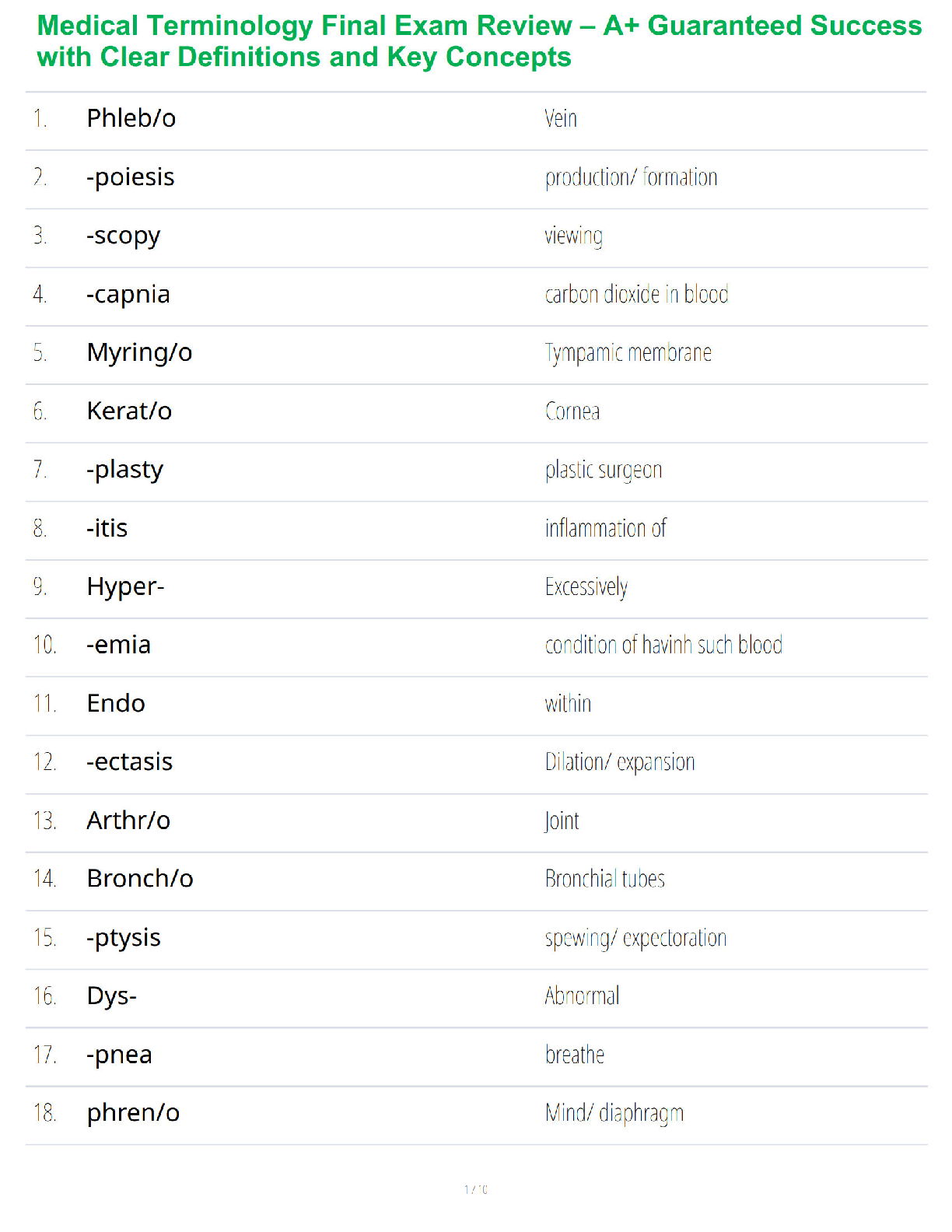
SKIN/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (A GUARANTEED)
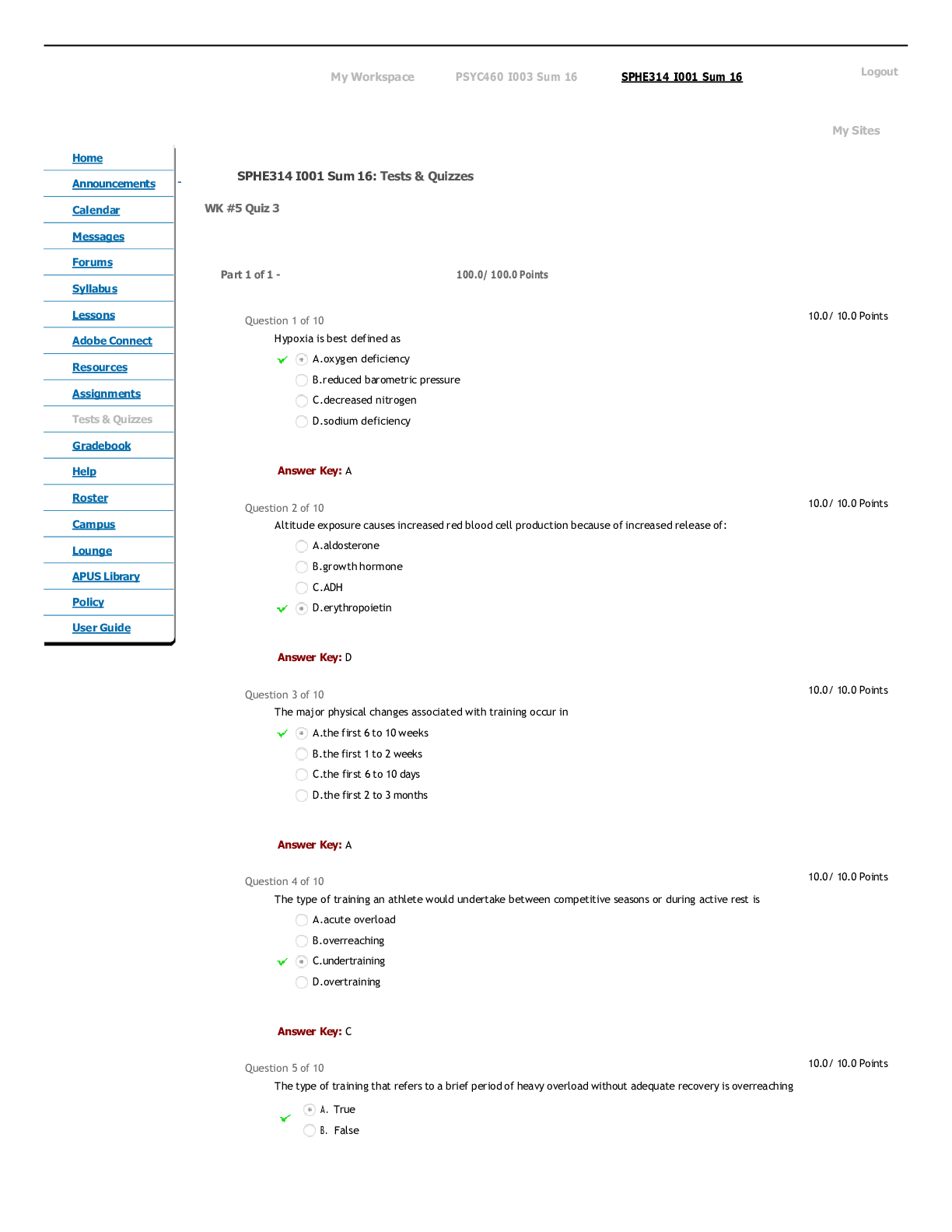
Name Cause Signs/Symptoms Diagnostics Treatments Concerns
Rocky Mtn. Spotted
Fever
Dog/Wood Tick bite
Rickettsia rickettsii
Petechiae starting on hands/feet progressing to
...
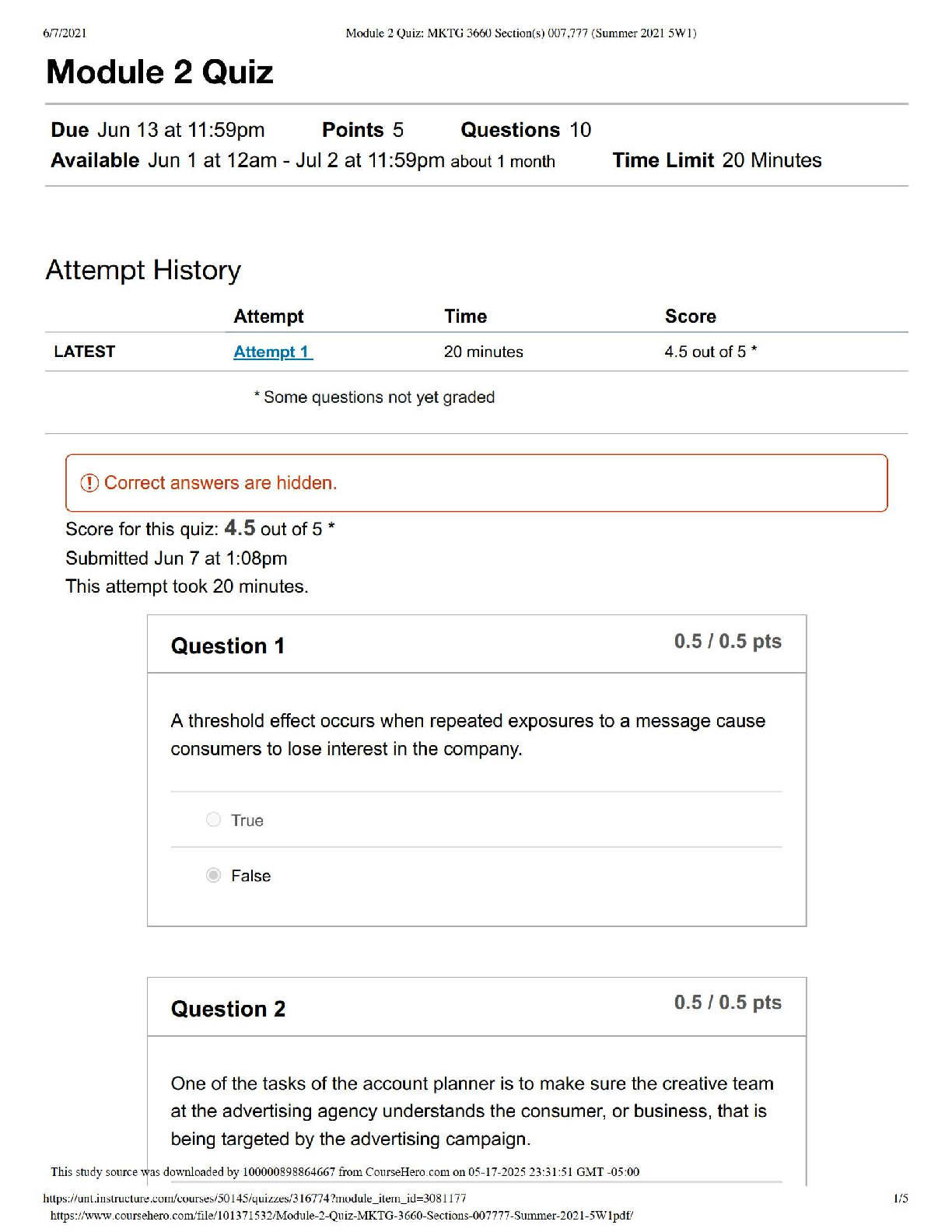
SKIN/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM (A GUARANTEED)
Name Cause Signs/Symptoms Diagnostics Treatments Concerns
Rocky Mtn. Spotted
Fever
Dog/Wood Tick bite
Rickettsia rickettsii
Petechiae starting on hands/feet progressing to
trunk 3rd day after high fever, severe headache,
myalgia, conjunctival injection, n/v, arthralgia
Antibody titers to rickettsia
Punch biopsy
CBC, LFT, CSF
Doxycycline 500mg BID x 21d
Can be fatal (3-9%)
Highest in
southeastern/south
central regions of US
Actinic Keratosis Slow-growing; Dry, round, red-colored lesions on
skin that do not heal; usually sun-exposed areas.
Small number lesions – cryotherapy
Large numbers – flurouracil cream (5%)
(5FU cream )
Pre-cancerous
Precursor to squamous
cell carcinoma
Psoriasis
Inherited; excessive
mitotic grown of
epithelial cells
Pruritic plaques “fine-silvery scales” found over
elbows, scalp, knees, gluteal folds
Auspitz sign: Pinpoint areas of bleeding remain
in the skin when a plaque is removed.
Topical steroids, Topical retinoids
(tazoratene), Tar preparations
UVB light and topical tar may induce
remissions
Guttate psoriasis: severe
form resulting from Gp A
strep infection
Tinea Versicolor
Yeast - Pityrosporum
orbiculare or
Pityrosporum ovale.
Hypopigmented round macules on
chest/shoulders/back; appear after skin is tanned
from sun
asymptomatic
KOH slide : hyphae & spores
“spaghetti & meatballs”
Topical selenium sulfide
Ketoconazole (Nizoral) BID x 2w
Oral antifungals
Atopic Dermatitis
(Eczema) Inherited pruritic rash
Pruritic rash on hands, flexural folds, and neck;
exacerbated by stress and environment
Starts as small vesicles that rupture leaving red,
weeping lesions that become licenhified and itchy
Topical steroids: Mild – hydrocortisone 1-
2.5% Medium – triamcinolone
Med/High potency (Halog) x 10d
Oral antihistamines for pruritis
Skin lubricants/hydrating baths to alleviate
dryness
Formation of fissures and
risk of infection
Acute cellulitis
Skin infection (staph)
of the dermis and
underlying tissues
2 forms: purulent/non�purulent
Purulent: Gm + staph aureus (MRSA), lower leg,
Non-purulent due to strep
I&C if boils
CBC if fever
Anon-purulent – dicloxacillin QID x10d;
Cefalexin or Clindamycin x 10d
MRSA: Doxycycline or Clindamycine
Td booster if >5yrs
Refer if s/s don’t resolve,
cellulitis not responding
to tx, spreading quickly,
DM,
immunocompromised
Osteomyelitis, sepsis
Erysipelas Subtype of cellulitis
from Gp A strept
Sudden onset one hot, indurated, red lesion with
clear demarcation. Usually on lower legs or cheeks
Hospitalization for infants,
immunocompromised
Bite wounds
Dogs & Cats (P.
multicoda) gram
negative
Humans (Eikenella
corrodens)
Human bite dirtiest of all
Cats higher risk of infection than dogs
Rabies: skunks, raccoons, foxes, coyotes: Immune
globulin and vaccine
Quarantine domestic animals for up to 10d
Augmentin 850mg x 10d
Clean, no sutures, tetanus
Follow-up 24-48 hours
Watch for closed-fist
injury (infection of the
joints)
80% cat bites become
infected
Hidradenitis
Suppurative
Bacterial infection of
axillary sebaceous
gland
Staph aureous (Gm +)
Acute onset painful, large, red nodules and
papules under one or both axilla that become
abscessed
C & S of drainage
Amoxicillin or Dicloxacillin PO BID x10d
Muproprion to lower nares and under
fingernails x2w
Antibacterial soap to axilla and groin
Avoid deodorant
Recurrences and scars
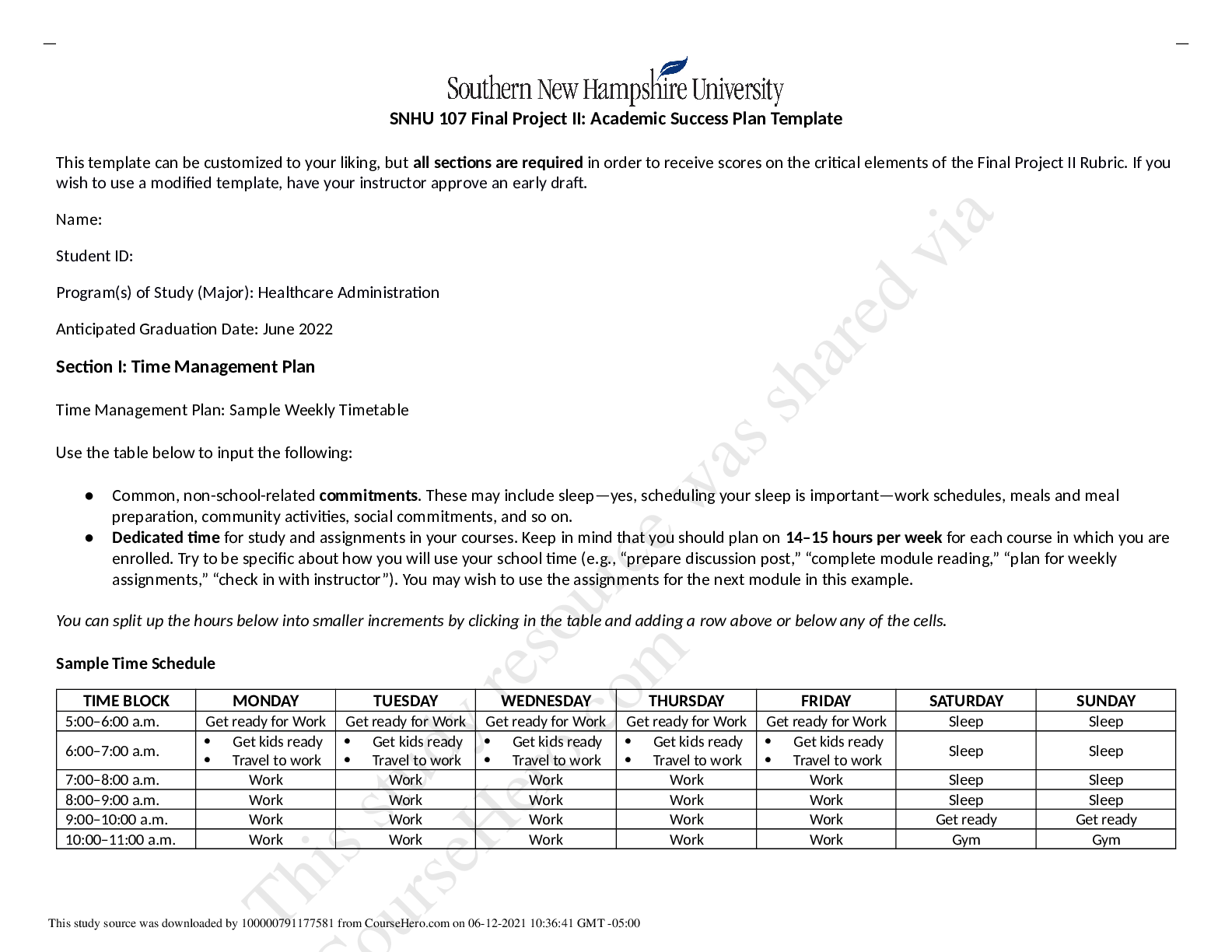
SKIN/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
SKIN/INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Name Cause Signs/Symptoms Diagnostics Treatments Concerns
Impetigo Gm + strep infection
More common in children and teens
Acute onset itchy, pink-red lesions that become
bullous, crusty and maculopapular (honey�colored)
Contagious and pruritic: worse in warm weather
2 types: bullous and nonbullous
C & S of crusts/wounds
Cephalexin or dicloxacillin QID x 10d
Azithromycin if PCN allergic 250 x 5d or
clindamycin x10d
If small amt of lesions – mupirocin ointment
2% x10d
Meningiococcemia Nisseria Menengitides
Gm -
sudden onset of sore throat, cough, fever,
headache, stiff neck, photophobia, and changes in
LOC
abrupt onset of petechial to hemorrhagic rashes
Lumbar puncture : CSF
Blood/throat cultures
CT or MRI of brain
Rocephin 2G IV q12h
Vancomycin IV q12h
Hospital isolation and supportive tx
Close contact prophylaxis: Riphampin q12h
x2d and meningococcal vaccine
Medical emergency –
REFER
College students in dorms
Erythema Migrans
(Lyme disease)
Borrelia burgdorferi
(tick)
Expanded red rash with central clearing (bulls�eye), feels hot to touch and rough texture;
common areas belt line, axilla, popliteal, groin
FLU-LIKE symptoms
Rash appears 7-14d after tick bite
Spontaneously resolves
Serum antibody titers (IgM
and IgG) Doxycycline BID or Tetracycline BID x 14d
Systemic infection with
organ shutdown
Guillian-Barre
Migratory arthritis
Varicella Zoster
Herpes-zoster
(Chickenpox or
Shingles)
Fever, pharyngitis, malaise
Chickenpox: Pruritic vesicular lesions beginning
at head expanding to trunk
Shingles: lesions at various stages along
dermatome
Viral culture
PCR for ZDV
Vaccine: >60
Tzank smear confirms
shingles
Acyclovir (zovirax) x 5d
Valacyclovir x 10d
Post-herpetic neuralgia
Herpes zoster
opthalmicus (corneal
blindness)
Pityriasis Rosea Unknown
Self-limiting; asymptomatic
Fine sclaes following skin lines: “Herald patch” or
“Christmas Tree” patch
Koplick spots
None – self-limiting Rule our secondary
syphilis
Scabies Sarcoptes scabiei
Severe pruritic rash, worse at night, between webs
of toes and fingers, axillae, groin, breasts, butt,
penis
Rash appears in linear burrows – can last up to 4
weeks
Wet mount of scraped rash
to view eggs under
microscope
Permethrin 5% cream to entire body – wash
off after 8-12h
Treat everyone in household;
clothes/bedding should be washed in hot
water
Tinea Infections
(Dermatophytosis) yeast
Capitis – head (most common)
Pedis – foot
Corporis – body
Cruris – jock itch
Manuum – hands
Barbrae – beard
KOH slide for hyphae and
spores
OTC topicals “ozole”
Oncyhomycosis Yeast Yellow thickening of nail – great toe most
common
Fungal cultures of nail Oral fluconazole 150-300mg weekly
Lamisil weekly for several weeks Monitor LFTs
Acne Vulgaris
Inflammation of the
sebaceous gland
High androgen levels,
bacteria, genetics
Open condomes (blackheads), closed condomes
(whiteheads), small papules and pustules
Mild: Prescription meds: Isotretinoin
(Retin-A), benzoyl peroxide with
erythromycin (Benzamycin) cream,
clindamycin topical (Cleocin).
Mod: Prescription topicals + tetracyclines
(after age 13)
Oral contraceptives: Yaz or Desogen
Before age 13 tetracycline
can stain teeth
permanently
Accutane category X –
females 2 forms of birth
control
[Show More]