rationale 4: Donepezil (Aricept) is hepatotoxic and requires monitoring of liver function tests (LFTs) in
any patient who is receiving this drug.
Global Rationale: Donepezil (Aricept) is hepatotoxic and requires monitoring of liver function tests
(LFTs) in any patient who is receiving this drug. Donepezil (Aricept) does not affect pulmonary function;
so monitoring of pulmonary function tests is not required. Donepezil (Aricept) does not affect pancreatic
function; so monitoring of serum amylase levels is not required. Donepezil (Aricept) does not affect
blood counts; so monitoring of complete blood counts (CBC) is not required.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-9 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 289
Question 15
Type: MCSA
Which degenerative disease of the central nervous system is the most common?
1. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
2. Alzheimer’s
3. Multiple sclerosis (MS)
4. Huntington’s chorea
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: ALS is not the most common disease.
Rationale 2: Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases are the most common degenerative diseases of the
central nervous system.
Rationale 3: MS is not the most common disease.
Rationale 4: Huntington’s chorea is not the most common disease.
Global Rationale: Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases are the most common degenerative diseases of
the central nervous system.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.7 Provide appropriate patient teaching that reflects developmental
stage, age, culture, spirituality, patient preferences, and health literacy considerations to foster patient
engagement in their care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-1 Identify the most common degenerative diseases of the central nervous
system.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 282
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Heat sensitivity, spascity, and visual impairment are symptoms most likely associated with which
disorder?
1. Parkinson’s disease
2. Multiple sclerosis (MS)
3. Alzheimer’s disease (AD)
4. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Parkinson’s disease has several symptoms, including muscle stiffness, pill-rolling activity,
and bradykinesia.
Rationale 2: Patients with multiple sclerosis often have fatigue, heat-sensitivity, spasticity, and visual
impairment.Rationale 3: Patients with AD have memory issues.
Rationale 4: Patient with ALS have progressive muscle weakness which eventually involves the
respiratory muscles.
Global Rationale: Patients with multiple sclerosis often have fatigue, heat-sensitivity, spasticity, and
visual impairment. Parkinson’s disease has several symptoms, including muscle stiffness, pill-rolling
activity, and bradykinesia. Patients with AD have memory issues. Patient with ALS have progressive
muscle weakness which eventually involves the respiratory muscles.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-7 Describe the signs and basis for development of multiple sclerosis symptoms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.3 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of multiple sclerosis.
Page Number: 282
Question 17
Type: MCSA
Pharmacotherapy for Parkinson’s disease is intended to
1. increase the amount of dopamine and reduce the amount of acetylcholine.
2. increase the amount of dopamine and acetylcholine.
3. reduce the amount of dopamine and increase the amount of acetylcholine.4. reduce the amount of dopamine and acetylcholine.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Parkinson’s disease results in the death of neurons that produce dopamine. The balance is
restored by increasing the levels of dopamine or by inhibiting the excitatory actions of acetylcholine.
Rationale 2: Parkinson’s disease results in the death of neurons that produce dopamine. Due to the
imbalance, dopamine is provided (levodopa), and anticholinergics can be administered as well.
Acetylcholine is not increased.
Rationale 3: Dopamine is not reduced.
Rationale 4: Dopamine is not reduced.
Global Rationale: Parkinson’s disease results in the death of neurons that produce dopamine. The
balance is restored by increasing the levels of dopamine or by inhibiting the excitatory actions of
acetylcholine.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-3 Explain the neurochemical basis for Parkinson’s disease, focusing on the roles
of dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 284
Question 18Type: MCSA
From a pharmacology standpoint, which statement best explains why levodopa is superior to
dopamine?
1. It crosses the blood–brain barrier.
2. It has fewer adverse effects.
3. It has less risk for addiction.
4. It can be administered orally.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Levodopa can cross the blood–brain barrier, but dopamine cannot. Levodopa
administration leads directly to dopamine synthesis.
Rationale 2: Levodopa does not have fewer side effects.
Rationale 3: There is no risk for addiction from either substance.
Rationale 4: Route of administration is not a factor.
Global Rationale: Levodopa can cross the blood–brain barrier, but dopamine cannot. Levodopa
administration leads directly to dopamine synthesis. Levodopa does not have fewer side effects. There is
no risk for addiction from either substance. Route of administration is not a factor.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-3 Explain the neurochemical basis for Parkinson’s disease, focusing on the roles
of dopamine and acetylcholine in the brain.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 284
Question 19
Type: MCSA
Which statement best explains why structural changes occur within the brains of people with
Alzheimer’s disease?
1. Increased acetylcholine levels
2. Increases in blood pressure and cholesterol levels
3. Chronic inflammation and oxidative cellular damage
4. Cerebral bleeding and associated hypoxia
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: There is no increase of acetylcholine levels.
Rationale 2: Blood pressure and cholesterol levels are not implicated.
Rationale 3: Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles that
most likely occur from chronic inflammation or oxidative cellular damage.
Rationale 4: Cerebral bleeding and associated hypoxia are not implicated.
Global Rationale: Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles
that most likely occur from chronic inflammation or oxidative cellular damage. There is no increase of
acetylcholine levels.
Blood pressure and cholesterol levels are not implicated. Cerebral bleeding and associated hypoxia are
not implicated.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral TherapiesQSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
degenerative diseases of the central nervous system.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 287
Question 20
Type: MCSA
Which drug would most likely be an initial treatment for a patient with Alzheimer’s disease?
1. Levodopa (Larodopa)
2. Haloperidol (Haldol)
3. Benztropine mesylate (Cogentin)
4. Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept)
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Levodopa (Larodopa) is used for Parkinson’s disease.
Rationale 2: Haloperidol (Haldol) can be used in some cases of Alzheimer’s disease, but due to its
adverse effects it is not frequently used.
Rationale 3: Benztropine mesylate (Cogentin) is used for Parkinson’s disease.
Rationale 4: Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept) is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and the most
frequently used drug for Alzheimer’s disease.Global Rationale: Donepezil hydrochloride (Aricept) is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor and the most
frequently used drug for Alzheimer’s disease. Levodopa (Larodopa) and benztropine mesylate (Cogentin)
are used for Parkinson’s disease. Haloperidol (Haldol) can be used in some cases of Alzheimer’s disease,
but due to its adverse effects it is not frequently used.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-6 Explain the goals of pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease and the efficacy
of existing medication.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 289
Question 21
Type: MCSA
Which statement is the most accurate regarding acetylcholinesterase inhibitors when used for
Alzheimer's disease?
1. They reverse the structural damage within the brain.
2. They increase synthesis of acetylcholine.
3. They increase enzymatic breakdown, leading to increased neuronal production.4. They intensify the effect of acetylcholine at the receptor.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Currently no drugs can reverse the structural damages associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Rationale 2: They do not increase acetylcholine synthesis or enzymatic breakdown.
Rationale 3: They do not increase enzymatic breakdown.
Rationale 4: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors intensify the effect of acetylcholine at the receptor.
Global Rationale: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors intensify the effect of acetylcholine at the receptor.
They do not increase acetylcholine synthesis or enzymatic breakdown. Currently no drugs can reverse
the structural damages associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-Explain the goals of pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease and the efficacy of
existing medication.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 287
Question 22
Type: MCMAWhat will the nurse include when teaching a caregivers' support group about Alzheimer's disease?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Glutamergic inhibitors are the most common class of drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease.
2. Depression and aggressive behavior are common with the disease.
3. Memory difficulties are an early symptom of the disease.
4. Chronic inflammation of the brain can be a cause of the disease.
5. Pharmacologic therapies are given to help improve memory in Alzheimer's disease.
Correct Answer: 2,3,4,5
Rationale 1: Glutamergic inhibitors are not the most common class of drugs for treating Alzheimer's
disease.
Rationale 2: Depression and aggressive behavior are common symptoms of the disease.
Rationale 3: Memory difficulties are an early symptom of Alzheimer's disease.
Rationale 4: It is suspected that chronic inflammation and excess free radicals can cause neuron damage
and contribute to the disease.
Rationale 5: The acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are the most widely used class of drugs for treating the
disease. These drugs work by increasing the availability of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is involved in
cognition, memory, and learning.
Global Rationale: Depression and aggressive behavior are common symptoms of the disease. Memory
difficulties are an early symptom of Alzheimer's disease. It is suspected that chronic inflammation and
excess free radicals can cause neuron damage and contribute to the disease. The acetylcholinesterase
inhibitors are the most widely used class of drugs for treating the disease. These drugs work by
increasing the availability of acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is involved in cognition, memory, and learning.
Glutamergic inhibitors are not the most common class of drugs for treating Alzheimer's disease.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-Explain the goals of pharmacotherapy for Alzheimer’s disease and the efficacy of
existing medication.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 287–288
Question 23
Type: MCMA
A patient is diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. What symptoms will the nurse most likely assess in this
patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Muscle weakness
2. Difficulty maintaining balance
3. Atrophy of the hands and legs
4. Slow shuffling gait
5. Progressive chorea
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Muscle weakness is a manifestation of multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 2: Difficulty maintaining balance is a manifestation of multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 3: Atrophy of the hands and legs is not a manifestation of multiple sclerosis.Rationale 4: A slow shuffling gait is not a manifestation of multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 5: Progressive chorea is not a manifestation of multiple sclerosis.
Global Rationale: Muscle weakness and difficulty maintaining balance are manifestations of multiple
sclerosis. Atrophy of the hands and legs is not a manifestation of multiple sclerosis. A slow shuffling gait
is not a manifestation of multiple sclerosis. Progressive chorea is not a manifestation of multiple
sclerosis.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-7 Describe the signs and basis for development of multiple sclerosis symptoms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.3 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of multiple sclerosis.
Page Number: 291
Question 24
Type: MCMA
The nurse observes a patient with Parkinson's disease having difficulty controlling hand movements.
What did the nurse observe in this patient?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Pill rolling2. Tremor
3. Stooped posture
4. Lack of arm swing
5. Difficulty bending the arms
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Pill rolling is a common behavior in progressive Parkinson's disease in which the patient
rubs the thumb and forefinger together in a circular motion resembling the motion of rolling a tablet
between two fingers.
Rationale 2: The hands develop a palsy-like continuous motion or shaking when at rest.
Rationale 3: A stooped posture would not influence the patient's ability to control hand movements.
Rationale 4: A lack of arm swing does not influence the patient's ability to control hand movements.
Rationale 5: Difficulty bending the arms does not influence the patient's ability to control hand
movements.
Global Rationale: Pill rolling is a common behavior in progressive Parkinson's disease in which the
patient rubs the thumb and forefinger together in a circular motion resembling the motion of rolling a
tablet between two fingers. The hands develop a palsy-like continuous motion or shaking when at rest.
A stooped posture, lack of arm swing, and difficulty bending the arms would not influence the patient's
ability to control hand movements.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-2 Describe symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 282
Question 25
Type: MCMA
A patient with Parkinson's disease is experiencing an increase in bradykinesia. What will the patient
demonstrate with this manifestation?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Slow speech
2. Difficulty chewing
3. Shuffling the feet when walking
4. Stooped posture
5. Lack of facial expression
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Slow speech is a manifestation of bradykinesia.
Rationale 2: Difficulty chewing is a manifestation of bradykinesia.
Rationale 3: Shuffling the feet when walking is a manifestation of bradykinesia.
Rationale 4: Stooped posture is not a manifestation of bradykinesia.
Rationale 5: Lack of facial expression is not a manifestation of bradykinesia.
Global Rationale: Slow speech, difficulty chewing, and a shuffling gait are manifestations of
bradykinesia. Stooped posture and lack of facial expression are not manifestations of bradykinesia.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological AdaptationQSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 20-2 Describe symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease.
Page Number: 282
Question 26
Type: MCMA
A patient with progressive multiple sclerosis will be started on alemtuzumab (Lemtrada). The nurse
should ensure which interventions are completed prior to initiating this therapy?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. A varicella zoster vaccination is scheduled.
2. A complete blood count (CBC) has been drawn.
3. A serum creatinine has been drawn.
4. A skin exam has been completed.
5. An indwelling urinary catheter is placed.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3,4
Rationale 1: The patient should have a varicella zoster vaccination at least 6 weeks prior to beginning
this therapy.
Rationale 2: A CBC should be obtained prior to treatment.Rationale 3: A serum creatinine should be obtained prior to treatment.
Rationale 4: A skin examination is necessary prior to treatment to monitor for melanoma.
Rationale 5: There is no reason to place an indwelling urinary catheter.
Global Rationale: The patient should have a varicella zoster vaccination at least 6 weeks prior to
beginning this therapy. A CBC and a serum creatinine should be obtained prior to treatment. A skin
examination is necessary prior to treatment to monitor for melanoma. There is no reason to place an
indwelling urinary catheter.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-8 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s
disease, ad multiple sclerosis based on their classification and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 293
Question 27
Type: MCMAThe nurse providing medications to a patient with multiple sclerosis realizes that the goals of medication
therapy for this patient include
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. modifying the progression of the disease.
2. treating acute exacerbations.
3. managing symptoms.
4. curing the disease.
5. remyelinating nerve fibers.
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: This is a goal of pharmacologic therapy for multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 2: This is a goal of pharmacologic therapy for multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 3: This is a goal of pharmacologic therapy for multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 4: This is not a goal of pharmacologic therapy for multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 5: This is not a goal of pharmacologic therapy for multiple sclerosis.
Global Rationale: Drugs can modify the progression of the disease, treat acute exacerbations, and
manage symptoms. They cannot cure the disease or remyelinate nerve fibers.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 20-8 Categorize drugs used in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s
disease, ad multiple sclerosis based on their classification and mechanism of action.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.2 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and
pharmacotherapy of Alzheimer’s disease.
Page Number: 287
Question 28
Type: MCMA
The nurse notes that a patient who has Parkinson’s disease often has twitching of the eye and increased
tremors when medications are being administered. The nurse discusses which changes in therapy with
the provider?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Increasing the dose of medications
2. Changing the interval between doses of medication
3. Using a liquid form of the medication
4. Scheduling a drug holiday
5. Adding an adjunctive drug
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: These findings may indicate a wearing-off time has occurred. The dose of medication may
need to be increased.
Rationale 2: These findings may indicate a wearing-off time has occurred. The timing of drug
administration may need to be changed.
Rationale 3: There is no indication that a liquid form of the medication is indicated.
Rationale 4: The patient needs to remain on the medication.
Rationale 5: These findings may indicate a wearing-off time has occurred. There may be a need to add
an adjunctive medication.Global Rationale: These findings may indicate a wearing-off time has occurred. The dose of medication
may need to be increased, the timing of drug administration may need to be changed, or an adjunctive
drug may need to be added. There is no indication that a liquid form of the medication is indicated. The
patient needs to remain on the medication.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 20-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
degenerative diseases of the central nervous system.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 295
Question 29
Type: MCMA
A nurse has provided medication education for a patient just diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease. The
nurse would evaluate that this instruction is successful when the patient makes which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “I guess I will have to give up eating my wife’s banana pudding.”
2. “I should add some wheat germ to my breakfast cereal.”
3. “I should add olive oil to the salads I eat at noon each day.”
4. “I have to become a vegetarian.”
5. “I will take my medication on an empty stomach.”
Correct Answer: 1,5
Rationale 1: Bananas are high in vitamin B6 and should be avoided when taking these medications.
Rationale 2: Wheat germ and fortified cereals should be avoided when taking these medications.
Rationale 3: Olive oil is not prohibited, but green vegetables should be limited.
Rationale 4: The patient does not need to follow a vegetarian diet but should reduce meat intake.
Rationale 5: These medications should be taken on an empty stomach.
Global Rationale: Bananas are high in vitamin B6 and should be avoided when taking these medications.
These medications should be taken on an empty stomach. Wheat germ and fortified cereals should be
avoided when taking these medications. Olive oil is not prohibited, but green vegetables should be
limited. The patient does not need to follow a vegetarian diet but should reduce meat intake.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 20-10 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
degenerative diseases of the central nervous system.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.3.4 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 295
Question 30
Type: MCMA
A patient who takes benztropine (Cogentin) has developed constipation. What treatment should the
nurse recommend?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “Try drinking a glass of wine each evening.”
2. “Take docusate (Colace) every evening.”
3. “Increase your fluid intake.”
4. “Taking a walk each day may help.”
5. “Stop taking your medication until your bowel function normalizes.”
Correct Answer: 3,4
Rationale 3: Increasing fluid intake is recommended to treat constipation.
Rationale 4: Exercising is recommended to treat constipation.
Chapter 21:
Question 1
Type: MCMA
The nurse teaches a class about muscle movement to a group of patients who have neuromuscular
disorders. What will the best plan of the nurse include?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Body movement depends on an intact spinal cord.
2. Body movement depends on proper functioning of muscles.
3. Body movement depends on intact nerves.
4. Body movement depends on proper endocrine functioning.
5. Body movement depends on the level of consciousness.
Correct Answer: 2,3
Rationale 1: Body movement does not depend on an intact spinal cord as portions of the body move
even if the spinal cord is damaged.
Rationale 2: Body movement depends on proper functioning of muscles.
Rationale 3: Body movement depends on intact nerves.
Rationale 4: Body movement does not depend on proper endocrine functioning.
Rationale 5: Body movement does not depend on the level of consciousness.
Global Rationale: Body movement depends on proper functioning of muscles. Body movement does not
depend on the level of consciousness. Body movement does not depend on an intact spinal cord as
portions of the body move even if the spinal cord is damaged. Body movement does not depend on
proper endocrine functioning.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-1 Identify the different body systems contributing to muscle movement.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 300
Question 2
Type: MCMA
The nurse teaches the patient with a neuromuscular disorder about nonpharmacological treatment of
muscle spasms. What will the best information include?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Application of heat or cold
2. Ultrasound
3. Massage
4. Relaxation techniques
5. Guided imagery
Correct Answer: 1,2,3
Rationale 1: Nonpharmacological treatment of muscle spasms includes application of heat or cold.
Rationale 2: Nonpharmacological treatment of muscle spasms includes ultrasound.
Rationale 3: Nonpharmacological treatment of muscle spasms includes massage.
Rationale 4: Relaxation techniques are not a type of nonpharmacological treatment for muscle spasms.
Rationale 5: Guided imagery is not a nonpharmacological treatment for muscle spasms.
Global Rationale: Nonpharmacological treatment of muscle spasms includes application of heat or cold,
ultrasound, and massage. Guided imagery is not a nonpharmacological treatment for muscle spasms.
Relaxation techniques are not a type of nonpharmacological treatment for muscle spasms.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral TherapiesQSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.17 Develop a beginning understanding of complementary and
alternative modalities and their role in health care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-2 Discuss pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies used to treat muscle
spasms and spasticity.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 300
Question 3
Type: MCSA
The patient is started on a medication to treat a neuromuscular disorder. What does the nurse teach as
the primary therapeutic goal of the medication?
1. To stop the patient's muscle spasms
2. To improve the patient's appearance
3. To promote exercise in the patient
4. To allow the patient increased independence
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Stopping muscle spasms can be achieved, but this is not the primary goal.
Rationale 2: Improving the patient's appearance is not a goal.
Rationale 3: Promoting exercise is not a goal.
Rationale 4: The therapeutic goals of pharmacotherapy include minimizing pain and discomfort,
increasing range of motion, and improving the patient's ability to function independently.
Global Rationale: The therapeutic goals of pharmacotherapy include minimizing pain and discomfort,
increasing range of motion, and improving the patient's ability to function independently. Stoppingmuscle spasms can be achieved, but this is not the primary goal. Promoting exercise is not a goal.
Improving the patient's appearance is not a goal.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-3 Explain the goals of pharmacotherapy with skeletal muscle relaxants.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 300
Question 4
Type: MCSA
The patient receives dantrolene (Dantrium) for muscle spasticity. Which lab result is a priority for the
nurse to assess?
1. Creatinine clearance
2. Serum amylase
3. Hemoglobin and hematocrit
4. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not significantly affect renal function; the creatinine clearance
test isn't a priority laboratory test to assess.Rationale 2: Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect pancreatic function; the serum amylase isn't a
priority laboratory test to assess.
Rationale 3: Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect hemoglobin or hematocrit; these laboratory tests
are not a priority to assess.
Rationale 4: Dantrolene (Dantrium) can cause hepatitis; the aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and
alanine aminotransferase (ALT) are the priority laboratory tests for the nurse to assess.
Global Rationale: Dantrolene (Dantrium) can cause hepatitis; the aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and
alanine aminotransferase (ALT) are the priority laboratory tests for the nurse to assess. Dantrolene
(Dantrium) does not affect hemoglobin or hematocrit; these laboratory tests are not a priority to assess.
Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not significantly affect renal function; the creatinine clearance test isn't a
priority laboratory test to assess. Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect pancreatic function; the serum
amylase isn't a priority laboratory test to assess.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 305
Question 5
Type: MCSAThe patient takes a skeletal muscle relaxer for back pain. A consulting physician orders hydroxyzine
(Vistaril) for the patient and he begins taking it. What will the best assessment by the nurse reveal?
1. Confusion
2. Hypertension
3. Respiratory depression
4. Delirium
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Confusion would not result from the use of these two medications.
Rationale 2: Hypertension would not result from the use of these two medications.
Rationale 3: Skeletal muscle relaxers and hydroxyzine (Vistaril) are both central nervous system (CNS)
depressants, and the patient needs to be assessed for respiratory depression.
Rationale 4: Delirium would not result from the use of these two medications.
Global Rationale: Skeletal muscle relaxers and hydroxyzine (Vistaril) are both central nervous system
(CNS) depressants, and the patient needs to be assessed for respiratory depression. Hypertension would
not result from the use of these two medications. Confusion would not result from the use of these two
medications. Delirium would not result from the use of these two medications.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: AssessmentLearning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 308
Question 6
Type: MCSA
The physician has ordered dantrolene (Dantrium) for a patient. What is a priority assessment by the
nurse prior to administering this medication?
1. Does the patient have gastric ulcer disease?
2. Does the patient have psoriasis?
3. Does the patient have gallbladder disease?
4. Is the patient pregnant or lactating?
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Gastric ulcer disease is not a contraindication to receiving dantrolene (Dantrium).
Rationale 2: Psoriasis is not a contraindication to receiving dantrolene (Dantrium).
Rationale 3: Gallbladder disease is not a contraindication to receiving dantrolene (Dantrium).
Rationale 4: Dantrolene (Dantrium) is a Pregnancy Category C drug, so pregnancy should be assessed
prior to administration.
Global Rationale: Dantrolene (Dantrium) is a Pregnancy Category C drug, so pregnancy should be
assessed prior to administration. Gastric ulcer disease is not a contraindication to receiving dantrolene
(Dantrium). Gallbladder disease is not a contraindication to receiving dantrolene (Dantrium). Psoriasis is
not a contraindication to receiving dantrolene (Dantrium).
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 305
Question 7
Type: MCSA
The physician prescribes cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) for the patient. When doing medication education,
what will the best information of the nurse include?
1. Increase the intake of fiber while taking this medication.
2. Restrict the intake of sodium while taking this medication.
3. Increase the intake of protein while taking this medication.
4. Do not drink any caffeine while taking this medication.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) has anticholinergic properties and can cause constipation, so the
patient should increase the intake of fiber while taking this medication.
Rationale 2: There is no need to limit sodium.
Rationale 3: There is no need to increase protein.
Rationale 4: There is no need to limit caffeine.
Global Rationale: Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) has anticholinergic properties and can cause constipation,
so the patient should increase the intake of fiber while taking this medication. There is no need to limit
sodium. There is no need to limit caffeine. There is no need to increase protein.Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-7 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
muscle spasms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 308
Question 8
Type: MCSA
The patient is treated for muscle spasms following a spinal cord injury. What is the best outcome for this
patient?
1. Patient will have stabilized vital signs.
2. Patient will have an improved self-concept.
3. Patient will sleep without pain.
4. Patient will have increased bladder tone.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Stabilization of vital signs is not an expected effect of this medication.Rationale 2: Relief of muscle spasms may help with self-concept, but this is not a direct effect of the
drug.
Rationale 3: Decreasing muscle spasms will help prevent pain that can interfere with sleep.
Rationale 4: This medication relaxes muscles, but it will not increase bladder tone.
Global Rationale: Decreasing muscle spasms will help prevent pain that can interfere with sleep. This
medication relaxes muscles, but it will not increase bladder tone. Stabilization of vital signs is not an
expected effect of this medication. Relief of muscle spasms may help with self-concept, but this is not a
direct effect of the drug.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of muscle spasms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 303
Question 9
Type: MCSA
The patient tells the nurse that she awakens frequently during the night because of leg and foot cramps.
What is the best response by the nurse?
1. "Ask your physician for a muscle relaxant."
2. "Increase your intake of vitamin B6."3. "Take a warm bath before going to bed."
4. "Apply heat to relieve the cramping."
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: It is premature to ask the physician for a muscle relaxant.
Rationale 2: Oral therapy with vitamin B6 may reduce the intensity and duration of leg muscle cramping.
Rationale 3: Taking a warm bath will relax the muscles but will not prevent cramping.
Rationale 4: Applying heat will relax the muscles but will not prevent cramping.
Global Rationale: Oral therapy with vitamin B6 may reduce the intensity and duration of leg muscle
cramping. It is premature to ask the physician for a muscle relaxant. Applying heat will relax the muscles
but will not prevent cramping. Taking a warm bath will relax the muscles but will not prevent cramping.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.15 Communicate care provided and needed at each transition in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.8 Implement evidence-based nursing interventions as appropriate for
managing the acute and chronic care of patients and promoting health across the lifespan.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Relationships between knowledge/science and quality and
safe nursing care.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-4 Describe the nurse’s role in the pharmacologic management of muscle spasms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 303
Question 10
Type: MCSAThe patient receives dantrolene (Dantrium). Which medication would the nurse evaluate as being
contraindicated with dantrolene (Dantrium)?
1. Verapamil (Calan)
2. Insulin
3. Clarithromycin (Biaxin)
4. Methylphenidate (Concerta)
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Verapamil (Calan) is a calcium channel blocker; combining this with dantrolene (Dantrium)
could lead to cardiovascular collapse.
Rationale 2: There isn't any contraindication to the use of dantrolene (Dantrium) and insulin.
Rationale 3: There isn't any contraindication to the use of dantrolene (Dantrium) and clarithromycin
(Biaxin).
Rationale 4: There isn't any contraindication to the use of dantrolene (Dantrium) and methylphenidate
(Concerta).
Global Rationale: Verapamil (Calan) is a calcium channel blocker; combining this with dantrolene
(Dantrium) could lead to cardiovascular collapse. There isn't any contraindication to the use of
dantrolene (Dantrium) and insulin. There isn't any contraindication to the use of dantrolene (Dantrium)
and methylphenidate (Concerta). There isn't any contraindication to the use of dantrolene (Dantrium)
and clarithromycin (Biaxin).
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 305
Question 11
Type: MCSA
The patient receives dantrolene (Dantrium) intravenously (IV). What will a priority assessment by the
nurse include?
1. Assessing the patient's urinary output
2. Assessing the patient's blood glucose
3. Assessing the patient's breath sounds
4. Assessing the patient's intravenous (IV) site
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect the patient's urinary output.
Rationale 2: Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect the patient's blood glucose.
Rationale 3: Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect the patient's breath sounds.
Rationale 4: Dantrolene (Dantrium) intravenous (IV) solution has a high pH and is very irritating to
tissue. The nurse should assess for infiltration of the intravenous (IV) site.
Global Rationale: Dantrolene (Dantrium) intravenous (IV) solution has a high pH and is very irritating to
tissue. The nurse should assess for infiltration of the intravenous (IV) site. Dantrolene (Dantrium) does
not affect the patient's blood glucose. Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect the patient's breath
sounds. Dantrolene (Dantrium) does not affect the patient's urinary output.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral TherapiesQSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-7 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
muscle spasms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 305
Question 12
Type: MCSA
Which list of treatment options would be considered optimal for treating a muscle spasm with an
unknown cause?
1. Anti-inflammatory agents, casting, and ultrasound
2. Analgesics, antibiotics, and heat application
3. Analgesics, muscle relaxants, and massage
4. Anti-inflammatory agents, immobilization, and fluid and electrolyte replacement
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Casting is not indicated for muscle spasms.
Rationale 2: Antibiotics are not indicated for muscle spasms.
Rationale 3: Muscle spasms can be treated with a variety of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic
methods. When the cause is unknown, a more general approach is indicated, such as analgesics, muscle
relaxants, and massage.Rationale 4: Fluid and electrolyte replacement can be indicated, if determined to be the cause;
immobilization is not indicated.
Global Rationale: Muscle spasms can be treated with a variety of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic
methods. When the cause is unknown, a more general approach is indicated, such as analgesics, muscle
relaxants, and massage. Antibiotics and casting are not indicated for muscle spasms. Fluid and
electrolyte replacement can be indicated, if determined to be the cause; immobilization is not indicated.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.17 Develop a beginning understanding of complementary and
alternative modalities and their role in health care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-2 Discuss pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies used to treat muscle
spasms and spasticity.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 300
Question 13
Type: MCSA
Which statement about skeletal muscle relaxants is correct?
1. They inhibit upper motor neuron activity within the central nervous system.
2. They work primarily by stimulating the peripheral nervous system.
3. They increase the amount of neurotransmitter within the muscles.4. They stimulate motor activity within the brainstem.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: The exact mechanism by which skeletal muscle relaxants work is not fully understood. It is
believed that they inhibit upper motor neuron activity, causing CNS depression.
Rationale 2: Stimulation of the peripheral nervous system is not the mechanism of action of muscle
relaxants.
Rationale 3: Muscle relaxants do not increase the amount of neurotransmitter.
Rationale 4: Muscle relaxants do not stimulate motor activity in the brainstem.
Global Rationale: The exact mechanism by which skeletal muscle relaxants work is not fully understood.
It is believed that they inhibit upper motor neuron activity, causing CNS depression. Stimulation of the
peripheral nervous system is not the mechanism of action of muscle relaxants. Muscle relaxants do not
increase the amount of neurotransmitter. Muscle relaxants do not stimulate motor activity in the
brainstem.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 21-3 Explain the goals of pharmacotherapy with skeletal muscle relaxants.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 300
Question 14
Type: MCSAThe nurse identifies a patient with a repeating pattern of muscle contraction of the leg for 5 seconds
followed by 2 seconds of relaxation as experiencing
1. a clonic spasm.
2. a tonic spasm.
3. spasticity.
4. dystonia.
Correct Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Clonic muscle spasms involve multiple, rapidly repeated contractions.
Rationale 2: Tonic spasms involve a single prolonged contraction.
Rationale 3: Spasticity involves a continuous state of contraction.
Rationale 4: Dystonia is a chronic neurological disorder that can cause spasticity.
Global Rationale: Clonic muscle spasms involve multiple, rapidly repeated contractions. Tonic spasms
involve a single prolonged contraction. Spasticity involves a continuous state of contraction, and
dystonia is a chronic neurological disorder that can cause spasticity.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-7 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
muscle spasms.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 300
Question 15
Type: MCSA
Which change is a common adverse effect of cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril)?
1. Alopecia
2. Tongue swelling
3. Drowsiness
4. Hypotension
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Alopecia is not an associated adverse effect.
Rationale 2: Tongue swelling is serious, but rare.
Rationale 3: All centrally acting agents have the potential to cause sedation.
Rationale 4: Tachycardia is possible but would likely lead to hypertension, not hypotension.
Global Rationale: All centrally acting agents have the potential to cause sedation. Tongue swelling is
serious, but rare. Tachycardia is possible but would likely lead to hypertension, not hypotension.
Alopecia is not an associated adverse effect.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 302
Question 16
Type: MCSA
Which statement describes the primary difference between centrally acting muscle relaxants and directacting antispasmodics?
1. Centrally acting agents inhibit neurons of the central nervous system, while direct-acting agents
stimulate neurons of the central nervous system.
2. Centrally acting agents stimulate neurons of the central nervous system, while direct-acting agents
stimulate neurons of the peripheral nervous system.
3. Centrally acting agents inhibit neurons of the central nervous system, while direct-acting agents work
at the level of the neuromuscular junction and skeletal muscles.
4. Centrally acting agents stimulate the central nervous system, while direct-acting agents inhibit
neuronal conduction of the central nervous system.
Correct Answer: 3
Rationale 1: Direct-acting agents do not work at the level of the neuromuscular junction and skeletal
muscles.
Rationale 2: Centrally acting agents inhibit neurons of the central nervous system.
Rationale 3: Centrally acting agents inhibit neurons of the central nervous system, while direct-acting
agents work at the level of the neuromuscular junction and skeletal muscles.
Rationale 4: Centrally acting agents inhibit neurons of the central nervous system.
Global Rationale: Centrally acting agents inhibit neurons of the central nervous system, while directacting agents work at the level of the neuromuscular junction and skeletal muscles.Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-5 Compare and contrast the roles of the following drug categories in treating
muscle spasms and spasticity: centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants, direct-acting antispasmodics,
and skeletal muscle relaxants for short medical procedures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 303
Question 17
Type: MCSA
Which patient suffering from muscle spasms should not receive the direct-acting antispasmodic
medication dantrolene sodium (Dantrium)?
1. 20-year-old suffering from a spinal cord injury
2. 57-year-old suffering from congestive heart failure
3. 40-year-old suffering from multiple sclerosis
4. 65-year-old suffering from a cerebral vascular accident
Correct Answer: 2
Rationale 1: Dantrolene sodium (Dantrium) is indicated for spinal cord injury.
Rationale 2: Dantrolene sodium (Dantrium) is contraindicated in patients with cardiac, pulmonary, and
hepatic problems.Rationale 3: Dantrolene sodium (Dantrium) is indicated for multiple sclerosis.
Rationale 4: Dantrolene sodium (Dantrium) is indicated for strokes.
Global Rationale: Dantrolene sodium (Dantrium) is contraindicated in patients with cardiac, pulmonary,
and hepatic problems. It is indicated for spinal cord injury, strokes, and multiple sclerosis.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 305
Question 18
Type: MCSA
Spasticity is most commonly caused by damage to what area of the body?
1. Cerebral cortex
2. Peripheral nerves
3. Brainstem
4. Spinal cordCorrect Answer: 1
Rationale 1: Spasticity usually results from damage to the motor area of the cerebral cortex.
Rationale 2: Spasticity is not likely to occur with damage to peripheral nerves.
Rationale 3: Spasticity usually results from damage to the motor area of the cerebral cortex. Spasticity is
not likely to occur with damage to the brainstem.
Rationale 4: Spasticity is not likely to occur with damage to the spinal cord.
Global Rationale: Spasticity usually results from damage to the motor area of the cerebral cortex.
Spasticity is not likely to occur with damage to peripheral nerves, the brainstem, or the spinal cord.
Cognitive Level: Remembering
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Physiological Adaptation
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-1 Identify the different body systems contributing to muscle movement.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.1 Examine etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations.
Page Number: 302
Question 19
Type: MCSA
Which statement is correct in regard to the muscle relaxant botulinum toxin type B (Myobloc)?
1. It can be classified as a cholinergic agonist.2. Increased muscle strength is often seen within a couple of weeks.
3. It can take 6 months for the effects to be seen.
4. In high doses, it is poisonous, causing the same symptoms food poisoning does.
Correct Answer: 4
Rationale 1: The drug works by blocking the release of acetylcholine from cholinergic nerve terminals.
Rationale 2: It generally takes 6 weeks to see the effects.
Rationale 3: Effects typically only last for 3–6 months.
Rationale 4: Botulinum toxin type B (Myobloc) is toxic in high doses. Clostridium botulinum is the
bacterium responsible for food poisoning.
Global Rationale: Botulinum toxin type B (Myobloc) is toxic in high doses. Clostridium botulinum is the
bacterium responsible for food poisoning. The drug works by blocking the release of acetylcholine from
cholinergic nerve terminals. It generally takes 6 weeks to see the effects, and they only last for 3–6
months. Patients taking this drug generally experience muscle weakness, not strength.
Cognitive Level: Understanding
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 21-5 Compare and contrast the roles of the following drug categories in treating
muscle spasms and spasticity: centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants, direct-acting antispasmodics,
and skeletal muscle relaxants for short medical procedures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 303Question 20
Type: MCMA
A patient tells the nurse, "I have been reading about using capsaicin as a treatment for muscle pain. Do
you know anything about that?" How should the nurse respond to this question?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Why don't you ask the doctor about whether it works or not?"
2. "I think you take a tablespoon twice a day."
3. "You should use a hot pad on the site prior to applying the capsaicin."
4. "Some patients report that capsaicin stings."
5. "Be certain to wash your hands after applying the capsaicin."
Correct Answer: 4,5
Rationale 1: The nurse should be prepared to discuss pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical methods
of symptom management, including complementary and alternative therapies. There is no reason to
defer to the health care provider.
Rationale 2: Capsaicin is used as a topical application when it is used for muscle pain.
Rationale 3: The patient should apply a cool compress to the application site prior to using capsaicin.
Rationale 4: Reddening of the skin and local stinging are the most common side effects.
Rationale 5: Capsaicin will cause burning of eyes or mucous membranes so the patient should carefully
wash hands after applying this ointment.
Global Rationale: Reddening of the skin and local stinging are the most common side effects. Capsaicin
will cause burning of eyes or mucous membranes so the patient should carefully wash hands after
applying this ointment. The nurse should be prepared to discuss pharmaceutical and nonpharmaceutical
methods of symptom management, including complementary and alternative therapies. There is no
reason to defer to the health care provider. Capsaicin is used as a topical application when it is used for
muscle pain. Reddening of the skin and local stinging are the most common side effects.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological IntegrityClient Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.17 Develop a beginning understanding of complementary and
alternative modalities and their role in health care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-2 Discuss pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies used to treat muscle
spasms and spasticity.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 303
Question 21
Type: MCMA
A nurse is providing discharge instruction for a patient who had onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) injected to
smooth the wrinkles across his forehead. The nurse would advise this patient to monitor for which
changes?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Chest pain
2. Urinary retention
3. Heart palpitations
4. Difficulty swallowing
5. Eye spasm
Correct Answer: 1,3,4
Rationale 1: Angina is an adverse effect of this medication.Rationale 2: Loss of bladder control is the adverse effect associated with onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox).
Rationale 3: Dysrhythmias may occur.
Rationale 4: Difficulty swallowing may occur.
Rationale 5: OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is used to treat eye spasm.
Global Rationale: Angina is an adverse effect of this medication. Dysrhythmias may occur, as may
difficulty swallowing. Loss of bladder control is the adverse effect associated with onabotulinumtoxinA
(Botox). OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is used to treat eye spasm.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-5 Compare and contrast the roles of the following drug categories in treating
muscle spasms and spasticity: centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants, direct-acting antispasmodics,
and skeletal muscle relaxants for short medical procedures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 305
Question 22
Type: MCMA
The parents of a 2-year-old who has cerebral palsy are only now beginning to accept that their child will
have a permanent disability. The nurse has been instructing the parents about the treatment for thespasticity their child is experiencing. Which statements by the parents indicate that the nurse should
plan additional teaching sessions?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "At some point, our child may require surgery to correct this spasticity."
2. "As long as we continue our child's medications, the spasticity can be controlled."
3. "Our physical therapy sessions should focus on flexing our child's muscles."
4. "We should repeat the exercises several times with each muscle group."
5. "It is best to give our child a rest from physical therapy by skipping 1 week a month."
Correct Answer: 2,3,5
Rationale 1: Surgery is sometimes necessary in these cases, so this statement reflects accurate
knowledge.
Rationale 2: Medication alone is generally not enough to control spasticity in these children. The
parents need additional teaching.
Rationale 3: The physical therapy sessions for spasticity focus on muscle stretching, not flexion. The
parents need additional teaching.
Rationale 4: Repetitive motion exercises are beneficial in reducing and controlling spasticity. The
parents have expressed accurate knowledge.
Rationale 5: Physical therapy should be routine and consistent in order to reduce or control spasticity.
These parents need additional teaching.
Global Rationale: Medication alone is generally not enough to control spasticity in these children. The
parents need additional teaching. The physical therapy sessions for spasticity focus on muscle
stretching, not flexion. The parents need additional teaching. Physical therapy should be routine and
consistent in order to reduce or control spasticity. These parents need additional teaching. Surgery is
sometimes necessary in these cases, so this statement reflects accurate knowledge. Repetitive motion
exercises are beneficial in reducing and controlling spasticity. The parents have expressed accurate
knowledge.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological IntegrityClient Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.17 Develop a beginning understanding of complementary and
alternative modalities and their role in health care.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 21-2 Discuss pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic therapies used to treat muscle
spasms and spasticity.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 303
Question 23
Type: MCSA
The patient's health care provider prescribed cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) for the treatment of neck
spasms. The patient reports that the medication is "not working," even though it has been a week since
the medication was started. What changes in this patient's plan of care would the nurse anticipate?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Increase in the dosage frequency
2. Discontinuation of the medication
3. Waiting a few more days for full medication effect
4. Change to a different medication
Correct Answer: 2,4
Rationale 1: Increasing the dosage frequency is not indicated.
Rationale 2: It is not yet time to discontinue the medication.
Rationale 3: Full effects of this medication may take two weeks.Rationale 4: It is not yet time to change medications.
Global Rationale: Full effects of this medication may take two weeks. Increasing the dosage frequency
is not indicated. It is not yet time to discontinue the medication or to change the medication.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 302
Question 24
Type: MCMA
The patient tells the nurse, "The doctor is going to start me on Botox for the muscle spasms in my neck.
I've always wanted to try that. It will make my face look younger." What information should the nurse
provide to this patient regarding onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox)?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. "Once you start on the medication, it may take a week or so before you notice a change in your skin."
2. "Be certain you take the medication with a full glass of water because it can be hard on your kidneys."3. "There are many different uses for that drug, depending on how it is administered."
4. "You may need additional treatments with the medication in a few months."
5. "You should be aware that side effects of the medication can occur hours or weeks after your
treatment."
Correct Answer: 3,4,5
Rationale 1: OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) in this patient's case will not change the skin.
Rationale 2: OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) is administered by injection into the muscle.
Rationale 3: OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) has many clinical indications. Action depends on the area
where the medication is administered.
Rationale 4: Repeated doses of onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) are often required.
Rationale 5: Side effects of onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) may not occur immediately upon
administration, and the patient should watch for their development for several hours to weeks later.
Global Rationale: OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) has many clinical indications. Repeated doses of
onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) are often required. Side effects of onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) may not
occur immediately upon administration, and the patient should watch for their development for several
hours to weeks later. Action depends on the area where the medication is administered.
OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox) in this patient's case will not change the skin. OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox)
is administered by injection into the muscle.
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.
AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: ImplementationLearning Outcome: 21-5 Compare and contrast the roles of the following drug categories in treating
muscle spasms and spasticity: centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants, direct-acting antispasmodics,
and skeletal muscle relaxants for short medical procedures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 303
Question 25
Type: MCMA
The nurse is discharging a 72-year-old man who was hospitalized after a muscle strain injury to his back.
One of the discharge prescriptions for this patient is cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) 10 mg three times per
day with food. The prescription is written for 90 tablets and there are three refills available. Which
information from this situation would alert the nurse for the need to collaborate with the patient's
health care provider?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The dosage amount is too low for the type of injury this patient sustained.
2. Cyclobenzaprine should be used with great caution in those over 65.
3. If taken as directed, the patient would be able to take the medication for 120 days.
4. Cyclobenzaprine is not effective for back pain.
5. Cyclobenzaprine should not be taken with food.
Correct Answer: 2,3,5
Rationale 1: The dosage of 10 mg three times daily is standard.
Rationale 2: The adverse reactions from cyclobenzaprine include confusion, hallucinations, and cardiac
events, which are more common in patients over 65.
Rationale 3: The manufacturer recommends that treatment not extend beyond 3 weeks or 21 days.
Rationale 4: Cyclobenzaprine is not effective for muscle spasm due to spinal cord injury but is useful in
the treatment of back pain from muscle strain.
Rationale 5: The drug may be taken with food or milk if gastric upset occurs.Global Rationale: The adverse reactions from cyclobenzaprine include confusion, hallucinations, and
cardiac events, which are more common in patients over 65. The manufacturer recommends that
treatment not extend beyond 3 weeks or 21 days. The drug may be taken with food or milk if gastric
upset occurs. The dosage of 10 mg three times daily is standard. Cyclobenzaprine is not effective for
muscle spasm due to spinal cord injury but is useful in the treatment of back pain from muscle strain.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 302
Question 26
Type: MCMA
A nurse is talking with a patient who has just been prescribed cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril). The nurse
would provide additional information if the patient made which statements?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. “My wife and I are driving our motor home to the beach tomorrow.”2. “I am going home to mow my lawn.”
3. “I take a nap every afternoon.”
4. “I just checked out a new book from the library.”
5. “I am taking my grandchildren to the zoo tomorrow.”
Correct Answer: 1,2,5
Rationale 1: The patient should avoid driving until the effects of the medication are known.
Rationale 2: The patient should not operate machinery until the effects of the medication are known.
Rationale 3: The medication will probably cause the patient to be drowsy.
Rationale 4: Reading is a quiet activity that does not require the use of dangerous equipment.
Rationale 5: It is not wise for the patient to be responsible for children until the effects of the
medication are known.
Global Rationale: The patient should not drive or operate machinery until the effects of the medication
are known. It is not wise for the patient to be responsible for children until the effects of the medication
are known. The medication will probably cause the patient to be drowsy.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: V.A.4 Delineate general categories of errors and hazards in care.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Evaluation
Learning Outcome: 21-6 For each of the drug classes listed in Drugs at a Glance, know representative
drug examples, and explain their mechanisms of action, primary action, and important adverse effects.MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 307
Question 27
Type: SEQ
The nurse suspects that a patient is developing malignant hyperthermia. Arrange these interventions in
the correct order of priority.
1. Start dantrolene therapy
2. Identify any signs and symptoms that support this suspicion.
3. Control associated symptoms
4. Discontinue medication that may cause malignant hyperthermia.
5. Maintain intravenous dantrolene
Standard Text: Click and drag the options below to move them up or down.
Correct Answer: 2,4,1,3,5
Global Rationale: Treatment of malignant hyperthermia requires rapid identification of signs and
symptoms, discontinuation of the triggering agent, institution of dantrolene therapy, control of
associated symptoms, and maintaining intravenous dantrolene.
Cognitive Level: AnalyzingClient Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Implementation
Learning Outcome: 21-7 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
muscle spasms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 307
Question 28
Type: MCMA
The nurse would plan to most closely observe which patients for the development of liver toxicity after
dantrolene (Dantrium) is initiated?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. A 49-year-old woman who has a history of esophagitis.
2. A 60-year-old man with pneumonia.
3. A 38-year-old woman who has type 2 diabetes.
4. An 18-year-old who injured his leg playing soccer.
5. A 26-year-old woman who has an ostomy.Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: A 49-year-old woman is in the high risk group.
Rationale 2: Risk is present for all patients, but there is nothing about this scenario that indicates risk is
particularly high.
Rationale 3: A 38-year-old woman is in the high risk group.
Rationale 4: Risk is present for all patients, but there is nothing about this scenario that indicates risk is
particularly high.
Rationale 5: Risk is present for all patients, but there is nothing about this scenario that indicates risk is
particularly high.
Global Rationale: Women over age 35 are at high risk for development of hepatotoxicity. While risk is
present for all patients, there is nothing in the other scenarios that indicates risk is particularly high.
Cognitive Level: Analyzing
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: I.B.3 Provide patient-centered care with sensitivity and respect for the diversity of
human experience.
AACN Essentials Competencies: IX.3 Implement holistic, patient-centered care that reflects an
understanding of human growth and development, pathophysiology, pharmacology, medical
management and nursing management across the health-illness continuum, across lifespan, and in all
healthcare settings.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Planning
Learning Outcome: 21-7 Use the nursing process to care for patients receiving pharmacotherapy for
muscle spasms.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.3 Apply the nursing process to pharmacotherapy, safe drug administration,
and client education.
Page Number: 308Question 29
Type: MCMA
A patient experienced malignant hyperthermia after receiving anesthesia and is being maintained on
dantrolene (Revonto). The nurse would increase assessment for which findings?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. Swelling at the IV site
2. Muscle weakness
3. Sore throat
4. Irritability
5. Anorexia
Correct Answer: 1,2
Rationale 1: Injection site reactions such as pain, redness, and swelling are adverse reactions.
Rationale 2: Muscle weakness is an adverse reaction.
Rationale 3: Sore throat is not associated with administration of dantrolene (Revonto).
Rationale 4: Irritability is not associated with administration of dantrolene (Revonto).
Rationale 5: Anorexia is not associated with administration of dantrolene (Revonto).
Global Rationale: Injection site reactions such as pain, redness, and swelling are adverse reactions.
Muscle weakness is an adverse reaction. Sore throat, irritability, and anorexia are not associated with
administration of dantrolene (Revonto).
Cognitive Level: Applying
Client Need: Physiological Integrity
Client Need Sub: Pharmacological and Parenteral Therapies
QSEN Competencies: III.A.1 Demonstrate knowledge of basic scientific methods and processes.AACN Essentials Competencies: III.1 Explain the interrelationships among theory, practice, and
research.
NLN Competencies: Knowledge and Science: Integration of knowledge from nursing and other
disciplines.
Nursing/Integrated Concepts: Nursing Process: Assessment
Learning Outcome: 21-5 Compare and contrast the roles of the following drug categories in treating
muscle spasms and spasticity: centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxants, direct-acting antispasmodics,
and skeletal muscle relaxants for short medical procedures.
MNL Learning Outcome: 3.6.2 Compare the classes of medications used in pharmacologic management.
Page Number: 308
Question 30
Type: MCMA
A patient calls the clinic and asks for a refill for a prescription for cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) that was
written a year ago. Which information from the medical record would the nurse draw to the prescriber’s
attention?
Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
1. The patient reported drinking wine each day with dinner.
2. The patient has been using nasal saline spray for allergies.
3. The patient was prescribed a MAO inhibitor last month.
4. The patient’s blood glucose was elevated at the last visit.
5. The patient had a ulnar fracture repaired a year ago.
Correct Answer: 1,3
Rationale 1: Alcohol should not be consumed while taking cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril).
Rationale 3: Concurrent use of cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) and MAOIs is contraindicated.
[Show More]