*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR 566 Midterm Study Guide | NR 566 midterm 2022-Chamberlain College of Nursing (All)
NR 566 Midterm Study Guide | NR 566 midterm 2022-Chamberlain College of Nursing
Document Content and Description Below
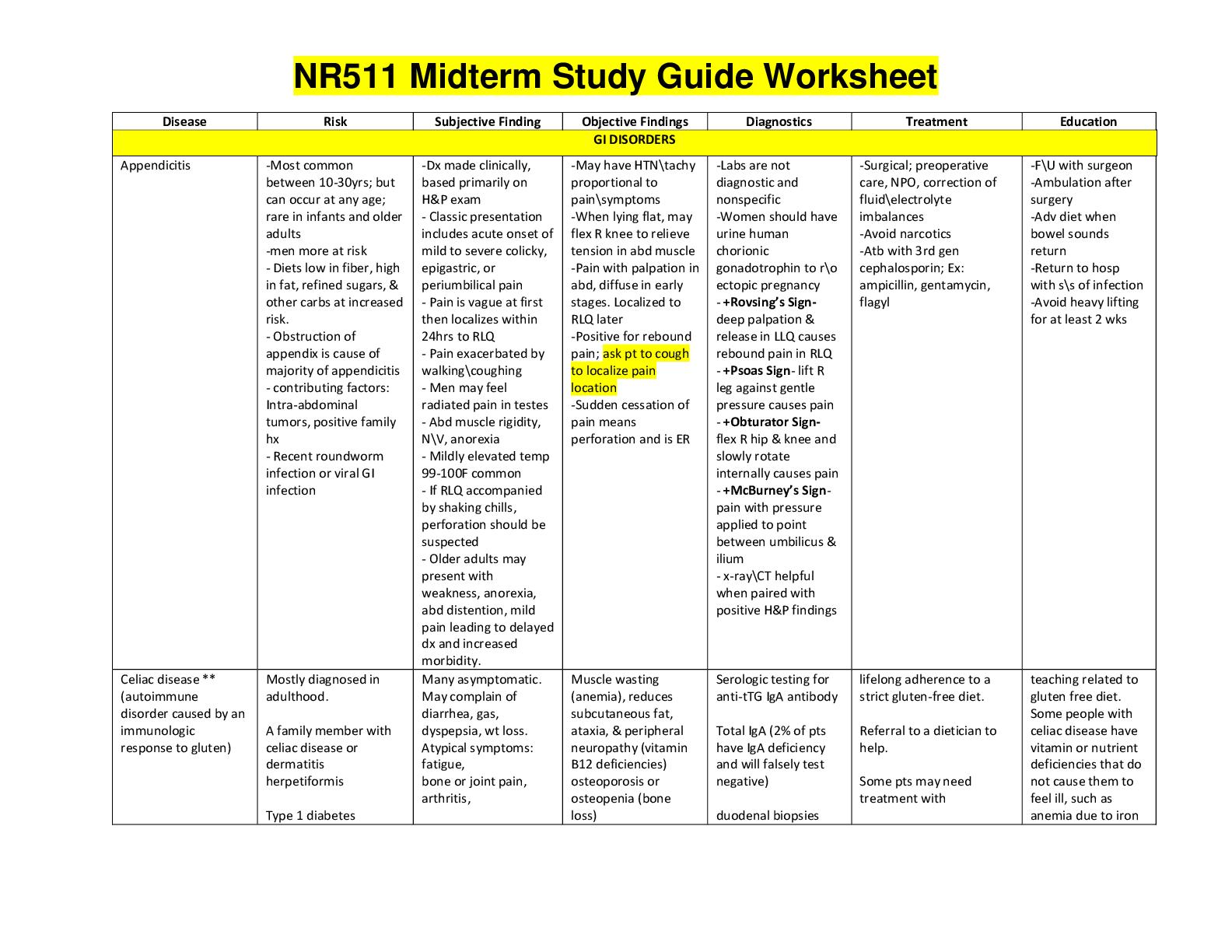
566 Midterm Study Guide WEEK 1 -Things to know about each of the major antibiotic drug classes · Contraindications and high-risk patients · Know examples of each of the major antibiotic drug cla... sses · Monitoring needs · Which ones require renal dosing adjustments and how much (i.e., 25%, 50%, etc.) · Patient education · Lifespan considerations including pregnancy · Indications for use Penicillins caution with patients allergic reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or carbapenems Treats infection cause by sensitive bacteria check culture to identify infecting organism Can order skin test to assess allergy status adjusted doses for patients with impaired renal fnx NARROW SPECTRUM PENICILLINS: PENICILLIN SENSITIVE(PEN G &PEN V) - Mechanism of Action : “Bactericidal”- Weakens the cell wall, causing bacteria to take up excessive amounts of water and rupture. Occurs by two actions simultaneously: inhibiting transpeptidases and activating autolysins which disrupts synthesis of the cell wall and promotes the active destruction resulting in cell lysis and death. -Examples: Penicillin G (Prototype Drug), Penicillin V, Nafcillin, Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin, Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Piperacillin Penicillin G- -First Penicillin Available and often referred to plainly as Penicillin -Bactericidal for gram negative and gram positive bacteria -Should be taken with medications whereas Penicillin V is stable in stomach acids. -Side Effects: Allergic reactions, pain at IM injection sites, prolonged (but reversible) sensory and motor dysfunction if injected into peripheral nerves, and neurotoxicity (seizures, confusion, hallucinations- if levels too high) . -Life Span Considerations: *Infants- Used safely in infants with bacterial infections including syphilis, meningitis, & group A streptococcus *Children/Adolescents- Common drug used to treat bacterial infections in children. *Pregnant- No well controlled studies but evidence suggests no 2nd or 3rd trimester fetal risk. *Breastfeeding- Amoxicillin is safe. Data is lacking about transmission of other PCNs from mother to infant through breast milk. *Older Adults- Doses should be adjusted in older adults with renal dysfunction. Penicillin Allergy: -Most common drug allergy to date with severity ranging from minor rash to anaphylaxis -Can possibly display cross sensitivity to cephalosporins and should not be used if possible -observed 30 minutes minimum post drug injection for adverse reactions -For history of PCN allergy, a skin allergy test can be done to assess current risk by injecting a tiny amount of allergen ID (only to be done where epinephrine and respiratory support is available if needed) Penicillin V- Stable in stomach acid (Pen G is not) Used for oral therapy, can be taken with meals NARROW SPECTRUM PENICILLIN: PENICILLIN RESISTANT: (Nafcillin, Oxacillin, Dicloxacillin) -Treats S. aureus and S. epidermidis Broad-Spectrum Penicillins ( Ampicillin & Amoxicillin ): -Most common side effects are rash and diarrhea (rash usually 3-10 days post TX start). -Therapy can be PO or IV and requires dosage adjustment for renal impairment -Treats Haemophilus influenzae, E. Coli, proteus mirabilis, enterococci, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae EXTENDED SPECTRUM PENICILLIN: (Piperacillin) -Treats same diseases as broad spectrum PLUS: *pseudomonas aeruginosa*, enterobacter spp, proteus, bacteroides fragilis, klebsiella spp -Can cause bleeding secondary to disrupting platelet function -Usually administered IV -Reduce dose in renal pt’s Cephalosporins (Cephalexin) -Bactericidal drug (similar to PCNs) -Increases activity against gram-negative agents -Increases ability to reach cerebral spinal fluid (CSF)-3rd,4th,5th generations -no routine lab monitoring -Administered IM or IV -Take cultures to determine sensitivity and infecting organism -Contraindicated in pt’s with severe allergic reaction to cephalosporins or penicillins - CAN CAUSE C. DIFF INFECTION (tell pt. To monitor for frequent stools) -Used to treat infants & neonates. Especially in otitis media and gonococcal and pneumococcal infections -Adverse Effects: Maculopapular rash, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis -Education: Patients should not consume alcohol First generation: tx’s staphylococci or streptococci Cefadroxil, Cefazolin, Cephalexin Second generation: TX’s H. Influenza, Klebsiella, pneumococci, staphylococci Cefaclor, Cefotetan, Cefoxitin, Cefurozime Third generation: tx’s pseudomonas aeruginosa, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Klebsiella, Serratia Cefdinir, Cefotaxime, Cefpodoxime, Ceftazidime, Ceftriaxone Fourth generation: Pseudomonas aeruginosa Cefepine, Ceftolozane/tazobactam Fifth generation: Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus Ceftaroline [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 34 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 16, 2022
Number of pages
34
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 16, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
129






.png)

.png)