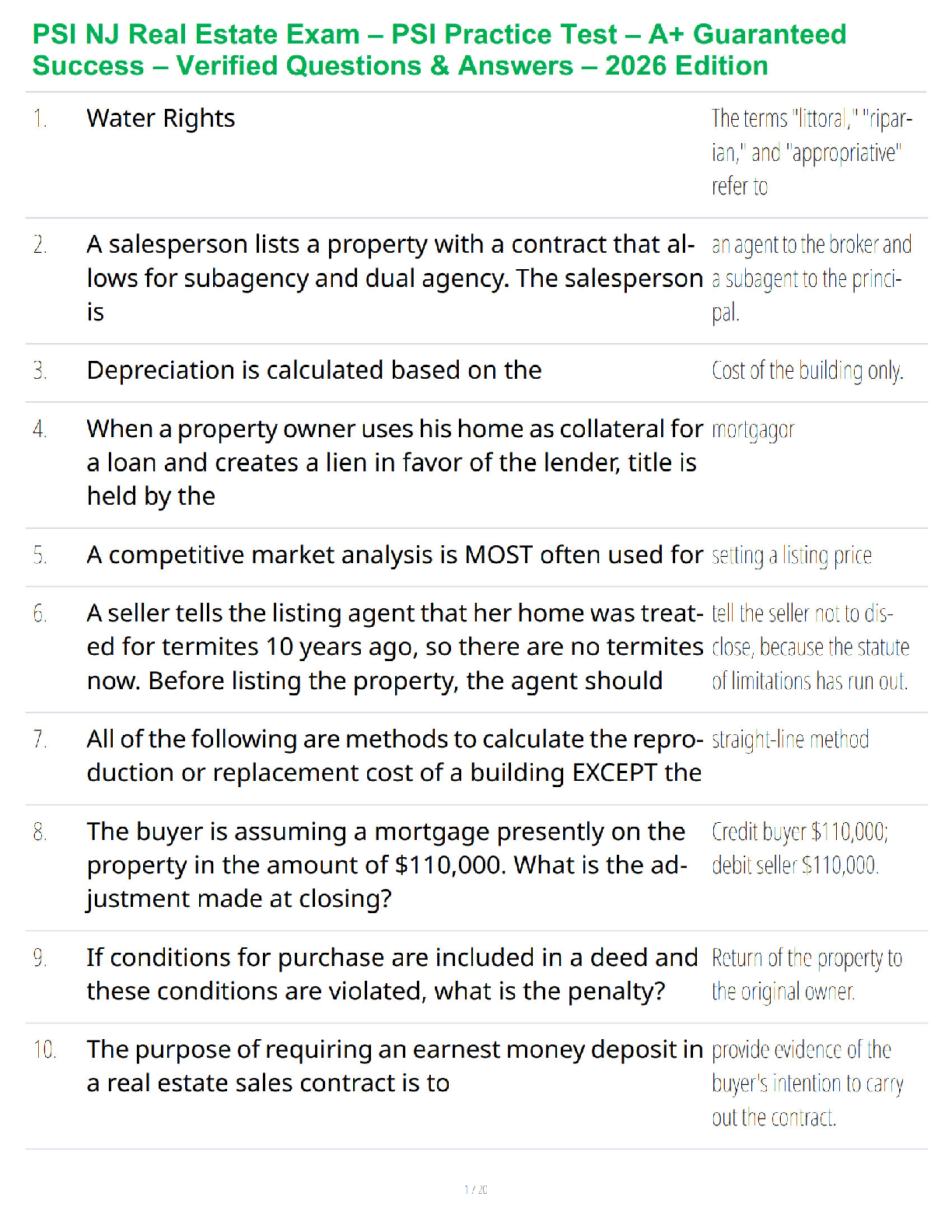
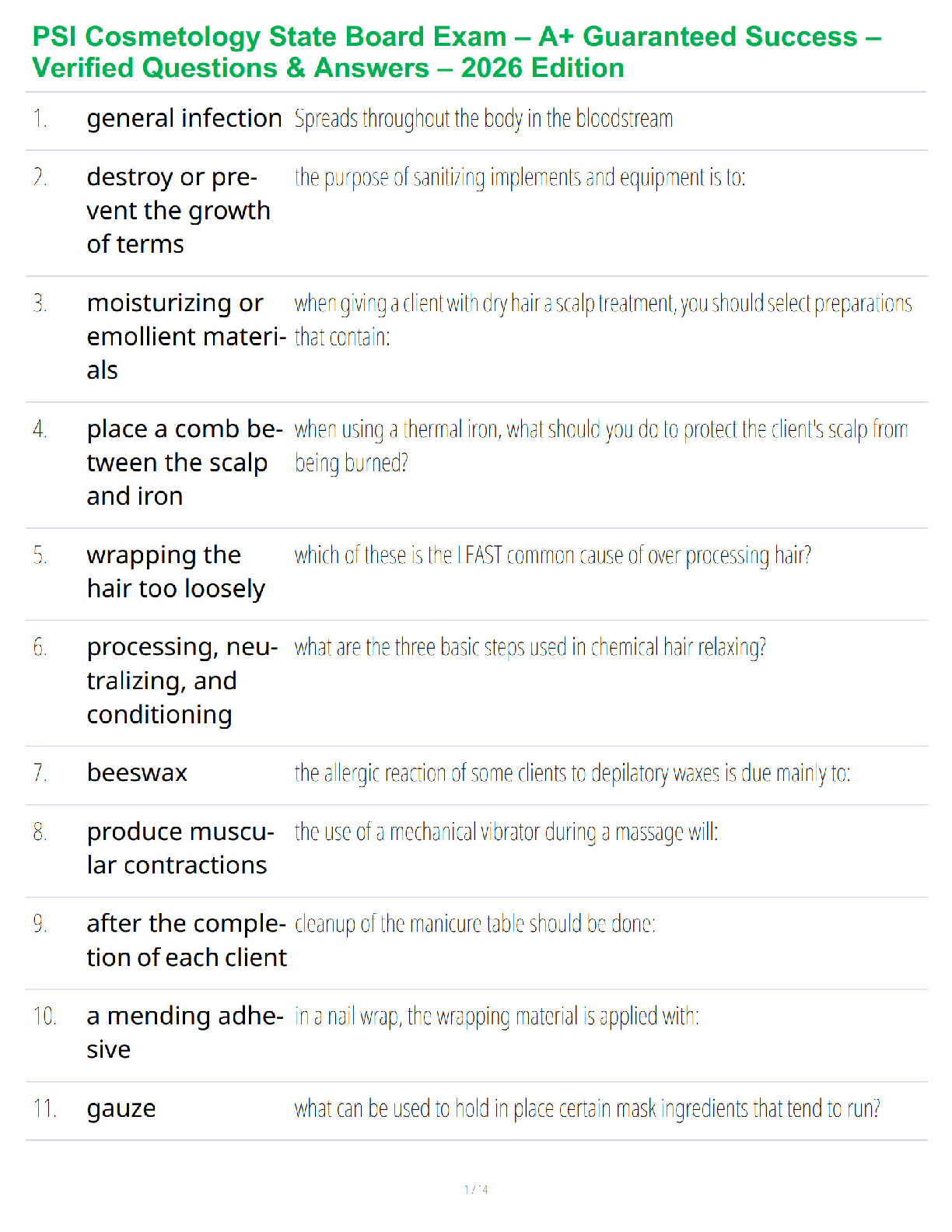
NR 508 Final Exam study guide (1) 2020
Cardiovascular management:
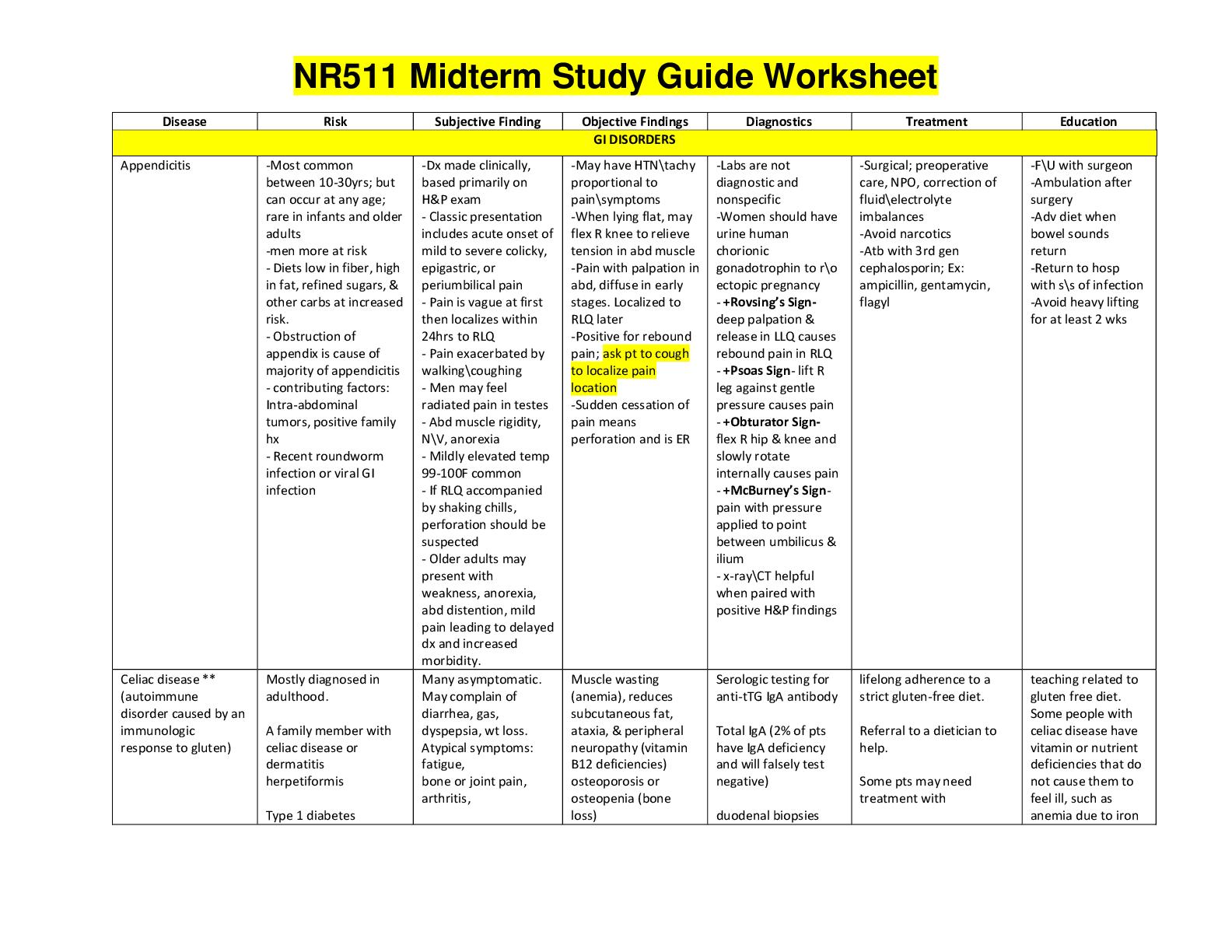
Know Initial treatment choices for HTN
Ace inhibitors and ARBs
Know first line treatment options for HTN for African Americans without renal impair
...
NR 508 Final Exam study guide (1) 2020
Cardiovascular management:
Know Initial treatment choices for HTN
Ace inhibitors and ARBs
Know first line treatment options for HTN for African Americans without renal impairment.
Thiazides
First line option for HTN for anyone with chronic kidney disease
ACEIs or ARBs, appropriate diuretic therapy, and dietary salt restriction make up the foundation for the treatment of HTN in CKD. Lisinapril and Furosomide.
IN most instances, the hypertensive CKD patient requires multiple drugs to reach goal blood pressure. Multiple antihypertensive drug combinations are possible in the CKD patient. One combination of note is that of an agent that blocks the effects of the renin-angiotensin system given together with a loop diuretic and any of several other drug classes.
Diuretics: types, uses side effects, names; preferred diuretic with renal impairment; side effect of post diuretic sodium retention; recognition that some diuretics are sulfa derivatives (carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, loop diuretics, thiazides, but NOT ethacrynic acid); management of edema
Thiazide diuretics increases amount of urine produced by reducing sodium re-absorbtion in the kidney. Another effect they have is to widen the blood vessels which also helps reduce blood pressure.
bendroflumethiazide , chlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, hydrochlorothiazide, indapamide, metolazone.
Loop diuretics are powerful diuretics that work in a part of the kidney called the loop of Henle where they reduce sodium, chloride and potassium reabsorption. This increases the amount of urine produced which helps reduce blood pressure and also helps remove any extra fluid that has been accumulating around the body (odema) or the lungs.
Furosemide (Lasix), Bumetanide (Bumex), Torsemide (Demadex), Chlorothiazide (Diuril)
Potassium sparing diuretics are weaker diuretics that have their effect by increasing the amount of water and sodium that passes through the kidneys to increase urine volume. Because there is no increase in the amount of potassium that is passed through the kidney sometimes you may end up with higher potassium levels. Examples are
Eplerenone (Inspra), Triamterene (Dyrenium), Spironolactone (Aldactone), Amiloride (Midamorgeneric), Spironolactone(CaroSpir)
SE= Acne, Alopecia, Ascites, Edema, Gender Dysphoria, Heart Failure, HTN, Hirsutism, Hypokalemia, Primary Hyperaldosteronism, Primary Hyperaldosteronism Diagnosis
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are weaker diuretics that act by increasing the amount bicarbonate, sodium, potassium and water excreted from the kidney. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are also used to reduce fluid levels in the eye and is sometimes used off-label for altitude sickness. An example is
Acetazolamide
SE=
side effects of diuretics may include changes in potassium, sodium, calcium or magnesium blood levels, changes in heartbeat, you may have dizziness, headache, tiredness, dry mouth, gastric upset, gout, increase sugar levels or muscles cramps. Related medical conditions: Edema, Congestive heart failure, Hypertension (high blood pressure), Ascites.
CHF drugs including diuretic choices Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are a good choice for people who have had a heart attack, because the medicine helps reduce the workload on the heart, diabetes, help protect the kidneys small amounts of protein in your urine (microalbuminuria), an early sign of kidney damage, prevent a heart attack or stroke.
SE= Hives, Irregular heartbeats (this could be caused by too much potassium in your blood), Dizziness or lightheadedness or fainting, Dry cough, Headache. Don’t take with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antacids, potassium supplements, certain diuretics, and lithium.
Captopril (Capoten)
Enalapril (Vasotec)
Fosinopril (Monopril)
Lisinopril (Prinivil, Zestril)
Perindopril (Aceon)
Quinapril (Accupril)
Ramipril (Altace)
Trandolapril (Mavik)
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (or Inhibitors) ARBs or Angiotensin-2 Receptor Antagonists) have had a heart attack, have coronary artery disease, have high blood pressure that hasn’t responded well to ACE inhibitors, have had many side effects from ACE inhibitors.
SE= headache, fainting, dizziness, nasal congestion, diarrhea, back pain, leg pain, arrhythmia,
Candesartan (Atacand), Eprosartan mesylate (Teveten), Irbesarten (Avapro), Losartin potassium, (Cozaar), Telmisartan (Micardis), Valsartan (Diovan)
Angiotensin-Receptor Neprilysin Inhibitors (ARNIs)
Sacubitril/valsartan
Channel Blocker (or inhibitor) the drug increases the diameter of blood vessels, reduce the force of contraction of the heart, and slow heart rate, all of which helps keep your heart from having to work as hard. This drug class reduces the heart rate, similar to another class of drugs called beta blockers. Also used to treat Angina (chest pain), Arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat)
SE= Calcium channel blockers should always be taken with a meal or a glass of milk to protect the stomach, don’t take with grapefruit juice or grapefruit. Weight gain, Swelling in the lower legs, feet, or ankles, dizzy, weight gain, Constipation, tired or drowsy, tachy, brady, and arrthymia, Coughing, wheezing, or problems with breathing or swallowing, Nausea, Numbness or a tingling sensation in the feet or hands. DON’T take with Other high blood pressure medications, including ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors or beta blockers, Diuretics, Some eye medications, Large amounts of vitamin D or calcium supplements, Drugs used to treat arrhythmia, Digitalis, also called digitoxin (Digoxin), Drugs that contain cortisone, or any corticosteroids
Diltiazem (Cardizem, Cartia, Dilacor XR, Diltia XT, Tiamate)
Verapamil (Calan, Covera-HS, Isoptin, Verelan)
Nifedipine (Adalat, Procardia, Procardia XL)
Nicardipine (Cardene)
Nimopidine (Nimotop)
Amlodipine (Norvasc, Lotrel)
Nisoldipine (Sular)
Isradipine (DynaCirc)
Bepridil (Vascor)
Felodipine (Plendil)
Beta Blockers are one of the most widely prescribed classes of drugs to treat hypertension (high blood pressure) and are a mainstay treatment of congestive heart failure. Beta-blockers work by blocking the effects of epinephrine (adrenaline) and slowing the heart's rate, thereby decreasing the heart’s demand for oxygen. Long-term use of beta-blockers helps manage chronic heart failure. Heart failure, High blood pressure, Angina, Abnormal heart rhythms, Heart attack. and sometimes prescribed for glaucoma, migraine headaches, anxiety, certain types of tremors, and hyperthyroidism.
SE= Fatigue, Cold hands, Headache, Upset stomach, Constipation, Diarrhea, Dizziness, Shortness of breath, Trouble sleeping, Loss of sex drive/erectile dysfunction, Depression.
Acebutolol (Sectral), Atenolol (Tenormin), Bisoprolol (Zebeta), Carvedilol (Coreg), Esmolol (Brevibloc), Inderal (propranolol), Normodyne, Trandate (labetalol), Metoprolol (Lopressor, Toprol-XL), Bisoprolol (Zebeta), Metoprolol succinate (Toprol XL), Carvedilol CR (Coreg CR)
Aldosterone Antagonists block the effects of a hormone produced naturally by your adrenal glands which can cause your heart failure to get worse. Aldosterone receptor antagonists affect the balance of water and salts going into your urine and are weak diuretics. They help lower blood pressure, reduce congestion and thus protect the heart.
SE= This drug can sometimes affect kidney function and can also increase potassium levels. This is especially important for patients who also use ACE inhibitors or ARBs. Your doctor will monitor your kidney function and potassium levels through regular blood tests.
Spironolactone (Aldactone), Eplerenone (Inspra)
Hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate (specifically benefits African Americans with heart failure)
Hydralazine and isosorbide dinitrate (combination drug) - (Bidil)
What do these types of medication do:
Anticoagulants (blood thinners) These drugs may be prescribed if you are a heart failure patient with atrial fibrillation, or have another problem with your heart where adding this drug is indicated. Anticoagulants are not used to treat heart failure without the presence of atrial fibrillation.
Cholesterol lowering drugs (statins) Your doctor may prescribe this class of medication if you have high cholesterol or have had a heart attack in the past. This class of drugs is not used to treat heart failure, but other conditions as indicated.
SE= Headache, Difficulty sleeping, Flushing of the skin, Muscle aches, tenderness, or weakness, myalgia), Drowsiness, Dizziness,Nausea or vomiting, Abdominal cramping or pain, Bloating or gas, Diarrhea, Constipation, Rash, memory loss, mental confusion, high blood sugar, and type 2 diabetes, Myositis , inflammation of the muscles, Elevated levels of CPK, or creatine kinase, and Rhabdomyolysis.
STATINS
Caduet® (amlodipine and atorvastatin)
Crestor® (rosuvastatin)
Juvisync® (sitagliptin/simvastatin)
Lescol® (fluvastatin)
Lescol XL (fluvastatin extended-release)
Lipitor® (atorvastatin)
Liptruzet™ (ezetimibe/atorvastatin)
Livalo® (pitavastatin)
Mevacor® (lovastatin)
Pravachol® (pravastatin)
Simcor® (niacin extended-release/simvastatin)
Vytorin® (ezetimibe/simvastatin)
Zocor® (simvastatin).
Advicor® (niacin extended-release/lovastatin)
Altoprev® (lovastatin extended-release)
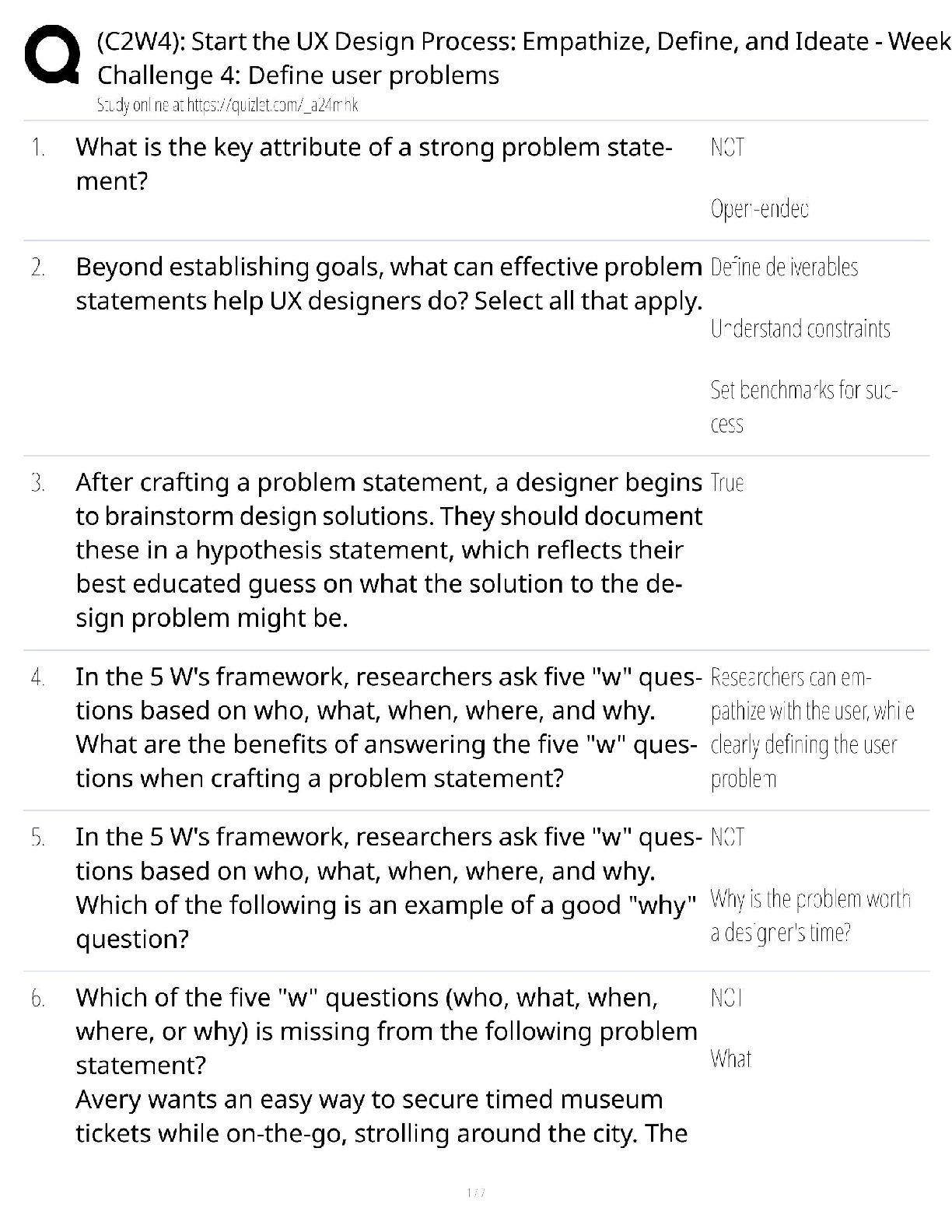
Neuro/Psych:
Migraine management and prophylactics
Almotriptan Malate Migraine, acute Adult
Aspirin Migraine Adult
Droperidol Migraine Adult
Eletriptan Hydrobromide Migraine, acute Adult
Frovatriptan Succinate Migraine, acute Adult
Ibuprofen Migraine Adult
Naratriptan Hydrochloride Migraine, acute Adult
Propranolol Hydrochloride Migraine; Prophylaxis Adult
Rizatriptan Benzoate Migraine, acute Adult
Sumatriptan Migraine, acute Adult
Sumatriptan Succinate Migraine, acute Adult
Sumatriptan Succinate/Naproxen Sodium Migraine, acute Adult
Timolol Maleate Migraine; Prophylaxis Adult
Topiramate Migraine; Prophylaxis Adult, Pediatric
Valproic Acid Migraine; Prophylaxis Adult
Zolmitriptan Migraine, acute
Herbal migraine management
Feverfew
Butterbur
Migraine medications to avoid in patients with asthma.
Ketorolac Tromethamine, Acetaminophen/Codeine Phosphate, Meperidine Hydrochloride, Timolol Maleate, Propranolol Hydrochloride, Butorphanol Tartrate, Naproxen Sodium, Ibuprofen, Aspirin
Methylphenidate (Ritalin)
SE= Heart failure, Increased blood pressure, Increased heart rate, Peripheral vascular disease, Raynaud's disease
ADHD management - stimulants including side effects, alternatives, age they may be used, strattera, which is the longest acting stimulant?
Stimulants
Adderall and Adderall XR (amphetamine mixtures) used in children
Concerta (methylphenidate, extended release) 10-12 hrs dose 1x day most are 6 & up
ConcertaR is 13-17
Daytrana (methylphenidate topical patch)
Dexedrine and Dexedrine Spansules (dextroamphetamine)
Pediatrics (3 to 5 years old; short-acting, Dexedrine): 2.5 mg orally once daily
Pediatrics (6 years old and older; short-acting, Dextrostat): 5 mg orally once or twice daily
Pediatrics (6 years old or older, long-acting, Dexedrine spansule): 5 to 10 mg orally once or twice daily; maximum 40 mg daily
Focalin and Focalin XR (dexmethylphenidate, immediate and extended release)
Metadate ER and and Metadate CD
Ritalin, Ritalin-SR, and Ritalin LA (methylphenidate, immediate and extended release) used in children 6 and up.
Vyvanse (lisdexamfetamine) up to 12 hours does once a day
Nonstimulants
Catapres (clonidine)
Strattera (atomoxetine) once a day last 24 hours
Tenex (guanfacine)
SE= psychotic symptoms, stroke, lower the seizure threshold, heart attack, twitching of a muscle group, especially in the face, caution in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder, rapid heart rate,
***************************************************CONTINUED*******************************************************
[Show More]














.png)









.png)