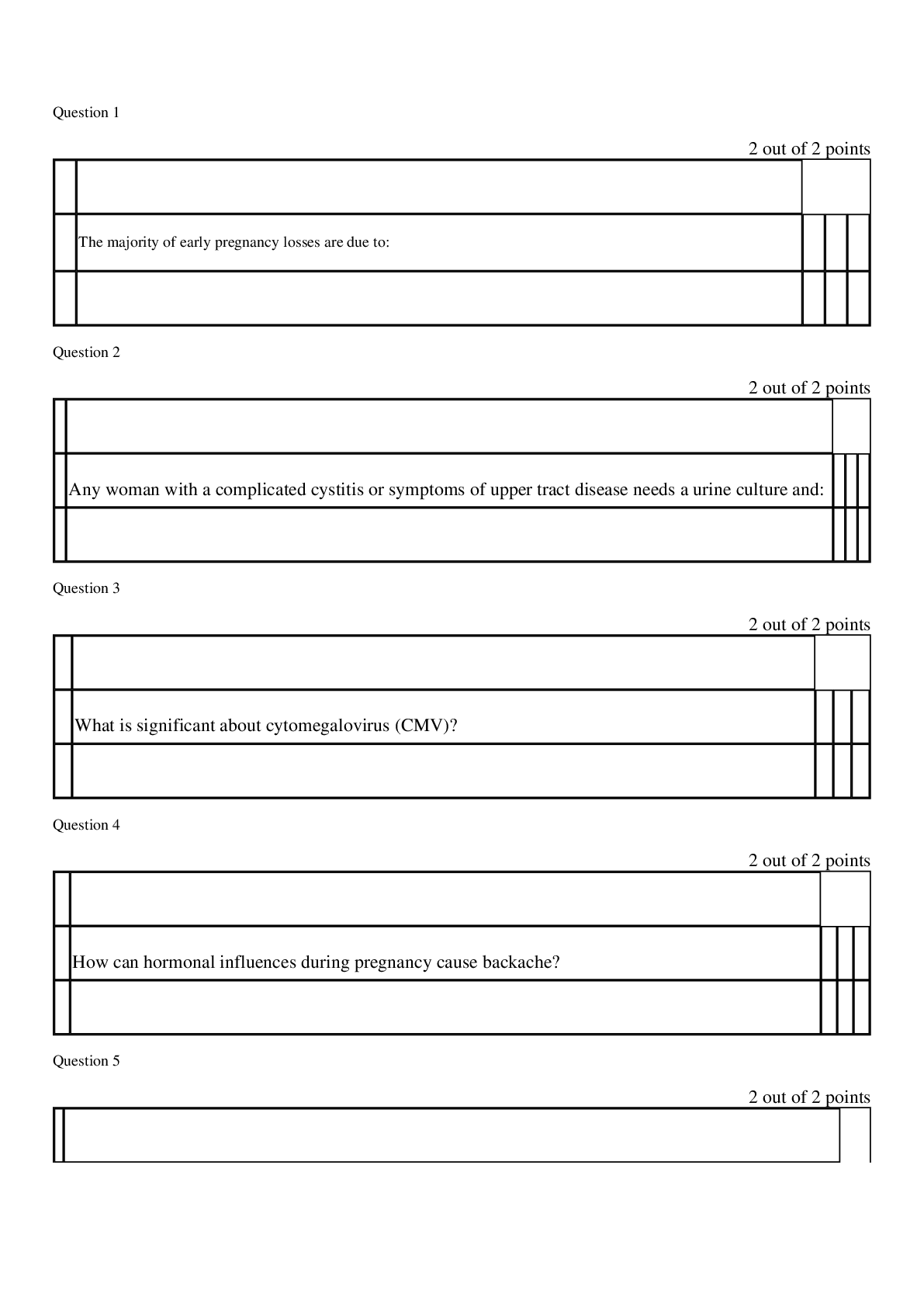
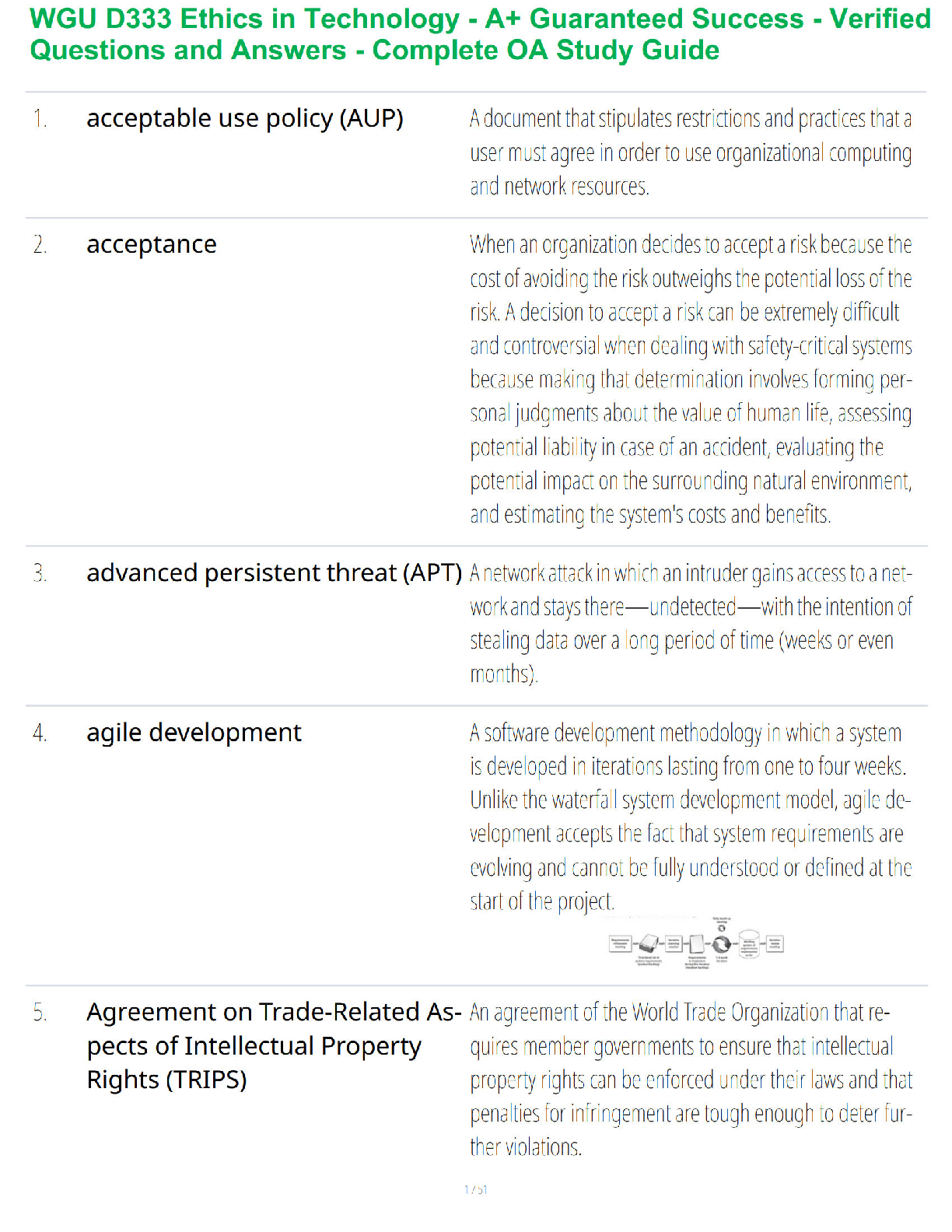
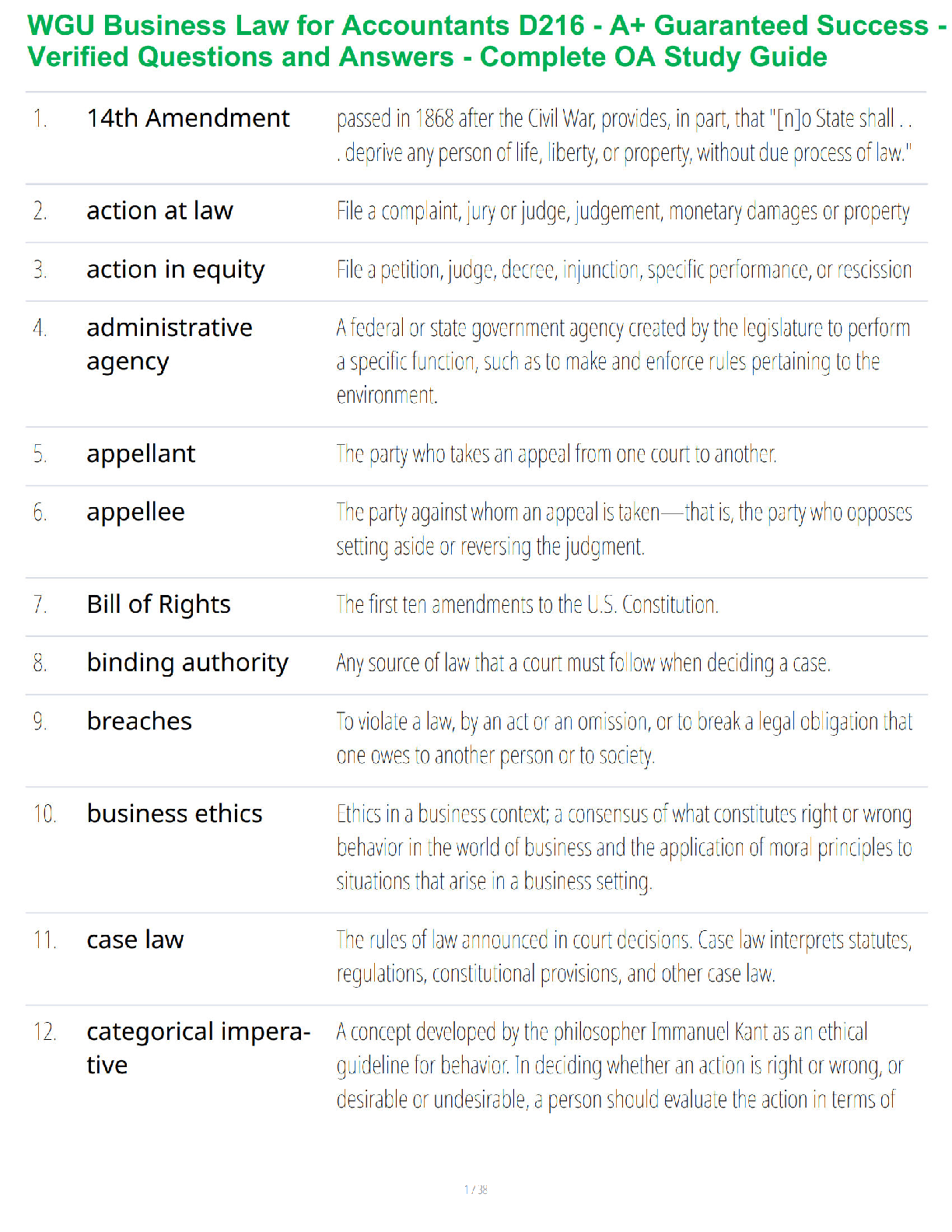
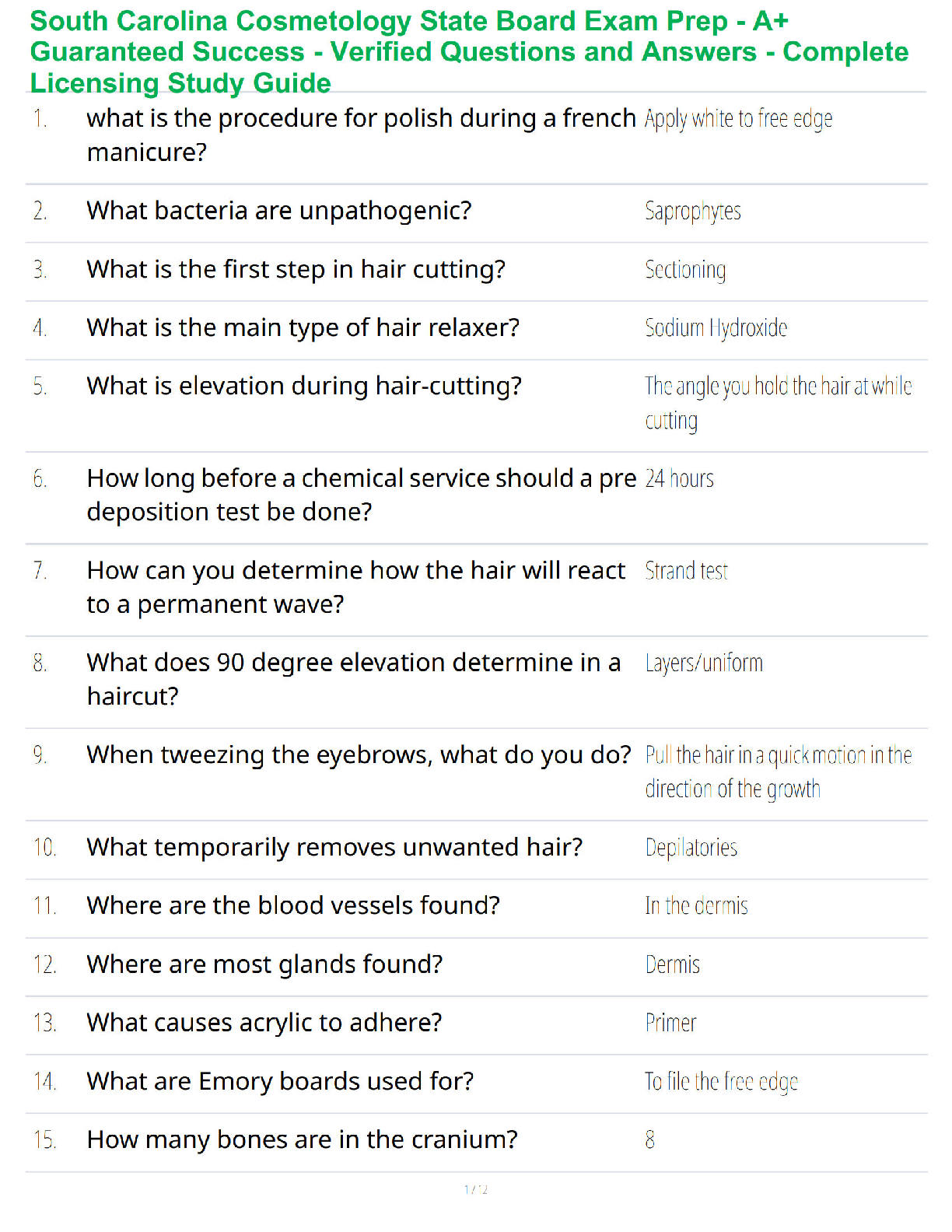
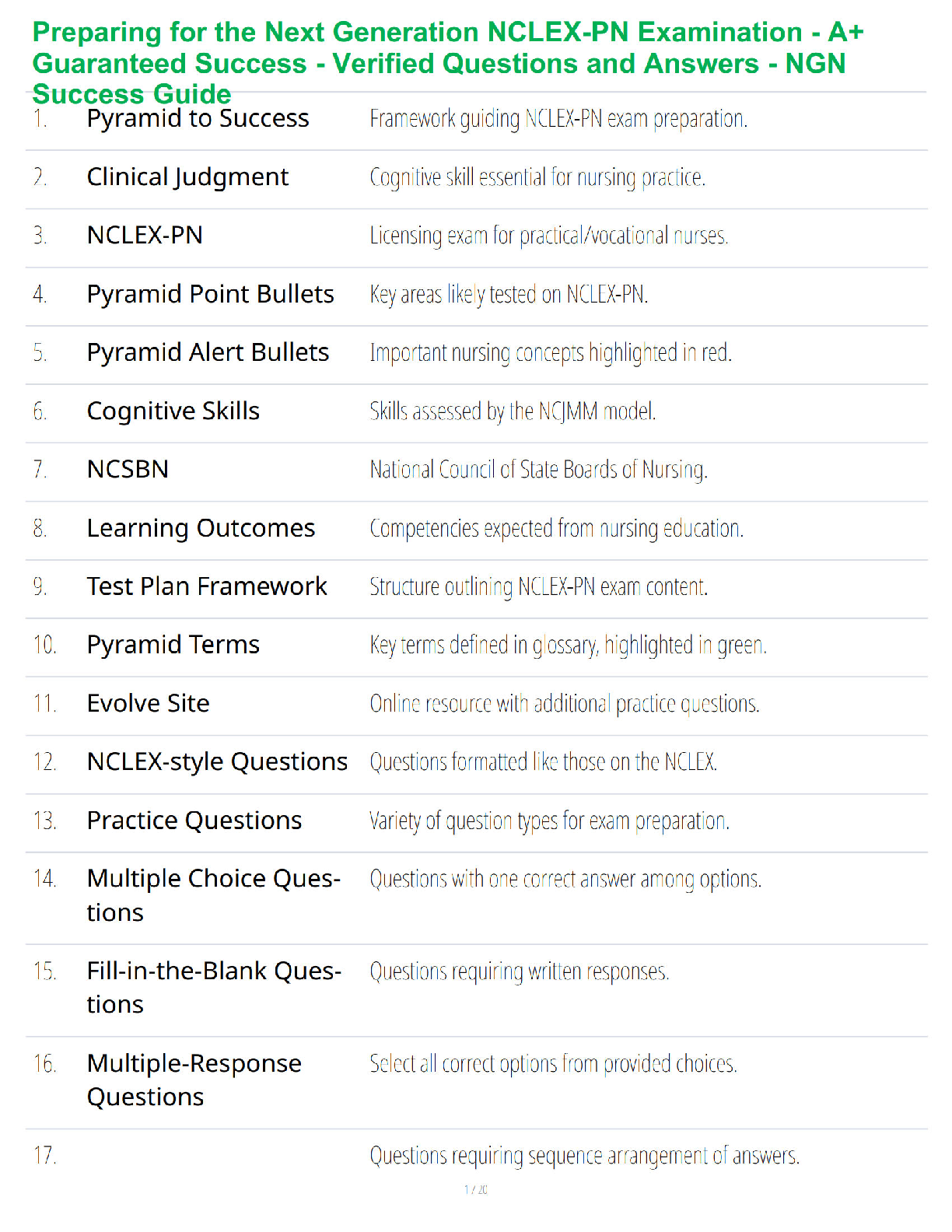
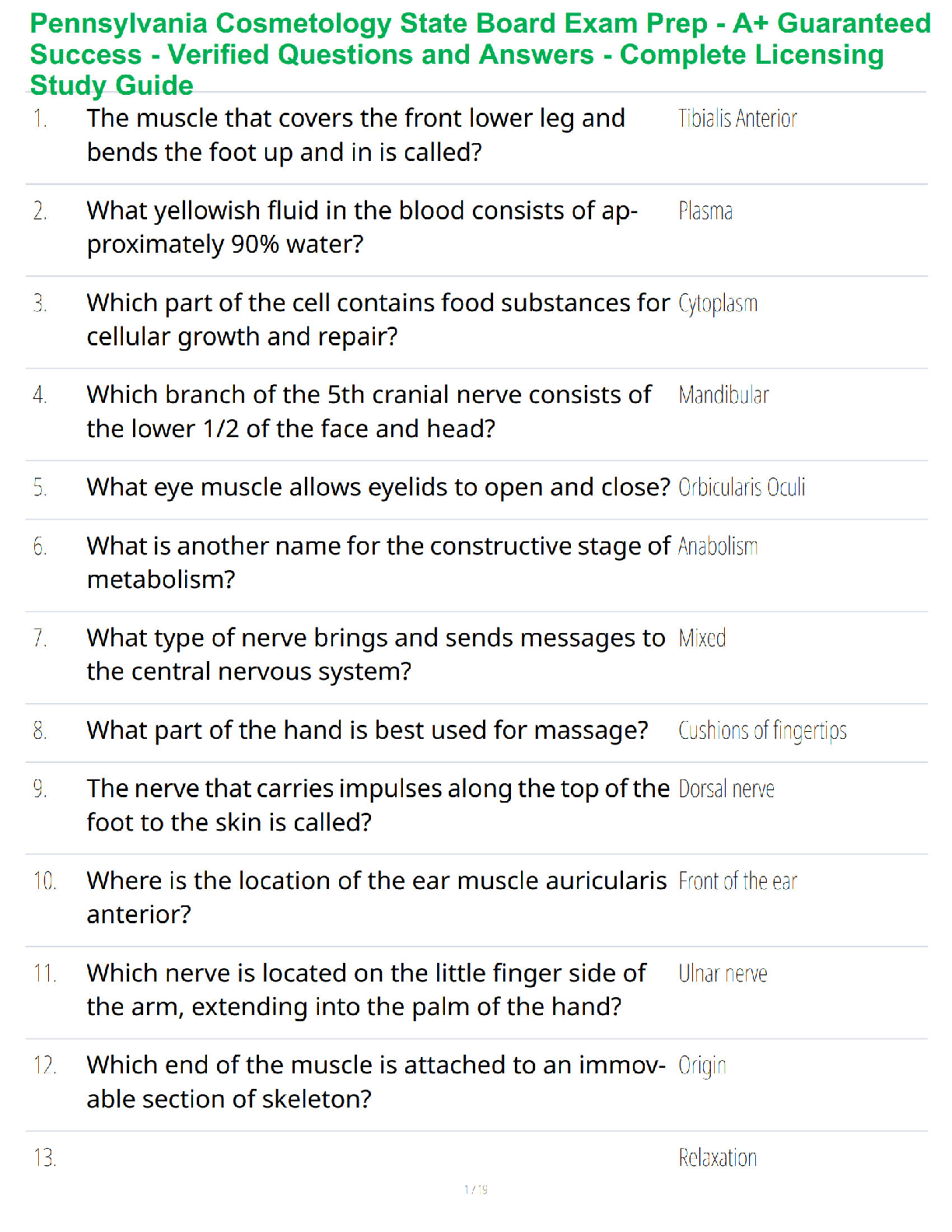
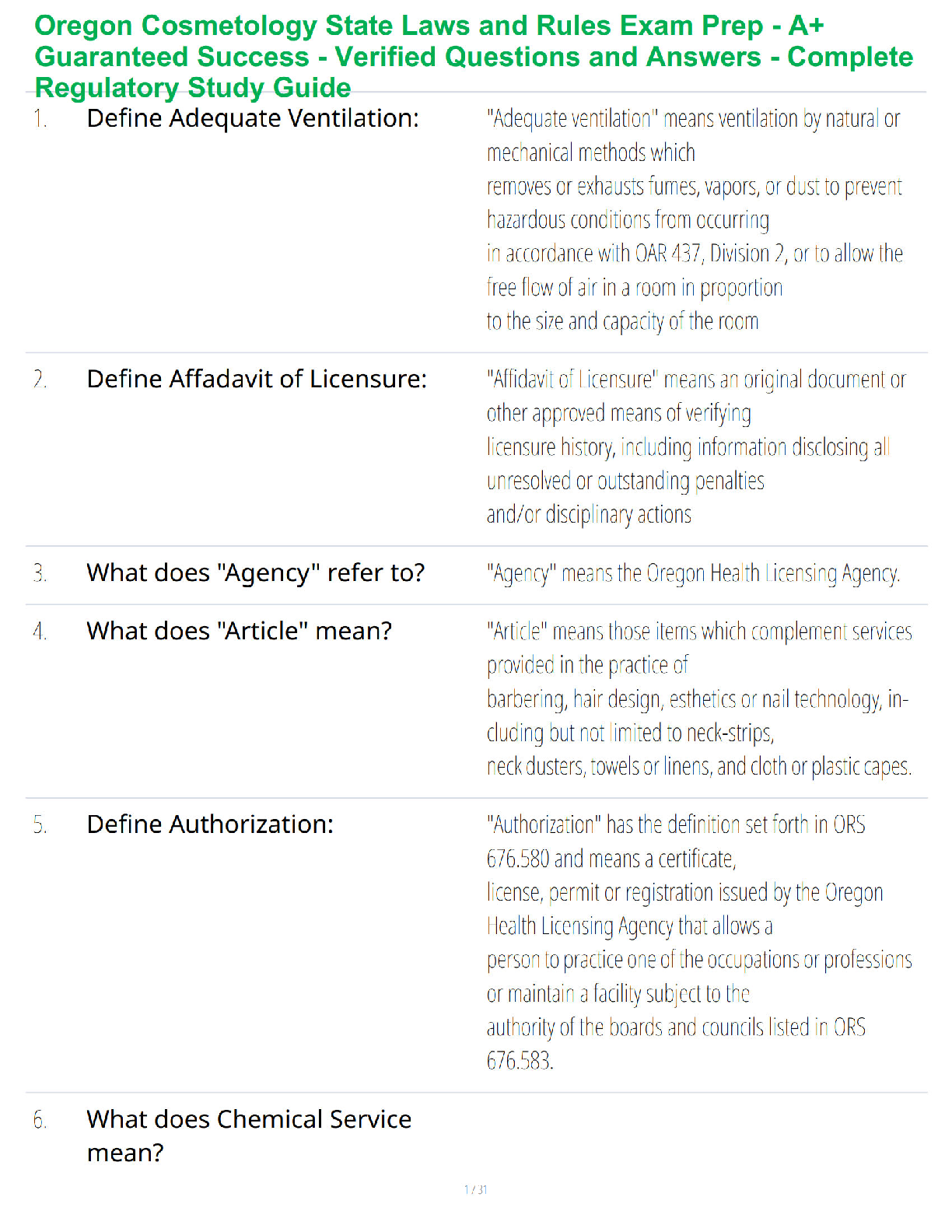
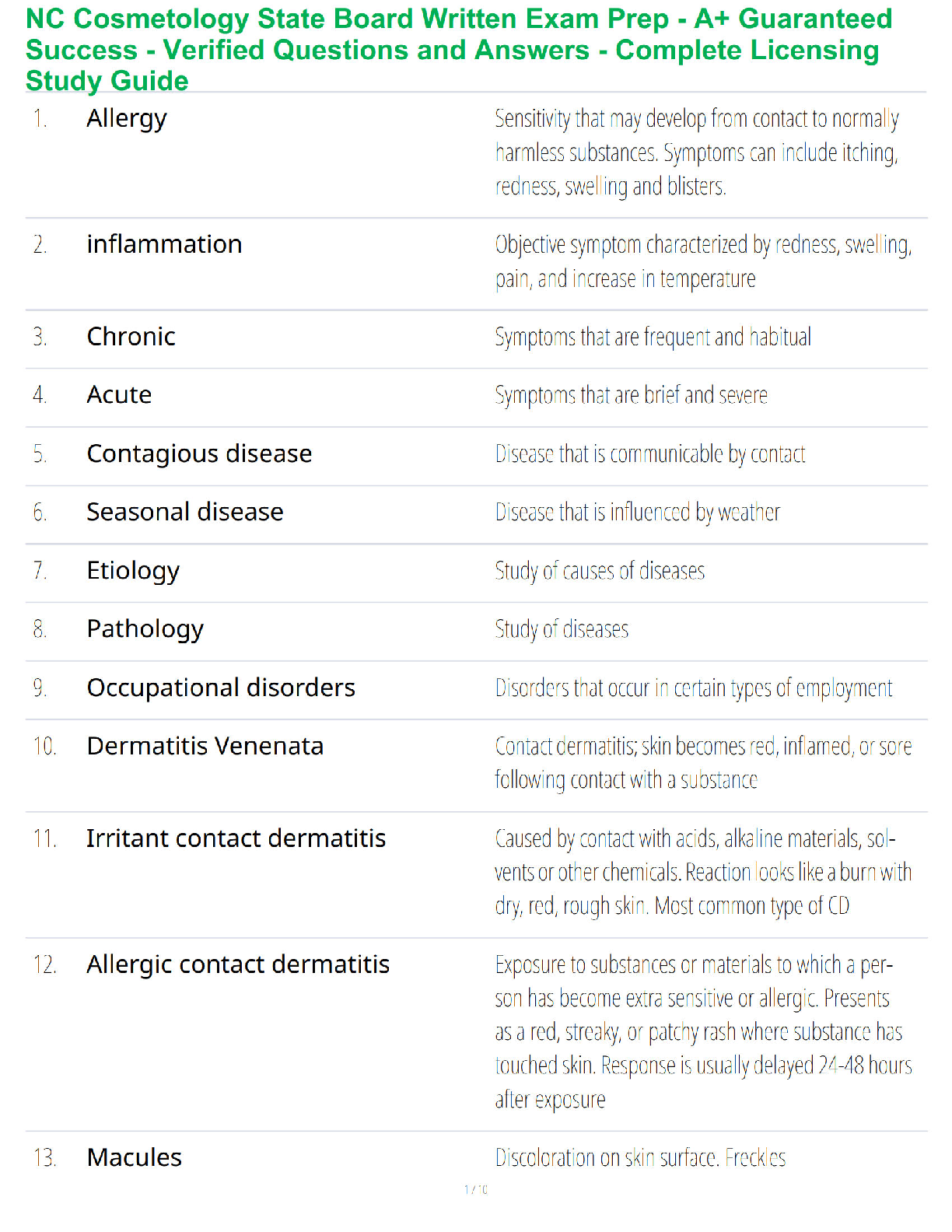
1. Conduct Disorder (Cruelty to
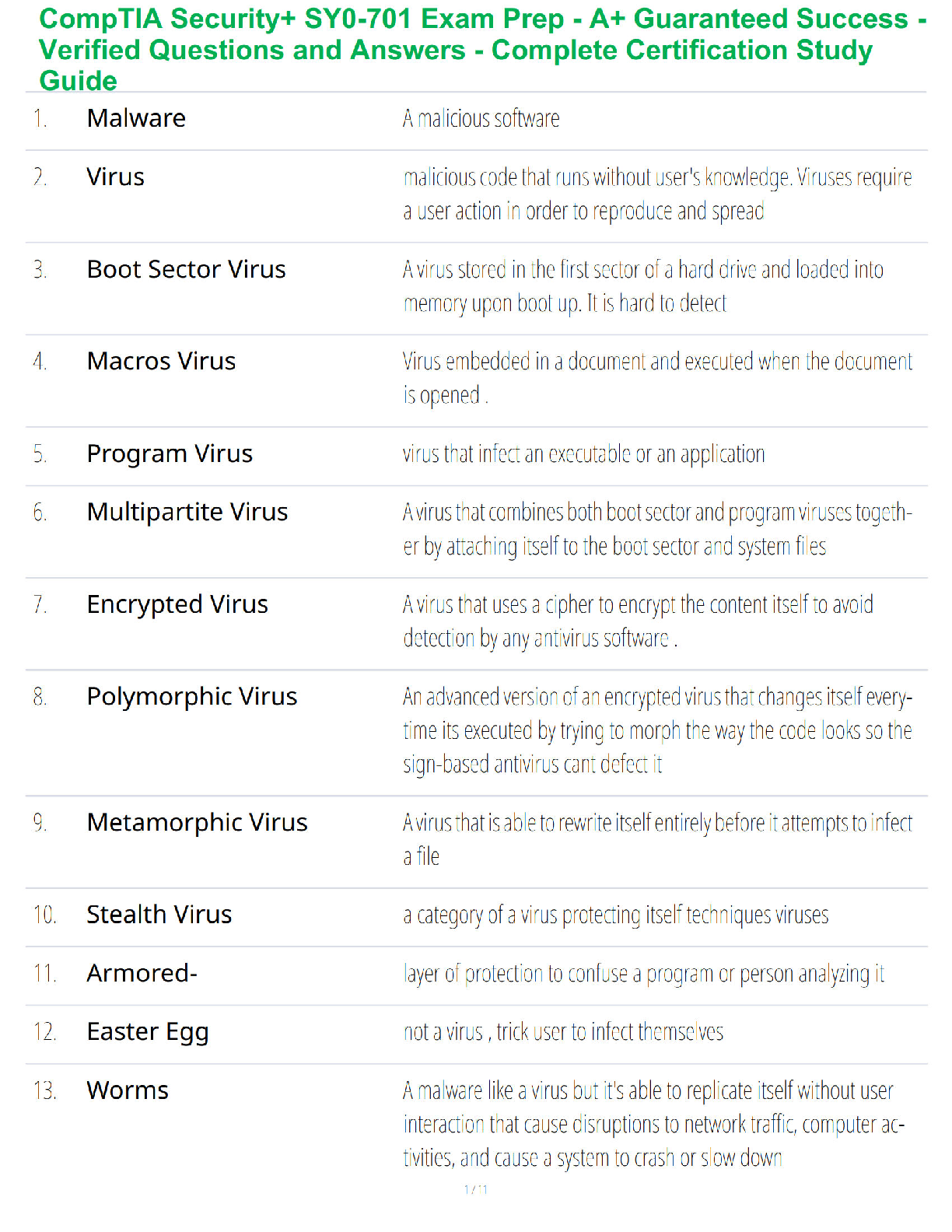
Animals)
Demonstrate a persistent pattern of behavior that violates the
rights of others or rules/norms of society.
In simpler words… CONDUCT DISORDER = BREAKS LAWS! MAKE
SURE THEY
...
1. Conduct Disorder (Cruelty to
Animals)
Demonstrate a persistent pattern of behavior that violates the
rights of others or rules/norms of society.
In simpler words… CONDUCT DISORDER = BREAKS LAWS! MAKE
SURE THEY ARE AWARE OF THE RULES OF THE UNIT AND ANY
CONSEQUENCES OF VIOLATING THOSE RULES
Categories include:
*Assess Aggression towards people & animals
*Destruction property
*Deceitfulness or theft
*Serious violation of rules
2. Alcohol Abuse It declines as you age!
3. A nurse is caring for a client with
bipolar disorder. Client comes to the
nurses’ station at 3 am asking the
nurse to call the doctor. Which
response is the most appropriate?
a. You are being unreasonable
b. Go back to your room & I will get in touch later
c. I can’t call the doctor until later unless it’s an emergency
d. You seem upset, can I help you?
4. Benztropine (Cogentin) Why is it given?
*To treat Parkinson disease and also to control tremors and
stiffness of the muscles due to antipsychotic medications
(antipsychotics 1st-gen)
Treats EPS symptoms: (usually the 1st choice – can be given PPX
*Acute dystonia- severe spasm of the tongue, neck, face, & back
(crisis)
*Parkinsonism- bradykinesia, rigidity, shuffling gait, tremors,
drooling
*Akathisia- inability to sit/stand still & continual pacing & agitation.
*Tardive dyskinesia- late EPS, involuntary movement of tongue &
face, such as lip smacking & tongue fasciculation, involuntary
movement of arms, legs, & trunk.
5. A client is sleepwalking. The nurse
should include following discharge
(SATA)
a. Clutter free
b. Sleep on the ground floor
c. Lock doors & windows
d. Alarm on bed
e. Hide car keysc
DO NOT rearrange furniture
6. A client fell & had an abrasion on the
forehead. Who can write an incident
report/variance report?
Anyone who actually SAW the incident can write it (NOT he said,
she said):
*CNA, LVN, or RN
the person who witnessed the fall (cosigned by the RN)
7. S/S of Acute Grief Grief is the inner emotional response to loss & is exhibited in as
many ways as there are individuals.
Emotional S/S: anger, restlessness, resentment, withdrawal,
hopelessness, & guilt
Somatic S/S: chest pain (tightness), palpitations, headaches, nausea,
changes in sleep, fatigue
8. S/S of ADHD Inability of a person to control behaviors requiring sustained
attention
S/S: impulsive, hyperactive, inattention, & not able to focus well
9. Erikson’s Stages of Development Trust vs. Mistrust (Infancy 0-1½ years)
*Forming attachment to mother, which lays foundation for later trust
in others.
Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt (Early Childhood 1½-3 years)
*Gaining some basic control of self & environment (toilet training,
exploration)
Initiative vs. Guilt (Preschool 3-6 years)
*Becoming purposeful & directive
Industry vs. Inferiority (School Age 6-12 years)
*Developing social, physical, & school skills
Identity vs. Role Confusion (Adolescence 12-20 years)
*Making transition from childhood to adulthood; developing sense of
identity
Intimacy vs. Isolation (Early Adulthood 20-25 years)
*Establishing intimate bonds of love & friendship
Generativity vs. Self-Absorption (Middle Adulthood 35-65 years)
*Fulfilling life goals that involve family, career, & society; developing
concerns that embrace future generations
Integrity vs. Despair (Later Years 65 years-death)
*Looking back over one’s life & accepting its meaning
[Show More]