1. Give an example of a neurotransmitter in each category below (answers may vary).
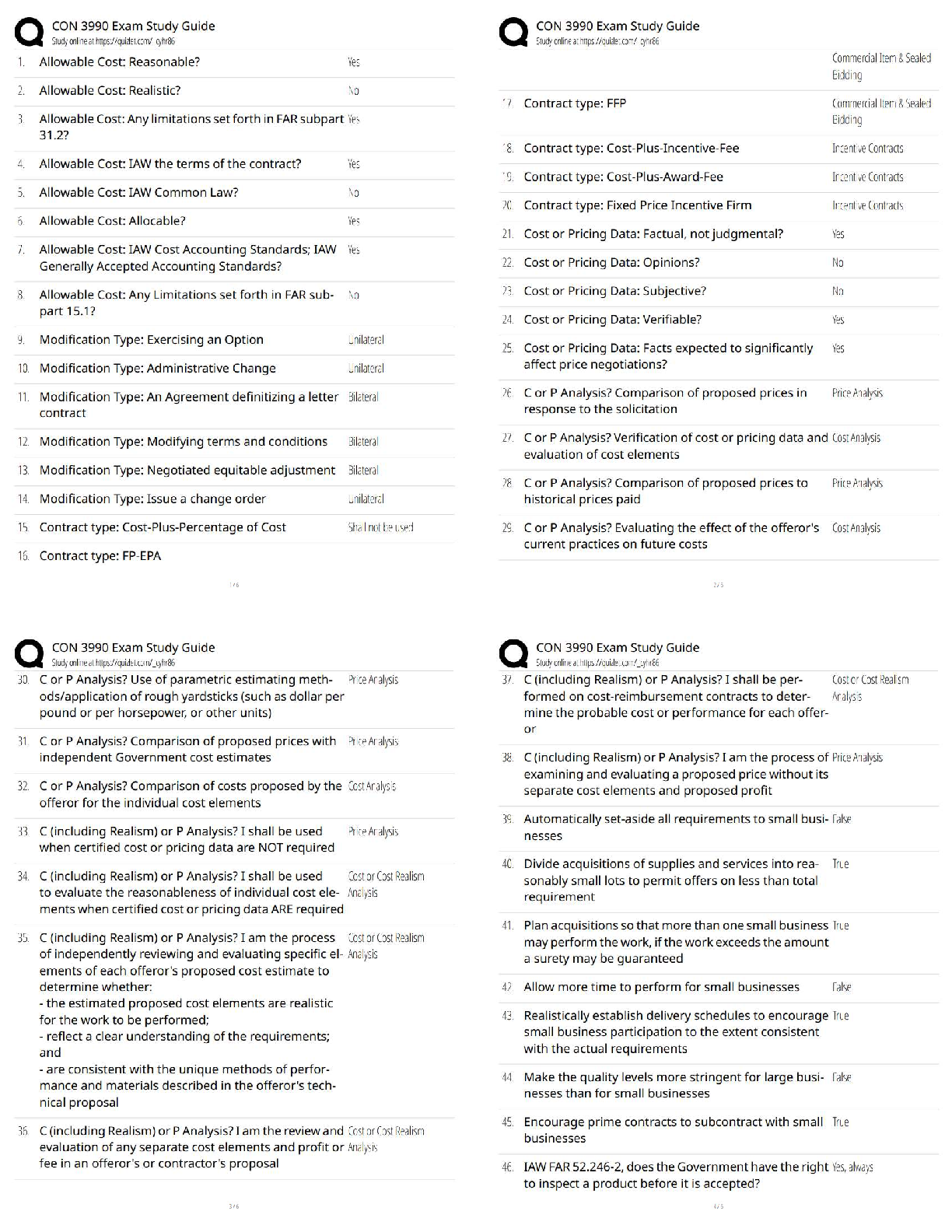
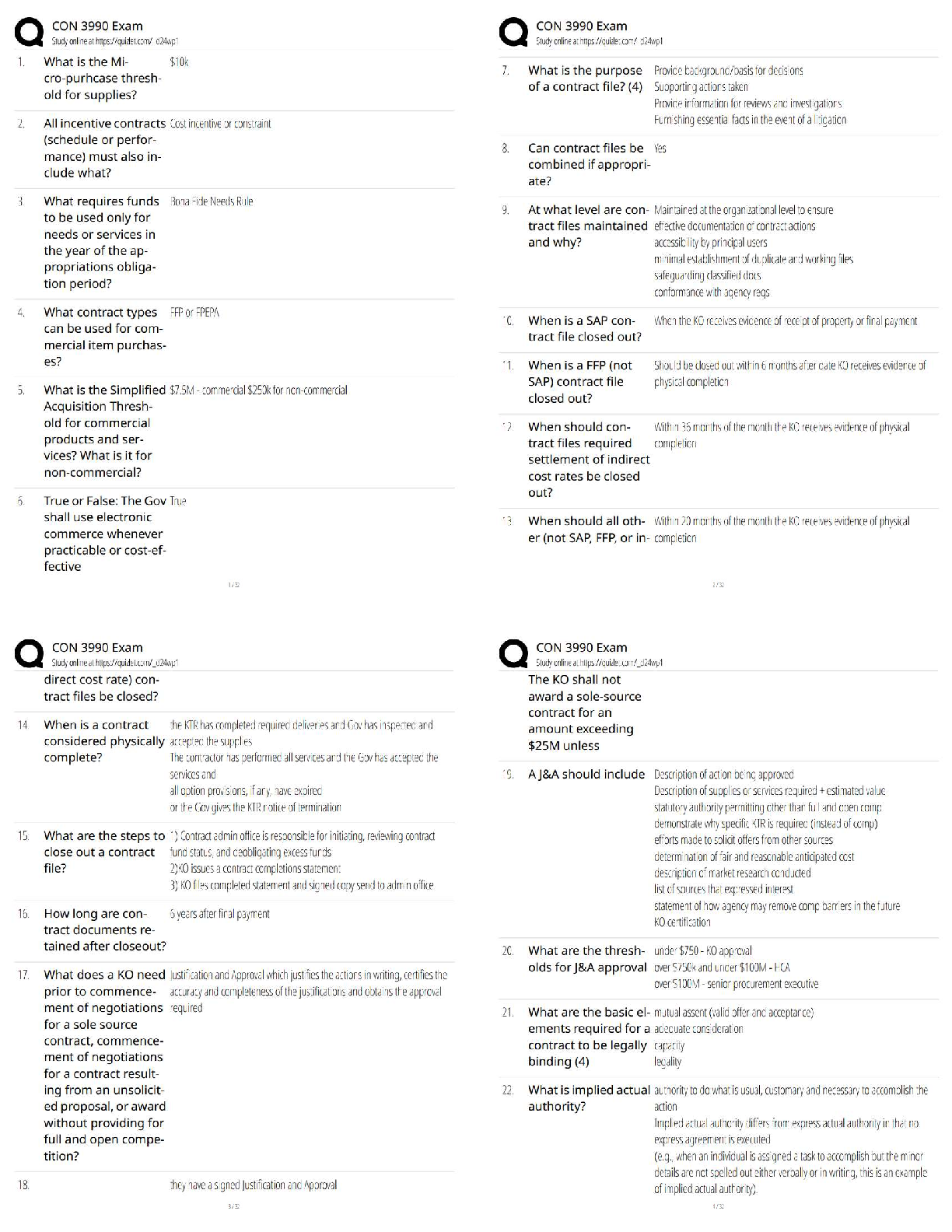
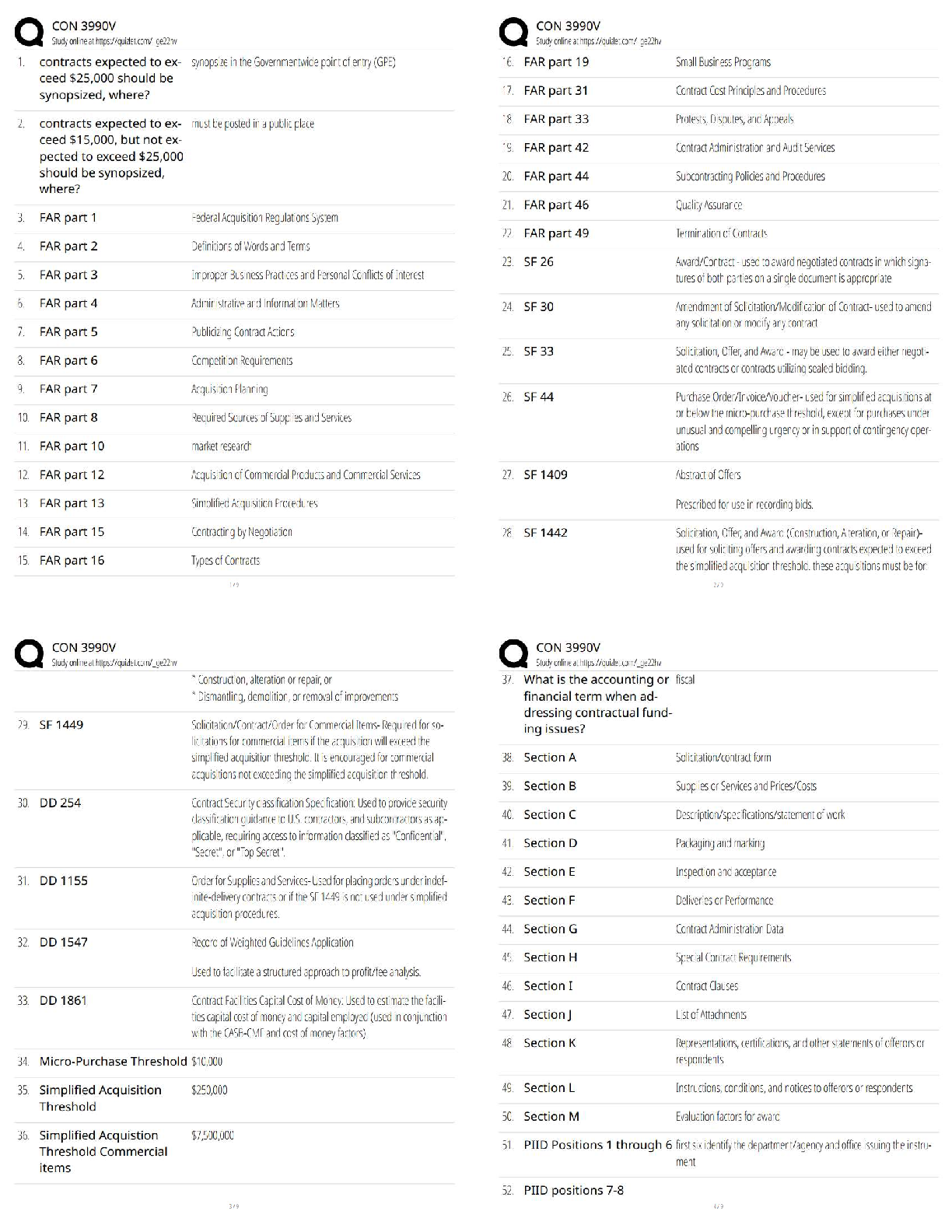
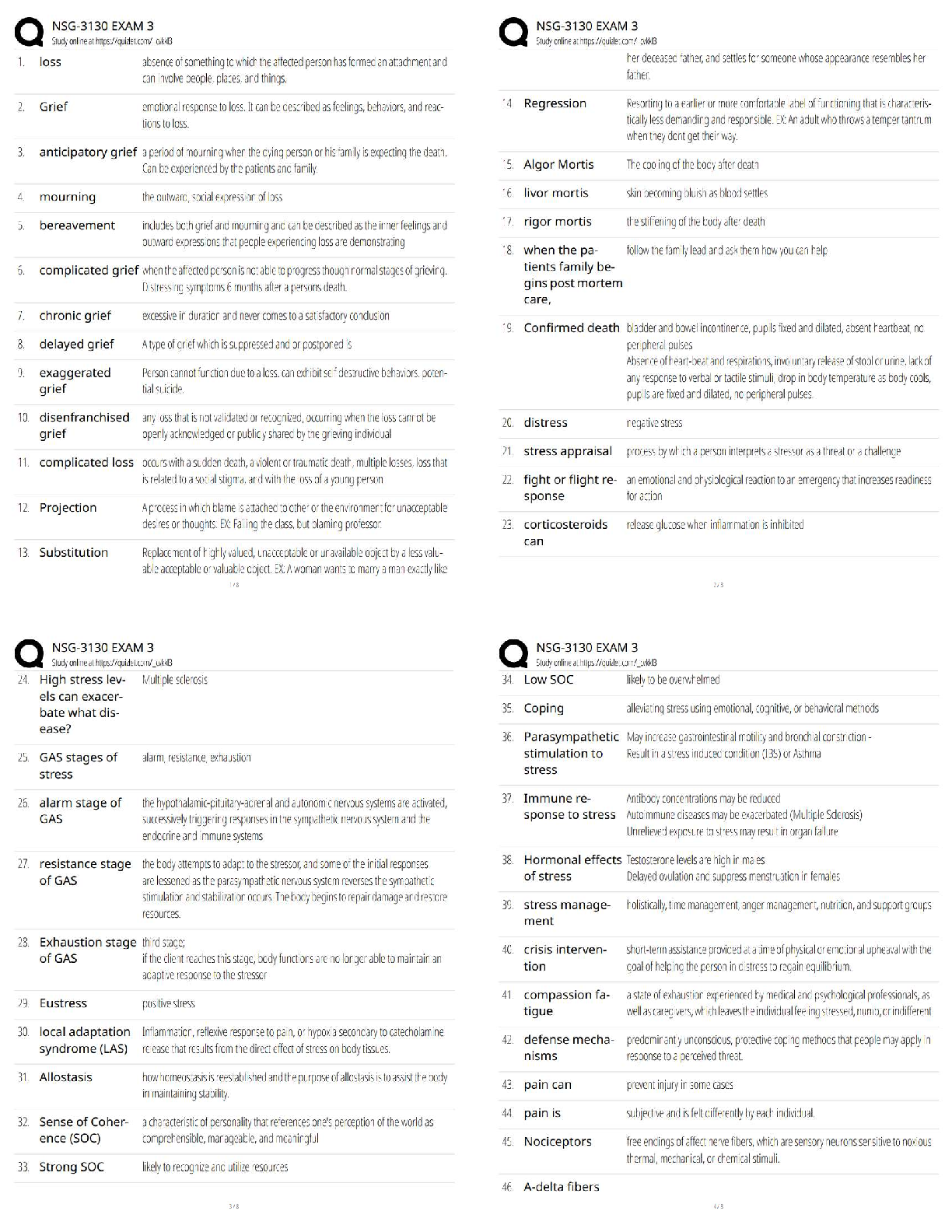
a) Purine
b) Biogenic amine
c) Amino acid
d) Peptide
Answer:
a) ATP
b) Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, histamine, serotoni
...
1. Give an example of a neurotransmitter in each category below (answers may vary).
a) Purine
b) Biogenic amine
c) Amino acid
d) Peptide
Answer:
a) ATP
b) Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, histamine, serotonin
c) Glutamate, aspartate, GABA, glycine
d) Substance P, methionine enkephalin, neurokinin A, neuropeptide K, neuropeptide, and any of the peptides listed in Figure 6.22
Textbook Reference: Categories of Neurotransmitters
3. Define and briefly describe the glutamate–glutamine cycle.
Answer: It is the process of glutamate recycling and synthesis, which rapidly terminates
the action of glutamate on the postsynaptic neuron. Glutamate is taken up into local glial
cells and converted to glutamine by glutamine synthase. Glutamine is then released from
the glial cells via the SN1 transporter, taken up into nerve terminals vial SAT2
transporters, and subsequently converted back to glutamate within the nerve terminal by
glutaminase.
Textbook Reference: Glutamate
4. Define excitotoxicity. Why is it clinically important?
Answer: Excitotoxicity results from an excessive release of glutamate in the brain during
brain trauma or disease that, itself, causes damage to the brain.
Textbook Reference: Glutamate
5. What are the three major types of ionotropic glutamate receptors, and why were they
given their specific names? Why are two types of these receptors considered to be
particularly important?
Answer: The three major types are NMDA, AMPA, and kainate receptors; they were
named after their respective exogenous agonists. NMDA and AMPA receptors are
particularly important because they are present in most central excitatory synapses.
Textbook Reference: Glutamate
6. What are the two major inhibitory neurotransmitters in the adult central nervous
system?
Answer: GABA and glycine
Textbook Reference: GABA and Glycine
[Show More]