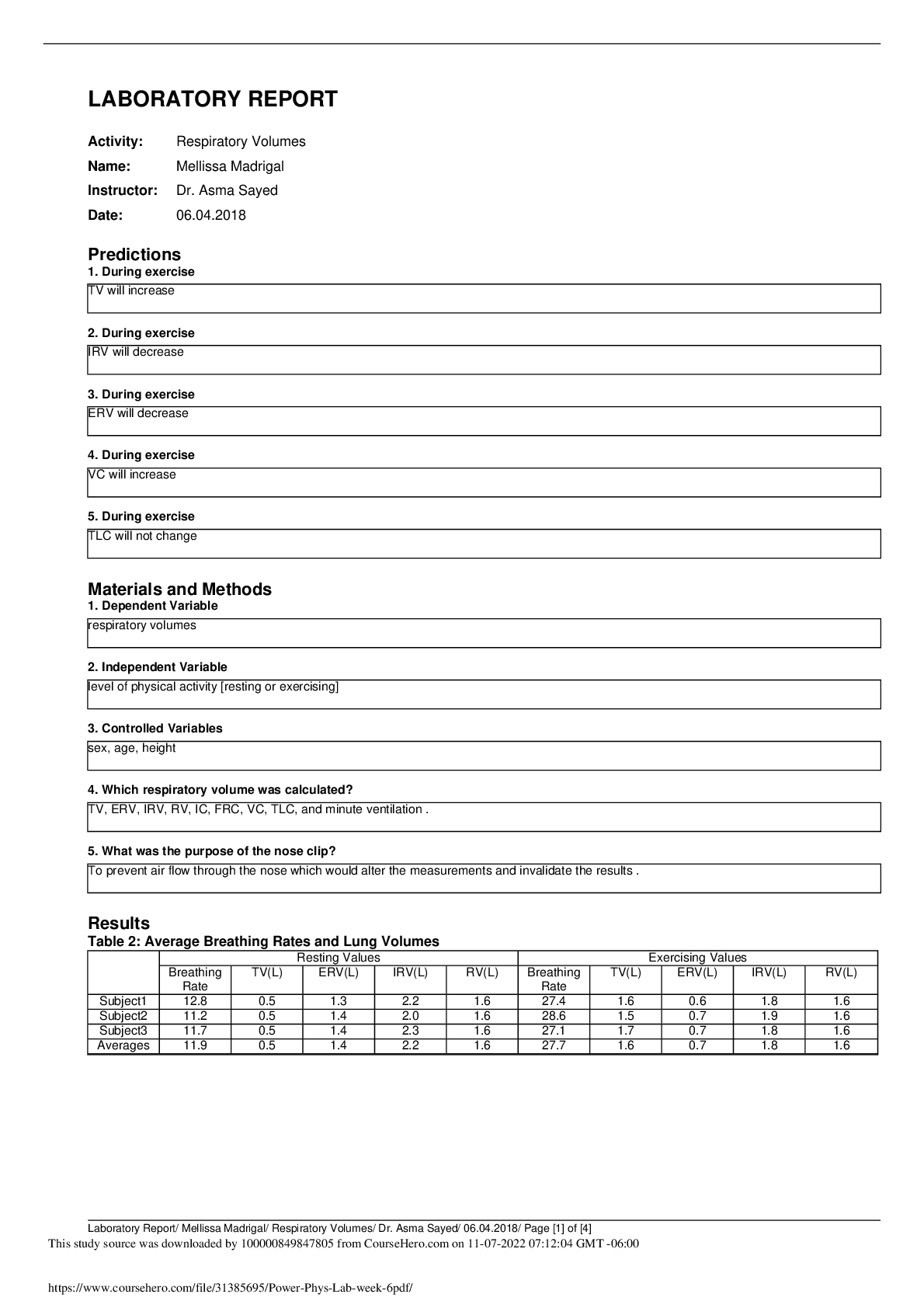
Report for Experiment #13
Simple Harmonic Motion
Kaleigh Schnell
Lab Partner: Jasmin Wilson
TA: Kunpeng Mu
September 20, 2016
Abstract
Simple Harmonic Motion is an everyday part of life that is not usually thought
...
Report for Experiment #13
Simple Harmonic Motion
Kaleigh Schnell
Lab Partner: Jasmin Wilson
TA: Kunpeng Mu
September 20, 2016
Abstract
Simple Harmonic Motion is an everyday part of life that is not usually thought about in much
detail. Simple Harmonic Motion is defined to be the motion of a mass on a spring when it is
subject to the linear elastic restoring force given by Hooke's Law. The motion is sinusoidal in
time and demonstrates a single resonant frequency. This lab looks at this definition and Newton’s
Second Law which states an object is said to be in equilibrium when the sum of all forces acting
on it add up to zero or no force means no acceleration.Introduction
This experiment studies oscillations of a glider on an air track, held by a spring on each side. The
point of the lab is to understand characteristics of oscillating motion: amplitude, period,
frequency, and phase and to explore harmonic motion that includes damping forces. There are
two investigations in this lab, the first Investigation looks at the basic apparatus of a glider on an
air track attached to the ends of the track by two springs. The experimenters are to determine the
amplitude A, the period T, the phase ø, and the spring constant k. The materials needed are an air
track with glider, two 7.4 cm long springs, computer, PASCO PASPort USB Link and Motion
Sensor, and six ring magnets. The second Investigation focusses more on damped harmonic
motion. This is looking at the effects of friction on harmonic motion. The friction in this lab is
caused by electromagnetic force which is generated by ring magnets placed on the glider. The
magnets moving along the track induce currents which transfer energy to the track and slow the
glider down.
Investigation 1
Setup & Procedure
[Show More]
.png)





.png)










.png)





.png)


