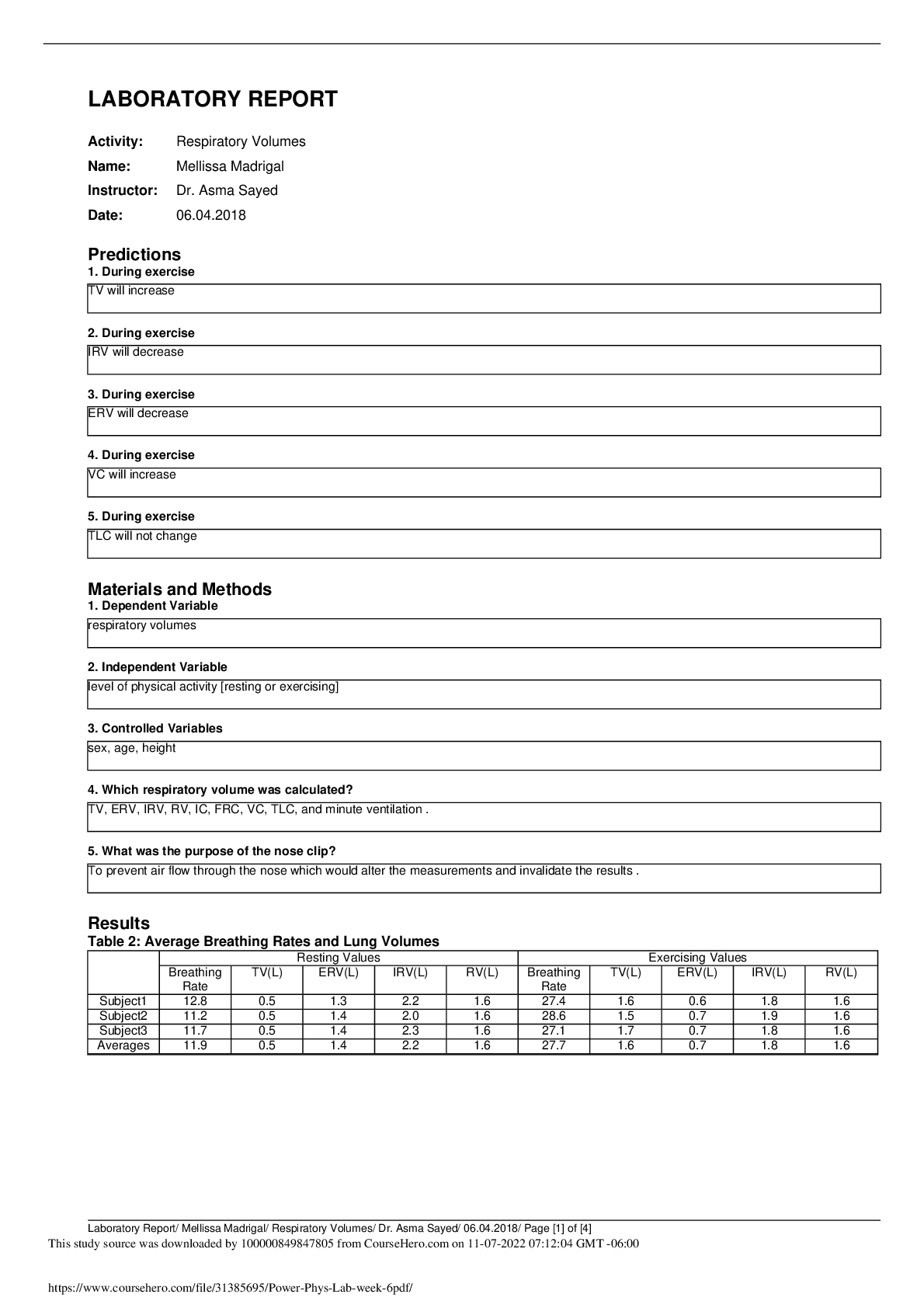
Report for Experiment #18
RC Circuits
10/24/17Introduction
The purpose of this lab was to study a new circuit element, the capacitor, and its function in a
circuit. Capacitors essentially store charge, and their geom
...
Report for Experiment #18
RC Circuits
10/24/17Introduction
The purpose of this lab was to study a new circuit element, the capacitor, and its function in a
circuit. Capacitors essentially store charge, and their geometrical design allows them to separate charge
by polarity. Once the stored charge is released, the energy can be reclaimed and made useful by other
circuit elements. Due to the nature of energy charging and discharging in capacitors, this circuit element
introduces time-varying currents. Two capacitors in parallel have capacitances that add together whereas
capacitors in series have capacitances that act like resistors in parallel. The overall goals of this
experiment were to measure the relationship between voltage and current in an RC circuit, to measure tau
or the time constant in an RC circuit, and to develop an intuition for the time-varying nature of the current
in an RC circuit.
Investigation 1
In this investigation, the change in voltage between the resistor and capacitor was studied. The
power supply was first connected to a 0.1 F capacitor with a 1k resistor and a switch in series. The power
supply was set to 6.0 V and checked with the voltmeter. The closest multimeter reading obtained was
6.005 V. The figure below shows the setup of the circuit with the multimeters to measure voltage
connected in parallel, and the power source represented by the +/- element.
Figure 1: Circuit set-up
The capacitor was discharged before being connected into the circuit. When the switch was
flipped, the voltage reading across the resistor was recorded every 10 seconds for 5 minutes. The
capacitor was discharged again and the experiment was repeated with respect to the voltage across the
capacitor. The raw data for this experiment is in Appendix A.
[Show More]













.png)









.png)





.png)


