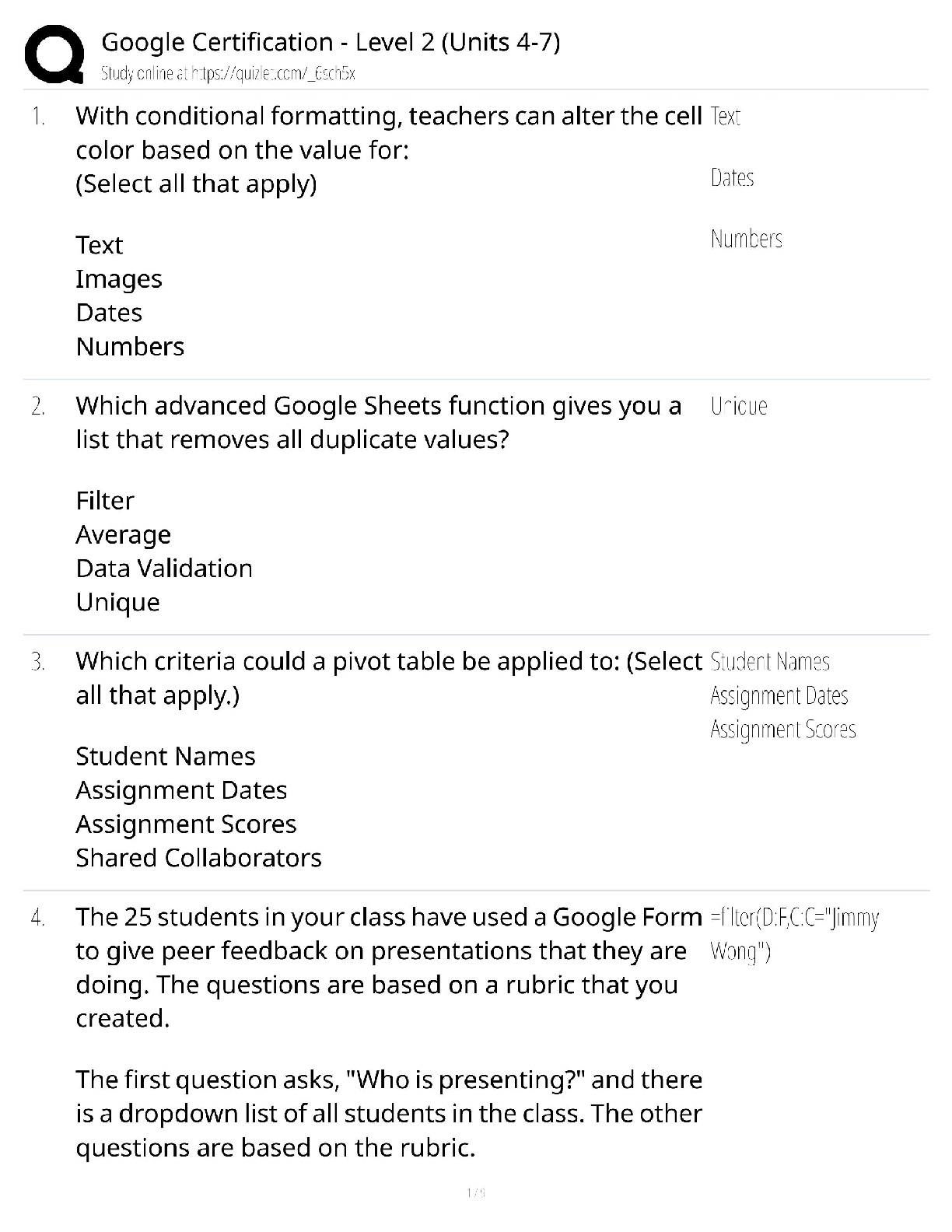
SCIENCE 101 > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Molecular Signaling within Neurons - Multiple Choice (All)
Molecular Signaling within Neurons - Multiple Choice
Document Content and Description Below
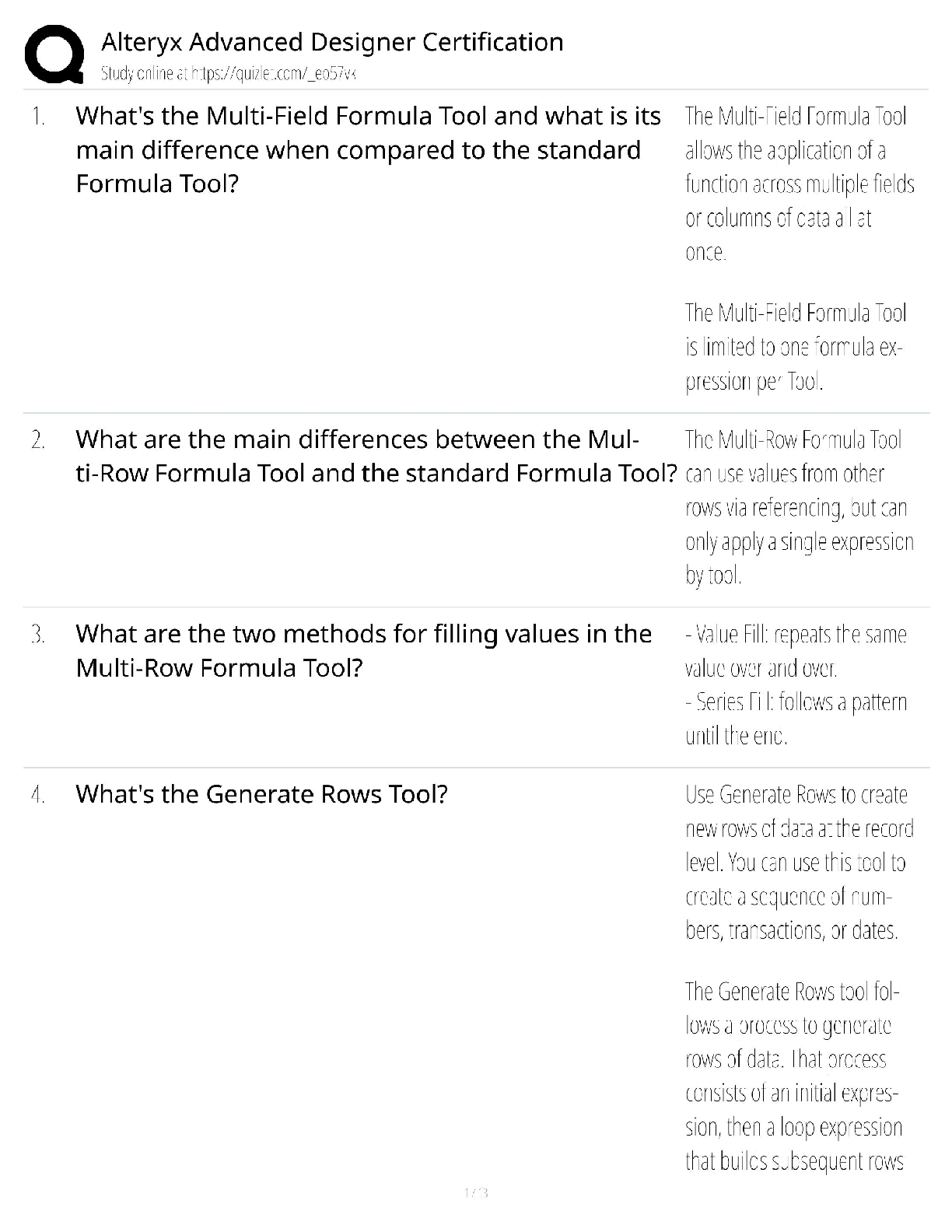
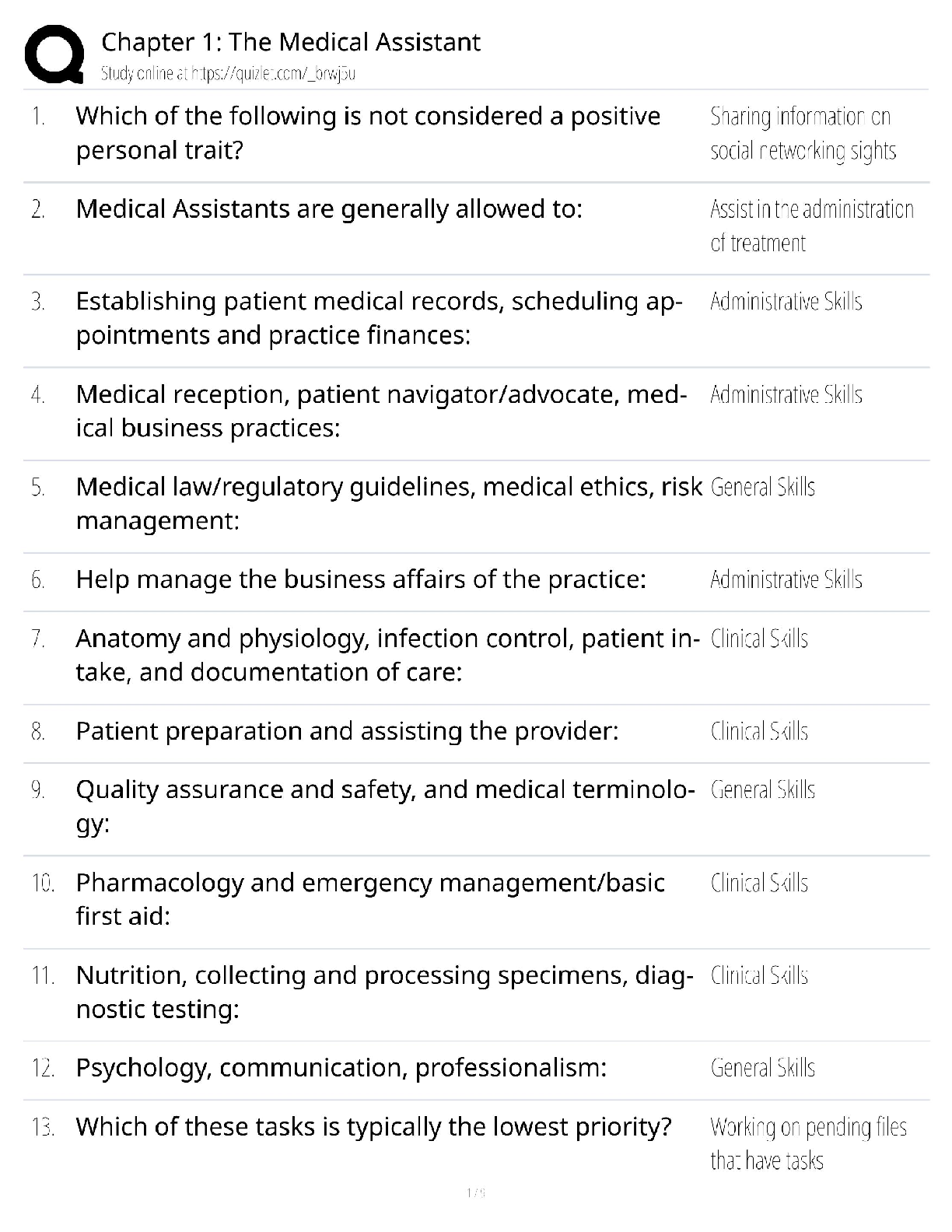
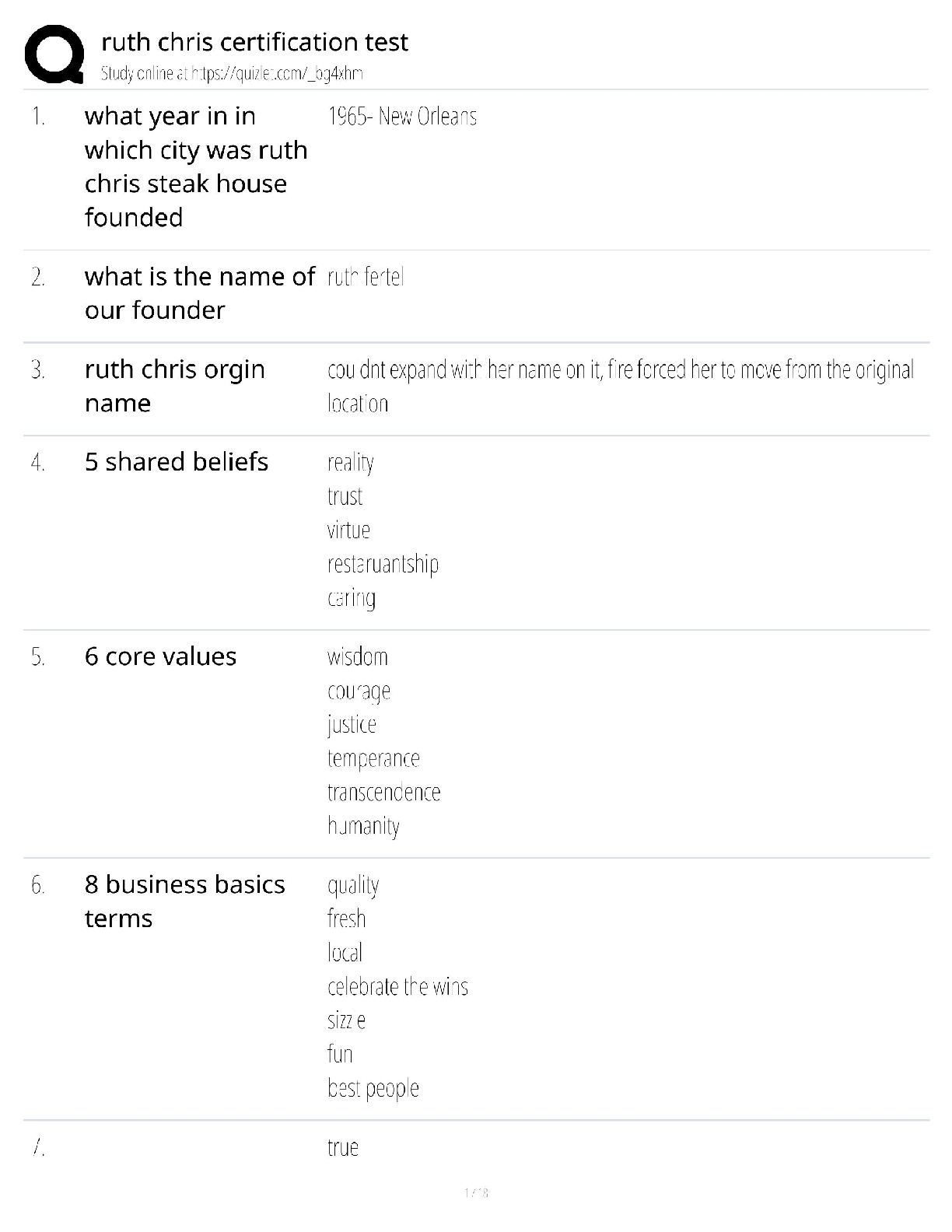
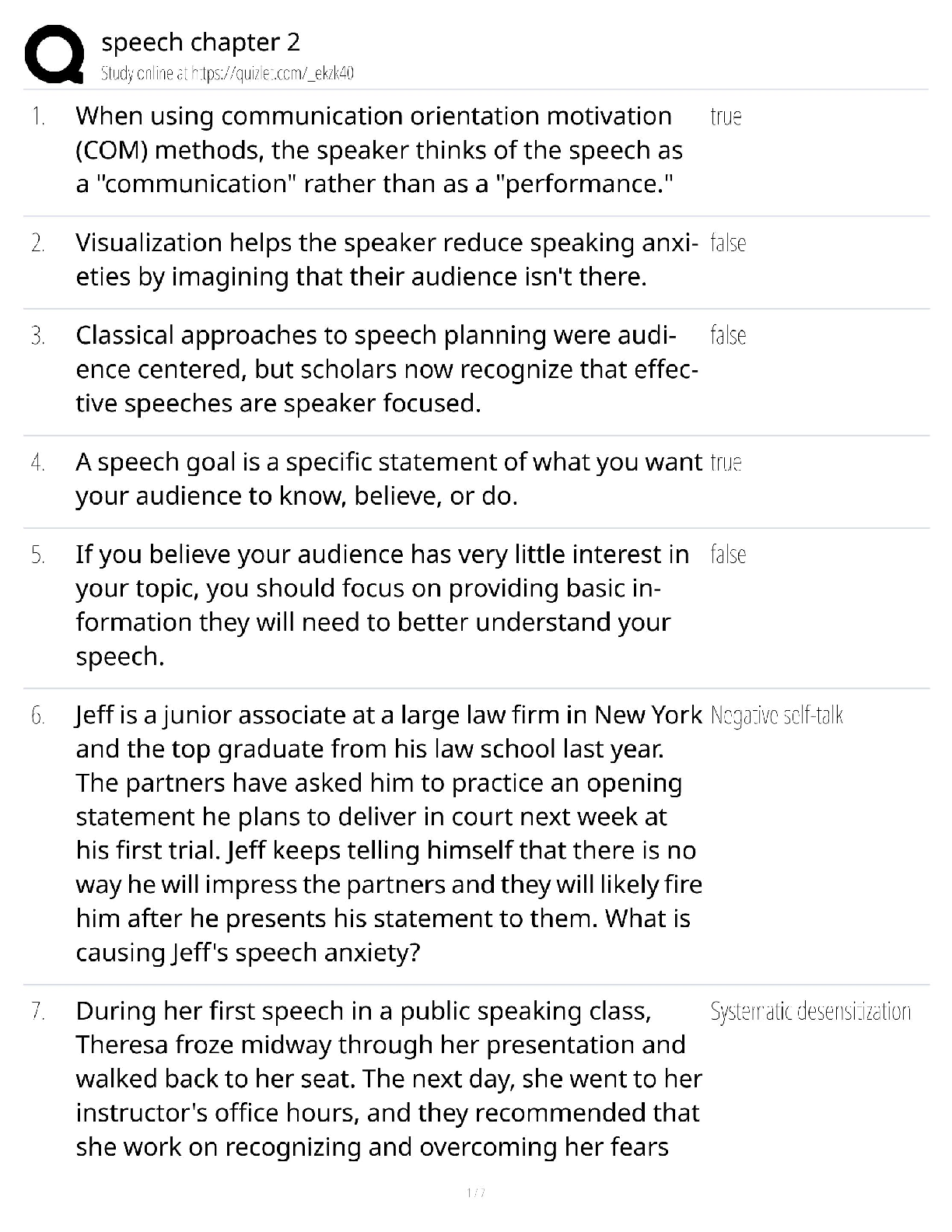
1. Which type of signaling do mature neurons most commonly use to communicate? a. Electrical only b. Chemical only c. A combination of electrical and chemical d. Paracrine e. Endocrine Answer: b ... Textbook Reference: Strategies of Molecular Signaling 2. The effector molecule at the synapse of an intercellular signal transduction process is a(n) a. ion. b. ion channel. c. neurotransmitter molecule. d. synaptic vesicle. e. G-protein. Answer: b Textbook Reference: Strategies of Molecular Signaling 3. What is the greatest advantage of the chemical signal transduction scheme? a. Signal amplification b. Activation of remote targets c. Activation of immediate targets d. Sequential nature e. Specificity Answer: a Textbook Reference: Strategies of Molecular Signaling 4. Which molecule belongs to a class of cell-associated signaling molecules? a. Thyroxin b. Integrin c. Acetylcholine d. Testosterone e. Nitric oxide Answer: b Textbook Reference: Activation of Signaling Pathways 5. Cell-permeant signaling molecules bind to which type of receptor? a. Channel-linked b. Enzyme-linked c. G-protein–coupled d. Intracellular e. All of the above Answer: d Textbook Reference: Receptor Types 6. Most enzyme-linked receptors affect the function of the target cell by a. phosphorylating intracellular target proteins. b. catalyzing synthesis of hormones in the cytoplasm. c. facilitating the assembly of the cytoskeleton. d. generating an action potential. e. dimerizing. Answer: a Textbook Reference: Receptor Types 7. To which subunit(s) of heterotrimeric G-protein does a guanine nucleotide bind? a. α b. β c. βγ subunit complex d. γ e. δ Answer: a Textbook Reference: G-Proteins and Their Molecular Targets 8. Which of the following is the first step in the process of activation of a heterotrimeric G-protein? a. The α subunit binds to β and γ subunits to form the inactive trimer. b. The α subunit binds to GDP. c. The G-protein binds to the activated receptor. d. The α subunit dissociates from the βγ complex. e. The α subunit binds to downstream effector molecules. Answer: c Textbook Reference: G-Proteins and Their Molecular Targets 9. In what way does the function of monomeric G-proteins differ from that of heterotrimeric G-proteins? a. Monomeric G-proteins are active in the GTP-bound state, heterotrimeric G-proteins are not. b. Heterotrimeric G-protein activation is controlled by guanine nucleotide exchange factors, monomeric G-protein activation is not. c. Heterotrimeric G-proteins relay signals from cell surface receptors to intracellular targets, monomeric G-proteins do not. d. Monomeric G-protein activity is terminated by hydrolysis of GTP, heterotrimeric Gprotein activity is not. e. Heterotrimeric G-protein activity is regulated by GAP proteins, monomeric G-protein activity is not. Answer: b Textbook Reference: G-Proteins and Their Molecular Targets 10. Which molecule is an effector directly downstream of an activated G-protein? a. Phospholipase C b. IP3 c. cAMP d. Protein kinase C e. Protein kinase A Answer: a Textbook Reference: G-Proteins and Their Molecular Targets 11. Which role does calmodulin play in the intracellular cascade triggered by Ca2+? a. It modulates the strength of Ca2+ binding to its downstream targets. b. It serves as a Ca2+ buffer. c. It enhances downstream effects of Ca2+ d. It binds to its downstream targets when activated by Ca2+ e. It serves as a Ca2+ sensor when neurotransmitter is released. Answer: d Textbook Reference: Second Messengers 12. In which direction do Ca2+ ions flow through ryanodine receptors? a. From the cytoplasm into the endoplasmic reticulum b. From the endoplasmic reticulum into the cytoplasm c. From the extracellular space into the cytoplasm d. From the cytoplasm into the extracellular space e. From the cytoplasm into synaptic vesicles Answer: b Textbook Reference: Second Messengers 13. Which second messenger originates from both extracellular and intracellular compartments? a. Ca2+ b. Cyclic AMP c. Cyclic GMP d. IP3 e. Diacylglycerol Answer: a Textbook Reference: Second Messengers 14. Which second messenger plays an important role in sensory transduction processes? a. Ca2+ b. Cyclic nucleotide c. Nucleotide d. IP3 e. Diacylglycerol Answer: b Textbook Reference: Second Messengers 15. Which of the following provides an example of a second messenger producing another second messenger? a. IP3 binds to its receptor, enabling the release of Ca2+ from the cytosol. b. Diacylglycerol fuses with PIP2, producing IP3. c. Phospholipase C acts on PIP2, splitting it into IP3 and diacylglycerol. d. Ca2+ binds to calmodulin, promoting its binding to downstream protein kinases. e. G-proteins activate adenylyl cyclase in the plasma membrane, causing it to produce cyclic nucleotides. Answer: a Textbook Reference: Second Messengers 16. The catalytic domain of a protein kinase a. transfers a carboxyl group to the relevant amino acid of the target protein. b. transfers a phosphate group to the relevant amino acid of the target protein. c. transfers ATP to the relevant amino acid of the target protein. d. binds to IP3 e. binds to Ca2+ ions. Answer: b Textbook Reference: Protein Kinases 17. Which statement about protein kinases in the brain is most accurate? a. They amplify second messenger signals. b. Most are important regulators of neuronal signaling. c. Each has a regulatory domain that inhibits the catalytic domain. d. The catalytic domain of a protein kinase is always inhibited. e. They can be activated only by second messengers. Answer: a Textbook Reference: Protein Kinases [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 28, 2022
Number of pages
5
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 28, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
144