Biochemistry Readiness Check
The 2nd OA Readiness Check is designed to give you additional practice with
new assessment-style questions to help prepare for success on the OA. Thus,
please try to mimic exam-like condit
...
Biochemistry Readiness Check
The 2nd OA Readiness Check is designed to give you additional practice with
new assessment-style questions to help prepare for success on the OA. Thus,
please try to mimic exam-like conditions by taking the test in one <2 hr sitting
without any study aids apart from your whiteboard/scrap paper. Note: Responses
cannot be edited. You will be able to see the results and feedback after
submitting the test. A score of 70% is required for OA approval. If you score
below 70%, please speak with a Course Instructor via appointment to discuss
next steps prior to retaking this test.
Points:
54/67
1
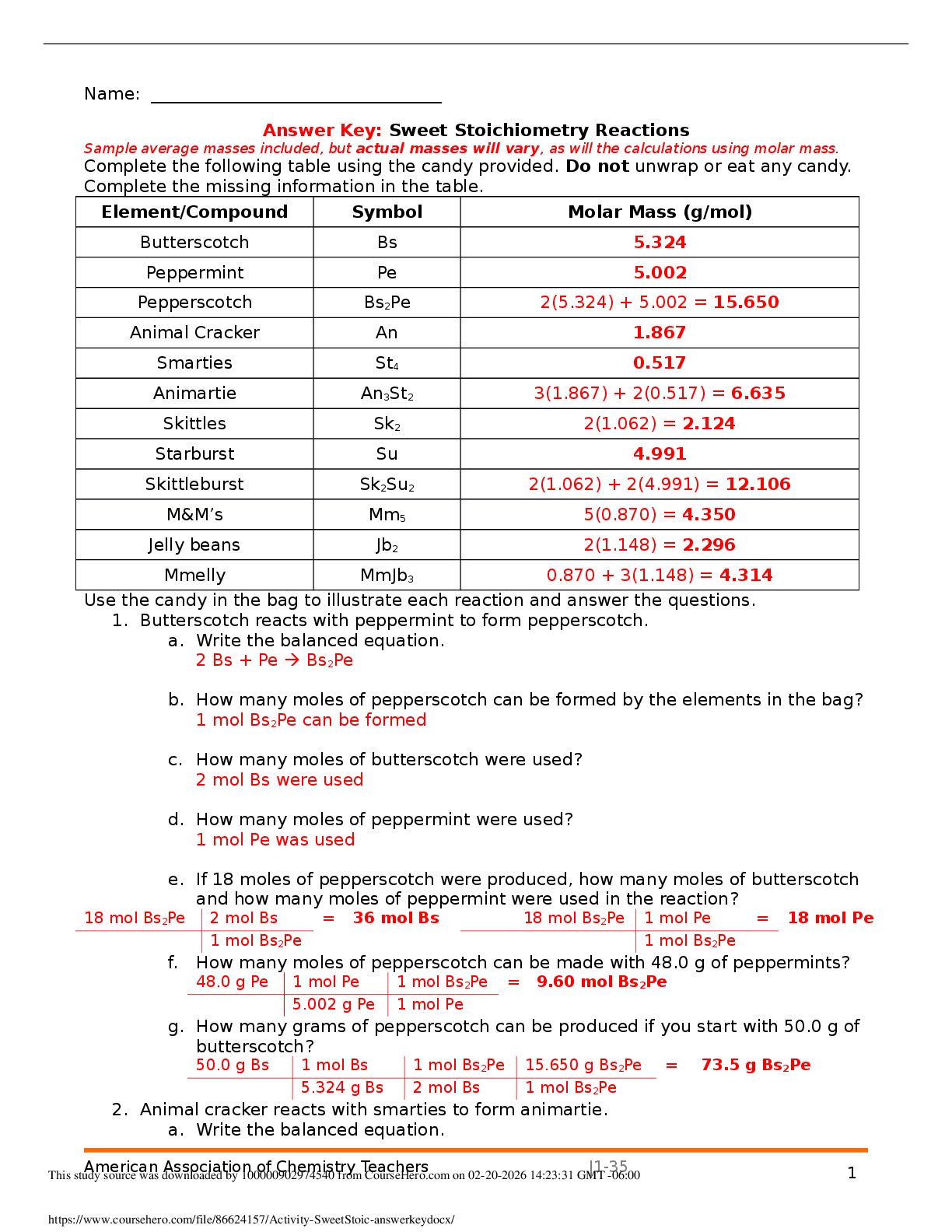
What is the complementary sequence to 3’ ATG CGA ATA 5’?
(1/1 Points)
3’ TAT TCG CAT 5’
The correct answer is 3' TAT TCG CAT 5'. Remember complementary means “Matching
or Pairing” You have to remember to pay attention to your numbers as well as your
letters (A-T, G-C, 5'-3'). The correct answer is 3’ ATG CGA ATA 5’ (original sequence) 5’
TAC GCT TAT 3’ (complementary sequence) But we asked for it in the 3’ direction, so
mirror answer to give correct answer: 3’ TAT TCG CAT 5’
3’ TAC GCT TAT 5’
3’ GAT AGC ATA 5’
5’ ATA AGC GTA 3’
2
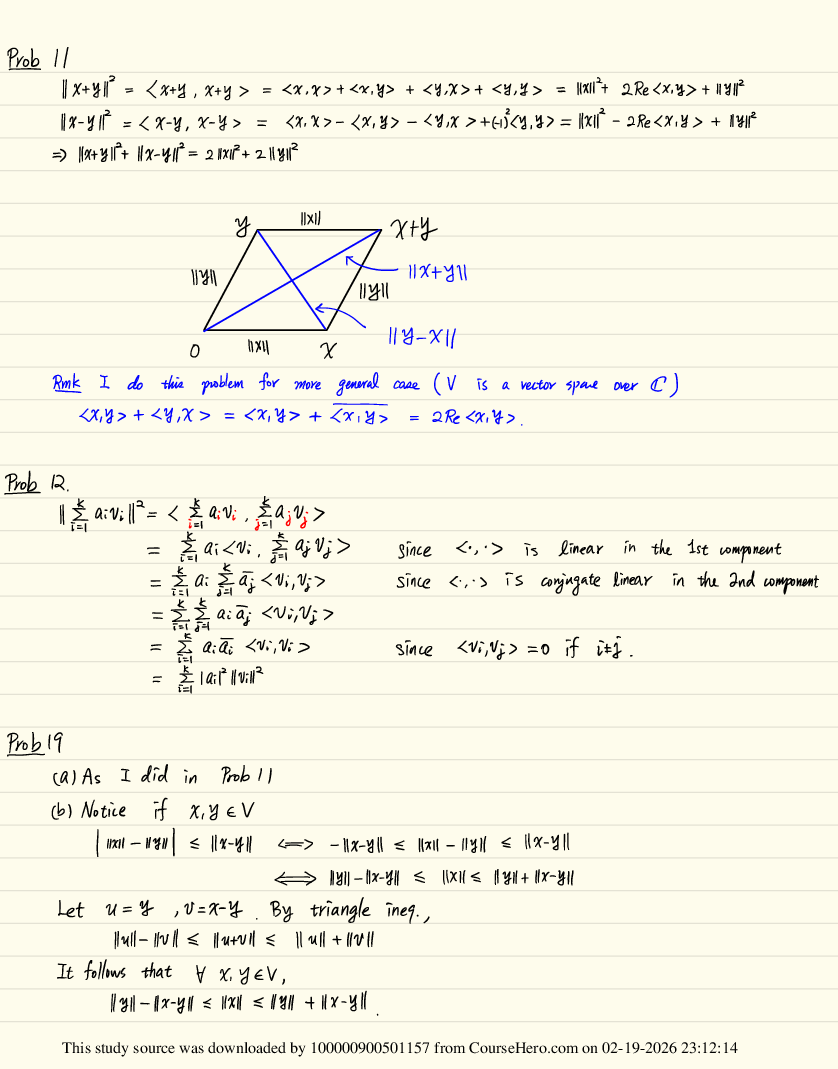
Which amino acid sequence would result from this Coding DNA strand?
3’ ATG CAG ATA 5’?
(0/1 Points)
Tyr Val Tyr
The correct answer is Ile Asp Val. We are starting at the coding strand, and have to
remember the relationship between coding DNA and mRNA. These two strands are non-
complementary and parallel. So we copy the coding strand , change T ---> U, and then
write the mRNA sequence: 3’ ATG CAG ATA 5’ coding 3’ AUG CAG AUA 5’ mRNA Mirror
by changing orientation: 5’ AUA GAC GUA 3’ Read chart Ile Asp Val (chart is in direction
of 5' ---> 3') If you chose Tyr Val Tyr, this answer is incorrect because this is the amino
acid sequence that results from the mRNA 5' UAC GUC UAU 3' which would have been
complementary to the given coding strand. Coding DNA is non-complementary and
parallel to mRNA.
Ile Gln Ile
Ile Asp Val
Leu His Lys
3
Which amino acid sequence would be made from this template DNA
strand? 5’ TAT TAC CGA 3’?
(1/1 Points)
Tyr Tyr Arg
Ile Met Ala
Ser Val Ile
The correct answer is Ser Val Ile because 5’ TAT TAC CGA 3’ template is complementary
and antiparallel so 3’ AUA AUG GCU 5’ but it is in the wrong orientation, so mirror 5’
UCG GUA AUA 3’ and read the chart Ser Val Ile
Ser His Gln
4
Which of the following are the correct components for a PCR reaction?
(1/1 Points)
dNTPs, Primer, RNA Polymerase, template RNA
dNTPs, Primer, DNA Polymerase, template DNA
The correct answer is dNTPs, Primer, DNA Polymerase, template DNA. Notice that all
components are about DNA. The Primer is even a DNA Primer.
ATP, Primer, mRNA polymerase; template mRNA
Acetyl CoA, RNA primer, DNA Ligase, Template phosphate
5
Assuming 100% reaction efficiency, how many DNA copies will be
produced after 5 PCR cycles, if we begin with 1 DNA template?
(1/1 Points)
16
32
The correct answer is 32. 2x2x2x2x2=32
64
10
6
Which of the following would represent a silent mutation if this is the
original sequence: 5’ AUC GUA ACA 3’?
(1/1 Points)
5’ AUC GGA ACA 3’
5' AUA GUA ACA 3'
The correct answer is 5' AUC GUA ACA 3' Ile Val Thr
5’ AUG GUA ACA 3’
5’ AUC GCA ACA 3’
7
If the original coding sequence is 5’ CGA TAC TTC AGA 3’ and it is
mutated to 5' CGA TAT TTC AGA 3', what type of mutation would have
taken place?
(0/1 Points)
Silent
Missense
The correct answer is silent mutation. The nucleotide sequence changes, but it codes for
the same amino acid. The coding sequence 5' TAC 3' corresponds to the mRNA
sequence 5' UAC 3' (Tyr), and the coding sequence 5' TAT 3' corresponds to the mRNA
sequence 5' UAU 3' (Tyr). Since the C changed to at T, this is a point mutation. If the
point mutation results in the same amino acid in the new sequence as in the original
sequence, the point mutation is a silent mutation.
Nonsense
Insertion
8
This learning objective is now tested in a different WGU course than
Biochemistry. Please select True.
True
The correct answer is Option 1 because an autosomal dominant disorder would be
inherited on numbered chromosomes, not sex chromosomes X or Y. Also, at least one
dominant allele (yellow box) needs to be present for the individual to have the dominant
disease.
False
9
This learning objective is now tested in a different WGU course than
Biochemistry. Please select True.
True
The correct answer is X- linked recessive because parents (carriers) do not have it (II-5-
6) but a child does (III-5). You will get the same result if you consider parents (carriers)
(I-1-2), who do not have the trait, but a child does (II-3). A third option that gives the
same result (X-linked recessive) is by considering parents (carriers) who do not have the
trait (III-1-2), and their child does (IV-1). The pattern is recessive because the selected
parents are carriers, and it is X-linked because only males have the trait.
False
10
This learning objective is now tested in a different WGU course than
Biochemistry. Please select True.
True
The correct answer is 50%. Homozygous recessive: aa Heterozygous: Aa When you see
"percentage" or "probability," think Punnett square. 50% of the children would be
expected to be Aa, and 50% of the children would be expected to be aa.
False
11
Which of the following describes an epigenetic change?
(0/1 Points)
Denaturation of template DNA to facilitate primer annealing.
Increased methylation of the promoter region of a tumor suppressor gene in a
developing fetus.
Thymine dimer formation resulting from UV radiation.
The correct answer is "Increased methylation of the promoter region of a tumor
suppressor gene in a developing fetus."
Mismatch mutation caused by mistakes made by DNA Polymerase during
replication.
12
Rett syndrome is a brain disorder that occurs almost exclusively in
females, causing severe deficits in language, learning, coordination
and other brain functions. Decreased expression of the MECP2 gene
causes Rett syndrome. Which of the following scenarios correctly
describes how Rett syndrome could be developed?
(0/1 Points)
A DNA-binding protein blocks RNA Polymerase from binding to the promoter
sequence, facilitating the transcription of the MECP2 gene.
The answer is "Transcription factors are unable to bind to the transcription start site of
the MECP2 gene because nucleosomes are tightly packed together." Think "increased
space gives increased access and increased expression." Gene expression is increased
when nucleosomes are widely spaced and transcription factors and RNA Polymerase are
able to bind to the transcription start site of the gene. In this question, decreased
expression is resulting from decreased space between the nucleosomes, so the RNA
Polymerase and transcription factors have decreased access to the transcription start
site of the gene. If you answered, "A DNA-binding protein blocks RNA Polymerase from
binding to the promoter sequence, facilitating the transcription of the MECP2 gene," this
answer is incorrect. Transcription factors are proteins that bind to the promoter region
on the 5' side of the gene to be expressed. The RNA Polymerase then binds to the
transcription start site.
Transcription factors are unable to bind to the transcription start site of the MECP2
gene because nucleosomes are tightly packed together.
Transcription activators cause nucleosomes to separate, exposing the MECP2 gene.
RNA Polymerase binds to the MECP2 gene and begins translation.
13
What happens when the incorrect base is added during the synthesis
of a DNA strand in DNA replication?
(1/1 Points)
The homologous chromosome is used to replace the incorrectly added base with the
correct one.
DNA Polymerase removes the incorrect base and adds in the correct base.
The correct answer is "DNA Polymerase removes the incorrect base and adds in the
correct base." DNA Polymerase repairs mismatch errors that occur during DNA
replication.
Thymine dimers occur.
Distortion of the double helix occurs and is repaired by RNA Polymerase.
14
What is the correct definition of nucleotide excision repair?
(1/1 Points)
Removal of a single damaged nucleotide
Damage to a few or several nucleotides are identified, then many nucleotides are
removed and all are replaced to repair the DNA segment
The correct answer is "Damage to a few or several nucleotides are identified, then many
nucleotides are removed and all are replaced to repair the DNA segment." In nucleotide
excision repair, several nucleotides are removed whereas, in BER (base excision repair),
a single nucleotide is removed.
Required when there are breaks in the double stranded DNA strand which causes
discontinuity in both strands
Insertion of a thymine dimer
15
If arginine is mutated to leucine within a protein, how would the
structure of the protein be affected?
(1/1 Points)
Ionic bonds will continue to form, allowing the protein to fold as normal.
Hydrophobic interactions will continue to occur resulting in normal folding.
Ionic bonds will no longer form, potentially causing the protein to misfold.
The correct answer is "Ionic bonds will no longer form, potentially causing the protein to
misfold." Since arginine is a positively-charged amino acid, it would have formed an
ionic bond with a negatively-charged amino acid in the protein. Leucine is not charged
and is hydrophobic, so it will not form this same ionic bond, and could lead to protein
misfolding.
Hydrophobic interactions will be broken, potentially causing aggregation.
[Show More]