*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > NR 508 Final Exam study guide (2) 2020 | NR 508 Advanced Pharmacology final exam guide, A++ Guide; C (All)
NR 508 Final Exam study guide (2) 2020 | NR 508 Advanced Pharmacology final exam guide, A++ Guide; Chamberlain College of Nursing.
Document Content and Description Below
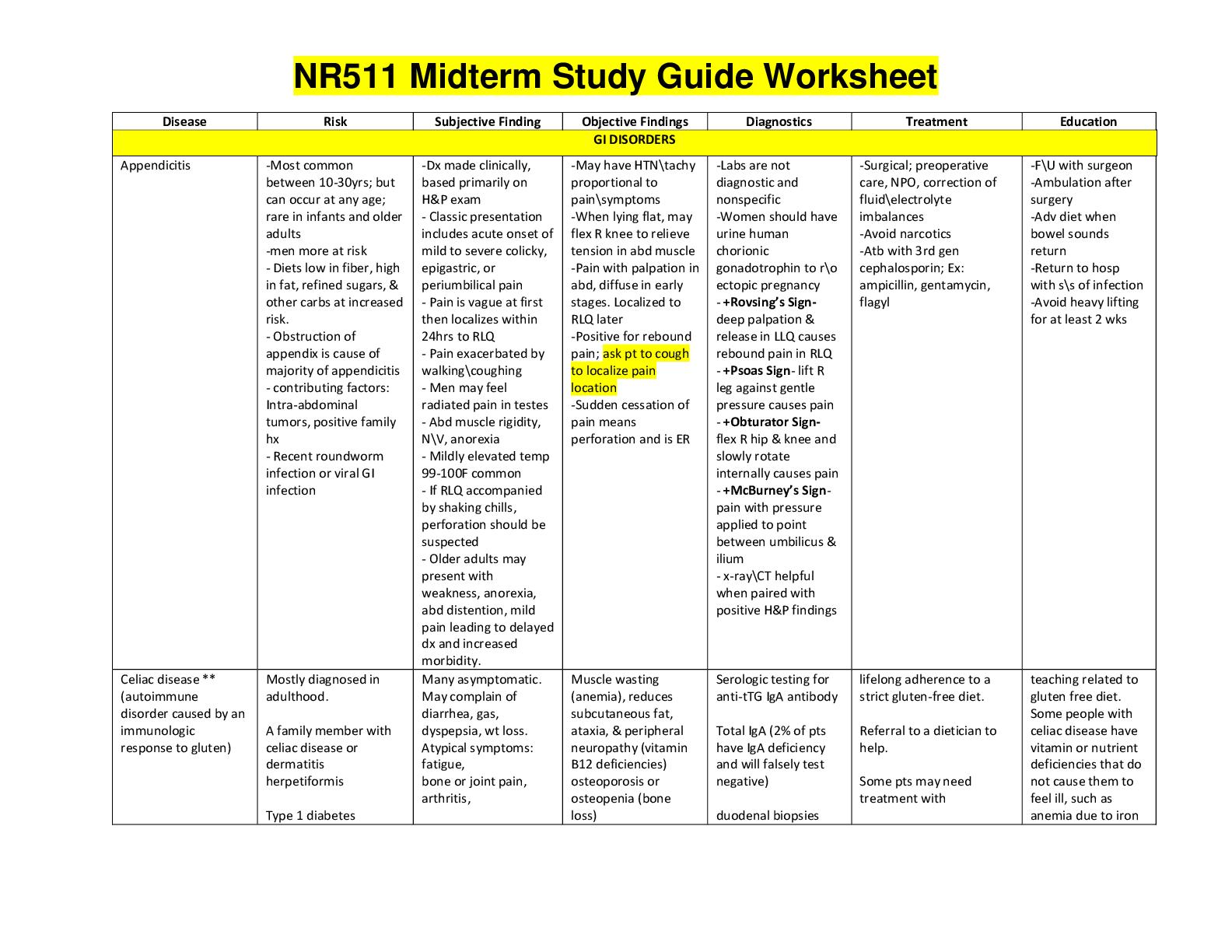
NR 508 Final Exam study guide (2) 2020 Cardiovascular management: 1. Know Initial treatment choices for HTN AceI- sartans Arbs- ipine, verapamil & diltazem Thiazide- iaside, chlorthalidone, imdap ... amide, metolazone calcium channel blocker 2. Know first line treatment options for HTN for African Americans without renal impairment. Calcium channel blockers Thiazide 3. First line option for HTN for anyone with chronic kidney disease Ace inhibitors ARB’s Diuretics: 4. Types, Uses, Side effects Thiazides (HCTZ) Uses- HTN, CHF, edema, useful in decreases calcium stone formation Off label HCTZ- osteoporosis and diabetes AE- hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, arrhythmias, metabolic alkalosis, fatigue, postural Hypotension Loop diuretics (furosemide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid) *preferred diuretics for renal Impairment Uses- CFH, HTN, nephrotic syndrome, cirrhosis, pulmonary edema AE-hypocalcemia, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, ototoxicity Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (acetazolamide) *weak diuretic Uses- edema, epilepsy, glaucoma, mountain sickeness AE- toxic epidermal necrolysis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, metabolic acidosis Potassium-sparing (spironolactone, eplerenone) Uses- CHF (in combo with thiazides or ACE and loop), HTN AE-gynomastia, n/v, erectile dysfuction, electrolyte imbalance, metabolic acidosis **postdiuretic sodium retention- It is important for pts to adhere to a low sodium diet. As drug concentrations fall, there is a period of positive sodium balance ** If a pt has a sulfa allergy= take ethacrynic acid 5. Preferred diuretic with renal impairment- Loop diuretics because they retain efficacy even with moderate renal insufficiency: such as furosemide, buetanide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid. Uses: Edematous states (HF, cirrhosis, pulmonary edema, nephrotic syndrome), hypercalcemia 6. Side effect of post diuretic sodium retention pg 374 As drug concentrations decrease, period of + Na balance, this is the post diuretic sodium retention If there is a high Na intake then Na lost with diuresis is offset.. diuretic resistance 7. Recognition that some diuretics are sulfa derivatives (carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, loop diuretics, thiazides, but NOT ethacrynic acid) Loops- Examples: furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide, ethacrynic acid "The Loop FURiously BUMmed my TORSo like ACID" Common side effects: orthostatic hypotension, excessive diuresis, tinnitus, vertigo, hyperuricemia note all these are precursors to toxicity Thiazides Hydrochlorothiazide, Chlorothoazide, , Chlorthalidone, Indapamide, Metolazone 1st line for HTN, Chronic Calcium Kidney Stones, HF, Idiopathic hypercalciuria, Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, Osteoporosis. Other common side effects: orthostatic hypotension, dizzy, drowsy, syncope, weakness, nausea, GI irritation, elevated BUN, depressed respirations lethargy Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors- Acetazolamide N/V/D, Drowsy, Parathesis, confusion, tinnitus, myopia, anorexia, change in taste; polyuria, mild electrolyte changes Uses: Edematous states ( HF, cirrhosis, pulmonary edema, nephrotic syndrome), hypercalcemia Ethacrynic Acid Note it's the only diuretic with "acid" in its name 8. Management of edema Loops for volume excess 9. CHF drugs including diuretic choices 1- Loops -fluid 2- ACEIs or ARBs 3-BB - Diastolic after stable (B-Day) 4- Digoxin - Systolic , AFib, (Dig A Syst) 5- Spironolactone - if above not effective 6- Nitrates & Hydralazine *AA only* Think Michael Jordan goes Hy in his NIkes CCBs ( Amlodipine/Felodipine) only for angina or HTN if EF is preserved 2- Clinical pearls for CHF- Improve SX: ACEIs, ARBs, BBs (metoprolol, Bisoprolol, Carvedilol) , Dig ( only after diuretics & ACEIs) Prolong survival: ACEIs, ARBS, BB, Hydralazine/Nitrates(AA only) Aldosterone Antagonists BB NEVER IN ACTIVE FAILURE Dig does not improve mortality but improves SX decreases Hospitalization.. CAUTION:: Loops without Spironolactone **with hyperkalemia DIG CAN BECOME TOXIC" Neuro/Psych: 10. Know migraine management and prophylactics (see migraine lecture) dark, quiet room *NSAIDS or APAP *Triptans (sumatriptan/imitrex, zolmatriptan/zomig, rizatriptan/maxalt) -nasal, oral, subq -use no more than 2d/wk -CI-recent use of MAOIs, ergots, or SSRIs, CVD, CAD, TIA, HTN, pregnancy *Ergots (ergotamine tartrate/cafergot) not used often, expensive -nasal, oral, rectal, IM, IV, siblingual -CI-recent use of triptans, CVD, CAD, TIA, HTN, pregnancy *Caffeine (Excedrin) *antiemetics Migraine prevention *beta blockers (metoprolol, propranolol, timolol) -takes 2-3 months for full benefit- can decrease frequency and severity by 50% -AE- drowsiness, exercise intolerance, depression -CI-CHF, asthma *anticonvulsants (valproate, topiramate) effective but both have major AE -valproate AE- dizziness, platelet dysfunction, hair loss, hepatotoxic, teratogenic -topiramate AE- cognitive dysfunction, weight loss, renal stones *butterbur- PA free only, otherwise can cause liver damage and severe illness 11. Herbal migraine management Butter bur root. It should be PA free or could result in liver damage. Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium) - Action: Antiinflammatory effects Uses: migraine prevention Interactions: Anticoagulants, antiplatelet drugs, aspirin (Pg. 99) 12. What drugs can cause serotonin syndrome? SSRIs and TRIPTANS 13. What migraine prophylactic medication class to avoid in patients with asthma. Beta Blockers such as Propranolol cyproheptadine (Periactin) - The drug may produce an atropine-like action, so it must be used with caution in patients treated for bronchial asthma (pg. 487) 14. Know the common side effects of methylphenidate Ritalin Most common: Nervousness & Insomnia Other common side effects: Decreased appetite Abdominal pain HA Depression Irritability Weight loss Rebound effect Side effects like if I don't have my stimulant COFFEE!! Page 453 Also: Temporary slowing of growth rate/Height and weight should be monitored with long term use ADHD management – 15. At what age can ADHD dx be made? DX typically before age 7 16. Stimulants including: Side effects -eg HA, tics, appetite suppression, elevated BP Stimulants: work by increasing “background” dopamine levels in the synapses. However, diagnostic trials of stimulant medications have failed to distinguish between children with and those without AD/HD. Amphetamine Like Drugs (Methylphenidate, ritalin, metadate, concerta) 1st LINE OF TREATMENT MOA: mild cortical stimulant with CNS actions similar to amphetamines. Inhibits reuptake of norepinephrine & dopamine Side effects: (may subside after a few weeks) common –These are drugs including methylphenidate and dexmethylphenidate Side effects Increased BP Exacerbation of behavior Agitation and aggression Watch for abuse Mania psychotic symptoms Blurred vision Temp stunting of growth Decreased appetite HA Depression Rebound SX NERVOUSNESS & INSOMNIA MOST COMMON monitor height weight and BP * Amphetamines - (Adderall, Vyvanse) MOA: Norepinephrine released from central noradrenergic neurons. Side effects: These drugs include dextroamphetamine Side effects Effects more severe initial days of TX Anorexia Weight loss Nausea Abdominal pain Diarrhea Xerostomia Constipation ** tics motor or phonetic May be unmasked* * Black Box warning sudden death with structural cardiac abnormalities*** Others- armodafinil (Nuvigil), modafinil (Provigil), Guanfacine (Intuniv), Clonidine (Kapvay) 17. At what age can medications for ADHD be prescribed? 6 YEARS AND UP Meds 6 and up RX of younger than 6 is off label 18. Which is the longest acting stimulant? Long Acting: methylphenidate (AMPHETAMINE LIKE DRUG) SR Concerta ( 12 HOURS), Metadate CD, Ritalin LA, Methylin, Daytrana Transdermal System, amphetamine/dextroamphetamine Adderall XR, clonidine Kapvay Atomoxetine is metabolized by the 2D6 enzyme system. Its half-life is 4 hours in most patients, although this may be prolonged to 30 to 40 hours in poor metabolizers (7% of population). Nonstimulant alternatives: 19. Strattera/ atomoxetine Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor used to treat ADHD As effective as stimulants Low abuse potential Black box increased risk of suicide Preg C Causes more vomiting and insomnia Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (Strattera- atomoxetine) not a controlled substance and it is not a stimulant MOA: reuptake of presynaptic norepinephrine. It does not bind to monoamine receptors in the brain, thereby decreasing the risk of adverse reactions compared with older norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors. Side effects: “black box” warning increased suicide risk, vomiting, insomnia, headache, rhinitis, upper abdominal pain, decreased appetite, constipation, increased cough, flu syndrome Half-life - Atomoxetine is metabolized by the 2D6 enzyme system. Its half-life is 4 hours in most patients, although this may be prolonged to 30 to 40 hours in poor metabolizers (7% of population). 20. Clonidine derivatives eg guanfacine (intuniv)- these tend to be most effective in younger boys with hyperactivity symptoms and can be helpful with insomnia armodafinil (Nuvigil), modafinil (Provigil), Guanfacine (Intuniv), Clonidine (Kapvay) Use in children younger than 6 years of age is off-label. Most effective in younger boys Hyperactive SX and insomnia Stimulate alpha 2 adrenoreceptors, reduce sympathetic outflow 21. Buproprion (wellbutrin) (it is an off-label use) – consider in adolescent who also has depressive symptoms Off label for ADHD CONSIDER IN ADOLESCENT WHO HAD DEPRESSION SX NOTE WITH ANY ALPHA AGONISTS OR ANTIDEPRESSANTS RISK FOR ADVERSE CARDIAC EVENTS 22. Know the treatment of Alzheimer’s and the education behind the medication management of the disease. (When are each of them indicated? What is their benefit?) cholinesterase inhibitors. Cholinesterase inhibitors (ChE inhibitors (this abbreviation may be seen on the exam) eg donepezil: Can be used at any stage; Helps with functioning Donepezil SEVERE Rivastigmine MILD TO MOD Galantamine MILD TO MOD THIS CLASS IS CONSIDERED 1ST LINE SPECIFICALLY DONEPEZIL, GALANTAMINE ER , and RIVASTIGMINE DUE TO THEIR ONCE A DAY DOSING THESE DRUGS ARE SHOWN TO DELAY PROGRESSION OF DEMENTIA SX THUS IMPROVING FUNCTION DOES NOT HALTER DISEASE OR CURE Continues............................................................................................... [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 31, 2020
Number of pages
17
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 31, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
115