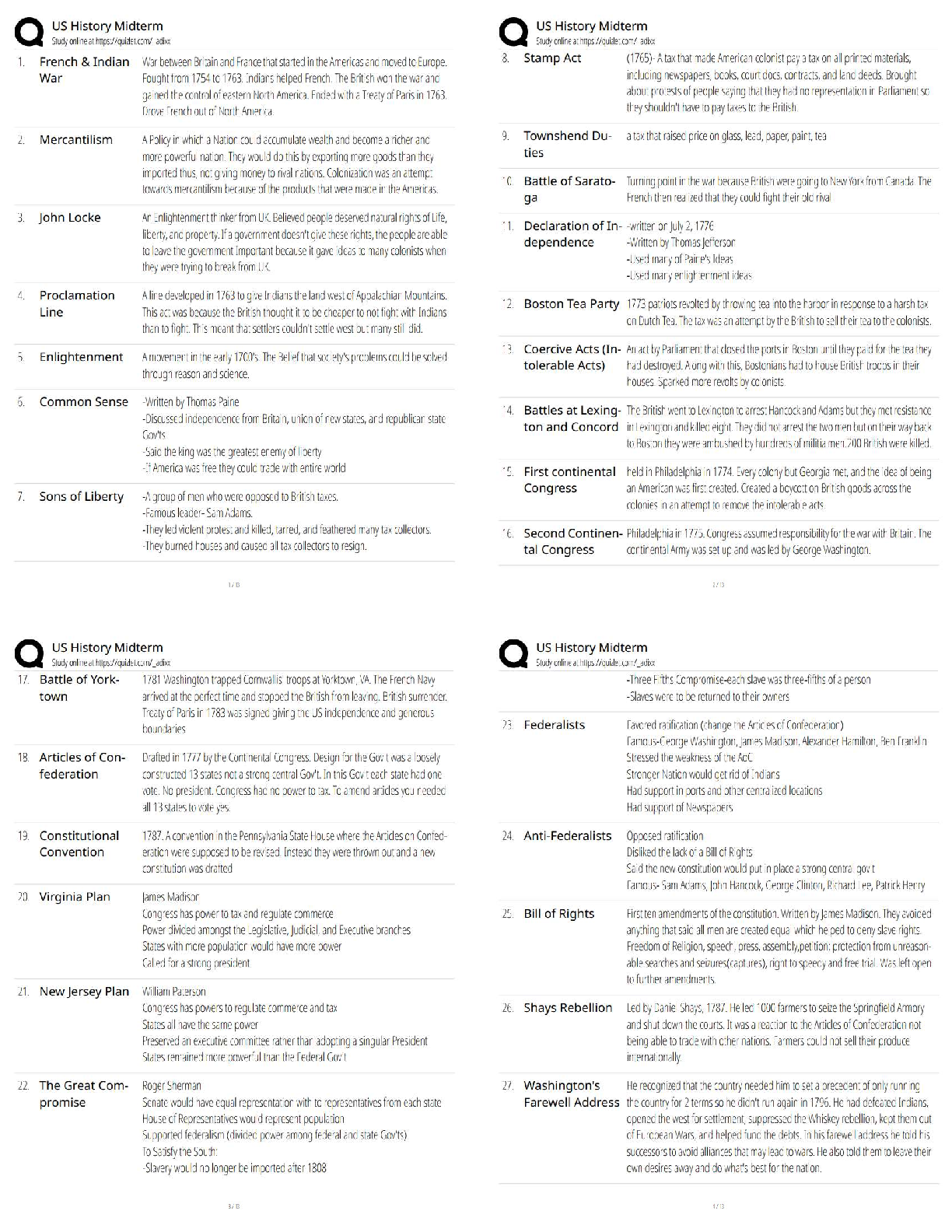
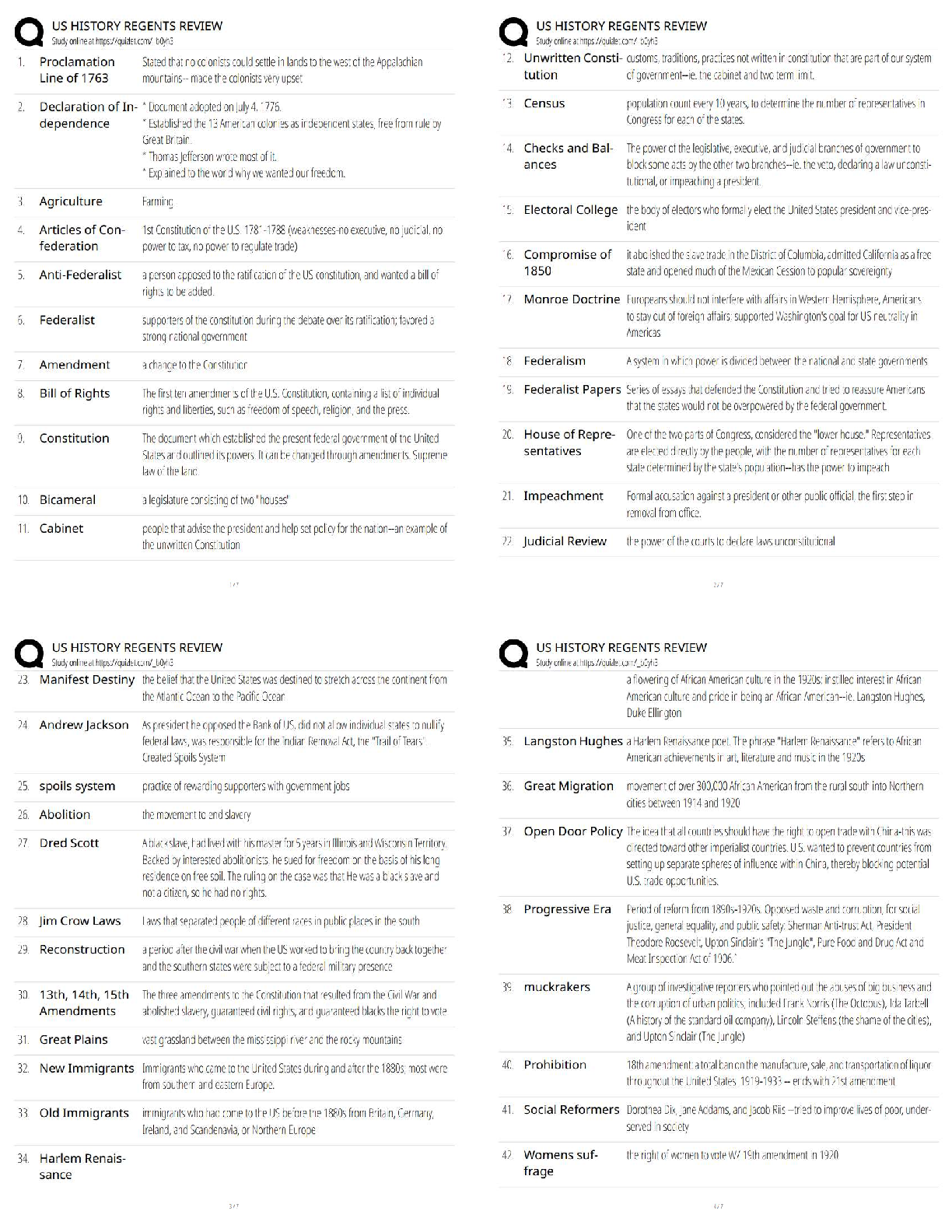
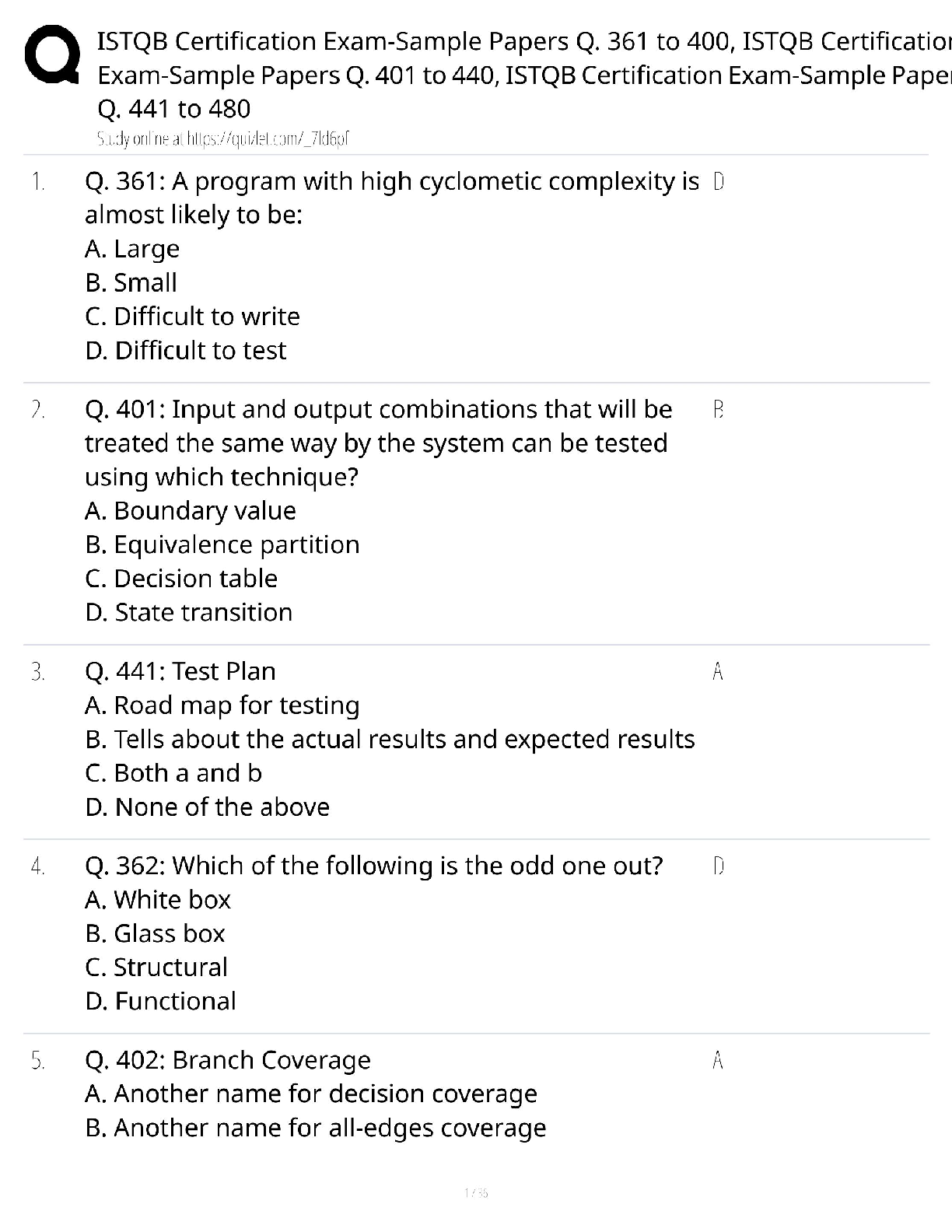
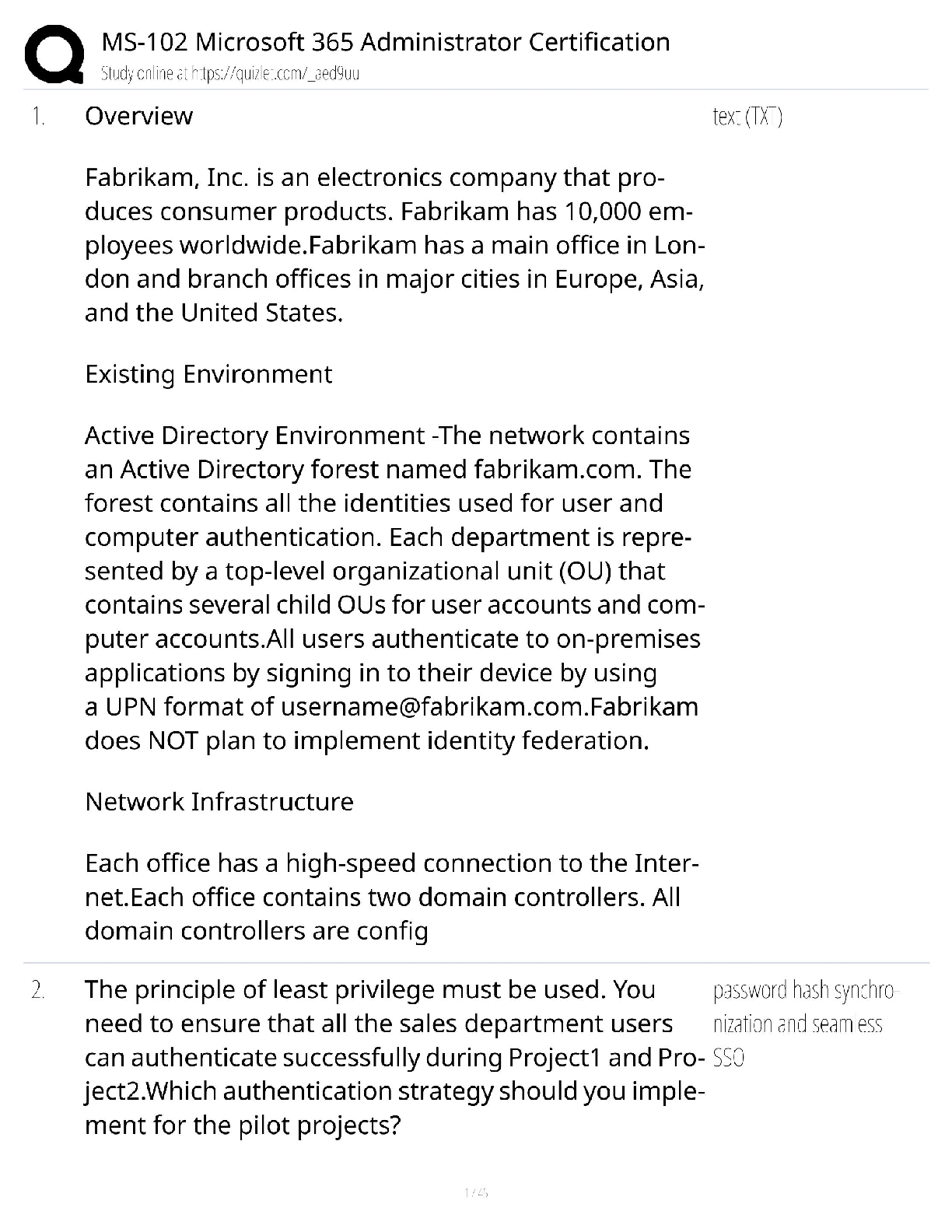
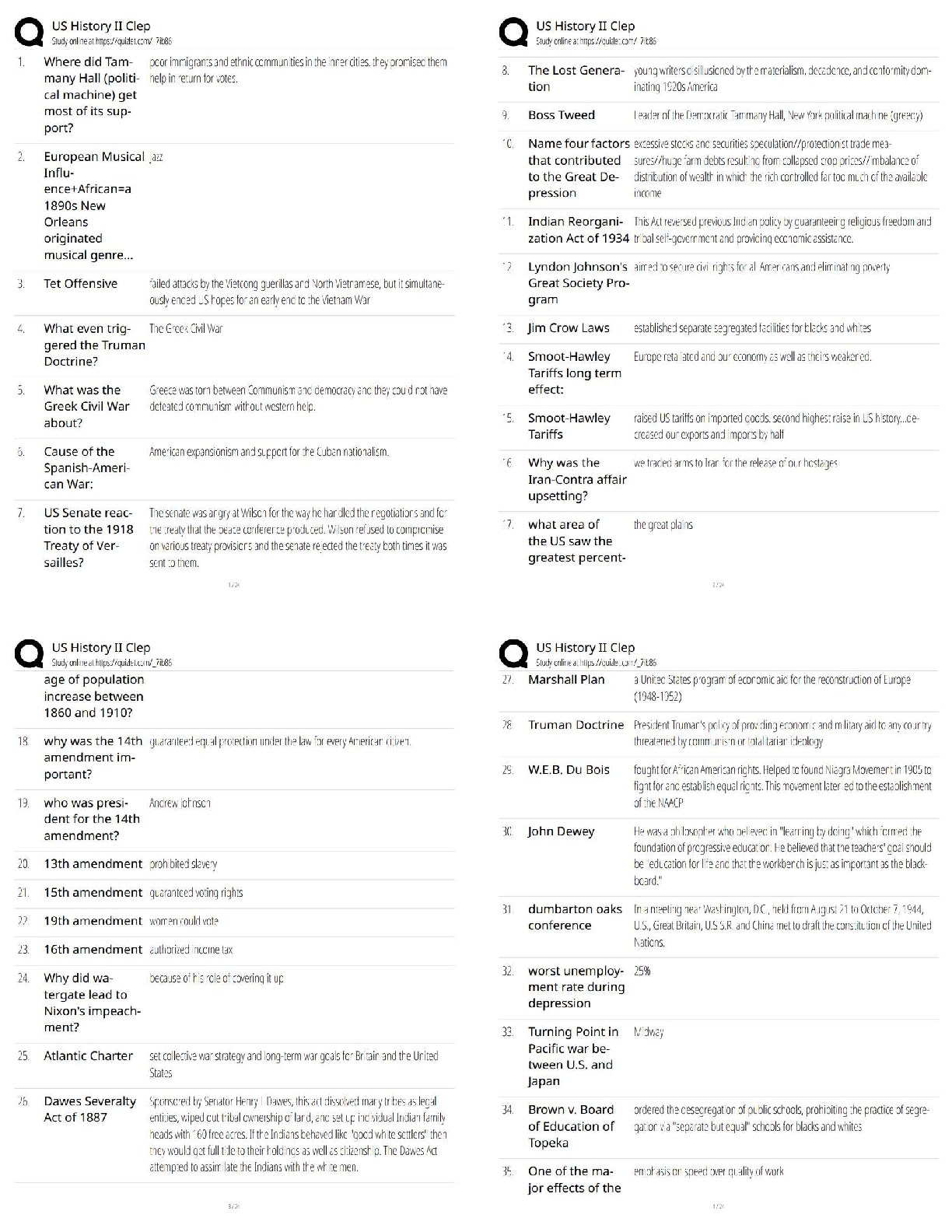
BIOL 261Midterm 2 exam review. Questions and Answers. 100% Correct.
Document Content and Description Below
BIOL 261
Midterm 2 Exam review
By: Stephanie Pacheco
03/17/20• Office:
GE 300.05 (knock on door to get into lab)
• E-mail: [email protected]
• Office hours:
Tuesday 1:00 - 2:00
Wedn
...
esday 10:00 – 12:001) Which of the following is not a key property of hereditary material?
a) It must be capable of being copied accurately.
b) It must encode the information necessary to form complex proteins.
c) It must be able to adapt to different cellular environments.
d) It must be (occasionally) mutable.
e) It must be stable.
2) Most DNA under normal physiological conditions (b DNA) would be correctly
described as which of the following?
a) a right handed helix, positively supercoiled, ~ 10 bases double per helix turn.
b) a left handed helix, negatively supercoiled, ~ 5 bases per double helix turn.
c) a right handed helix, negatively supercoiled ~10 bases per double helix turn.
d) a left handed helix, positively supercoiled ~ 5 bases per double helix turn.
e) a left handed helix, negatively supercoiled ~ 10 bases per double helix turn.
Version A3) Which of the following is least related to DNA stability under normal
physiological conditions ?
a) Two covalently bound, external strands.
b) Covalent strands bound by many hydrogen bonds.
c) The strands are overwound in a right handed helix.
d) Internal hydrophyllic interactions stabilize hydrogen bonds.
e) Externally stabilized by the polar nature of water interacting with charged
phosphate groups.
4) What is the Okazaki sequence from the following duplex DNA where the leading
strand is being synthesized from right to left?
3‟ TATACGCG 5‟ lagging strand
5‟ ATATGCGC 3‟ leading strand
a) 5‟ TATACGCG 3‟
b) 3‟ TATACGCG 5‟
c) 3‟ ATATGCGC 5‟
d) 5‟ ATATGCGC 3‟
e) 5‟ GCGCATAT 3‟5 ) Which of the following is NOT directly involved in DNA replication in
E. coli?
a) Helicase
b) Topoisomerase
c) DNA polymerase I
d) Single-strand binding protein
e) DNA polymerase II
6) The diagram below depicts a portion of a replicating DNA molecule.
Which strands are the templates for lagging strands?
a) A+B
b) C+D
c) A+D
d) B+C
e) A+C7) Please choose the answer containing correct groups presenting at the
1‟ position and 3 „ in a deoxyribose nucleotide.
a) nitrogenous base and phosphate group
b) OH and H
c) OH and phosphate group
d) nitrogenous base and OH
e) phosphate and H
8) You report the partial sequence of a new gene and submit it as
GACTTCAAGGG. By convention, the sequence you have submitted should
be taken by readers to represent the:
a) Template strand
b) Bottom strand
c) Strand that is 5‟ to 3‟ left to right
d) Strand that is 3‟ to 5‟ left to right
e) Promoter9) Dictyostelium discoideum has relatively fragile DNA, with a genome
consisting of only 13.7% guanine. What percent adenine are in these cells ?
a) 13.7%
b) 27.4%
c) 72.6%
d) 36.3%
e) 18.2%
10) Which of the following prokaryotic RNA polymerase subunits is part of
the core enzyme that binds to DNA ? (b – binding, a – assembly)
a) σ (sigma factor)
b) β (beta)
c) β‟ (beta prime)
d) α (alpha)
e) ω (omega)11) The following DNA double helix is read from right to left by an RNA polymerase.
What mRNA sequence would it express?
5‟ TAGCTAGCT 3‟ template strand
3‟ ATCGATCGA 5‟ coding strand
a) 5‟ UAGCUACGU 3‟
b) 5‟ AUCGAUCGA 3‟
c) 3‟ UAGCUAGCU 5‟
d) 3‟ AUCGAUCGA 5‟
e) 5‟ UAGCUAGCU 3‟
12) The translation system consists of 5 major components. Which of the following
involves small adaptor molecules that mediate codon translation into specific amino
acids ?
a) Messenger RNA
b) Transfer RNA
c) Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
d) Ribosome
e) Initiation and elongation factors.13) Which of the following proteins functions in the transcription of eukaryotic pre
mRNAs ?
a) RNA polymerase
b) RNA polymerase I
c) RNA polymerase II
d) RNA polymerase III
e) RNA polymerase IV
14) The carboxyl tail domain (CTD) is a key component of RNA polymerase II. Which
of the following is not one of its functions ?
a) When it is phosphorolated, RNA polymerase begins transcribing
DNA.
b) It is involved with capping enzymes in adding the 5‟ cap.
c) It has a role in removing nucleosomes and rewinding them after DNA is
transcribed. (FACT)
d) It interacts with RNA splicing machinery to join exons.
e) It is involved in adding the polyA tail.15) How is transcription terminated in eukaryotes?
(a) The ribosome reaches the Shine Dalgarno sequence and falls off the DNA strand
(b) The RNA polymerase recognizes a termination sequence.
(c) Rho binds to the rut site, destabilizing the interaction between RNA polymerase and
the DNA strand.
(d) TBP binds to the DNA causing the RNA polymerase to fall off the DNA strand.
16) What are the amino acids of the polypeptide expressed by the gene in the DNA
sequence below?
5'-ACG TCA GTG GCA CAT AAT CGC GGT-3'
3‟ TGC AGT CAC CGT GTA TTA GCG CCA-5‟
(a) methionine-tyrosine-glutamine
(b) threonine-alanine-isoleucine
(c) methionine-cystine-histidine
(d) methionine tryptophan-arginine
(e) none of the above17) Which of the following is the correct sequence of 5 events that initiate prokaryote
translation ?
events
i) binding of Shine - Delgano sequence to the small ribosome subunit
ii) recruitment of the large subunit
iii) IF1 and IF3 recruit the small ribosome subunit
iv) IF2 recruits fMet tRNA
v ) Initiation factors dissociate from ribosome
a) i >ii > iii .> iv > v
b) iii > iv > i > v > ii
c) ii > iv > iii > i > v
d) iv > ii > iii > i > v
e) none of the above
18) The first tRNA leaves an intact ribosome with both subunits at the_______.
a) A site
b) P site
c) E site
d) B site
e) C site19) In the absence of glucose, lac operon regulation is best described as:
a) Negative inducible
b) Negative repressible
c) Positive repressible
d) Positive inducible
e) Positive repressible or negative inducible
20) If lactose-metabolizing enzymes are produced whether or not lactose is
present (constitutive), a mutation in which gene is the likely cause?
a) lac I
b) Operator
c) Promoter
d) lac Z
e) either A or B is correctNegative Control Positive Control
Inducible
(de-represses a gene,
turns a gene on,
promotes transcription)
Lac operon control
- Inducer (lactose)
binds repressor,
releases from operator,
expression ON
RNA Polymerase
- Can only bind
promoter when DNA
unwound from
nucleosome, inducer
bound near promoter
(TBP binding TATA box,
eukaryotic)
Repressible
(stops/slows expression
of a gene, must be
bound first by corepressor)
Trp regulation
- Repressor produced
by trp R site, can only
bind operator after trp
binds (ON)
Glucose-cAMP
- Glucose represses
cAMP, CAP can’t bind
5’end of promoter, lac
operon off, little
transcription21) Ionizing radiation damages DNA by
a) causing dimers or strand breakage.
b) causing base substitution
c) depurinating the DNA.
d) a process called intercalation.
e) replication slippage.
22) If the I-O+P+Z-Y+ strain of bacteria is tested in the presence of glucose,
which of the following will be observed in high (+) or low (-) copy number or
expression levels ?
b-galactosidase Permease
Lactose present Lactose Absent Lactose present Lactose Absent
a) + - + -
b) + + + +
c) - - - -
d) - - + -
e) + + - -23) If the Is P+O+Z-Y+/F’ P+OcZ+Y-, strain of bacteria is tested in the absence of
glucose, which of the following will be observed in high (+) or low (-) copy number
or expression levels ?
b galactosidase Permease
Lactose present Lactose Absent Lactose present Lactose Absent
a) + - + -
b) + + + +
c) - - - -
d) - - + -
e) + + - -
24) Which is not part of the lac operon?
a) Repressor
b) Activator protein
c) Operator
d) Promoter
e) Structural gene25) Which of the following statements about the role of tryptophan in the
regulation of its metabolic pathway is correct ?
a) Tryptophan binds to the 5‟ upstream sequence blocking the polymerase
from expressing trp mRNA.
b) Tryptophan binds to the trp repressor causing it to bind to the operator
sequence blocking transcription.
c) Tryptophan binds to the trp repressor causing it to detach from the operator
allowing expression
d) Tryptophan does not have a role in the global regulation of its synthesis.
e) High tryptophan blocks tryptophan repressor expression.
26) In the RNAi regulatory pathway, the DICER enzyme:
a) cuts RNA polymerase into non-functional pieces.
b) binds single stranded mDNA and converts to to double stranded RNA.
c) cuts double-stranded RNA into shorter duplex (double stranded) molecules.
d) binds mRNAs of genes to be repressed.
e) unwinds double stranded mRNA.27) T to A or G toT mutations are
a) transition mutations.
b) transversion mutations.
c) translation mutations.
d) transcription mutations.
e) conditional mutations.
28) Over a wide range of x-ray doses, when the radiation dose is increased,
which is the best description of how the mutation rate changes in response ?
a) increases exponentially.
b) increases linearly.
c) stays constant.
d) is a diminishing exponential.
e) changes independently.29) You believe that there has been a reciprocal translocation between genes A
and B in a species of plant that you are studying. The genes are known to be on
different chromosomes in a closely related species. Which of the data below
would support that a reciprocal translocation had happened?
a) The two genes show a recombination frequency of 50%.
b) The two genes show a recombination frequency of 0%.
c) The two genes show linkage.
d) The recombination frequency of linked genes drops to zero.
e) The recombination frequency decreases.
30) Base substitutions in coding regions that result in changed amino acids are
called
a) conditional mutations.
b) transversions.
c) missense mutations.
d) nonsense mutations.
e) silent mutations.31) Which of the following large chromosome mutations never recombines ?
a) duplications
b) translocations
c) inversions
d) deletions
e) all of the above
32) How many synonymous changes can be made by single base-pair
substitution starting with the codon CGG (arg) ?
a) None
b) Two
c) Three
d) Four
e) Six1) Which of the following is not related to DNA stability under normal
physiological conditions ?
a) Two covalently bound, external strands.
b) Covalent strands bound by many hydrogen bonds.
c) The strands are overwound in a right handed helix.
d) Internal hydrophyllic interactions stabilize hydrogen bonds.
e) Externally stabilized by the polar nature of water interacting with
charged phosphate groups.
2) The primasome which is located on the lagging strand side of the
replication fork is made up of two different proteins. What are they?
a) A topoisomerase and primase
b) A primase and helicase
c) DNA polymerase and primase
d) Ligase and DNA polymerase
e) Helicase and ligase
Version B3) Which of the following translation rules is incorrect?
a) There are start (AUG) codons.
b) There is no space or extra nucleotides between codons.
c) The codons do not overlap.
d) Triplet reading is from the 3‟ end to the 5‟ end.
e) There are 3 possible stop signals (UAG, UAA, UGA).
4) Replication of the bottom DNA strand labeled “B*” would involve:
a) Discontinuous synthesis -- of the lagging strand
b) Discontinuous synthesis – of the leading strand
c) Continuous synthesis – of the lagging strand
d) Continuous synthesis – of the leading strand
e) None of the above5) Which of the following investigators was/were responsible for the following
discovery? Chemicals from heat-killed S cells were purified. The chemicals were
tested for the ability to transform live R cells. The transforming agent was found
to be DNA.
a) Frederick Griffith
b) Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase
c) Oswald Avery, Maclyn McCarty, and Colin MacLeod
d) Erwin Chargaff
e) Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl
6) Most DNA under normal physiological conditions (b DNA) would be correctly
described as which of the following?
a) a right handed helix, positively supercoiled, ~ 10 bases double per helix turn.
b) a left handed helix, negatively supercoiled, ~ 5 bases per double helix turn.
c) a right handed helix, negatively supercoiled ~10 bases per double helix turn.
d) a left handed helix, positively supercoiled ~ 5 bases per double helix turn.
e) a left handed helix, negatively supercoiled ~ 10 bases per double helix turn.7) What is the Okazaki sequence from the following duplex DNA where the leading
strand is being synthesized from left to right?
5’ ATATGCGC 3’ lagging strand
3’ TATACGCG 5’ leading strand
a) 5’ TATACGCG 3’
b) 3’ TATACGCG 5’
c) 3’ ATATGCGC 5’
d) 5’ ATATGCGC 3’
e) none of the above
8) Please choose the answer containing correct groups presenting at the 2’ position and
5’s in a deoxyribose nucleotide.
a) H and phosphate
b) nitrogenous base and H
c) OH and H,
d) nitrogenous base and phosphate
e) phosphate and OH9) Which of the following is not true about the carboxyl tail domain of RNA polymerase II
?
a) It is highly phosphorylated
b) It recognizes the termination sequence (RNA polymerase)
c) It attaches the 5’ cap
d) It attaches the 3’ tail
e) splices out introns
10) Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and
transcription?
a) Nucleotides are added to the 5’ end of the newly synthesized strand
b) A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3’ hydroxyl and the 5’ phosphate
c) Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence
d) Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming
e) Both RNA and DNA polymerase initiate at promoter sequences11) If there is 20% of T in the DNA double stands, how many G would you
expect in this DNA
a) 10%
b) 15%
c) 20%
d) 25%
e) 30%
12) Which of the following prokaryotic RNA polymerase subunits is
responsible for its assembly and interacting with regulatory proteins ?
a) σ (sigma factor)
b) β (beta)
c) β‟ (beta prime)
d) α (alpha)
e) ω (omega)13) The following DNA double helix is read from left to right by an RNA
polymerase. What would be the primary mRNA sequence?
5‟ TAGCTAGCT 3‟ coding strand
3‟ ATCGATCGA 5‟ template strand
a) 5‟ UAGCUACGU 3‟
b) 5‟ AUCGAUCGA 3‟
c) 3‟ UAGCUAGCU 5‟
d) 3‟ AUCGAUCGA 5‟
e) 5‟ UAGCUAGCU 3‟
14) Which of the following proteins functions in the transcription of most
eukaryotic ribosomal RNAs (r RNA)?
a) RNA polymerase
b) RNA polymerase I (rRNA)
c) RNA polymerase II (mRNA)
d) RNA polymerase III (tRNA, small RNAs)
e) RNA polymerase IV15) Which of the following statements about RNA splicing is entirely correct?
a) Alternative splicing is the process where different exons and introns are recombined from the
same transcript to produce different proteins.
b) Intron cuts at the 5‟ splice site are almost always signaled by the transcript sequence GU and
at the 3‟end, AG.
c) Splicing the mRNA transcript happens after the pre mRNA transcript is terminated (post –
translational processing)
d) Splicesomes remove exons and join introns to make mRNA.
e) Splicesome proteins catalyze intron removal at 5‟AG and 3‟ GU, whereas the small nuclear
RNA component recognizes these cutting sites.
16) What are the amino acids of the polypeptide expressed by the gene in the DNA sequence
below?
5'-ACG TCA TTC GTA CAT AAT CGC GGT-3'
3‟ TGC AGT AAG CAT GTA TTA GCG CCA-5‟
(a) methionine-tyrosine-glutamine
(b) threonine-alanine-isoleucine
(c) methionine-valine-histidine
(d) methionine tryptophan-arginine
(e) none of the above17) Choose the answer that has the actual sequence of the first events in protein
synthesis.
events
1. An aminoacyl-tRNA binds to the A site.
2. A peptide bond forms between the new amino acid and met-tRNA.
3 met- tRNA leaves the P site, and the ribosome translocates
4 GDP occupies the A site and met- tRNA is in the E site.
5. (n-formly) met-tRNA translocates to the P site.
a) 1> 3> 2> 4>5
b) 4>1> 2> 5>3
c) 5> 4>3> 2> 1
d) 4> 1> 3> 2> 5
e) 5> 1> 2> 3> 4
18) Translational initiation in prokaryotes starts at... and amino acids are attached to tRNAs
by enzymes called… .
A. TATA box, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
B. Shine-Dalgarno, aminoacyl-tRNA transferase
C. TATA box, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
D. Shine-Dalgarno, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
E. Shine-Dalgarno, charged aminoacyl-tRNA19) In the presence of glucose and absence of lactose the lac operon is best
described as:
a) Negative inducible
b) Negative repressible
c) Positive repressible
d) Positive inducible
e) Positive repressible and negative inducible
20) What is the function of the permease enzyme in the lac metabolism?
a) To digest the other breakdown product of galactose
b) To transport lactose into the cell
c) To up regulate the lac operon
d) To form a complex with B-galactosidase which in turn cleaves
lactose
e) The function is unknown.Negative Control Positive Control
Inducible
(de-represses a gene,
turns a gene on,
promotes transcription)
Lac operon control
- Inducer (lactose)
binds repressor,
releases from operator,
expression ON
RNA Polymerase
- Can only bind
promoter when DNA
unwound from
nucleosome, inducer
bound near promoter
(TBP binding TATA box,
eukaryotic)
Repressible
(stops/slows expression
of a gene, must be
bound first by corepressor)
Trp regulation
- Repressor produced
by trp R site, can only
bind operator after trp
binds (ON)
Glucose-cAMP
- Glucose represses
cAMP, CAP can’t bind
5’end of promoter, lac
operon off, little
transcription21) Which one of the following statements about eukaryotic gene regulation is correct?
a) Large polycistronic transcripts are common.
b) Most regulation is positive, involving activators rather than repressors.
c) Transcription and translation are mechanistically coupled.
d) Transcription does not involve promoters.
e) Transcription generally occurs in heterochromatic nuclear areas.
22) If the I-O+P+Z+Y- strain of bacteria is tested in the presence of glucose
which of the following will be observed in high (+) or low (-) copy number or expression
levels ?
b galactosidase Permease
Lactose present Lactose Absent Lactose present Lactose Absent
a) + - + -
b) + + - -
c) + + + +
d) + - - -
e) none of the above23) If the I+ P+O+Z-Y+/F‟P+OcZ+Y-, strain of bacteria is tested in the absence of glucose
which of the following will be observed in high (+) or low (-) copy number or expression
levels ?
b galactosidase Permease
Lactose present Lactose Absent Lactose present Lactose Absent
a) + - + -
b) + + - -
c) + + + -
d) + - - -
e) none of the above
24) What would be the effect of a mutation in the operator that did not allow lac repressor
binding?
a) The lacZYA genes would not be expressed
b) The lacZYA genes would be expressed constitutively
c) The genes would be inducible by lactose
d) The lacZYA genes would be repressed by lactose
e) None of the above25) Which of the following statements, concerning regulation of trp operon expression by
attenuation, is correct?
a) The leader peptide sequence encodes enzymes required for tryptophan synthesis.
b) The leader peptide sequence contains no tryptophan residues.
c) Rapid translation of the leader peptide allows completion of the mRNA transcript.
d) Rapid translation of the leader peptide prevents completion of the mRNA transcript.
26) Which of the following statements correctly describes how gene expression is downregulated (or mRNA is degraded) through RNAi ?
a) RNA molecules cause cleavage of double-stranded DNA of specific genes.
b) short single stranded RNAs associated with a RISC/Argonaut protein bind to
complementary mRNAs.
c) The DICER enzyme binds to and cleaves mRNAs.
d) RNAi involves binding of long RNA (>100 bases) to a target gene to inactivate it.
e) The Argonaut protein unwinds double stranded mRNA rendering it non-functional.27) T to C or A to G mutations are
a) transition mutations.
b) transversion mutations.
c) translation mutations.
d) transcription mutations.
e) conditional mutations
28) A spontaneous mutation usually originates as an error in:
a) Transcription
b) Replication
c) Translation
d) Reverse transcription
e) Splicing29) Base substitutions that create a new stop codon are called:
a) transitions.
b) permissive mutations.
c) missense mutations.
d) nonsense mutations.
e) silent mutations.
30) Which of the following large chromosome mutations is associated with no
viable recombination heterozygotes recovered from crosses of homozygous
parentals ?
a) Duplications
b) reciprocal translocations
c) Inversions
d) Deletions
e) all of the above31) Which of the following has biological significance for DNA methylation in E.
coli?
a) To orient DNA during cell division
b) To allow the recognition of a newly synthesized strand
c) To stabilize the tautomeric shift of Guanine, reducing mutations
d) To strengthen the hydrogen bonds between bases, reducing mutations
e) To signal a gene is turned off.
32) How many silent mutations can result from a single base substitution in the
unique tryptophan codon UGG?
a) 0
b) 3
c) 6
d) 9
e) none of the above
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages






.png)

.png)