Chapter 5: Employee Motivation: Foundations and Practices October 10th, 2010
• Motivation refers to the forces within a person that affect the direction, intensity, and
persistence of voluntary behavior
o Is one of th
...
Chapter 5: Employee Motivation: Foundations and Practices October 10th, 2010
• Motivation refers to the forces within a person that affect the direction, intensity, and
persistence of voluntary behavior
o Is one of the 4 essential drivers of individual behavior and performance
• Employee Needs and Drives
o Needs are deficiencies that energize or trigger behaviors to satisfy those needs
A satisfied need doesn’t motivate
o Drives are instinctive or innate tendencies to seek certain goals or maintain
internal stability
Needs are typically produced by drives, but strengthened through learning
(reinforcement) and social forces
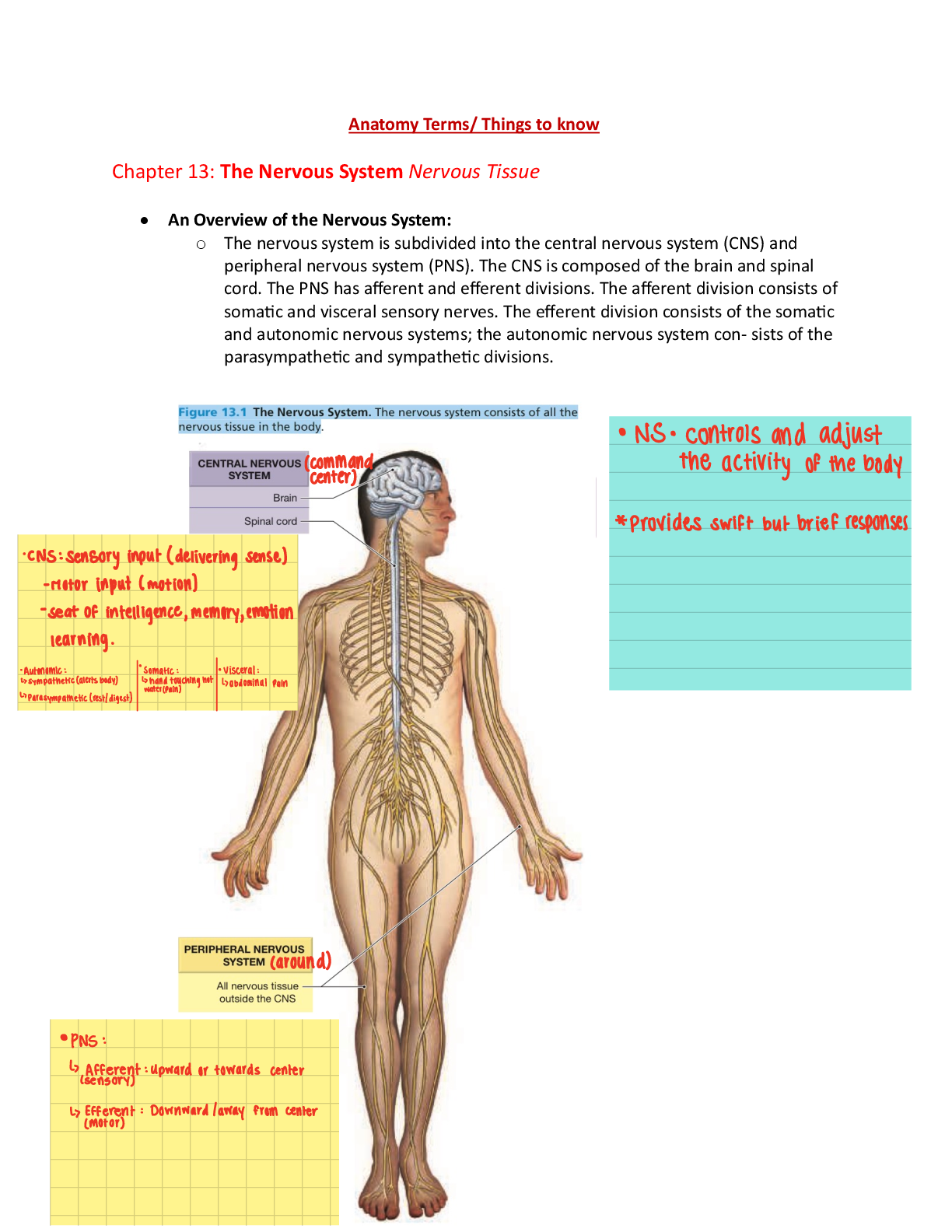
o Maslow’s needs hierarchy theory is a motivation theory of needs arranged in a
hierarchy, whereby people are motivated to fulfill a higher need as a lower one
becomes gratified (has little or no scientific support).
The hierarchy of 5 basic categories:
• Physiological needs (food, air, water, shelter) is at the bottom
• Safety (a secure and stable environment and the absence of pain,
threat, or illness)
• Belongingness
• Esteem (self-esteem through personal achievement and social
esteem through recognition and respect from others)
• Self-actualization the need for self-fulfillment in reaching one’s
potential
We are motivated simultaneously be several needs, but the strongest
source is the lowest unsatisfied need at the time
• The bottom 4 groups are deficiency needs because they become
activated when unfulfilled
• Self-actualization is a growth need because it continues to develop
even when unfulfilled
Reasons why Maslow’s model and other needs hierarchy theories don’t
work:
• They don’t capture the entire variety of needs that people
experience
• Gratification of one need level doesn’t necessarily lead to
increased motivation to satisfy the next higher need level
• It assumes that need priorities shift over months or years, whereas
the importance of a particular need likely changes more quickly
with the situation
• People don’t seem to fit into one universal needs hierarchy
o Needs hierarchies are unique, not universal, because a
person’s needs are strongly influenced by his or her values
o Four-Drive theory is both holistic (it pulls together the various drives and needs)
and humanistic (it considers human thought and social influences rather than just
instinct.
According to four-drive theory, everyone has the:
• Drive to acquire: the drive to seek, take, control, and retain objects
and personal experiences
o Is the foundation of competition and the basis of our need
for esteem
• Drive to bond: the drive to form social relationships and develop
mutual caring commitments with others
o Motivates people to cooperate
• Drive to learn: the drive to satisfy our curiosity, to know and
understand ourselves and the environment around us
• Drive to defend: includes defending our relationships, our
acquisitions, and our belief systems
o The drive to defend is always reactive – is triggered by
threat
o The other 3 are always proactive – we actively seek to
improve our acquisitions, relationships, and knowledge
All four drives are innate, universal, and independent of each other
o Recall: every meaningful bit of information we receive is quickly and
unconsciously tagged with emotional markers that swirl around our conscious
process of logically analyzing that information - Our motivation to act is therefore
a result of rational thinking influenced by these emotional markers
The four drives determine which emotional markers, if any, are attached to
the perceived information
Four-drive theory further explains that the process is conscious
(humanistic) rather than instinctive, because these drives produce
independent and often competing signals that require our attention
Our conscious analysis of competing demands from the four drives
generates needs that energize us to act in ways acceptable to society and
our own moral compass
o The main implication of four-drive theory is that companies need to ensure that
individual jobs and workplaces provide a balanced opportunity to
[Show More]



.png)





.png)