*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NURS6541: Pediatrics Midterm Study Guide (Walden University). All The review Notes Section 1 to 20. (All)
NURS6541: Pediatrics Midterm Study Guide (Walden University). All The review Notes Section 1 to 20.
Document Content and Description Below
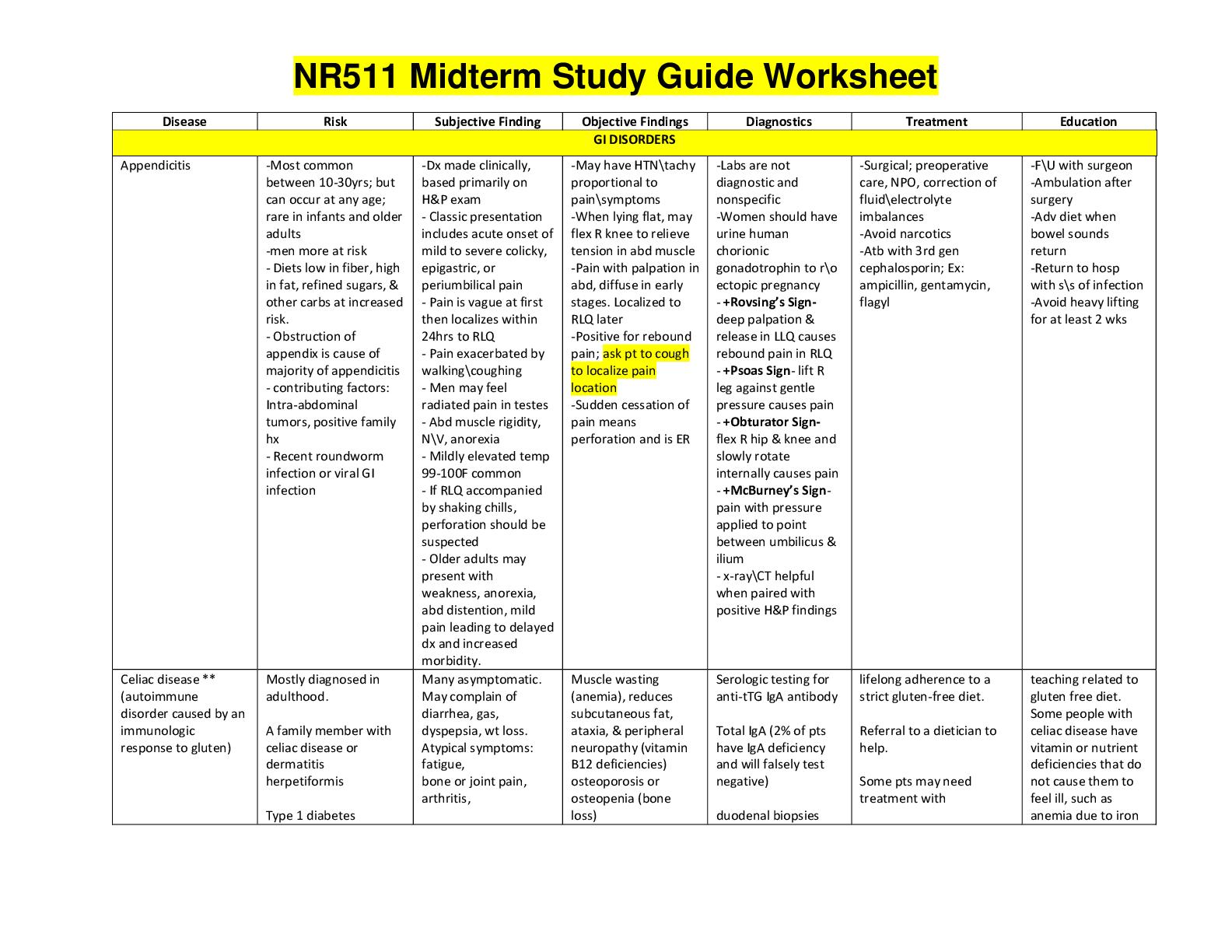
Section 1 Emily Turner 1. Children are able to sit without extra support at what age? 6-8 month olds should be able to sit briefly without extra support, 7-9 months old sit well independently. ... 4. Child abuse questions: • What age is it appropriate to have certain types of fractures? Metaphyseal fractures, multiple differently aged posterior rib fractures, complex or multiple skull fractures, spinous process or scapular fractures are suspicious in children. • When should you be concerned about a young infant with tons of bruises (eg - if they are not walking yet would be unusual)? Long bone fx are unusual in young infants. • When is it necessary for you to report? Anytime you suspect any sort of abuse. • Who do you report to? CPS. • Do you face any repercussions? Should not. • Any fracture in a non-ambulatory infant without clear accidental and consistent mechanism should raise a red flag. (items 4, 5 and 29 in this guide address child abuse) 6. Contraindications of vaccinating children. Who should not receive a live vaccine? Immunocompromised, allergic reaction to a previous dose or component of vaccine, history of intussusception for Rotavirus See CDC sheet “vaccines by medical indication” https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/imz/child-indications.html Immunocompromised should not receive: Rotavirus, MMR, influenza (LAIV) or varicella 7. Young boy with mental retardation. He was a premie. They give a scenario. What caused his mental retardation? eg - understand congenital abnormalities, infections, preemie complications, chromosomal aberrations, brain tumor, serum blood levels Section 2 Melissa Burris 8. Newborns: What type of vitamin deficienc\ies cause problems? eg - vitamin A, B1, C, D and K Vitamin A Deficiency: Anorexia, dry skin, increased risk for infection, keratinization of epithelial cells of the respiratory tract,night blindness, corneal lesions. 10. What are the benefits of breastfeeding? eg - lower incidence of many diseases Breast milk is rich in vitamins,minerals,fat, proteins (including immunoglobulins and antibodies), carbohydrates (especially lactose), and promotes growth and development. 12. Review early reflexive responses in newborns. eg -babinski, moro, swimming and rooting Babinski Reflex:Occurs after the sole of the foot has been firmly stroked. The big toe then moves 13. Be familiar with language development. eg - red flags, when should kids be speaking in 3-4 word sentences, complete sentences, etc. 12-18M - uses all vowels, may constants, articulates 15-20 words and understands 50 18-24M -imitates two word combinations, begins to combine words, begins to use pronouns, names self 14. Which adolescent is at greatest risk for developing anorexia nervosa? Be familiar with this disorder. Section 4 Myesha Shultz 18. When to start measuring blood pressure P. 759 annually beginning at 3 y/o 19. Role play with exam techniques and when to start toddlers and young preschoolers p. 362 22. What age of growth and development GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT AGE MOTOR SOCIAL Newborn (1 week-1 month) Fixates on faces, lifts head for moments when prone and turns side to side, sleeps 3-4 hours at a time (16-18 total in 24 hours) Blinks, Cries, comforted by being held and fed 2 months Lifts head, neck, and upper chest when prone, some head control when upright, will shake rattle before 4 months Coos, smiles, shows interest in visual and auditory stimulus Section 5 Ann Quinlan 23. Piaget’s development stages, ex: sensory motor etc. Sensorimotor stage (age birth-2yrs): Dramatic growth and learning occurs. At this stage they acquire knowledge through sensory experiences and manipulating objects. Their entire experience occurs through basic reflexes, senses, and motor responses.They learn how to perform physical actions like crawling and walking. They learn all about language. 24. Temperament • Activity: Does the child move all the time or are they not very active? What is the activity level? Recognize their normal level of activity and plan high energy activities as much as possible. 25. Dietary: When to wean? Start table foods? The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends breastfeeding as the sole source of nutrition for your baby for about 6 months. When you add solid foods to your baby’s diet, continue breastfeeding until at least 12 months. You can continue to breastfeed after 12 months if you and your baby desire. However, mothers in the United States have tended to wean much earlier than in most other countries 26. Comprehensive development and when to refer. (Warning signs of when to refer for a comprehensive developmental eval. Speech, developmental milestones, etc.) THIS IS A VERY VERY BROAD QUESTION. I RECOMMEND REVIEWING FROM THE BOOK. 27. Physical 27. Physical development of female puberty: The process that begins with breast development (thelarche), then the growth of pubic and axillary hair (pubarche), and finally the first menses (menarche). Section 6 Amy Gass Roberts 28. Abnormal language development Textbook Pg 78 Red Flags Language disorders • Aphasia (difficulty understanding or speaking parts of language due to a brain injury or how the brain works). 29. The most common form of child abuse in pediatric care - Neglect, then Physical Abuse (items 4, 5 and 29 in this guide address child abuse) pg 332-333 in text. Four categories: Neglect, psychological, physical, and sexual. Children less than 1 yr have highest rate of victimization. 30. Explanation for small size in infant - weight below the 10th percentile for gestational age, Babies born weighing less than 5 pounds, 8 ounces are considered low birth weight. Some babies are small because their parents are small. But most babies who are small for gestational age have growth problems that happen during pregnancy 31. Presentation of congenital cytomegalovirus, down syndrome, craniopharyngioma (all cause low birth weight) Section 7 Courtney Kunze 33. Poor weight gain (what type of therapy might they need?) Scenario: lab studies with electrolytes, H&H. What is causing poor weight gain? Look up sweat chloride testing, growth hormone determination, etc. 34. Advice for well-child at visits. eg - 2 week old, what info do you give mom and dad? 40. Refusal bowel patterns on toilet Two behaviors associated with stool toileting refusal may require the intervention of the pediatrician. The first is stool withholding causing constipation which can result in rectal impaction and primary encopresis. The second is lack of successful toilet training by 42 months of age. Section 9 Shana Light What are some common features of 12 mo old, 2yo, 5yo behavior? 44. Stranger anxiety - Section 10 Setoria James 49. TB tests (what could a positive result indicate?) Mantoux skin test is an intradermal injection of 0.5-5ml tuberculin units that should produce a palpable wheal of 6-10mm induration. Read the test at 48-72 hours, measuring induration not erythema. The following are considered positive for latent infection or active TB: S99ection 11 Beth Lax 54. Well child check-ups help track growth and development, prevention by administering vaccines, time to discuss concerns, and builds a team approach to care. School: Readiness, established routines, school attendance, friends; after-school care and activities, parent-teacher communication.Safety: Car safety (also see #2 and #60), safety during physical activity, water safety, sun protection, harm from adults, firearm safety Use belt-positioning booster seat in the backseat Ensure child uses safety equipment (helmet, pads). Be a role model and always wear a helmet Teach child to swim; supervise around water Use sunscreen; wear hat; avoid prolonged exposure when sun is at its strongest, between 11:00 am and 3:00 pm 59. Erickson’s stages of development Erickson expanded on Freud’s theories-each stage presents problems that an individual seeks to master. He believed if problems were not resolved, they would be revisited again at future stages. 61. Bullying - Ultimate goal is to stop bullying before it starts through prevention programs in schools and community resources. • Defined by CDC as unwanted aggressive behaviors by another youth or group of youths-- very common in school setting (higher in middle than in high schoolI • Involves an observed or perceived power imbalance and behaviors are likely to be repeated multiple times Section 13 Amy Holt 65. Regular screening in adolescents 66. Peak height velocity by Tanner stage for adolescent girls 67. Erickson’s Stage for adolescent: Section 14 Ashley Esquibel 70. Common substance abuse middle school p.384 Alcohol is the most common, followed by marijuana Section 16 Courtney Kunze 82. Allergic rhinitis (management options) Definition: an inflammatory condition of the nasal mucosa. AR is mediated by an IgE response to environmental allergens Signs & Symptoms: nasal pruritus, sneezing, rhinorrhea, and nasal congestion. Frequently there is associated palate, throat, ear, and eye itching as well as eye redness, puffiness, and watery discharge. Boggy, white nasal mucosa Differential Diagnosis: nonallergic rhinitis, acute/chronic sinusitis, viral rhinosinusitis Treatment: Second-generation oral antihistamines are preferred to first-generation agents because they cause less or no sedation. Cetirizine has been found to be Section 17 Monica Hevron 87. Requires hospitalizations: epilglotitis, retropharyngeal abscess, cervical adenitis, orbital cellulitis *Epiglottitis (815-817) requires hospitalization because of the risk of sudden airway occlusion Section 18 Luis Sanchez 92. How long is head circumference routinely measures: birth to 3 years at routine wellness visits 93. Snellen test results are and be able to explain Visual acuity is usually measured with a Snellen chart. ... "Normal" vision is 20/20. This means that the test subject sees the same line of letters at 20 feet that person with normal vision sees at 20 feet. 20/40 vision means that the test subject sees at 20 feet what a person with normal vision sees at 40 feet. 99. Dx, s/s of strep throat, viral tonsillitis, epiglottitis, diphtheria • Strep throat- streptococcal pharyngitis bacterial infection of throat. Signs and symptoms fever of 101 or higher, red swollen tonsils, white patches in the throat, 100. Sinusitis and the location of sinuses - Sinusitis is an inflammation or swelling of the tissue lining the sinuses. Healthy sinuses are filled with air. But when they become blocked and filled with fluid, germs can grow and cause an infection 103. Diagnostic criteria for autism spectrum disorder: The diagnosis of ASD is made clinically in children who meet established diagnostic criteria for ASD based on history and observation of behavior. *contraindicated in gallbladder disease, pregnancy, malabsorption syndromes and in sensitivity to the drug ** Side effects: fatty stool, GI upset: fiber supplements may help with these S/ [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 60 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 29, 2020
Number of pages
60
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 29, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
117




-3-168.png)