*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NUR2474 Pharmacology for Professional Nursing – Examination Blueprint – Final Exam (All)
NUR2474 Pharmacology for Professional Nursing – Examination Blueprint – Final Exam
Document Content and Description Below
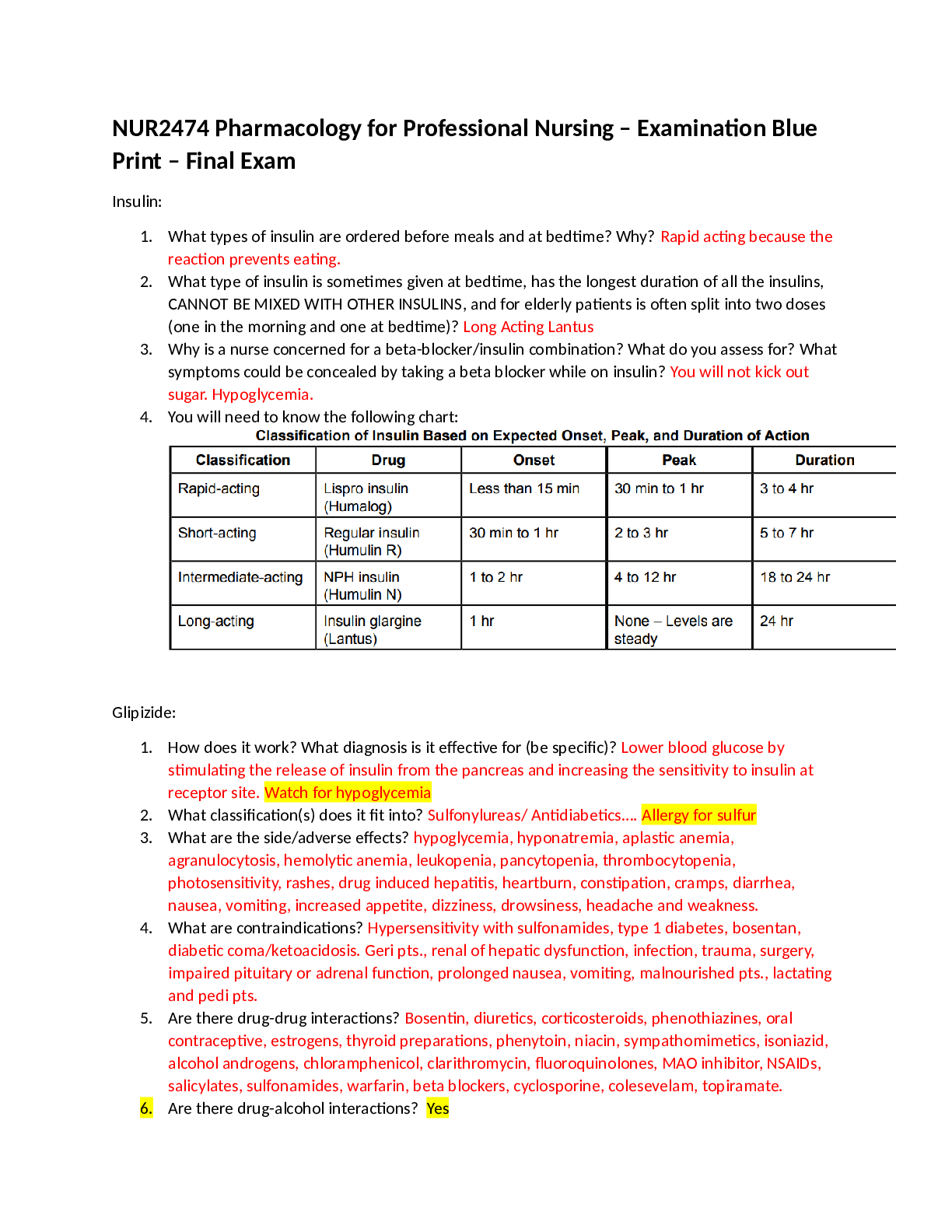
NUR2474 Pharmacology for Professional Nursing – Examination Blueprint – Final Exam Insulin: DM 1, DM 2, Gestational Diabetes – HYPOGLYCEMIA IS A DANGEROUS ADVERSE EFFECT AND HIGH PRIORITY FOR ... TREATMENT o What types of insulin are ordered before meals and at bedtime? Lispro and Regular; Lantus (hs, not with meals) Why? SUGAR DROPS OVERNIGHT and this can be DANGEROUS so NO NPH at bedtime o What type of insulin is sometimes given at bedtime, has the longest duration of all the insulins, CANNOT BE MIXED WITH OTHER INSULINS, and for elderly patients is often split into two doses (one in the morning and one at bedtime)? Insulin Glargine (Lantus) is usually given once a day at bedtime. Elderly individuals often have their dose split in two and are administered one dose in the morning and one dose at night; In addition, sometimes insulin lispro is given in a sliding scale with a snack in the evening. It does not last throughout the night - that’s what we want to avoid. *Insulin aspart protamine in combo with insulin aspart would NOT be given in the evening, as it lasts too long. *NPH would peak at exactly the WRONG TIME. Do not give that one at bedtime. o Why is a nurse concerned for a beta-blocker/insulin combination? Beta Blockers can mask some of the symptoms of hypoglycemia What do you assess for? What symptoms could be concealed by taking a beta blocker while on insulin? Symptoms of hypoglycemia: Feeling shaky. Being nervous or anxious. Sweating, chills, and clamminess. Irritability or impatience. Confusion. Fast heartbeat. Feeling lightheaded or dizzy. Hunger. You will need to know the following chart: Onset: When the medicine starts to work (when the blood sugar is going to start to go down). Peak: Usually when the medicine is at its highest level, and you get the highest effect (in this case it equates to the times when you see the lowest blood sugars). Duration: How long the medication is going to last in effectiveness (how long is it going to affect blood sugars). MOST ORAL ANTI-DIABETICS (ORAL HYPOGLYCEMICS): Type 2 Diabetes. Most do not work for type 1 diabetes, do not risk it with babies we use regular insulin for gestational diabetes. Glipizide (Glucotrol): o How does it work? is in a class of medications called sulfonylureas. Glipizide lowers blood sugar by causing the pancreas to produce insulin (a natural substance that is needed to break down sugar in the body) and helping the body use insulin efficiently. o What diagnosis is it effective for? Type 2, less than 5 years, no end organ damage, young enough o What classification(s) does it fit into? Oral hypoglycemic, Anti-diabetic, o What are the side/adverse effects? Hypoglycemia, diarrhea.constipation, nausea, vomiting, upset stomach, loss of appetite. Headache, weight gain, o What are contraindications? low blood sugar. pituitary hormone deficiency. a condition where the adrenal glands produce less hormones called Addison's disease. glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. hepatic porphyria. a type of blood disorder where the red blood cells burst called hemolytic anemia. alcoholism. o Are there drug-drug interactions? Do not take if allergic to sulfa o Are there drug-alcohol interactions? Do not take with alcohol o Are there drug-food interactions? Take with breakfast (this person will still need to be checking their BS at least once a day) Metformin: o How does it work? works by reducing the amount of sugar your liver releases into your blood. It also makes your body respond better to insulin. o What diagnosis is it effective for? Type 2, less than 5 years, no end organ damage, young enough o What classification(s) does it fit into? Oral hypoglycemic, Anti-diabetic o What are the side/adverse effects? Can be harsh on end organs, esp. kidneys. It's best to take metformin with a meal to reduce the side effects. IF SOMEONE IS GOING TO HAVE CONTRAST FOR A CT: THE METFORMIN IS STOPPED PRIOR TO HAVING THE CONTRAST. If they are taking metformin, and they come into an ER and a CT with contrast is ordered, do not blindly send the patient to CT, LET THE PROVIDER KNOW AND THEY WILL ORDER IT WITHOUT CONTRAST. Since it is so hard on the kidneys, drink plenty of water. o What are contraindications? Kidney disease, heart attack; stroke; diabetic ketoacidosis (blood sugar that is high enough to cause severe symptoms and requires emergency medical treatment); a coma; or heart or liver disease Acarbose: o How does it work? What diagnosis is it effective for? by slowing the action of certain chemicals that break down food to release glucose (sugar) into your blood. Slowing food digestion helps keep blood glucose from rising extremely high after meals o What classification(s) does it fit into? alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, which also includes miglitol (Glyset); anti-diabetic, oral hypoglycemic agent o What are the side/adverse effects? Diarrhea, flatulence o What are contraindications? hypersensitivity, diabetic ketoacidosis, liver cirrhosis, inflammatory bowel disease, or colonic ulceration [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 03, 2022
Number of pages
16
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 03, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
133















.png)
, All Correct, Download to Score A.png)
, Correct, Download to Score A.png)



.png)


