*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR511 Midterm Exam Study Guide[GRADED A+ ] (All)
NR511 Midterm Exam Study Guide[GRADED A+ ]
Document Content and Description Below
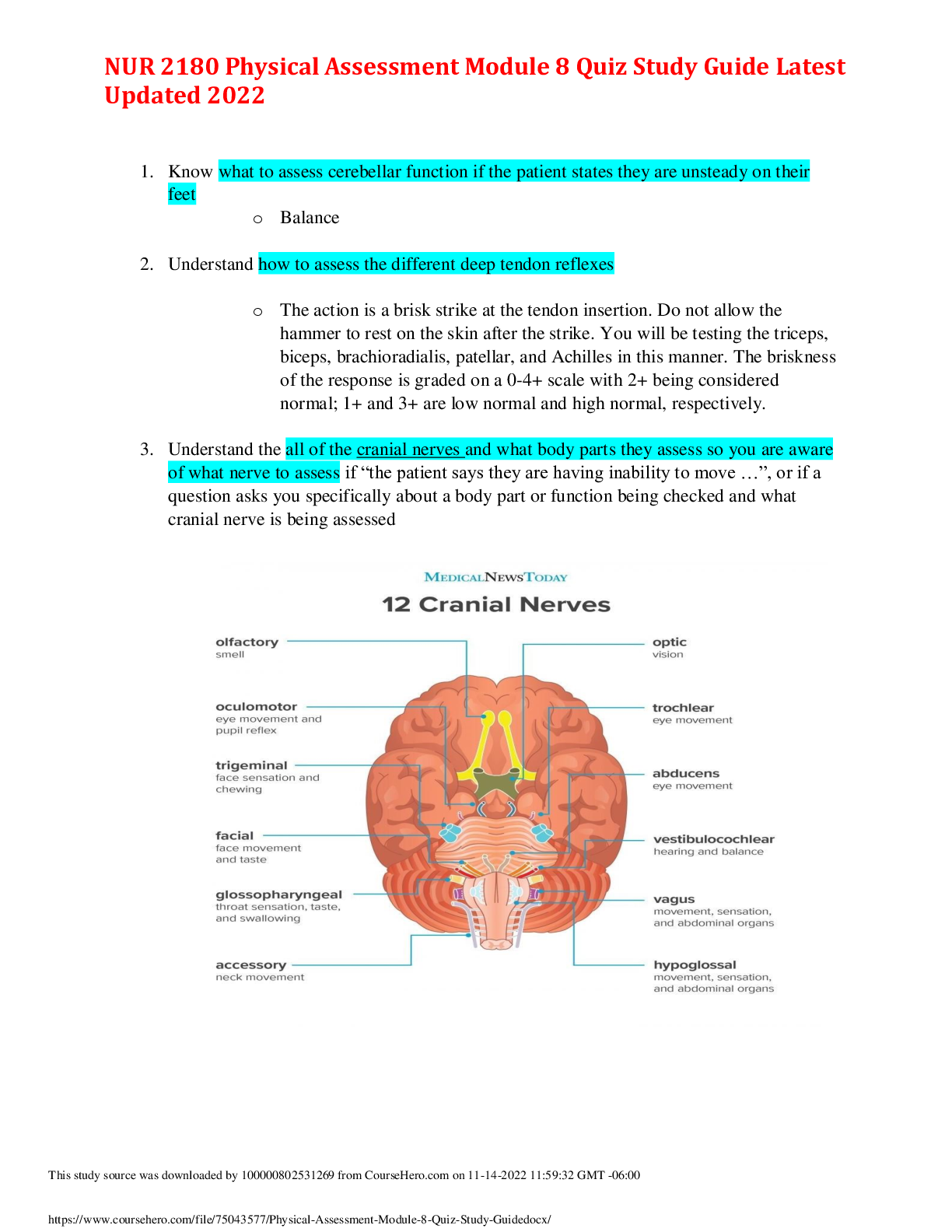
NR511 Midterm Exam Study Guide Week 1 1. Define diagnostic reasoning: type of critical thinking Critical thinking involves the process of questioning one’s thinking to determine if all poss... ible avenues have been explored and if the conclusions that are being drawn are based on evidence Diagnostic reasoning then includes a systematic way of thinking that evaluates each new piece of data as it either supports some diagnostic hypothesis or reduces the likelihood of others. 2. Discuss and identify subjective & objective data Subjective: what the patient reports; complaints of; tells you Example: fevers, chills, lethargy, headache, blurred vision, ST, etc. Is the “S” part of the SOAP note which includes the CC, HPI, & ROS Objective: what you can see, hear, or feel as part of your clinical exam; also includes laboratory data and tests results Example: thin, obese, normocephalic, rapid stress test +, etc. Is the “O” part of the SOAP note 3. Discuss and identify the components of the HPI Should be focused on the complaint and relevant symptoms Detailed breakdown of the CC, written out as the OLDCARTS acronym Onset, Location, Duration, Characteristics, Aggravating Factors, Relieving Factors, Treatments, Severity. Duration: not referring to the onset of the symptom. Rather, it is an assessment of whether the symptom is constant or if it comes and goes. Severity: level of pain, impact on work/school or ADLs. 4. Describe the differences between medical billing and medical coding Medical coding is the use of codes to communicate with payers about which procedures were performed and why Medical billing, on the other hand, is the process of submitting and following up on claims made to a payer in order to receive payment for medical services rendered by a healthcare provider. 5. Compare and contrast the 2 coding classification systems that are currently used in the US healthcare system Common Procedural Terminology (CPT) system: offers the official procedural coding rules and guidelines required when reporting medical services and procedures performed by physician and nonphysician providers Recognized universally and also provide a logical means to be able to track healthcare data, trends, and outcomes. Each service or procedure is represented by a five-digit code that is presented in six sections, including 1. Evaluation & Management 2 2. Anesthesiology 3. Surgery 4. Radiology 5. Pathology 6. Medicine International Classification of Diseases (ICD) system: we are in the tenth revision of the system, and, therefore, the classification system is known as ICD-10 ICD-10 codes are shorthand for the patient’s diagnoses, which are used to provide the payer information on the necessity of the visit or procedure performed. This means that every CPT code must have a diagnosis code that corresponds. 6. Discuss how specificity, sensitivity & predictive value contribute to the usefulness of the diagnostic data When we describe the specificity of a test, we are referring to the ability of the test to correctly detect a specific condition. If the patient has the condition but testing is negative, we describe this as a false negative. If the patient does not have the condition but the test result is positive, this is considered to be a false positive test. When a test is very sensitive, we mean it has few false negatives. The higher the sensitivity, the lesser the likelihood of a false negative. A sensitivity of 99% means that it is very unlikely for a false negative result. Predictive value is the likelihood that the patient actually has the condition and is, in part, dependent upon the prevalence of the condition in the population. If a condition is highly likely, a positive test result is more likely to be accurate. If a condition is very unlikely, a positive test needs to be questioned and perhaps additional testing would need to be done. 5 things to consider before ordering a test: cost, convenience, sensitivity, specificity, risk of missing a condition (predictive value) 7. Discuss the elements that need to be considered when developing a plan Evidence based care: providing care and making treatment and screening choices based on current research findings. Generally, EBP refers to using research findings from multiple studies that are convincing enough that a consensus is formed recommending the findings be used for clinical decision-making or practice guidelines. EBP also involves inclusion of patient and provider preferences, patient values, and cultural considerations in the clinical decision-making process. Guidelines should be followed in the majority of cases unless there is a clear rationale for deviating from them to serve the particular needs of the patient. Elements include clinical state and circumstances, patient’s preferences and actions, research evidence, and clinical expertise 8. Discuss a minimum of three purposes of the written history and physical in relation to the importance of documentation It is an important reference document that gives concise information about a patient's history and exam findings. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 44 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 22, 2021
Number of pages
44
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
78







.png)