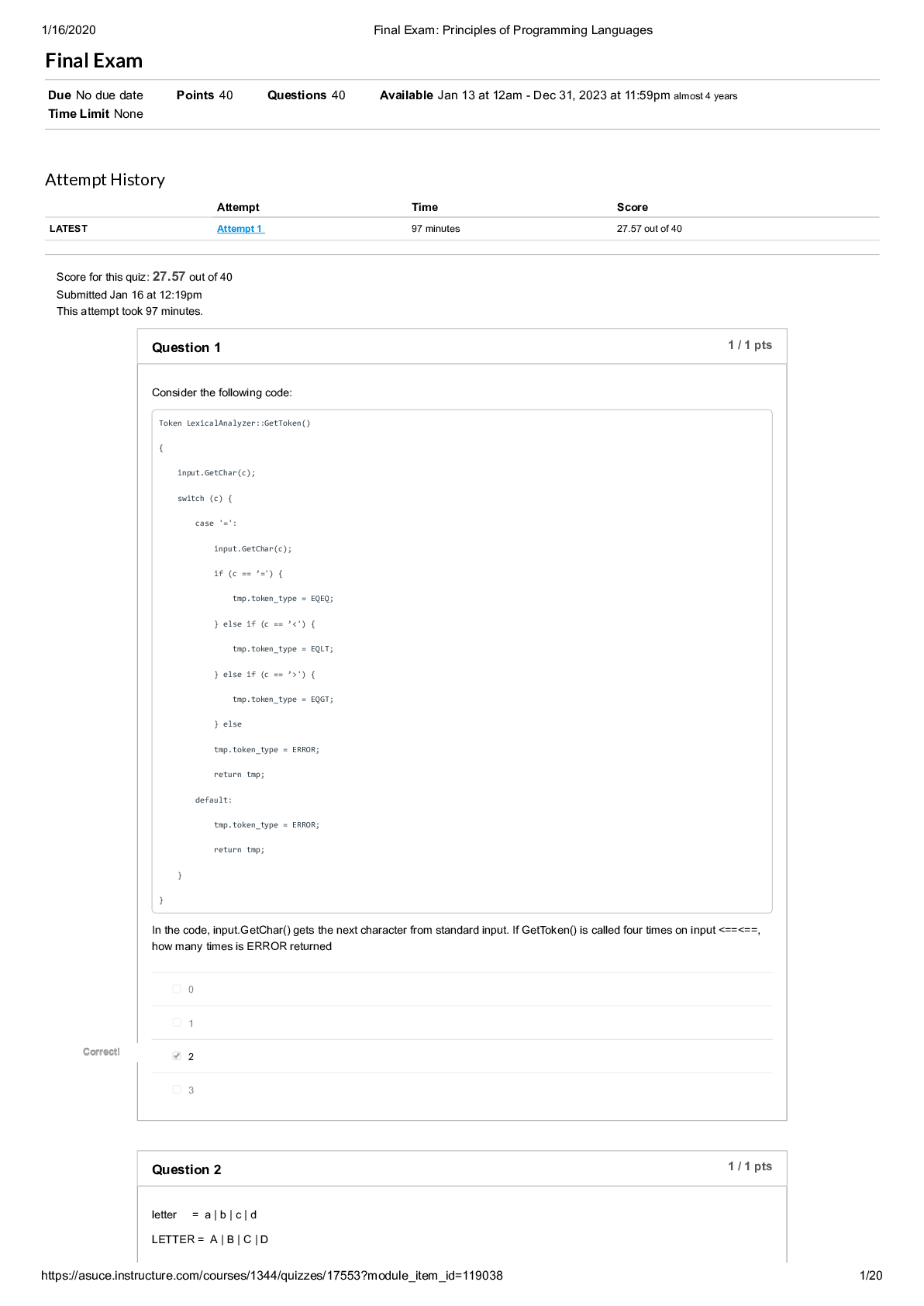
Final_Exam__Principles_of_Programming_Language_saveeeee. Arizona State University CSE 47708
$ 10
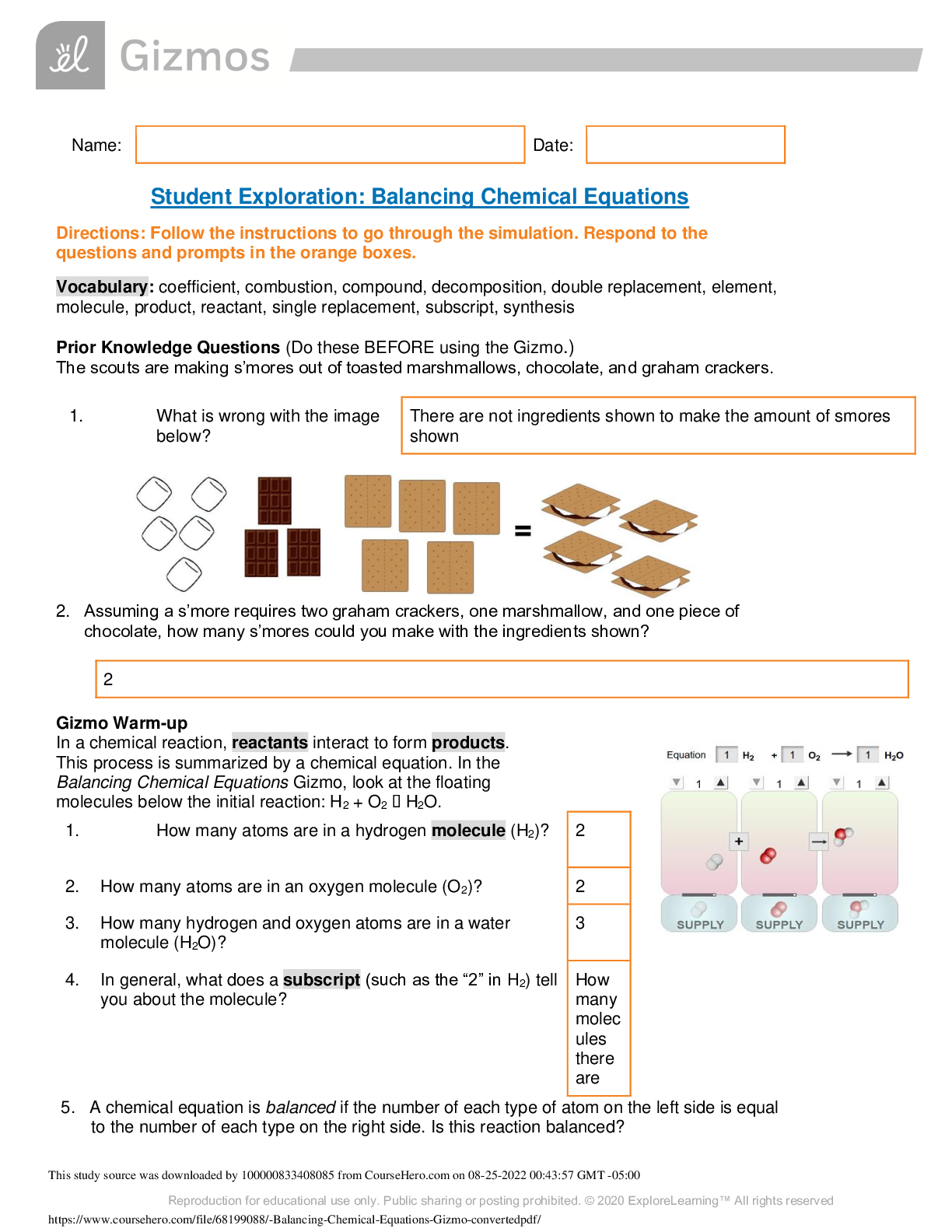
Balancing Chemical Equations Gizmo converted | all answers 100% correct | 4 pages
Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > BIOL 1150_1151 Exam 3. Study Guide and Exam Prep. Contains 40 Questions and Answers. (All)
Dr. Anderson NAME____________________________________ BIOL 1150/1151 Lecture Exam 3 Multiple Choice Questions: Please select the best answer from the choices provided. [35 questions at 1 point each ... ] 1. Skeletal muscle is a type of: a. Epithelial tissue b. Connective tissue c. Muscle tissue d. Nervous tissue 2. Which of the following muscle tissue types is largely under “voluntary” nervous system control? a. Smooth muscle tissue b. Cardiac muscle tissue c. Skeletal muscle tissue 3. The chemical bonds that hold the muscle proteins actin and myosin together result from the equal sharing of electrons between atoms of similar electronegativities known as: a. Hydrogen bonds b. Ionic bonds c. Nonpolar covalent bonds d. Polar covalent bonds 4. Chloride ions readily ionize in water and frequently form ionic bonds with important ions of the nervous system sodium and potassium. Chloride ions have a negative one charge meaning that: a. They have one more proton than electron b. They have one more electron than proton c. They have one more electron than neutron d. They have one more proton than neutron 5. Which of the following is a function of the muscular system? a. produces movement b. synthesizes steroids c. removes lactic acid d. produces red blood cells 6. Many groups of neurotransmitters produced in neurons are protein-based. Based on this information you would then expect neurons to have many: a. Nuclei b. Mitochondria c. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum d. Lysosomes 7. The sodium/potassium protein pump found in neurons that actively moves these respective ions against their concentration gradients is an example of a __________ protein. a. Passive diffusion b. Facilitated diffusion c. Active transport d. Exocytosis Use the following images to identify the indicated parts of the connection between a motor neuron and a muscle cell: 8. a. T tubule b. Synaptic clef c. Sarcoplasmic reticulum d. Synaptic vesicle e. Myofibril 9. a. T tubule b. Synaptic clef c. Sarcoplasmic reticulum d. Synaptic vesicle e. Myofibril 10. a. T tubule b. Synaptic clef c. Sarcoplasmic reticulum d. Synaptic vesicle e. Myofibril 11. a. T tubule b. Synaptic clef c. Sarcoplasmic reticulum d. Synaptic vesicle e. Myofibril 12. a. T tubule b. Synaptic clef c. Sarcoplasmic reticulum d. Synaptic vesicle e. Myofibril 13. Overuse, misuse, and age are some of the factors that contribute to excessive stress on a tendon, causing inflammation known as ________. a. tetanus b. tendinitis c. spasms d. bursitis 14. What would happen to soldiers exposed to a chemical warfare agent that blocked acetylcholine membrane receptors on skeletal muscle cells? a. They would have convulsive and spasmodic muscle contractions b. They would be paralyzed c. The would experience muscle tetanus d. There would be no unusual physiological effect If the inside of the neuron is negatively charged compared to the outside, the neuron is in the __________________. a. retraction period b. resting state c. action potential d. excitatory phase 16. The concentrations of sodium and potassium ions inside and outside a resting neuron are very different due primarily to: a. Passive diffusion b. Facilitated diffusion c. Active transport d. Osmosis 17. If a metabolic disorder were to occur that slowed down the rate of Na/K protein pumps in the nerve cells of an individual, how would this affect the resting membrane potential of a neuron? a. It would be more positive b. It would be more negative c. It would not change the neurons resting potential 18. Novocaine is a local anesthetic that blocks a particular neuron cell membrane protein in order to prevent action potential from being generated in neurons that conduct pain signals to the brain. Which of the following neuron proteins does novocaine block to prevent the action potential from initially depolarizing (becoming more positive)? a. Sodium-potassium pump b. Potassium leak channels c. Potassium ion gated channels d. Sodium ion gated channels 19. Neurons with a myelin sheath carry impulses _____________ unmyelinated cells. a. slower than b. faster than c. at the same speed as 20. Which of the following is a chemical signal that diffuses across the gap between adjacent neurons to convey a message to the next cell? a. neurotransmitter b. synapse c. dendrite d. action potential 21. The sarcoplasmic reticulum stores ions that are necessary for skeletal muscle contractions. Which of the following ions does it store? a. Mg++ b. Fe++ c. Na+ d. Ca++ Which functions in the attachment of muscle to bone? a. synergistic b. tetanus c. ligaments d. tendons 23. The electrical impulse transmitted by a neuron is caused by the movement of _____. a. molecules b. electrons c. free radicals d. ions 24. Why does a person continue to breathe heavily afer prolonged activity? a. because of a lack of water b. to relieve fatigue c. to relieve O2 debt d. no reason 25. Someone who has broken an arm and has had a cast on it for months will notice a distinct shrinking of the arm once the cast is removed. Why does this happen? a. The cast has reduced blood flow to the muscle tissue to reduce swelling. b. If the muscles are not used they will atrophy. c. The other arm was used more to compensate for the unused one, and it's become stronger. d. If the person was right-handed, they'll become lef-handed. 26. This type of hormone characteristically requires a second messenger. a. lipid-soluble b. steroid c. water-soluble d. prostaglandin 27. Cancer cells ofen fail to respond to certain hormones because they lack these cell membrane features important in binding with that specific hormone. a. DNAs b. dockers c. targets d. receptors 28. Hormones that are hydrophilic in nature interact with receptors at the cell surface. The reason for this is_______. a. Binding at the surface elicits a more rapid response b. Hydrophilic compounds cannot cross the plasma membrane c. The hormones bind and are physically transported to the cytoplasm d. Not true. All hormones cross the plasma membrane before binding. 29. Which of the following carry impulses toward the nerve cell body? a. dendrite b. glial cells c. axon d. Schwann cells Choose the term that describes muscles that oppose one another. a. antagonistic b. synergistic c. contrary d. pairing 31. Hormones have direct effects on cells that _____. a. are located relatively close to the glands releasing the hormones b. come into contact with the hormones via the blood c. have become diseased and must change their behavior d. are able to recognize the hormones using receptor proteins 32. What are specialized membrane proteins that actively transport sodium and potassium ions across the plasma membrane? a. Na/Cl pump b. Na/Mn pump c. Na/K pump d. Na pump 33. The receptor for a steroid hormone can be found ________. a. At the outer surface of the cell b. Spanning the phospholipid bilayer c. In the cytoplasm d. Inside a lysosome 34. One class of hormones are the lipid-insoluble or protein-based hormones made up of __________ subunits. a. Carbohydrate b. Amino acid c. Fatty acid d. Nucleic acid 35. ATP is used as an energy source for nearly all cellular metabolic processes. Which of the following macromolecules, if available, is used preferentially for ATP synthesis? a. Amino acids b. Lipids c. Carbohydrates d. Nucleic acids BIOL-1150-Exam-3-with-keydoc/Short Answer Questions: Please choose three of the following to answer as thoroughly as possible. [3 questions at 5 points each] 1. Describe, in order the steps for generating a resting and action potential and how each of the four membrane pumps and channels affect the charge potential inside the neuron PAGE 118 2. List the four basic categories of good food safety practices and provide a brief explanation for each. Clean, separate, cook, chill 3. Describe the action of a typical steroid hormone by answering the following questions: How does it interact with the target cell membrane? What characteristics of the hormone lead to this interaction? How does the hormone generate a response in the target cell? 4. Describe or draw the structure of an average neuron. Be sure to note all of the important cellular structures, organelles, and cellular extensions. Indicate the direction of flow for an action potential down a neuron. PAGE 117 5. Ralph decides to make a meal for some of his friends. He uses a variety of foods to prepare the meal, including some home-canned green beans that his mother gave him. Unfortunately, he gave his friends a mild case of botulism food poisoning. His friends reported blurred vision and trouble speaking due to a flaccid paralysis of the muscle cells by the botulinum toxin. Based on what you know about muscle contraction propose a mechanism by which this toxin might inhibit muscle contraction. i. The toxin has created a missing link in the chain that the muscle doesn’t realize so it cant contract but the brain is trying to get it to 6. You have determined that a certain hormone exists, but are not sure whether it interacts at the cell surface or in the cytoplasm. Describe an experimental protocol that you could use to determine this. Be sure to explain how the properties of the hormone would aid in this determination. [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 1 out of 6 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 12, 2022
Number of pages
6
Written in
All
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 12, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
248
Scholarfriends.com Online Platform by Browsegrades Inc. 651N South Broad St, Middletown DE. United States.
We're available through e-mail, Twitter, Facebook, and live chat.
FAQ
Questions? Leave a message!
Copyright © Scholarfriends · High quality services·