*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > NURSING 01 (SOLVED MCQ) CHAPTER The Child with Respiratory Dysfunction (All)
NURSING 01 (SOLVED MCQ) CHAPTER The Child with Respiratory Dysfunction
Document Content and Description Below
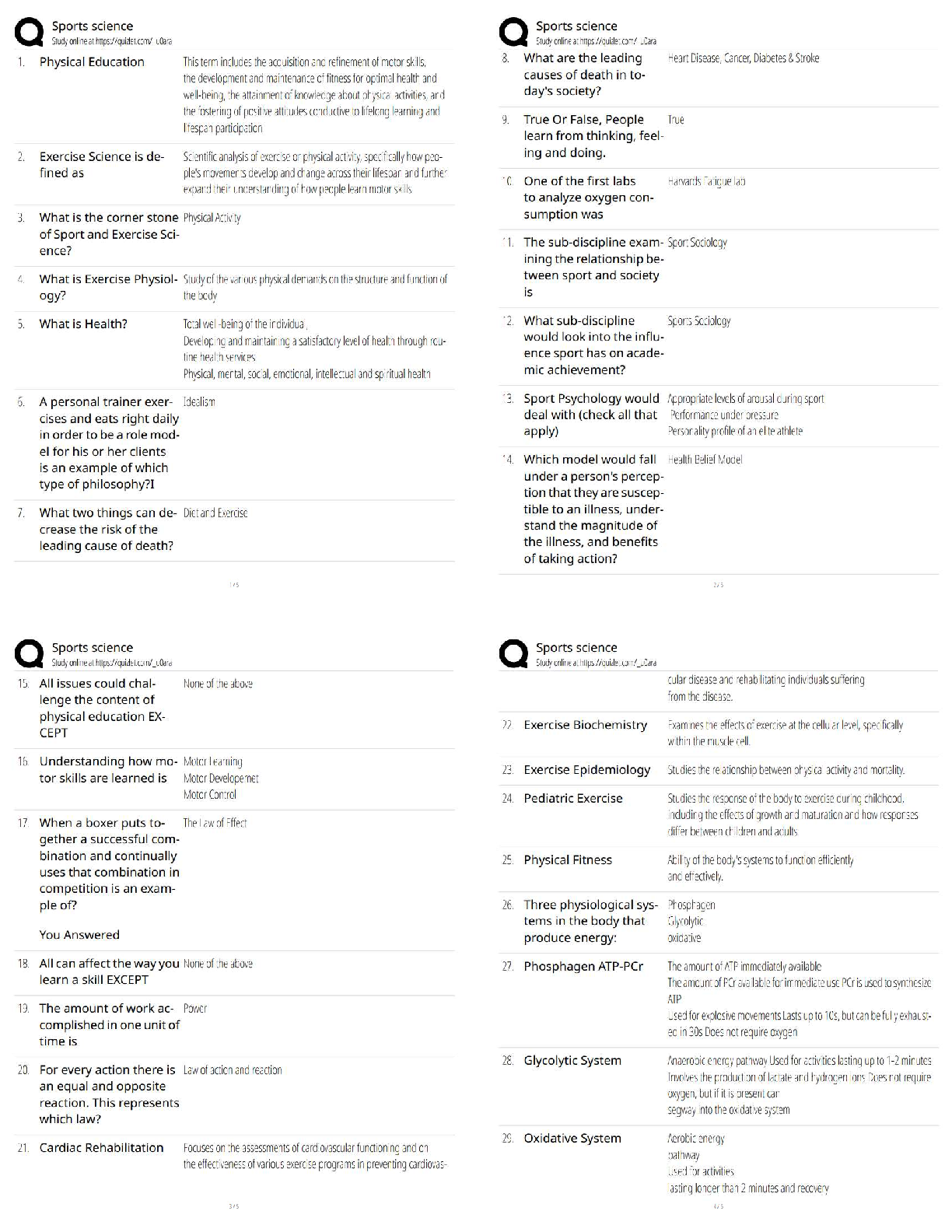
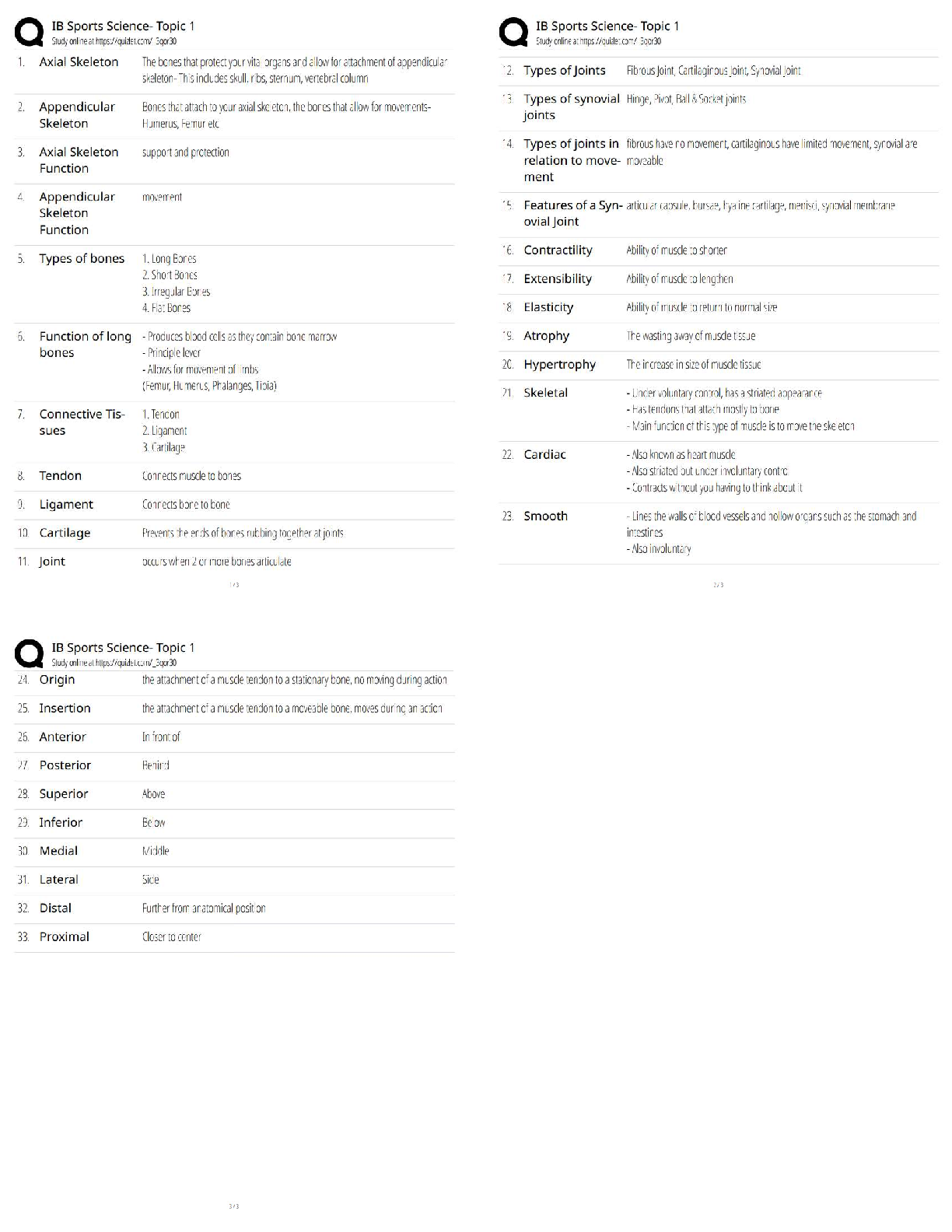
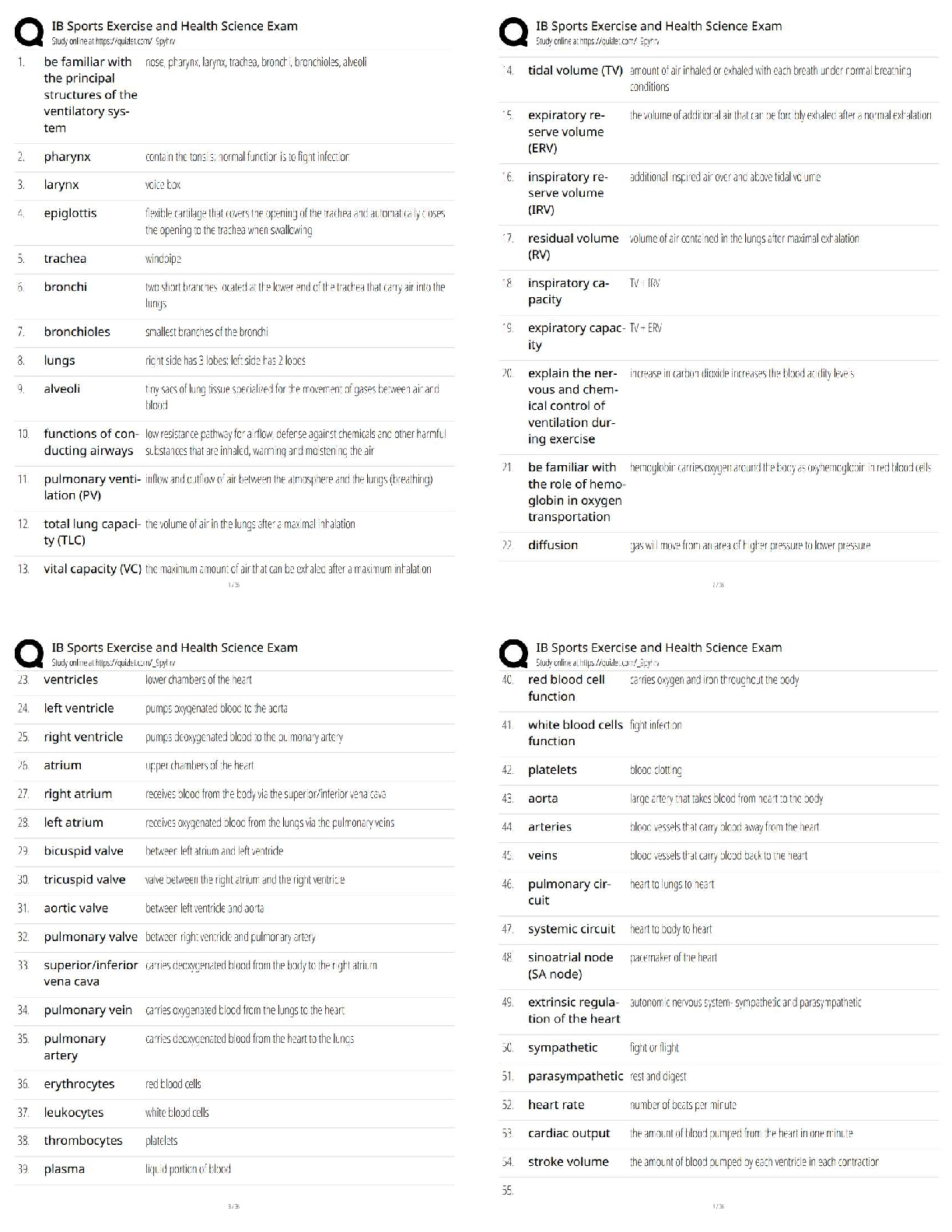
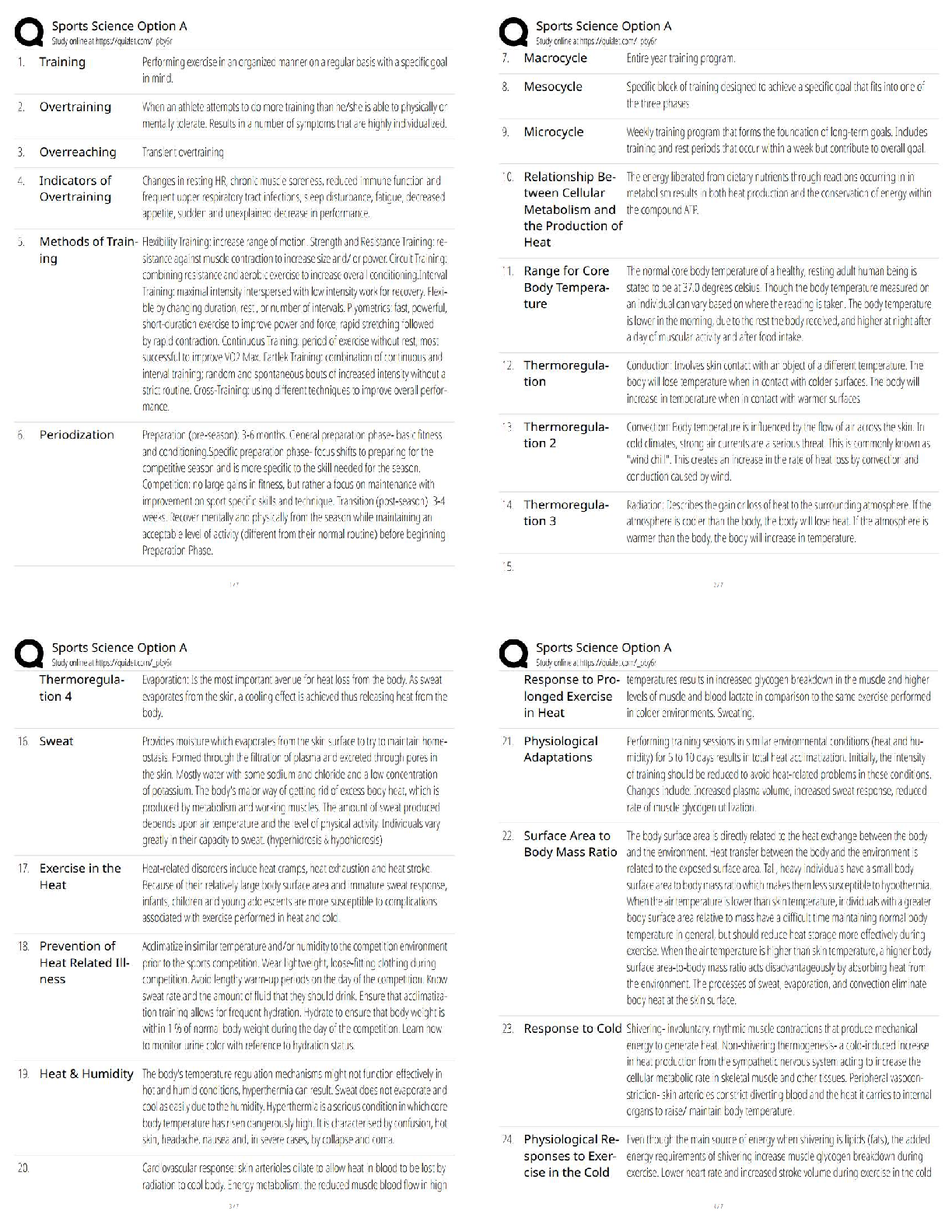
Chapter 23: The Child with Respiratory Dysfunction MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The nurse is teaching nursing students about normal physiologic changes in the respiratory system of toddlers. Which best descri ... bes why toddlers have fewer respiratory tract infections as they grow older? a. The amount of lymphoid tissue decreases. b. Repeated exposure to organisms causes increased immunity. c. Viral organisms are less prevalent in the population. d. Secondary infections rarely occur after viral illnesses. ANS: B Children have increased immunity after exposure to a virus. The amount of lymphoid tissue increases as children grow older. Viral organisms are not less prevalent, but older children have the ability to resist invading organisms. Secondary infections after viral illnesses include Mycoplasma pneumoniae and group A -hemolytic streptococcal infections. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand REF: 707 TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 2. A nurse is charting that a hospitalized child has labored breathing. Which describes labored breathing? a. Dyspnea b. Tachypnea c. Hypopnea d. Orthopnea ANS: A Dyspnea is labored breathing. Tachypnea is rapid breathing. Hypopnea is breathing that is too shallow. Orthopnea is difficulty breathing except in upright position. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Remember REF: 709 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 3. Which explains why cool-mist vaporizers rather than steam vaporizers are recommended in home treatment of childhood respiratory tract infections? a. They are safer. b. They are less expensive. c. Respiratory secretions are dried. d. A more comfortable environment is produced. ANS: A Cool-mist vaporizers are safer than steam vaporizers, and little evidence exists to show any advantages to steam. The cost of cool-mist and steam vaporizers is comparable. Steam loosens secretions, not dries them. Both may promote a more comfortable environment, but cool-mist vaporizers present decreased risk for burns and growth of organisms. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand REF: 708TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 4. Decongestant nose drops are recommended for a 10-month-old infant with an upper respiratory tract infection. Instructions for nose drops should include which action? a. Avoid using for more than 3 days. b. Keep drops to use again for nasal congestion. c. Administer drops until nasal congestion subsides. d. Administer drops after feedings and at bedtime. ANS: A Vasoconstrictive nose drops such as phenylephrine (Neo-Synephrine) should not be used for more than 3 days to avoid rebound congestion. Drops should be discarded after one illness because they may become contaminated with bacteria. Vasoconstrictive nose drops can have a rebound effect after 3 days of use. Drops administered before feedings are more helpful. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 709 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Pharmacologic and Parenteral Therapies 5. Which is an appropriate nursing intervention when caring for an infant with an upper respiratory tract infection and elevated temperature? a. Give tepid water baths to reduce fever. b. Encourage food intake to maintain caloric needs. c. Have child wear heavy clothing to prevent chilling. d. Give small amounts of favorite fluids frequently to prevent dehydration. ANS: D Preventing dehydration by small frequent feedings is an important intervention in the febrile child. Tepid water baths may induce shivering, which raises temperature. Food should not be forced; it may result in the child vomiting. The febrile child should be dressed in light, loose clothing. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 710 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 6. The parent of an infant with nasopharyngitis should be instructed to notify the health professional if the infant displays which clinical manifestation? a. Fussiness b. Coughing c. A fever over 99° F d. Signs of an earache ANS: D If an infant with nasopharyngitis shows signs of an earache, it may mean a secondary bacterial infection is present and the infant should be referred to a practitioner for evaluation. Irritability is common in an infant with a viral illness. Cough can be a sign of nasopharyngitis. Fever is common in viral illnesses. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning REF: 714MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 7. It is generally recommended that a child with acute streptococcal pharyngitis can return to school: a. when sore throat is better. b. if no complications develop. c. after taking antibiotics for 24 hours. d. after taking antibiotics for 3 days. ANS: C After children have taken antibiotics for 24 hours, they are no longer contagious to other children. Sore throat may persist longer than 24 hours after beginning antibiotic therapy, but the child is no longer considered contagious. Complications may take days to weeks to develop. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand REF: 715 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Pharmacologic and Parenteral Therapies 8. A child is diagnosed with influenza, probably type A disease. Management includes which recommendation? a. Clear liquid diet for hydration b. Aspirin to control fever c. Amantadine hydrochloride (Symmetrel) to reduce symptoms d. Antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection ANS: C Amantadine hydrochloride may reduce symptoms related to influenza A if administered within 24 to 48 hours of onset. It is ineffective against type B or C. A clear liquid diet is not necessary for influenza, but maintaining hydration is important. Aspirin is not recommended in children because of increased risk of Reye syndrome. Acetaminophen or ibuprofen is a better choice. Preventive antibiotics are not indicated for influenza unless there is evidence of a secondary bacterial infection. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 717 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Pharmacologic and Parenteral Therapies 9. Chronic otitis media with effusion (OME) is differentiated from acute otitis media (AOM) because it is usually characterized by: a. a fever as high as 40° C (104° F). b. severe pain in the ear. c. nausea and vomiting. d. a feeling of fullness in the ear. ANS: D OME is characterized by feeling of fullness in the ear or other nonspecific complaints. Fever is a sign of AOM. OME does not cause severe pain. This may be a sign of AOM. Nausea and vomiting are associated with otitis media. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment REF: 718MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 10. Parents have understood teaching about prevention of childhood otitis media if they make which statement? a. “We will only prop the bottle during the daytime feedings.” b. c. “Breastfeeding will be discontinued after 4 months of age.” “We will place the child flat right after feedings.” d. “We will be sure to keep immunizations up to date.” ANS: D Parents have understood the teaching about preventing childhood otitis media if they respond they will keep childhood immunizations up to date. The child should be maintained upright during feedings and after. Otitis media can be prevented by exclusively breastfeeding until at least 6 months of age. Propping bottles is discouraged to avoid pooling of milk while the child is in the supine position. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Analyze TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning MSC: Area of Client Needs: Health Promotion and Maintenance 11. An 18-month-old child is seen in the clinic with AOM. Trimethoprim- sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim) is prescribed. Which statement made by the parent indicates a correct understanding of the instructions? a. “I should administer all the prescribed medication.” b. c. “I should continue medication until the symptoms subside.” “I will immediately stop giving medication if I notice a change in hearing.” d. “I will stop giving medication if fever is still present in 24 hours.” ANS: A Antibiotics should be given for their full course to prevent recurrence of infection with resistant bacteria. Symptoms may subside before the full course is given. Hearing loss is a complication of AOM. Antibiotics should continue to be given. Medication may take 24 to 48 hours to make symptoms subside. It should be continued. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 718 TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Pharmacologic and Parenteral Therapies 12. An infant’s parents ask the nurse about preventing OM. Which should be recommended? a. Avoid tobacco smoke. b. Use nasal decongestant. c. Avoid children with OM. d. Bottle-feed or breastfeed in supine position. ANS: A Eliminating tobacco smoke from the child’s environment is essential for preventing OM and other common childhood illnesses. Nasal decongestants are not useful in preventing OM. Children with uncomplicated OM are not contagious unless they show other upper respiratory tract infection (URI) symptoms. Children should be fed in an upright position to prevent OM. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 719 REF: 719TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 13. The nurse is assessing a child with acute epiglottitis. Examining the child’s throat by using a tongue depressor might precipitate which symptom or condition? a. Inspiratory stridor b. Complete obstruction Sore throat c. d. Respiratory tract infection ANS: B If a child has acute epiglottitis, examination of the throat may cause complete obstruction and should be performed only when immediate intubation can take place. Stridor is aggravated when a child with epiglottitis is supine. Sore throat and pain on swallowing are early signs of epiglottitis. Epiglottitis is caused by H. influenzae in the respiratory tract. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand REF: 721 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 14. Which type of croup is always considered a medical emergency? a. Laryngitis b. Epiglottitis c. Spasmodic croup d. Laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB) ANS: B Epiglottitis is always a medical emergency needing antibiotics and airway support for treatment. Laryngitis is a common viral illness in older children and adolescents, with hoarseness and URI symptoms. Spasmodic croup is treated with humidity. LTB may progress to a medical emergency in some children. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand REF: 721 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Assessment MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 15. The nurse encourages the mother of a toddler with acute laryngotracheobronchitis (LTB) to stay at the bedside as much as possible. The nurse’s rationale for this action is described primarily in which statement? a. Mothers of hospitalized toddlers often experience guilt. b. The mother’s presence will reduce anxiety and ease child’s respiratory efforts. c. Separation from mother is a major developmental threat at this age. d. The mother can provide constant observations of the child’s respiratory efforts. ANS: B The family’s presence will decrease the child’s distress. It is true that mothers of hospitalized toddlers often experience guilt but this is not the best answer. The main reason to keep parents at the child’s bedside is to ease anxiety and therefore respiratory effort. The child should have constant monitoring by cardiorespiratory monitor and noninvasive oxygen saturation monitoring, but the parent should not play this role in the hospital. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 723TOP: Integrated Process: Teaching/Learning MSC: Area of Client Needs: Psychosocial Adaptation 16. A school-age child had an upper respiratory tract infection for several days and then began having a persistent dry, hacking cough that was worse at night. The cough has become productive in the past 24 hours. This is most suggestive of which diagnosis? a. Bronchitis b. Bronchiolitis c. Viral-induced asthma d. Acute spasmodic laryngitis ANS: A Bronchitis is characterized by these symptoms and occurs in children older than 6 years. Bronchiolitis is rare in children older than 2 years. Asthma is a chronic inflammation of the airways that may be exacerbated by a virus. Acute spasmodic laryngitis occurs in children between 3 months and 3 years. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Understand REF: 723 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Diagnosis MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 17. Which frequency is recommended for childhood skin testing for tuberculosis (TB) using the Mantoux test? a. Every year for all children older than 2 years b. Every year for all children older than 10 years c. Every 2 years for all children starting at age 1 year d. Periodically for children who reside in high-prevalence regions ANS: D Children who reside in high-prevalence regions for TB should be tested every 2 to 3 years. Annual testing is not necessary. Testing is not necessary unless exposure is likely or an underlying medical risk factor is present. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Remember REF: 729 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Reduction of Risk Potential 18. Which consideration is the most important in managing tuberculosis (TB) in children? a. Skin testing annually b. Pharmacotherapy c. Adequate nutrition d. Adequate hydration ANS: B Drug therapy for TB includes isoniazid, rifampin, and pyrazinamide daily for 2 months and two or three times a week for the remaining 4 months. Pharmacotherapy is the most important intervention for TB. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 730 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Pharmacologic and Parenteral Therapies19. The mother of a toddler yells to the nurse, “Help! He is choking to death on his food.” The nurse determines that lifesaving measures are necessary based on which symptom? a. Gagging b. Coughing c. Pulse over 100 beats/min d. Inability to speak ANS: D The inability to speak is indicative of a foreign-body airway obstruction of the larynx. Abdominal thrusts are needed for treatment of the choking child. Gagging indicates irritation at the back of the throat, not obstruction. Coughing does not indicate a complete airway obstruction. Tachycardia may be present for many reasons. PTS: 1 DIF: Cognitive Level: Apply REF: 732 TOP: Integrated Process: Nursing Process: Implementation MSC: Area of Client Needs: Physiologic Integrity: Physiologic Adaptation 20. The nurse is caring for a child with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) associated with sepsis. Nursing actions should include: a. forcing fluids. b. monitoring pulse oximetry. [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 18 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$12.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 08, 2021
Number of pages
18
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 08, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
182

.png)





.png)