Statistics > STUDY GUIDE > understandable means of developing probability distribution for theoretical distribution. (All)
understandable means of developing probability distribution for theoretical distribution.
Document Content and Description Below
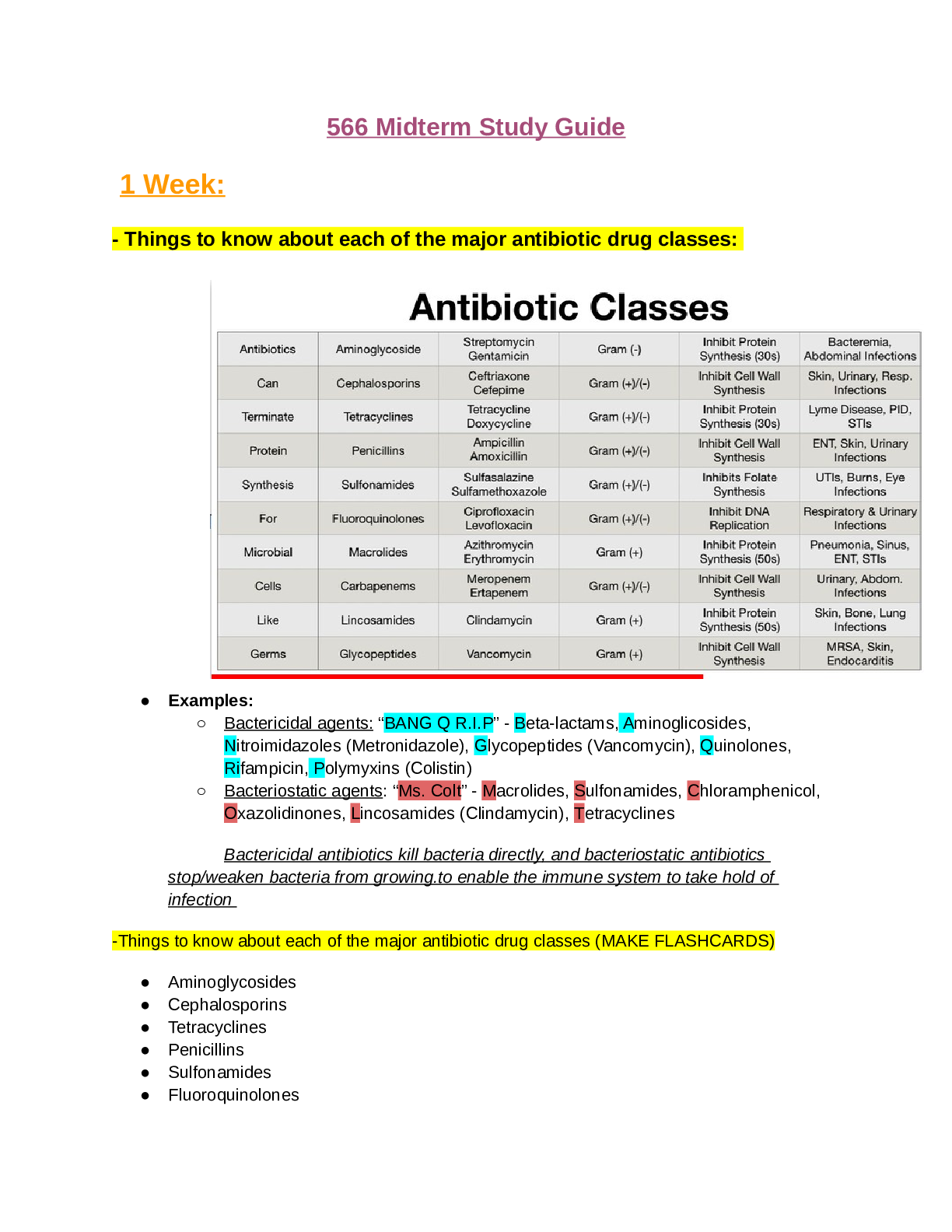
Random experiment The results can be occurred in random way or can’t be expected in advance before going to do particular experiment. For example Flip a fair coin, then results are known suc ... h as ‘head’ and ‘tail’ but we cannot expect which result will happen. Roll a die once, then results are known such 6 faces but we cannot expect which result will happen. However we can expect the chance to get some desired outcome from any trail Sample space The total number of possible outcomes from any trail is called Sample space. This is denoted by ‘S’ For example 1. Flip a coin then its sample space S ={H, T} = 2 2. Roll a die, then its sample space S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6} = 36 3. If a card is drawn is from 52 shuffled pack of cards, then its sample space S = {26 Black, 26 Red} or {Spade, club, heart and diamond} = 52 4. If a student is assigned to particular homework in a week, then that student can do that homework from the possible chances are S = {MON, TUE, WED, THU, FRI, SAT and SUN} Event The set of desired outcomes in a sample space is called the event. Usually it is donated by ‘E’ For example 1. If you want to get a head from a coin flipping, then its desired event E = {H} = 1 2. If you want to get even number from a die rolling, then its desired event E = {2, 4, 6} = 3 3. If you want to get diamond card for the picking a card from 52 shuffled pack of cards, then its desired event E = {13Diamonds} = 13 Probability of any desired outcome Probability of any desired outcome is defined as the number of possible desired outcomes over total number of possible outcomes. For example What is the probability of getting one head when we flip two coins? Explanation Total number of possible outcomes S = {HH, HT, TH, TT} = 4 Number of possible desired outcomes E = {HT, TH} = 2 Therefore the probability of getting one head = 2/4 = ½ [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 53 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 31, 2021
Number of pages
53
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 31, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
67








.png)
 (1).png)














