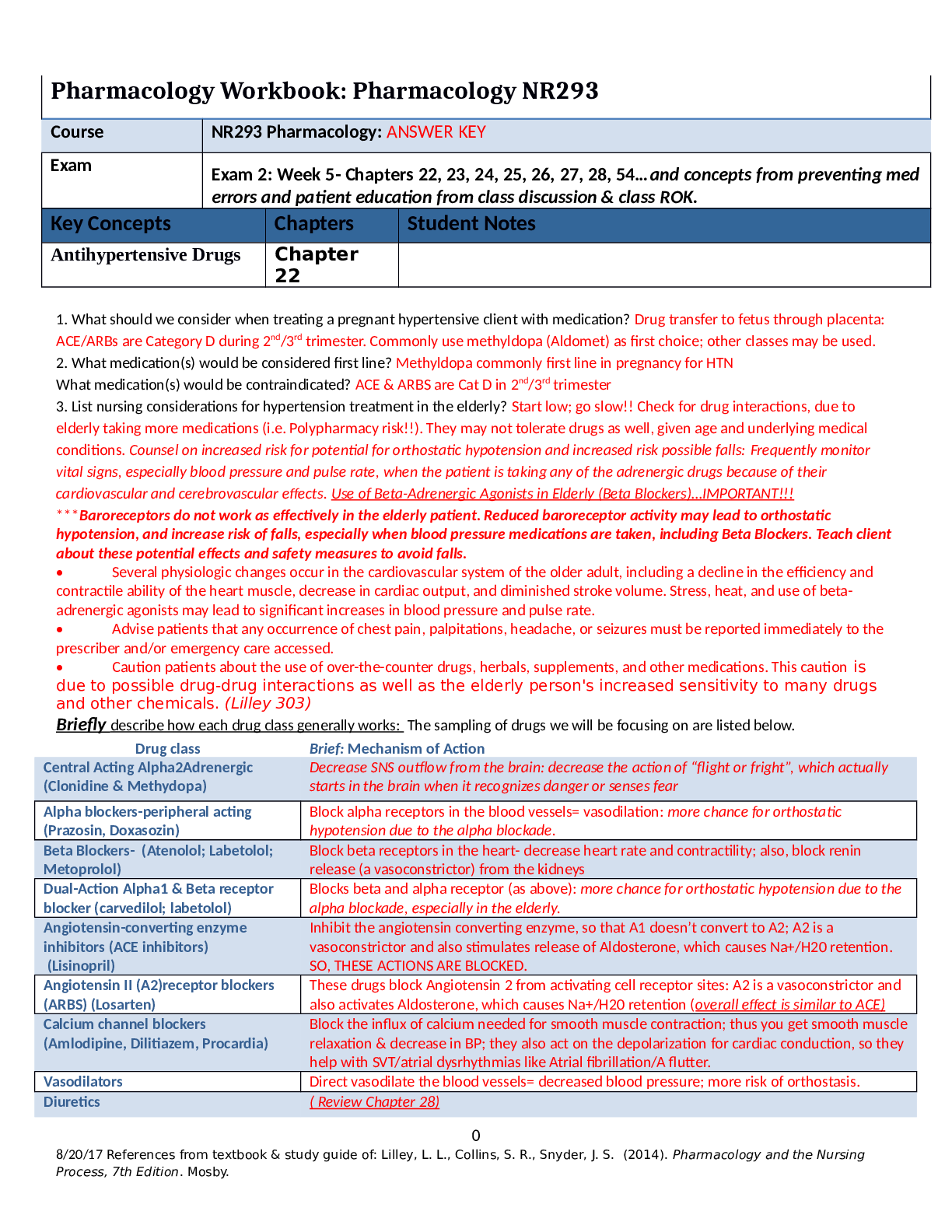
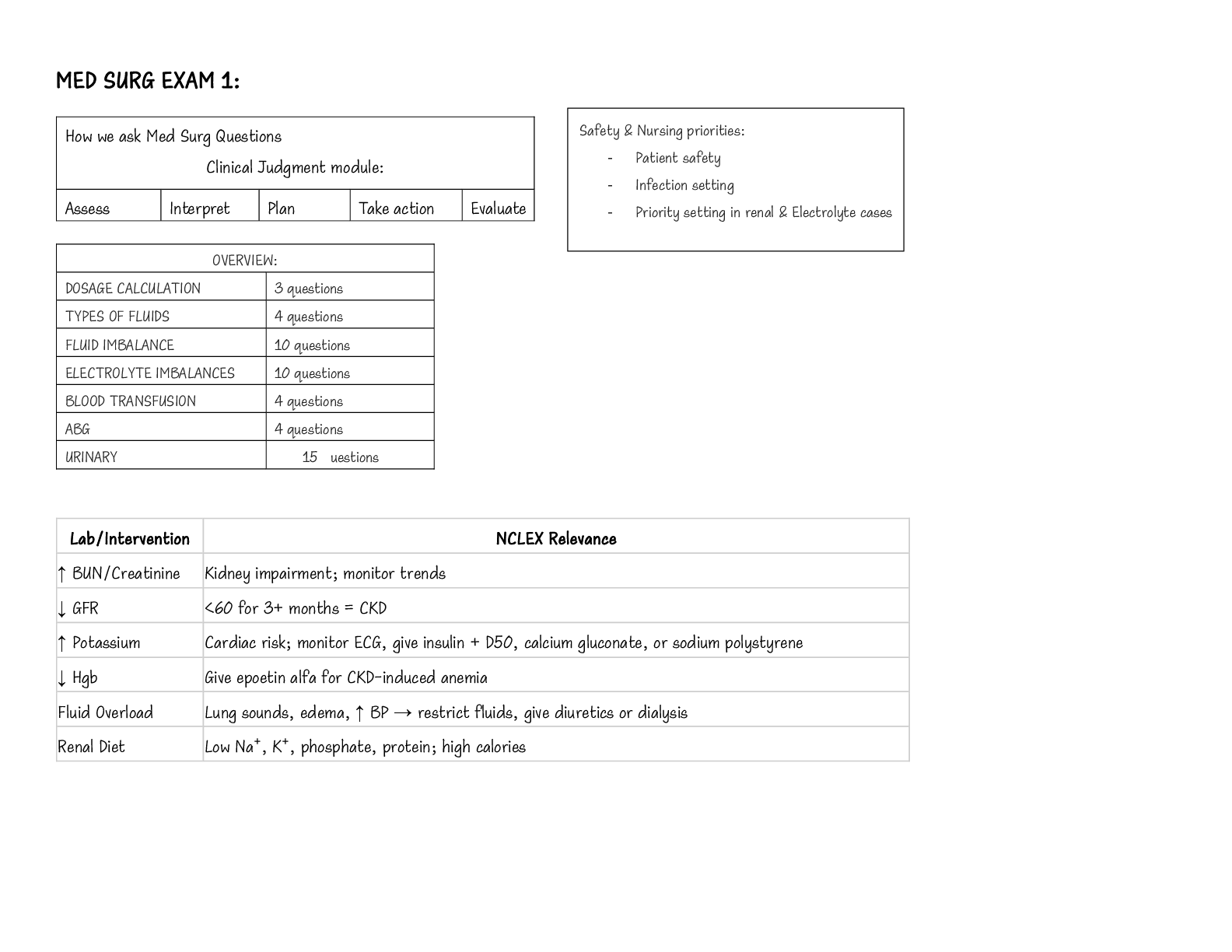
1. Be able to identify normal and abnormal values for vital signs.
● Normal BP: 120/80
● Normal Pulse: 60-100 Beats/Min
● Normal Temp: 96.4 F - 99.1 F
● Normal Resp: 10-20 Breaths/Min
● Normal O2: 97-100 %
● Abnorm
...
1. Be able to identify normal and abnormal values for vital signs.
● Normal BP: 120/80
● Normal Pulse: 60-100 Beats/Min
● Normal Temp: 96.4 F - 99.1 F
● Normal Resp: 10-20 Breaths/Min
● Normal O2: 97-100 %
● Abnormal BP: Lower than 90/60 or Higher than 140/90
● Abnormal Pulse: Lower than 60 or higher than 100 Beats/Min
● Abnormal Temp: Lower than 95 F or higher than 100 F
● Abnormal Resp: Lower than 10 or higher than 20 Breaths/Min
● Abnormal O2: 96% and below
2. Be able to compare temperature values obtained by different routes.
● Oral Temp: Place the thermometer in the mouth under the tongue and advise
patient to keep mouth closed. (98.6 F)
● Axillary Temp: Place the thermometer in the armpit and leave it in place. (Usually
1 C lower than oral temp)
● Tympanic Membrane (Ear) Temp: Place thermometer in the ear but do not force
it in or occlude the ear canal. (Usually 0.3 C - 0.6 C higher than oral temp)
● Rectal Temp: Use only when other routes are not available (Usually 1 C higher
than oral temp)
3. Be able to compare Centigrade and Fahrenheit temperatures.
● C to F Formula: (C*9/5) +32
● F to C Formula: (F-32) *5/9
4. What is an appropriate reason for doing a health history?
● The purpose of obtaining a health history is to gather subjective data from the
patient and/or the patient’s family so that the healthcare team and the patient can
collaboratively create a plan that will promote health, address acute health
problems, and minimize chronic health conditions.
5. Why would a nurse do a focused assessment?
● Focused assessments are done in response to a specific problem recognized by
the assessor as needing further assessment of a body system.
Chapter 1
1. What is the basic purpose for doing assessment?
● Assessment is the first and most critical phase of the nursing process. If data
collection is inadequate or inaccurate, incorrect nursing judgments may be made
that adversely affect the remaining phases of the process.
● Assessment is analyzing and synthesizing data, making judgments about the
effectiveness of nursing interventions, and evaluating client care outcomes.
● Although the assessment phase of the nursing process precedes the other
phases (diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation), it is ongoing and
continuous throughout all phases of the nursing process.
● The end result of a nursing assessment is the formulation of nursing diagnoses
that require nursing care, the identification of collaborative problems that require
interdisciplinary care, the identification of medical problems that require
immediate referral, or client teaching for health promotion.
2. Review the ANA definition of nursing.
● Nursing is the protection, promotion, and optimization of health and abilities,
prevention of illness and injury, facilitation of healing, alleviation of suffering
through the diagnosis and treatment of human response, and advocacy in the
care of individuals, families, groups, communities, and populations.
3. Extra Chapter Notes:
● Assessment is collecting objective and subjective data. This includes physiologic,
psychological, sociocultural, developmental, and spiritual data. The nurse also
assesses how the client interacts within their family and community.
● A comprehensive health assessment consists of a health history and physical
examination.
● The purpose of a nursing health assessment is to collect holistic subjective and
objective data to determine a client’s overall level of functioning in order to make
a professional clinical judgment.
● Preparing for the assessment: review the client’s medical record, avoid
premature judgments that may alter your ability to collect accurate data, validate
information from the chart with the client and be prepared to collect additional
data, educate yourself about the client’s diagnoses and lab test performed, take
a minute to reflect on your own feelings about the client to avoid biases and
judgment, and obtain and organize materials that you will need for the
assessment.
● Steps of health assessment: Collection of subjective data, collection of objective
data, validation of data, and documentation of data.
● Collecting subjective data: Subjective data are sensorimotor symptoms (pain and
hunger), feelings (happiness and sadness), perceptions, desires, beliefs,
preferences, ideas, values, and personal information that can be elicited and
verified only by the client. This is the interviewing/ health history process. The
major areas of subjective data include, biographical info, history of present health
concern, personal health history, family history, and health and lifestyle practices.
● Collecting objective data: This type of data is directly observed by the examiner
and is obtained by using the 4 physical examination techniques (inspection,
palpation, percussion, and auscultation) These data include: physical
characteristics, body functions, appearance, behavior, measurements, and
results of lab testing.
● Validating assessment data: Serves to ensure that the assessment process is not
ended before all relevant data have been collected. It helps to prevent
documentation of inaccurate data.
● Documenting data: This forms the database for the entire nursing process and
provides data for all other members of the healthcare team.
● Step 2 of the nursing process: analysis of of assessment data to come up with a
nursing diagnosis. A nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment about individuals,
family or community responses to actual and potential health problems and life
processes. It provides the basis for selecting nursing interventions to achieve
outcomes for which the nurse is accountable.
● Process of data analysis: identify abnormal data and strengths, cluster the data,
dram inferences and identify problems, propose possible nursing diagnoses,
check for defining characteristics of those diagnoses, confirm or rule out nursing
diagnoses, and document conclusions.
● Factors affecting health assessment: the client’s culture, spirituality, family and
community.
[Show More]

.png)



.png)