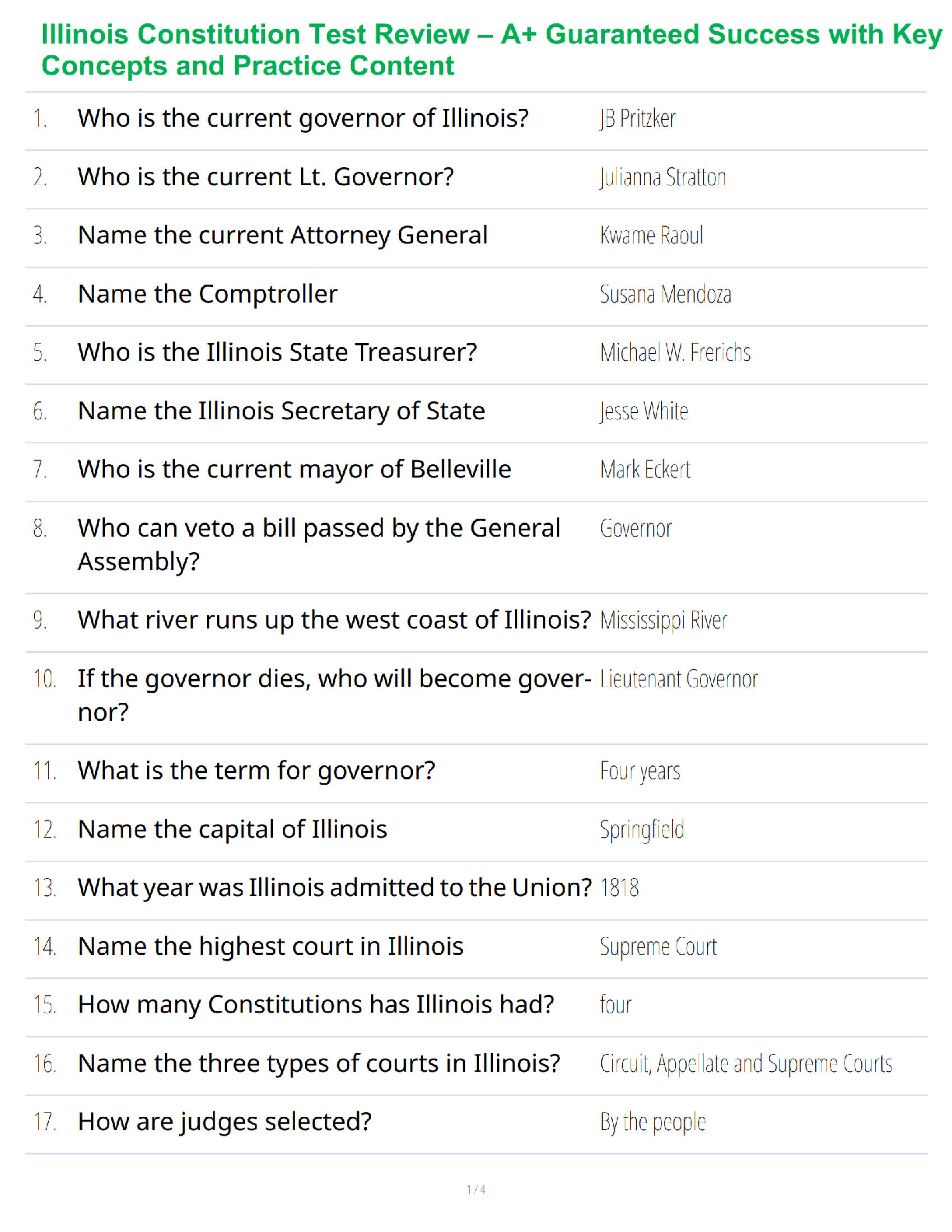
NR-507 Mid-Term Study Guide simultaneous responsive (A GUARANTEED)
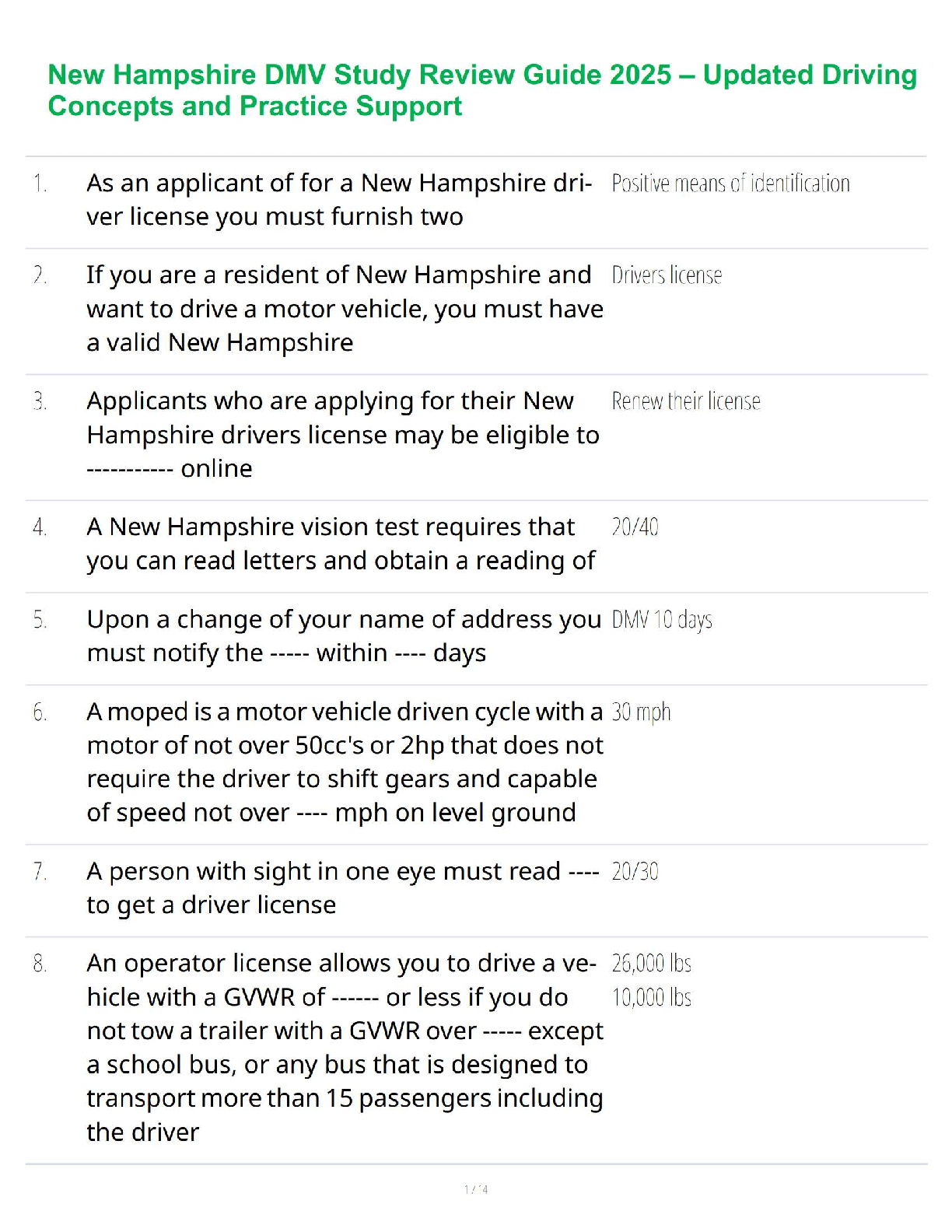
This study guide is for the 50 question multiple choice Mid-Term exam that will be given
during Week 4. It will cover the following concepts:
PULMON
...
NR-507 Mid-Term Study Guide simultaneous responsive (A GUARANTEED)
This study guide is for the 50 question multiple choice Mid-Term exam that will be given
during Week 4. It will cover the following concepts:
PULMONARY:
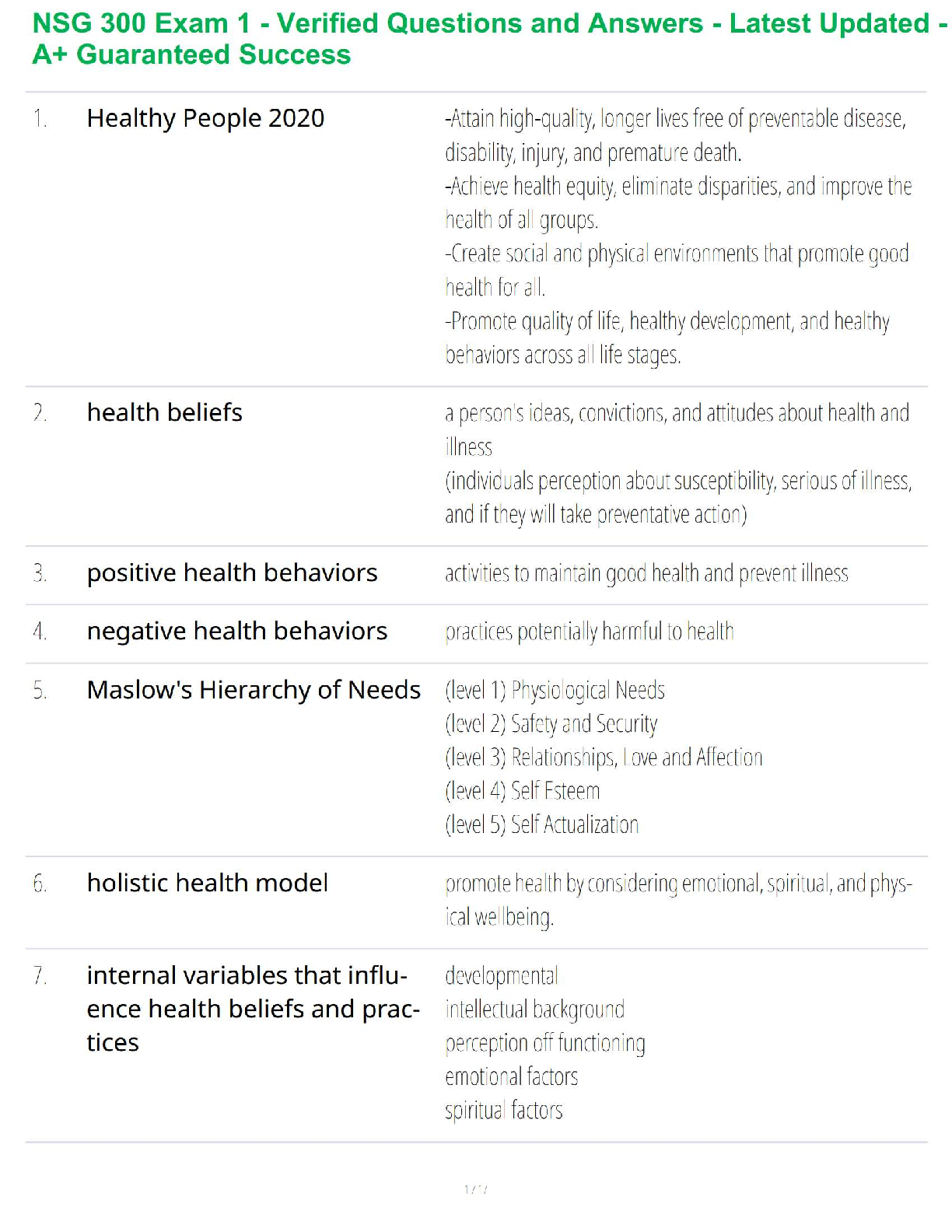
review concepts related to anticholinergic drugs and the treatment for asthma�Asthma is a chronic disease characterized by airway inflammation bronchial hyper
reactivity and smooth muscle spasm intermittent reversible airflow obstruction. Asthma
is caused by complex interaction of genetic and environmental factors. As a matter of
fact over 100 different genetic mutations have been implicated as possible links to the
development of asthma. Asthma results in excess mucus production and accumulation
hypertrophy of bronchial smooth muscle airflow obstruction decreased alveolar
ventilation.
• bronchitis and associated pathogenesis; smooth muscle hypertrophy à increased
bronchoconstriction
• hypertrophy and hyperplasia of goblet cells à mucus hypersecretion
• epithelial cell metaplasia à non-ciliated squamous cells
• migration of more WBCs to site à inflammation & fibrosis in bronchial wall
• thickening and rigidity of bronchial basement membrane à narrowing of bronchial
passageways
chronic bronchitis and related acid/base disturbances- air being trapped in alveoli
results in hypercapnia (CO2) retention and respiratory acidosis
perfusion- High CO2 creastes unfavorable conditions for gas exchange so there is
decreased O2 exchange via ventilation/perfusion mismatch. Decreased perfusion of
pulmonary capillaries with oxygenated blood results in chronic pulmonary hypoxia and
cyanosis. Perfusion is gas exchange or the actual exchange of O2 andCO2 in the
bloodstreat and occurs via the alveoli and pulmonary capillaries. Without effective
ventilation we cannot have effective perfusion. Air has to get to the alveoli and
pulmonary capillaries in order for perfusion to occur.
blood flow between the heart and lungs�asthma signs and symptoms- Symptoms- coughing, wheezing shortness of breath rapid
breathing chest tightness
bronchioles,- The bronchioles are a three layer tube like structure surrounding the
lumen or air passageway. The innermost layer, closest to the lumen, is composed of
columnar epithelial cells and mucus producing goblet cells. The outermost layer is
composed of smooth muscle cells, responsible for the ability of the airways to constrict
and dilate. The middle layer, called the lamina propria, is embedded with connective
tissue cells, as well as immune cells. These immune cells include a number of different
kinds of white blood cells located here to help protect the airways. However, in the case
of asthma, this protective feature goes into overdrive, causing an inflammatory
response that damages host tisse.
alveolar hyperinflation with asthma - The plugs of mucus and pus from this
inflammatory process can block alveolar passageways, leading to air-trapping and
hyperinflation more signs and symptoms consistent with the diagnosis of asthma. This
process is illustrated in this image which shows the airway pathology in its entirety mast
cell degranulation triggered by the excessive amounts of IGE that have airingly formed
this individual that will bind that allergen as it enters the airway that mast cell
degranulation releases chemicals that releases mucus production and accumulation as
well as chemicals that contribute to smooth muscle constriction that smooth muscle
constriction along with mucus plugs that form result in hyperinflation of the alveoli and
eventual erosion of airway tissue
polycythemia vera; Poor ventilation, leading to decreased perfusion, causes Right to
Left “shunting” to occur. This is the phenomenon where deoxygenated blood passes
from the RV to lungs to the LV without adequate perfusion (gas exchange). In response
to the chronic low level of oxygen in the blood, the kidneys compensate by increasing
secretion of erythropoietin, the primary hormone responsible for stimulating red blood
cell production. As a result of increased RBC production, clients with chronic bronchitis
exhibit an elevated hematocrit and can develop a condition known as secondary
polycythemia vera.
mechanism of action of anticholinergic drugs to treat asthma
CARDIOVASCULAR: review concepts related to cardiac output,
[Show More]