Questions and Answers > Arizona State University AST 113 ASTRONOMY Lab 8
Document Content and Description Below
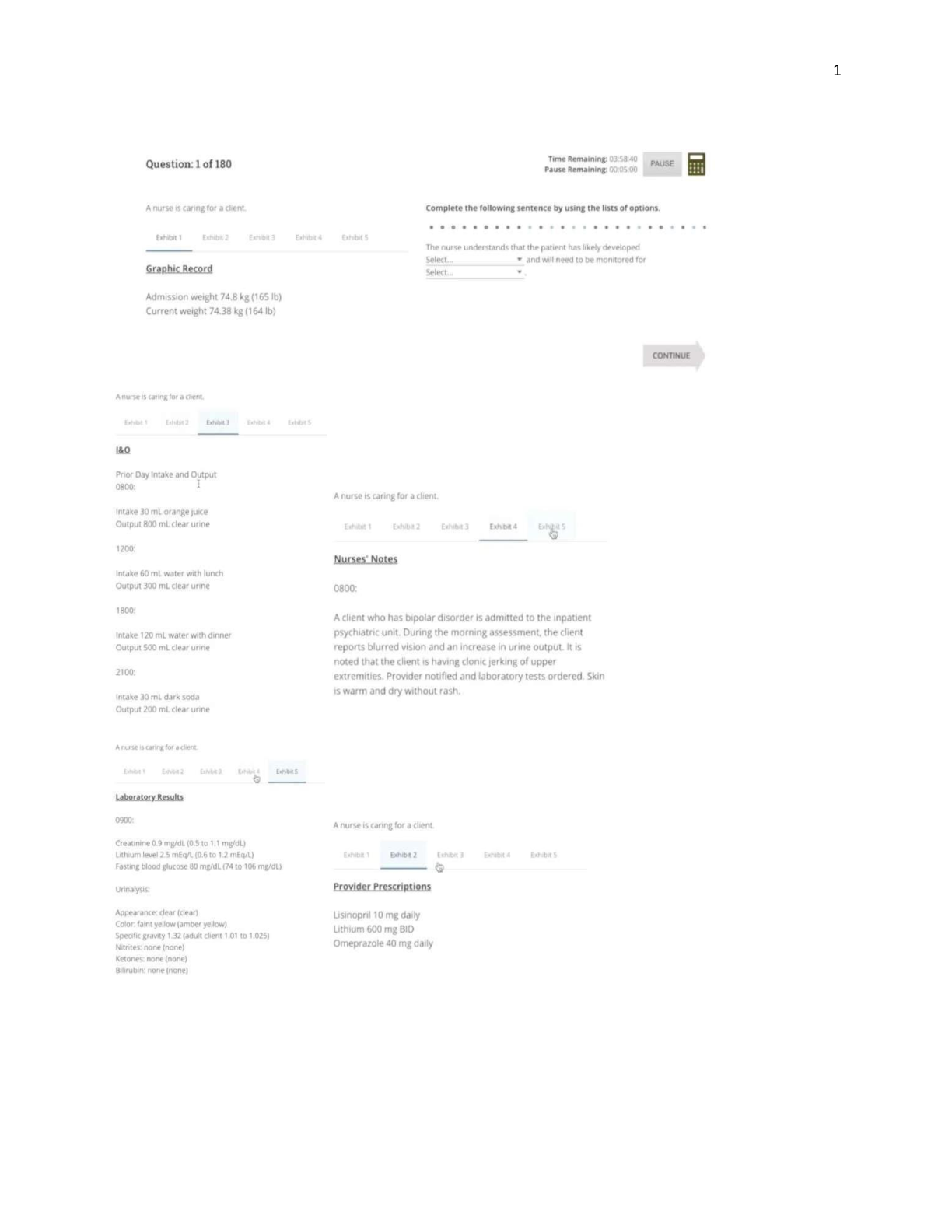
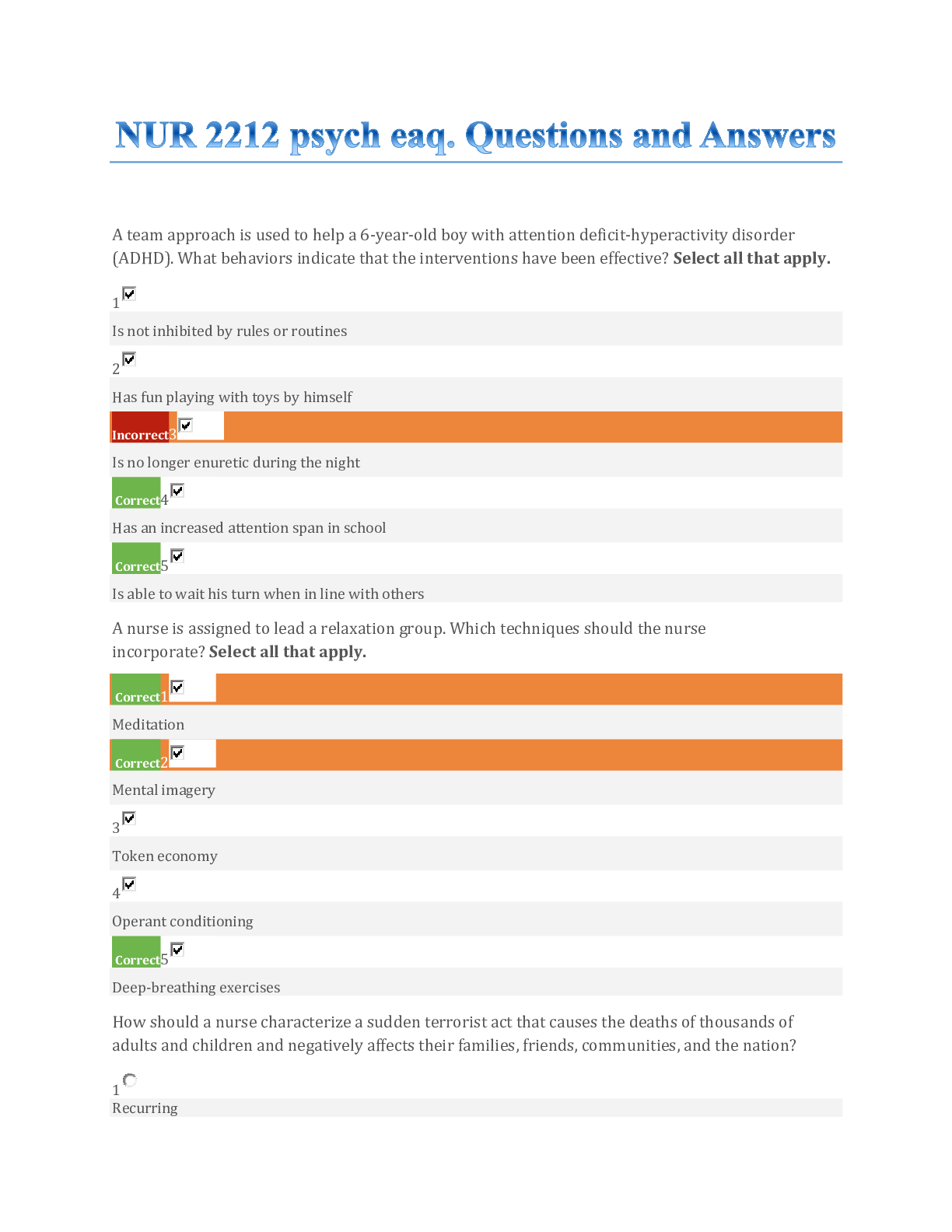
Arizona State University AST 113 ASTRONOMY Lab 8 Lab 8 QUESTION 1 1. Section I. Overview of Mars Please read the following Space.com article about Mars in order to answer Questions 1 - 5 below. ... 1. Read this article: Mars Facts: Life, Water and Robots on the Red Planet 2. Proceed to answer Questions 1 - 5 below. QUESTION 1 Select the best answer for each question below from the list on the right. 2 points H. J. QUESTION 2 1. Choose ALL of the items that are TRUE about the Valles Marineris canyon on Mars. It is longer than the Grand Canyon in Arizona It is deeper than the Grand Canyon in Arizona If placed in the United States, it could nearly reach from the Pacific Coast to the Atlantic Coast Water is still flowing in the canyon today It is about as wide as Australia 2 pointsQUESTION 3 1. Mars had many craters on its surface in the past, but today, there are very few craters because the old ones have all eroded away and no new ones have formed. Tru e Fals e 2 pointsQUESTION 4 1. Even though the diameter of Mars is only about half the diameter of the Earth, the Olympus Mons volcano on Mars is much higher than the tallest mountain on Earth (which is Mount Everest at a height of 8,848 meters or 29,029 feet). Tru e Fals e 2 pointsQUESTION 5 1. Choose ALL of the items that are TRUE about Mars. Mars has ice at the north and south poles that is made out of water and carbon dioxide. In the 1800s, some people thought Martians lived on Mars and built water canals across the planet due to early sketches made of Mars using poorly made telescopes. The atmosphere of Mars is mostly made of Carbon Dioxide. The gas in Mars' atmosphere was created long ago by plant life on Mars which died out about 75 million yrs ago. The atmosphere of Mars is less dense (atoms per cubic centimeter) than the atmosphere of Earth. Dust storms on Mars can produce winds with speeds up to 60 mph but the dust blocking out the sun is more of an issue to the solar panels on the rovers than the issue of the rovers being tipped over by the force of the wind. Section II. Identifying Features In this section, you will learn about the various types of surface features on Mars... like craters, canyons, eject, lava tubes, and other cool things! Be sure to read the "Feature Charts" document below. The questions in this section are directly related to the information in the document. It explains how to identify many of the surface features on Mars. In addition to the Features Chart docoment, there is a video lecture that talks about the features and provides additional information useful for the quesitons. 1. Review this description of surface features on Mars: Feature Charts.pdf 2. Watch this short video: 3. If you want to refer back to specific content in the above material, this table may help: Feature | Page | Start Location in Video Craters | 1 | 0:00 Volcanos 2-3 2:15 Canyons 4 4:00 Water 5 5:30 Sediments - 7:25 Wind 6-7 9:15 2 pointsQUESTION 6 1. Figure 1. What caused the highlighted features in Figure 1? A. Mini volcanic eruptions B. Frozen water C. Dust devils D. Collapsed lava tubes 2 pointsQUESTION 7 1. Figure 2. Based upon the shape of the tear-drop islands highlighted in Figure 2, choose the most likely direction of water flow. North is towards the top of the image and South is towards the bottom. West is to the left and East is to the right. A. Flow is towards the South - Southeast direction B. Flow is towards the North - Northwest direction C. Flow is from the East to the West D. Flow is from the West to the East 2 pointsQUESTION 8 1. Figure 3. Choose the answer which best describes the features in Figure 3. Sand dunes caused by wind Disturbed soil caused by dust devils. Carbon dioxide which went through repeated freezing and thawing cycles Volcanic ash 2 pointsQUESTION 9 1. Figure 4. Identify the highlighted feature in Figure 4. Collapsed lava tube Channel cut by water Tectonic crack from shifting plates beneath the surface Sand dunes 2 pointsQUESTION 10 1. Figure 5. Choose the best description of the highlighted featues in Figure 5. Light shadows Lava ash Sand dunes Wind streaks Section III. Measuring and Classifying Mars Surface Features In this section, you will be given an image in which various surface features are highlighted. You will be asked to either identify features, state a property of the features, or make a measurement of the features. Instructions are given for each part of the section below to help you answer the questions. You will want to have your ruler and calculator handy for the remainder of the lab. You can place your ruler directly against your computer screen to make the measurements needed. Part A. Measurement of Features 1. Read the instructions for the next two questions: Measuring Widths and Depths of Features.pdf 2. For all of the images in Section III, the real width of the image (left edge to right edge) is 18 km on Mars. 2 pointsQUESTION 11 1. Figure 6. Calculate the width of the channel identified as Feature A in Figure 6. Remember that the black arrow at the top of the image spans 18 km. 1 km 11 km 3 km 7 km 3 pointsQUESTION 12 1. Referring to Figure 6 again (above), what is the depth of the crater highlighted as Feature B? Remember to convert from km to meters. 400 meters 40 meters 100 meters 250 meters Section III. Part B. Relative Age Analysis In this part, you will learn about and follow the process that scientists use to determine the relative age of surface features on Mars and other planes. The "Analyzing Features" document explains how determine which features are older than others. 1. Read this document: Relative Ages.pdf 3 pointsQUESTION 13 1. Figure 7. In Figure 7, what type crater is Crater A? Preserved Modified Destroyed Newly formed 2 pointsQUESTION 14 1. Referring to Figure 7 again (above), what type of crater is Crater B? Preserved Modified Destoryed None of the above 2 pointsQUESTION 15 1. Referring to Figure 7 again (above), what type of crater is Crater C? Preserv ed Modifie d Destroy ed Sinkhol e 2 pointsQUESTION 16 1. Referring to Figure 7 again (above), what type of crater is Crater D? Preserv ed Modifie d Destroy ed Volcano 2 pointsQUESTION 17 1. Figure 8. Select the correct relative ages of Features A, B, and C in Figure 8. Featu re A Read Answer Items for Question 17 Featu re B Read Answer Items for Question 17 Featu re C Read Answer Answer 1. Oldest 2. Neither the oldest nor the youngest (somwhere in the middle) 3. Youngest 1. 2. 3. Items for Question 17 2 pointsQUESTION 18 1. Figure 9. Select the correct relative ages of Features A, B, and C in Figure 9. Featu re A Read Answer Items for Answer 1. Oldest 2. Neither the oldest nor the youngest (somwhere in the 2. Question 18 Featu re B Read Answer Items for Question 18 Featu re C Read Answer Items for Question 18 middle) 3. Youngest 2 pointsQUESTION 19 1. Section III. Part C. Putting It All Together Here we will combine the steps we practiced in the previous sections. The figure below will be used for the remaining questions. The figure shows the same image twice. On the left, the image has various lines drawn on top of it to suggest important distances in the questions below. On the right, the image has regions and features color coded and labeled as Feature A, B, or C. Remember that the width of each image is 18 km on the surface of Mars. You will want your ruler again in some of the questions below. 1. 3. Figure 10. First, we will identify the structures we are measuring. What is Feature A in the image on the right in Figure 10? 1. Volcano center 2. Collapsed sink-hole 3. Impact Crater 4. Ancient dried up lake bed 2 pointsQUESTION 20 1. Referring to Figure 10 again (above), what is the Feature B in the right image? 1. Ejecta 2. Landslide 3. Glacier 4. Dust devil track 2 pointsQUESTION 21 1. Referring to Figure 10 again (above), what is Feature C in the right image? 1. Sand dunes 2. Windstreak 3. Fissure 4. Polar ice spots 2 pointsQUESTION 22 1. Referring to Figure 10 again (above), what is the diameter of Feature A in the right image? Hint: The image on the left-hand side can be used to help you with these measurements. Don't forget that the actual width of each image on the surface of Mars is 18 km. 1. 34 km 2. 8.5 km 3. 3.7 km 4. 17 km 3 pointsQUESTION 23 1. Referring to Figure 10 again (above), what is the diameter of the Feature B in the right image? 1. 8.5 km 2. 34 km 3. 20 km 4. 40 km 3 pointsQUESTION 24 1. Referring to Figure 10 again (above), what is the depth of the crater labeled Feature C? Hint: Use the fact that the solar incidence angle was 57.9 degrees. 1. 0.28 meters 2. 680 meters 3. 54 meters 4. 1400 meters [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 23 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)
.png)
Arizona State University AST 113 ASTRONOMY Lab 1- Lab 14 All Scenarios <Questions and Answers>
Questions and Answers > Arizona State University AST 113 Lab 1. All Scenarios Questions and Answers > Arizona State University AST 113 ASTRONOMY Lab 2 Questions and Answers > Arizona State Unive...
By Kirsch 3 years ago
$49
14
Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 08, 2022
Number of pages
23
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 08, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
348