*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > College of Lake County/ NUR 134/ NUR134. Over 450 Diabetic Questions, Answers and Explanations. Best (All)
College of Lake County/ NUR 134/ NUR134. Over 450 Diabetic Questions, Answers and Explanations. Best for Quich Exam Preparation.
Document Content and Description Below
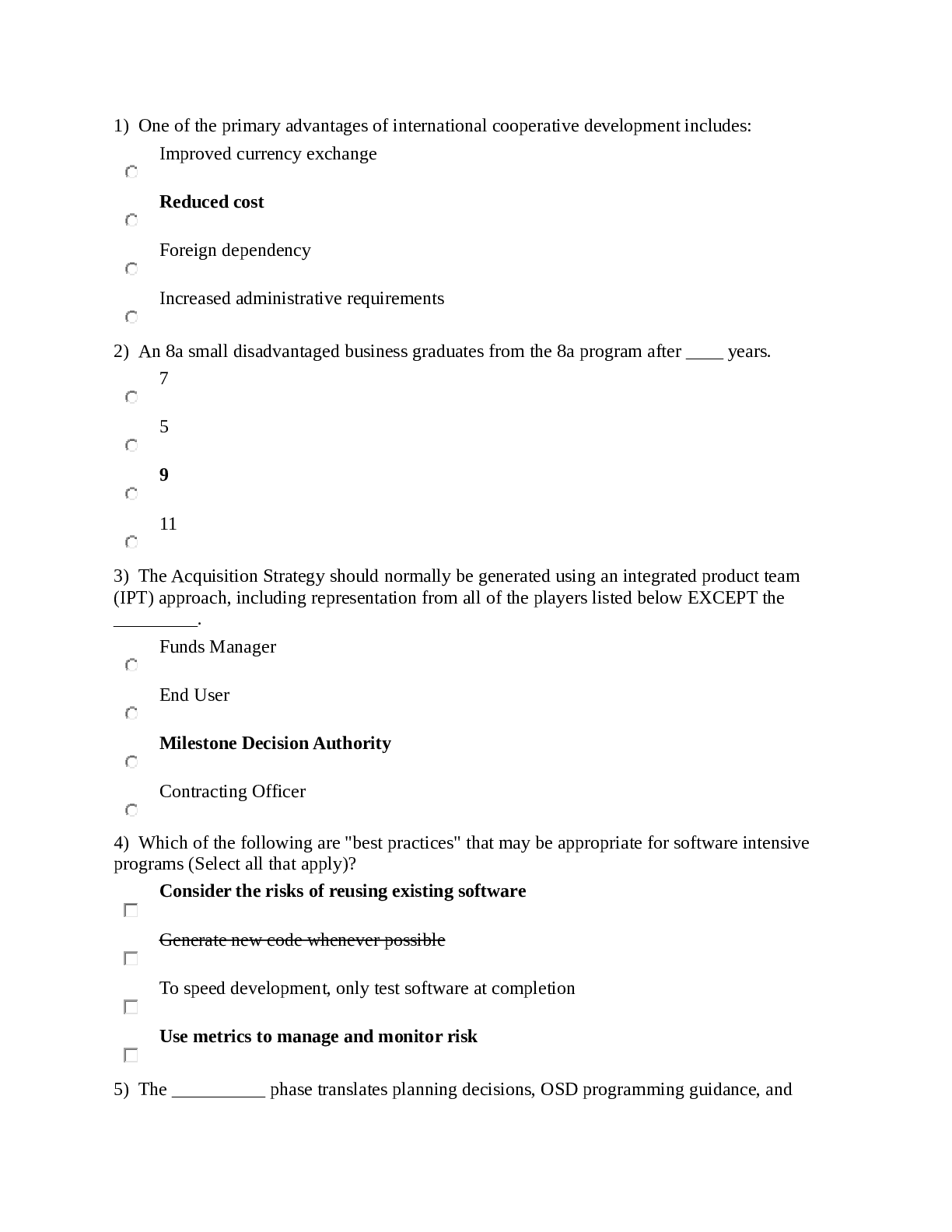
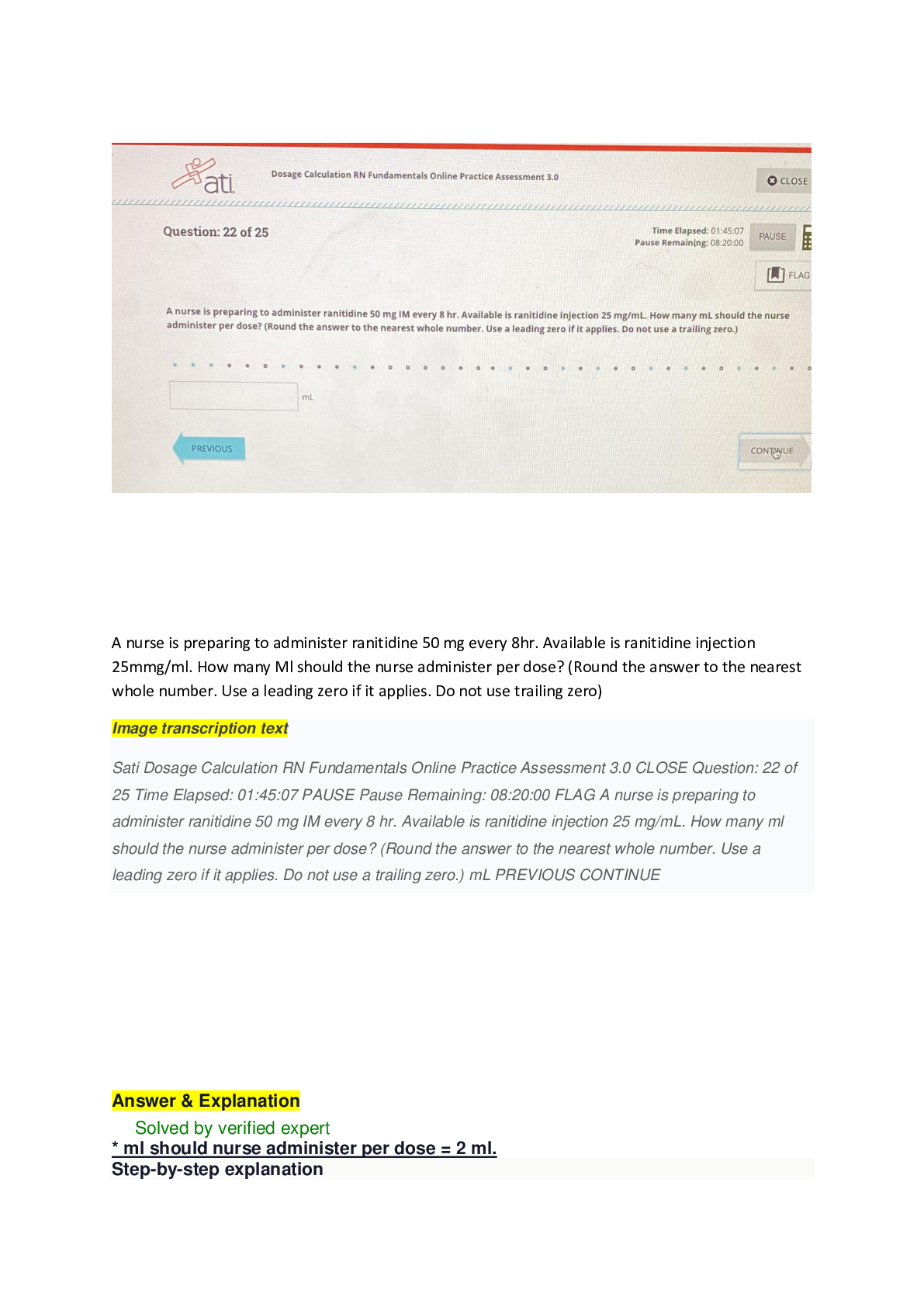
"1. A patient with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus asks the nurse what ""type 2"" means in relation to diabetes. The nurse explains to the patient that type 2 diabetes differs from type 1 di ... abetes primarily in that with type 2 diabetes a. the pt is totally dependent on an outside source of insulin b. there is a decreased insulin secretion and cellular resistance to insulin that is produced c. the immune system destroys the pancreatic insulin-producing cells d. the insulin precursor that is secreted by the pancreas is not activated by the liver The benefits of using an insulin pump include all of the following except: "a. By continuously providing insulin they eliminate the need for injections of insulin b. They simplify management of blood sugar and often improve A1C c. They enable exercise without compensatory carbohydrate consumption d. They help with weight loss A 54-year-old patient admitted with type 2 diabetes, asks the nurse what "type 2" means. Which of the following is the most appropriate response by the nurse? "1. ""With type 2 diabetes, the body of the pancreas becomes inflamed." 2. "With type 2 diabetes, insulin secretion is decreased and insulin resistance is increased." 3. "With type 2 diabetes, the patient is totally dependent on an outside source of insulin." 4. "With type 2 diabetes, the body produces autoantibodies that destroy b-cells in the pancreas."" "A client is admitted to the hospital with signs and symptoms of diabetes mellitus. Which findings is the nurse most likely to observe in this client? Select all that apply: "1. Excessive thirst 2. Weight gain 3. Constipation 4. Excessive hunger 5. Urine retention 6. Frequent, high-volume urination A client is brought to the emergency department in an unresponsive state, and a diagnosis of hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome is made. The nurse would immediately prepare to initiate which of the following anticipated physician's prescriptions? 1. Endotracheal intubation 2. 100 units of NPH insulin 3. Intravenous infusion of normal saline 4. Intravenous infusion of sodium bicarbonate "A client is taking Humulin NPH insulin daily every morning. The nurse instructs the client that the most likely time for a hypoglycemic reaction to occur is: A) 2-4 hours after administration B) 4-12 hours after administration C) 16-18 hours after administration D) 18-24 hours after administration "A client who is started on metformin and glyburide would have initially presented with which symptoms? "a. Polydipsia, polyuria, and weight loss b. weight gain, tiredness, & bradycardia c. irritability, diaphoresis, and tachycardia d. diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss A client with diabetes mellitus demonstrates acute anxiety when first admitted for the treatment of hyperglycemia. The most appropriate intervention to decrease the client's anxiety would be to 1. administer a sedative 2. make sure the client knows all the correct medical terms to understand what is happening 3. ignore the signs and symptoms of anxiety so that they will soon disappear 4. convey empathy, trust, and respect toward the client 4. The most appropriate intervention is to address the client’s feelings related to the anxiety A client with diabetes melllitus has a blood glucose of 644mg/dl. The nurse interprets that this client is most at risk of developing which type of acid base imbalance? "A. Metabolic acidosis B. Metabolic alkalosis C. Respiratory Acidosis D. Respiratory Alkalosis" A client with DKA is being treated in the ED. What would the nurse suspect? 1. Comatose state 2. Decreased Urine Output 3. Increased respirations and an increase in pH. 4. Elevated blood glucose level and low plasma bicarbonate level. A client with type I diabetes is placed on an insulin pump. The most appropriate short-term goal when teaching this client to control the diabetes is: "1) adhere to the medical regimen 2) remain normoglycemic for 3 weeks 3) demonstrate the correct use of the administration equipment. 4) list 3 self care activities that are necessary to control the diabetes" "A diabetic patient has a serum glucose level of 824 mg/dL (45.7 mmol/L) and is unresponsive. Following assessment of the patient, the nurse suspects diabetic ketoacidosis rather than hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome based on the finding of "a. polyuria b. severe dehydration c. rapid, deep respirations ) d. decreased serum potassium" "A frail elderly patient with a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus has been ill with pneumonia. The client’s intake has been very poor, and she is admitted to the hospital for observation and management as needed. What is the most likely problem with this patient? "A. Insulin resistance has developed. B. Diabetic ketoacidosis is occurring. C. Hypoglycemia unawareness is developing. D. Hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic coma. A home health nurse is at the home of a client with diabetes and arthritis. The client has difficulty drawing up insulin. It would be most appropriate for the nurse to refer the client to: "A) A social worker from the local hospital B) An occupational therapist from the community center C) A physical therapist from the rehabilitation agency D) Another client with diabetes mellitus and takes insulin" A nurse is caring for a client with type 1 diabetes mellitus. which client complaint would alert the nurse to the presence of a possible hypoglycemic reaction? "1. Tremors 2. Anorexia 3. Hot, dry skin 4. Muscle cramps "A nurse is caring for a client admitted to the emergency department with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). In the acute phase, the priority nursing action is to prepare to: "A. Correct the acidosis B. Administer 5% dextrose intravenously C. Administer regular insulin intravenously D. Apply a monitor for an electrocardiogram." A nurse is caring for a client with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Which client complaint would alert the nurse to the presence of a possible hypoglycemic reaction ? A. Tremors B. Anorexia C. Hot, Dry skin D. Muscle cramps a nurse is interviewing a client with type 2 diabetes mellitus. which statement by the client indicated an understanding of the treatment for this disorder? "1. ""i take oral insulin instead of shots"" 2. ""by taking these medications I am able to eat more"" 3. ""when I become ill, I need to increase the number of pills I take"" 4. ""the medications I'm taking help release the insulin I already make"" A nurse is preparing a plan of care for a client with diabetes mellitus who has hyperglycemia. The priority nursing diagnosis would be: 1. Deficient knowledge 2. Deficient fluid volume 3. Compromised family coping 4. Imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements A nurse is preparing a teaching plan for a client with diabetes Mellitus regarding proper foot care. Which instruction is included in the plan? 1. Soak feet in hot water 2. apply a moisturizing lotion to dry feet but not between the toes 3. Always have a podiatrist cut your toenails, never cut them yourself 4. avoid using mild soap on the feet "A nurse performs a physical assessment on a client with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Findings include a fasting blood glucose of 120 mg/dL, temp of 101 F, pulse of 88 bpm, respirations of 22, and blood pressure of 100/72. Which finding would be of most concern to the nurse? "1. Pulse 2. Respiration 3. Temperature 4. Blood pressure" "A nurse should recognize which symptom as a cardinal sign of diabetes mellitus? "a. Nausea b. Seizure c. Hyperactivity d. Frequent urination A patient is admitted with diabetes mellitus, has a glucose level of 380 mg/dl, and a moderate level of ketones in the urine. As the nurse assesses for signs of ketoacidosis, which of the following respiratory patterns would the nurse expect to find?" A-Central apnea B-Hypoventilation C-Kussmaul respirations D- Cheyne-Stokes respirations" "A patient with type 1 diabetes has received diet instruction as part of the treatment plan. The nurse determines a need for additional instruction when the patient says, "a. ""I may have an occasional alcoholic drink if I include it in my meal plan."" b. ""I will need a bedtime snack because I take an evening dose of NPH insulin."" c. ""I will eat meals as scheduled, even if I am not hungry, to prevent hypoglycemia."" d. ""I may eat whatever I want, as long as I use enough insulin to cover the calories. "An 18-year-old female client, 5'4'' tall, weighing 113 kg, comes to the clinic for a non-healing wound on her lower leg, which she has had for two weeks. Which disease process should the nurse suspect the client is developing? A. Type 1 diabetes B. Type 2 diabetes C. Gestational diabetes D. Acanthosis nigricans" "An adolescent client with type I diabetes mellitus is admitted to the emergency department for treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis. Which assessment findings should the nurse expect to note? "a) sweating and tremors b) hunger and hypertension c) cold, clammy skin and irritability d) fruity breath and decreasing level of consciousness An external insulin pump is prescribed for a client with DM. The client asks the nurse about the functioning of the pump. The nurse bases the response on the information that the pump: " a. Gives small continuous dose of regular insulin subcutaneously, and the client can self-administer a bolus with an additional dosage from the pump before each meal. b. Is timed to release programmed doses of regular or NPH insulin into the bloodstream at specific intervals. c. Is surgically attached to the pancreas and infuses regular insulin into the pancreas, which in turn releases the insulin into the bloodstream. d. Continuously infuses small amounts of NPH insulin into the bloodstream while regularly monitoring blood glucose levels" Analyze the following diagnostic findings for your patient with type 2 diabetes. Which result will need further assessment? A) BP 126/80 B) A1C 9% C)FBG 130mg/dL D) LDL cholesterol 100mg/dL Blood sugar is well controlled when Hemoglobin A1C is... "a. Below 7% b. Between 12%-15% c. Less than 180 mg/dL d. Between 90 and 130 mg/dL" During a diabetes screening program, a patient tells the nurse, "My mother died of complications of type 2 diabetes. Can I inherit diabetes?" The nurse explains that " a.) as long as the patient maintains normal weight and exercises, type 2 diabetes can be prevented. b.) the patient is at a higher than normal risk for type 2 diabetes and should have periodic blood glucose level testing. c.) there is a greater risk for children developing type 2 diabetes when the father has type 2 diabetes. d.) although there is a tendency for children of people with type 2 diabetes to develop diabetes, the risk is higher for those with type 1 diabetes." B " "Excessive thirst and volume of very dilute urine may be symptoms of: "A. Urinary tract infection B. Diabetes insipidus C. Viral gastroenteritis D. Hypoglycemia" In educating a client with diabetes, what response would reveal need for further education? "A. I should avoid tights B. I should take good care of my toenails C. I should not go more than 3 days without washing my feet D. I should avoid going barefoot and should wear clean socks Of which of the following symptoms might an older woman with diabetes mellitus complain? 1) anorexia 2)pain intolerance 3) weight loss 4) perineal itching One of the benefits of Glargine (Lantus) insulin is its ability to: a. Release insulin rapidly throughout the day to help control basal glucose. b. Release insulin evenly throughout the day and control basal glucose levels. c. Simplify the dosing and better control blood glucose levels during the day. d. Cause hypoglycemia with other manifestation of other adverse reactions. Patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus may require which of the following changes to their daily routine during times of infection? "a. no change b. less insulin c. more insulin d. oral diabetic agents" answer C: during times of infection and illness diabetic patients may need even more insulin to compensate for increased blood glucose levels. Polydipsia and polyuria related to diabetes mellitus are primarily due to: "a. The release of ketones from cells during fat metabolism b. Fluid shifts resulting from exposure to high levels of hyperglycemia c. Damage to the kidneys from exposure to high levels of glucose d. changes in RBCs resulting from attachment of excessive glucose to hemoglobin" b. Fluid shifts resulting from the osmotic effect of hyperglycemia Rationale: The osmotic effect of glucose produces the manifestations of polydipsia and polyuria. . "Prediabetes is associated with all of the following except: " a. Increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes b. Impaired glucose tolerance c. Increased risk of heart disease and stroke d. Increased risk of developing type 1 diabetes" "ANSWER: D Persons with elevated glucose levels that do not yet meet the criteria for diabetes are considered to have prediabetes and are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Weight loss and increasing physical activity can help people with prediabetes prevent or postpone the onset of type 2 diabetes." Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include all of the following except: "a. Advanced age b. Obesity c. Smoking d. Physical inactivity" Smoking "Additional risk factors for type 2 diabetes are a family history of diabetes,impaired glucose metabolism, history of gestational diabetes, and race/ethnicity. African-Americans, Hispanics/Latinos, Asian Americans, Native Hawaiians, Pacific Islanders, and Native Americans are at greater risk of developing diabetes than whites." "The client diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes has a glycosylated hemoglobin (A1c) of 8.1%. Which interpretation should the nurse make based on this result? 1.This result is below normal levels. 2.This result is within acceptable levels. 3.This result is above recommended levels 4.This result is dangerously high. 3.(CORRECT) This result parallels a serum blood glucose level of approximately 180 to 200 mg/dL. An A1c is a blood test that reflects average blood glucose levels over a period of 2-3months; clients with elevated blood glucose levels are at risk for developing long-term complications. "The client diagnosed with type 1 diabetes is receiving Humalog, a rapid-acting insulin, by sliding scale. The order reads blood glucose level: <150, zero (0) units; 151 to 200, three (3) units; 201 to 250, six (6 units); >251, contact health-care provider. The unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) reports to the nurse the client's glucometer reading is 189. How much insulin should the nurse administer to the client? 3 units The client's result is 189, which is between 151 and 200, so the nurse should administer 3 units of Humalog insulin subcutaneously. The client diagnosed with Type I diabetes is found lying unconscious on the floor of the bathroom. Which interventions should the nurse implement first? A. Administer 50% dextrose IVP. B. Notify the health-care provider. C. Move the client to ICD. D. Check the serum glucose level. A) admin 50% dextrose IVP. The nurse should assume the client is hypoglycemic and administer IVP dextrose, which will rouse the client immediately. If the collapse is the result of hyperglycemia, this additional dextrose will not further injure the client. "The guidelines for Carbohydrate Counting as medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus includes all of the following EXCEPT: a. Flexibility in types and amounts of foods consumed b. Unlimited intake of total fat, saturated fat and cholesterol c. Including adequate servings of fruits, vegetables and the dairy group d. Applicable to with either Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes mellitus b. Unlimited intake of total fat, saturated fat and cholesterol" B. You want to be careful of how [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 130 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 16, 2021
Number of pages
130
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 16, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
177