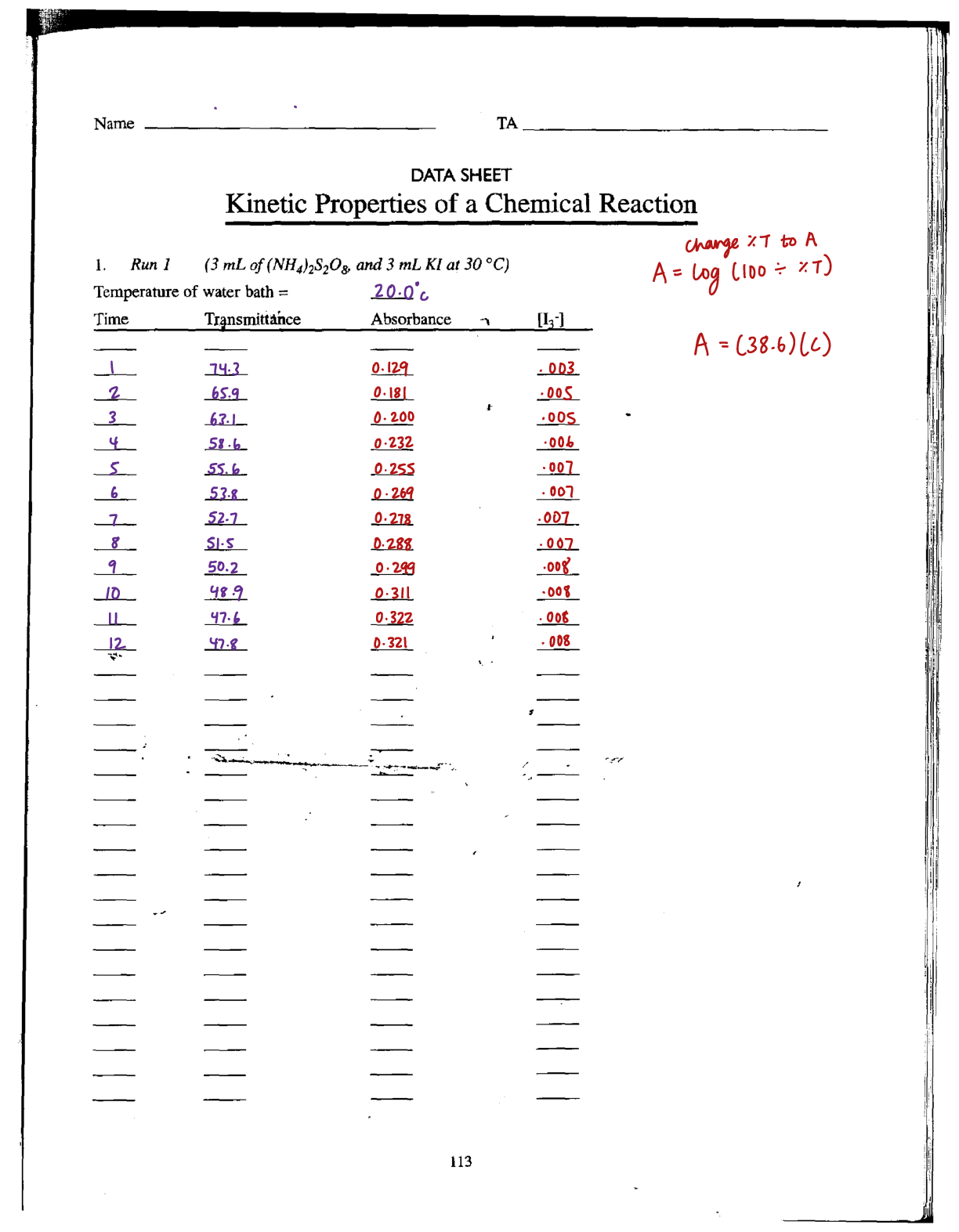
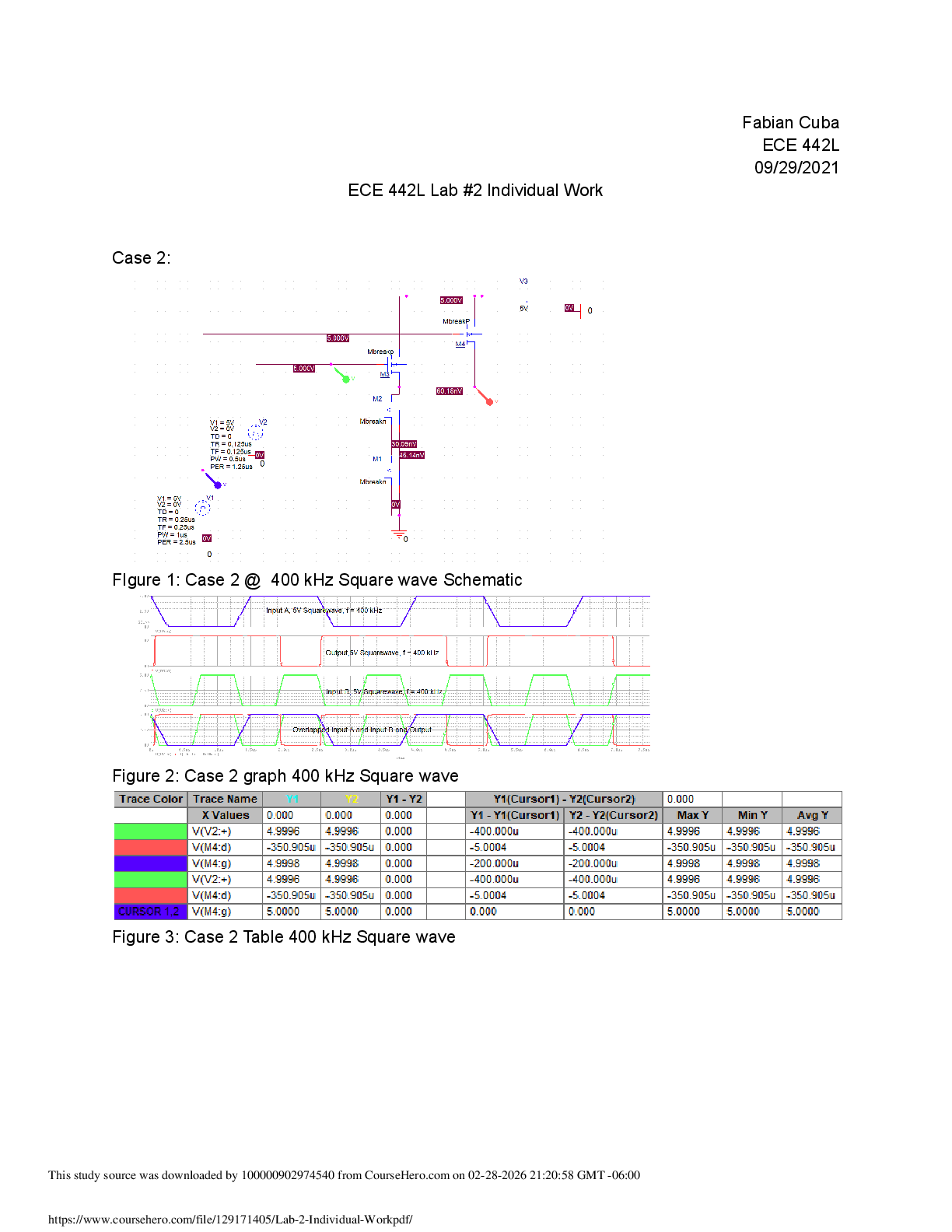
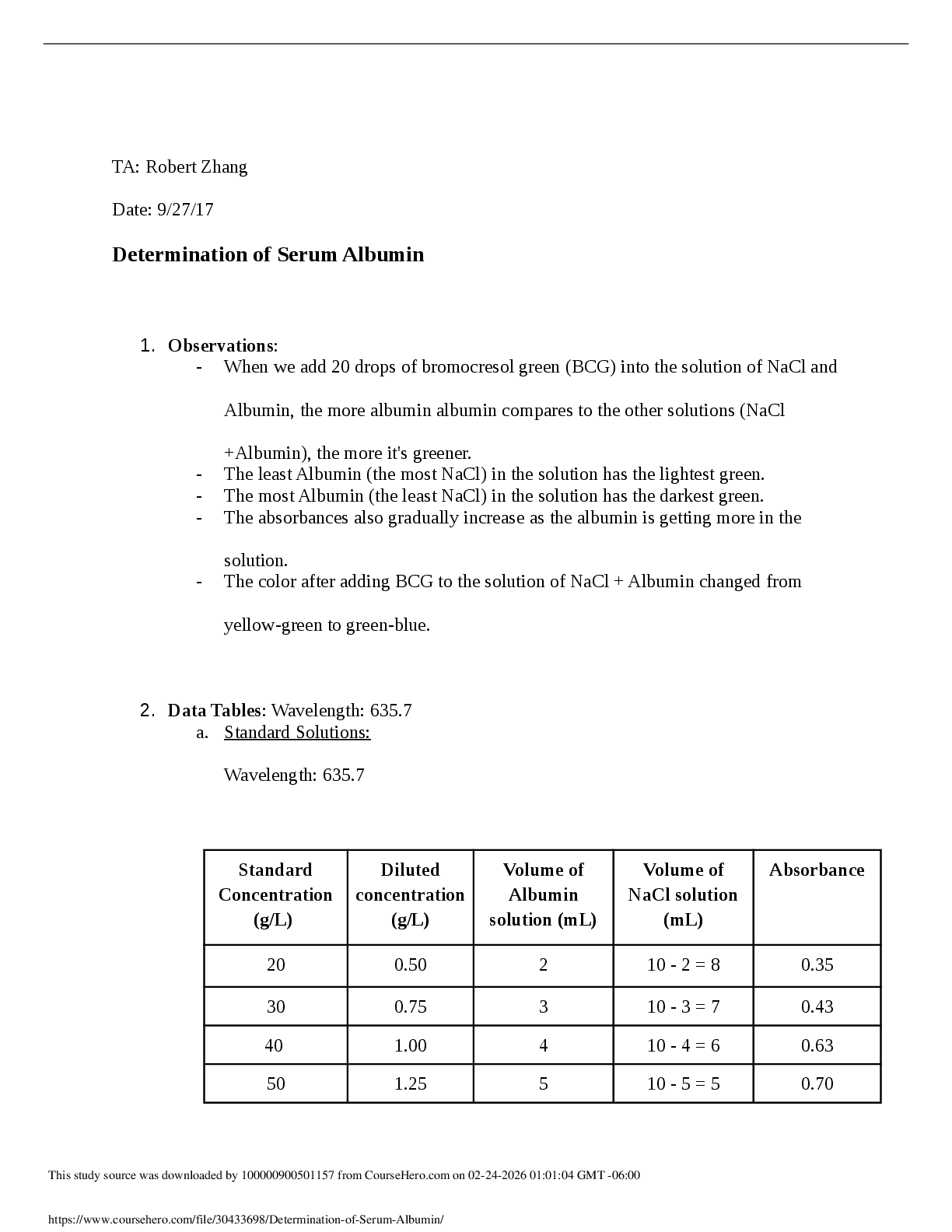
Activity 7.3 Tolerances
Introduction
The term variation describes the degree to which an object or idea differs from
others of the same type or from a standard. Examples of variation are everywhere
you look. When you
...
Activity 7.3 Tolerances
Introduction
The term variation describes the degree to which an object or idea differs from
others of the same type or from a standard. Examples of variation are everywhere
you look. When you see yourself in the mirror, you notice the left side of your face is
not exactly the same as the right side. There is a variation. Or, if you see identical
twins, they are not exactly the same. Likewise, no two manufactured objects are the
same. A degree of variation will exist.
The use of tolerancing in engineering design provides a means by which variance
can be controlled within acceptable limits so that parts of a product fit together in a
way that allows the product to function properly. In the field of mathematics and
science, tolerances are used regularly. You will see reference to an allowance or
tolerance given in many settings. After completing this activity, take note when you
see tolerances given in the media or on product labels.
In this activity you will analyze engineering drawings, identify tolerances, explain the
meaning and purpose of those tolerances, and calculate allowances between mating
parts of a product. You will also assess the need for tolerances in the manufacture of
a consumer product and create part drawings to specify your recommended
tolerances.
Equipment
Engineering notebook
Pencil
Highlighter
Procedure
1. Study the drawings below to identify specified tolerances.
a. Highlight each dimension that has a tolerance associated with it using
something like a highlight marker.
b. Identify the type of tolerance in each highlighted example by labeling each
tolerance dimension with one of the following: limit dimensions, unilateral
tolerance, or bilateral tolerance.
c. Label each identified tolerance with a separate letter, A through Z.
d. Beginning on a new page in your engineering notebook for each part,
record the letter of each tolerance identified on that part drawing, the type
of tolerance, a short written phase that describes the dimensional variation
allowed for that dimension, the tolerance (a number representing the total
allowed dimensional variation), and an explanation as to why that
© 2012 Project Lead The Way, Inc.
Introduction to Engineering Design Activity 7.3 Tolerances – Page 1particular dimension requires a tolerance. You may wish to duplicate the
following table in your notebook to organize your notes
[Show More]
.png)





.png)