(UOP) HCS 588 MEASURING PERFORMANCE STANDARDS COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAM REVIEW Q & A 2024
$ 13

OCR Oxford Cambridge and RSA Tuesday 21 June 2022 — Morning GCSE (9—1) History A (Explaining the Modern World) J410/12 The English Reformation c.i520-c.1550 with Castles: Form and Function C.IOOO—1750 Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes
$ 6

Test Bank For Educating Exceptional Children 15th Edition by Samuel Kirk, James J Gallagher, Mary Ruth Colem Chapter 1-13
$ 19

Organizational Behaviour Improving Performance And Commitment In The Workplace 6CE © 2025 By Jason A. Colquitt, Jeffery A. LePine, Michael J. Wesson, Ian Gellatly, TEST BANK
$ 19
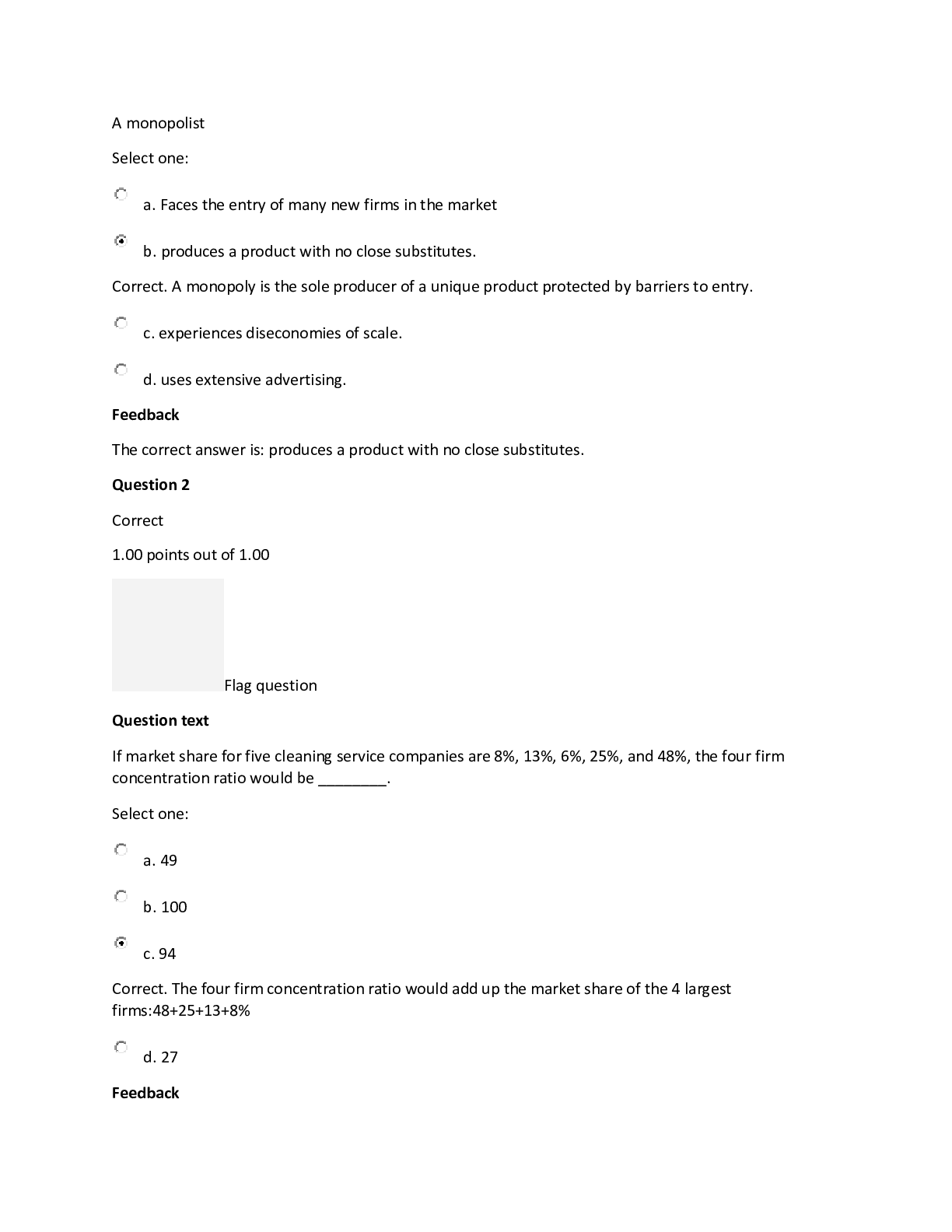
Homework 8_Monopoly
$ 12

Fundamentals Retake 2019
$ 20

NR599 Week 2 Midweek Comprehension Questions/Summary
$ 5

Governmental and Nonprofit Accounting 11th Edition by Freeman, Shoulders, McSwain, Scott TEST BANK