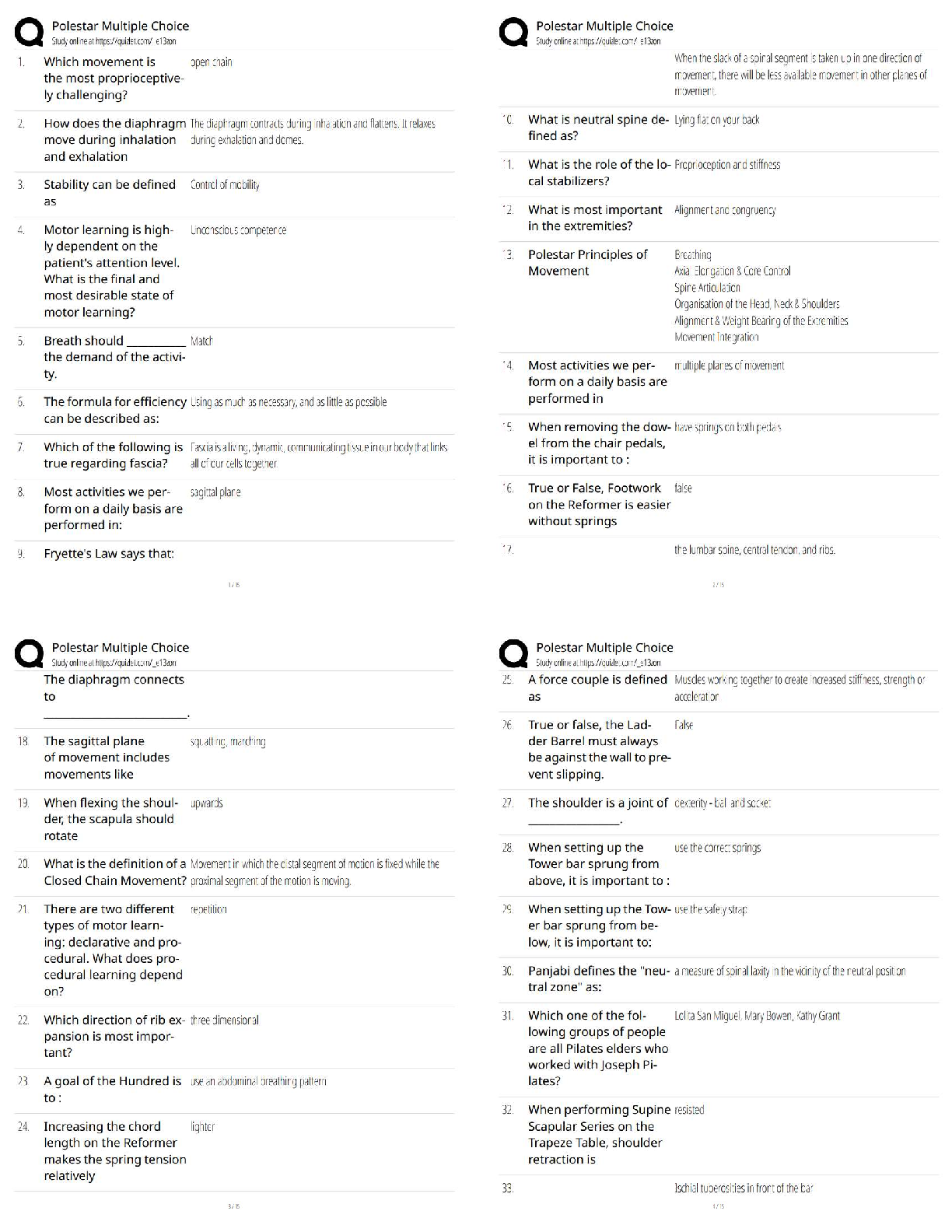
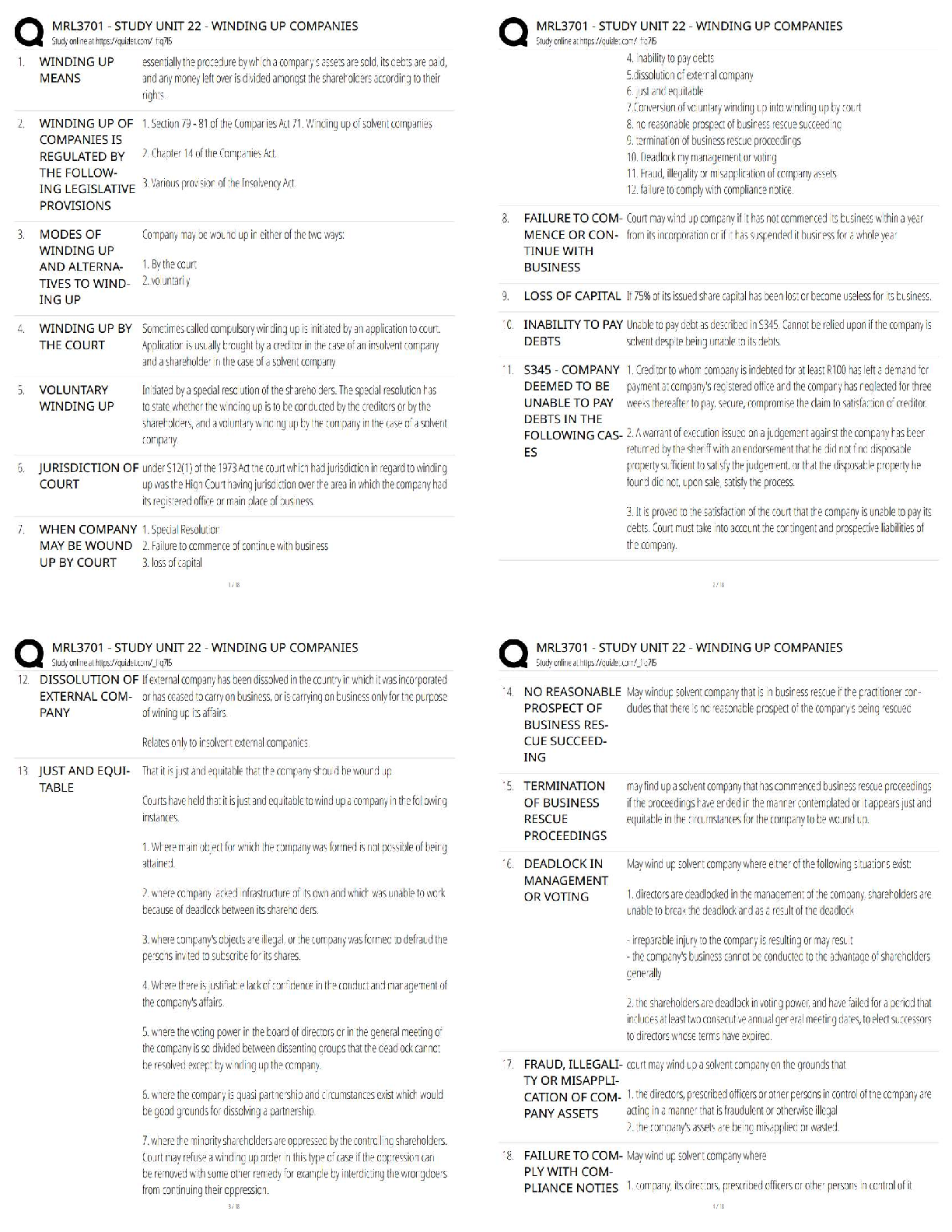
1. A theory is an abstract, untestable explanation of some events.
F
A theory is testable.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 38 OBJ: LO: 03-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
...
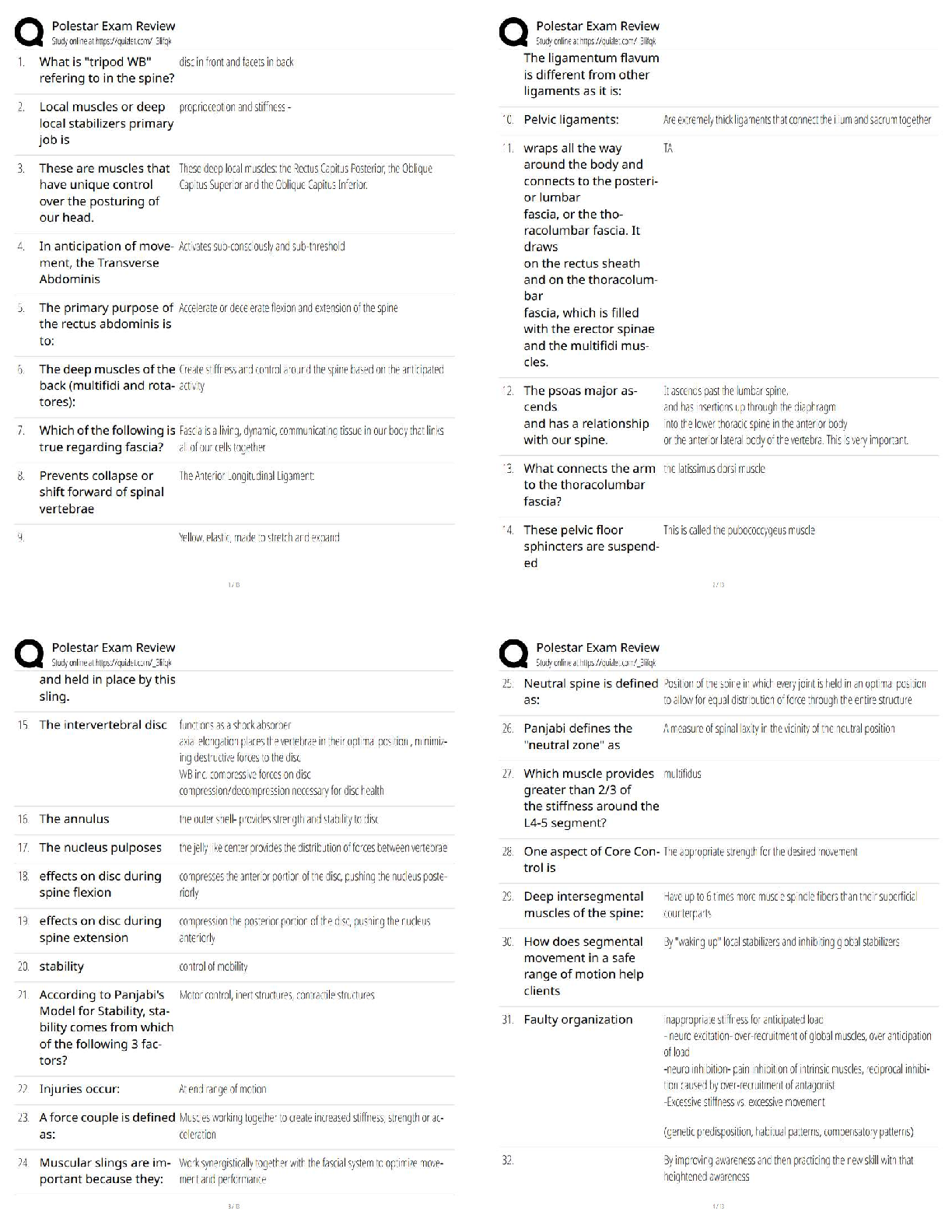
1. A theory is an abstract, untestable explanation of some events.
F
A theory is testable.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 38 OBJ: LO: 03-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
2. Knowledge and confirmation are the two purposes of theory.
F
Understanding and predicting are the two purposes of theory.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 38 OBJ: LO: 03-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
3. Theories allow researchers to build on previous knowledge.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 39
OBJ: LO: 03-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
4. A concept is a generalized idea about a class of objects, attributes, or occurrences.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 39
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
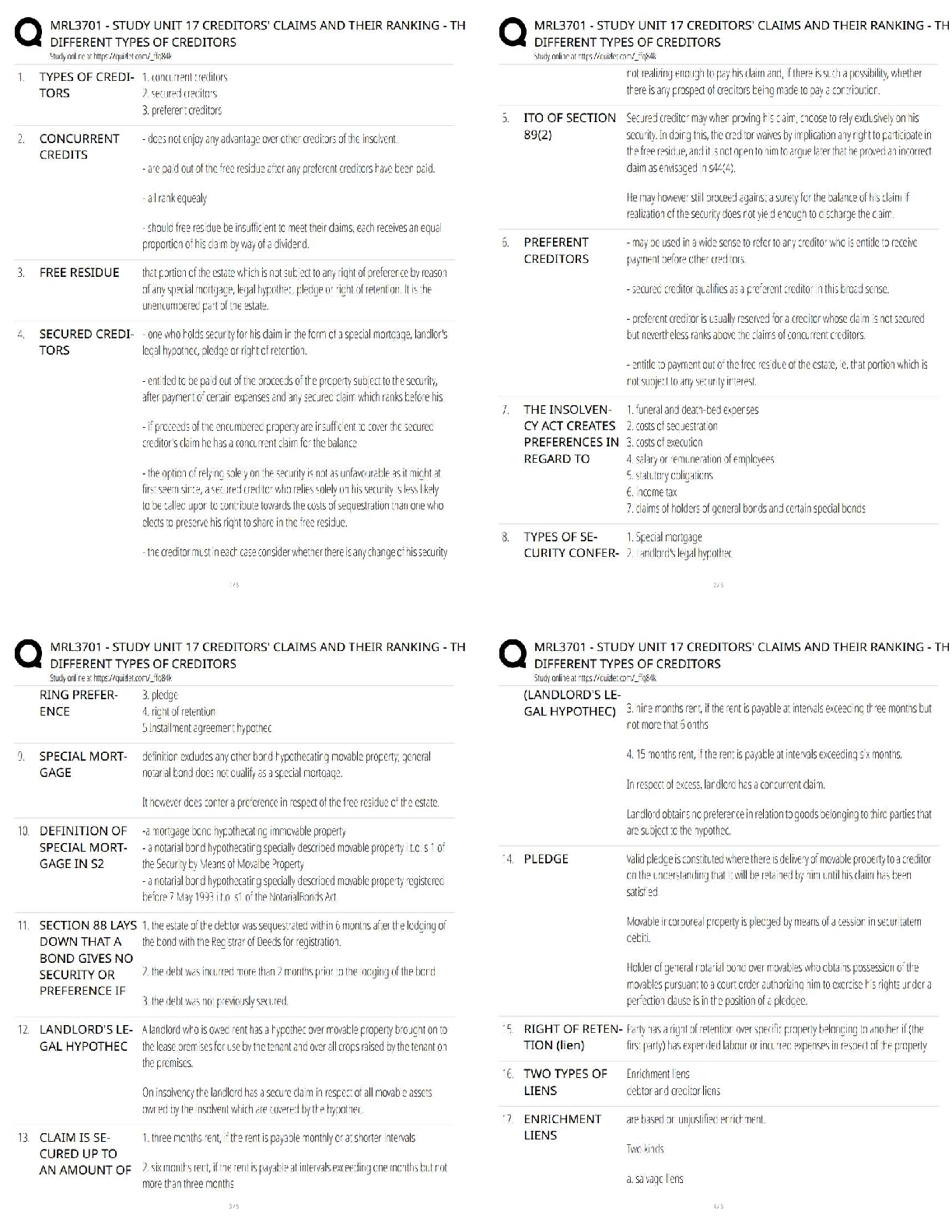
5. Risk aversion is an example of a construct.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 39
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
6. The hierarchy of theory organizes concepts in sequence from the most concrete and individual to the most general.
F
This is the ladder of abstraction.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 40 OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
7. As concepts become more abstract, the easier it is to measure them.
F
As concepts become more abstract, they are less amenable to measurement.
PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 40 OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
8. The empirical level of the ladder of abstraction is the level of knowledge that is verifiable by experience or observation.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 40
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
9. The basic or scientific business researcher operates at two levels: on the abstract level of concepts (and hypotheses) and on the empirical level of variables ( and propositions).
F
The abstract level is represented by propositions, and the empirical level represents hypotheses.
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 40 OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
10. The term inherent construct refers to a concept that is not directly observable or measurable.
F
This is a latent construct.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 40 OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
11. In its simplest form, a research hypothesis is a “guess” about the outcome of a research study.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 41
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
12. Empirical testing means that something has been examined against reality using data.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 41
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
13. A concept is a formal statement explaining some outcome.
F
This is a hypothesis.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 41 OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
14. Statistics can be used to prove that a research hypothesis is true.
F
Statistics cannot prove a hypothesis is true. Because our results are based on statistics, there is always the possibility that our conclusion is wrong.
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 42 OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
15. The process of identifying the actual measurement scales to asses the variables of interest is known as operationalizing.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 42
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
16. In most scientific situations there is typically only one theory to explain certain phenomena.
F
In most scientific situations there are alternative theories to explain certain phenomena.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 43 OBJ: LO: 03-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
17. Theories are derived from deductive reasoning and selective reasoning.
F
Theories are derived from deductive reasoning and inductive reasoning.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 43 OBJ: LO: 03-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
18. Deductive reasoning derives a conclusion about a general knowledge based on specific instances.
F
This is more descriptive of inductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning derives a conclusion about a specific instance based on general knowledge.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 43 OBJ: LO: 03-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
19. The scientific method is a set of prescribed procedures for establishing and connecting theoretical statements about events, for analyzing empirical evidence, and for predicting events yet unknown.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 44
OBJ: LO: 03-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
20. The first step in the scientific method is to formulate concepts and propositions.
F
This is the second step. The first step is the assessment of relevant existing knowledge of a phenomenon.
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 44 OBJ: LO: 03-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
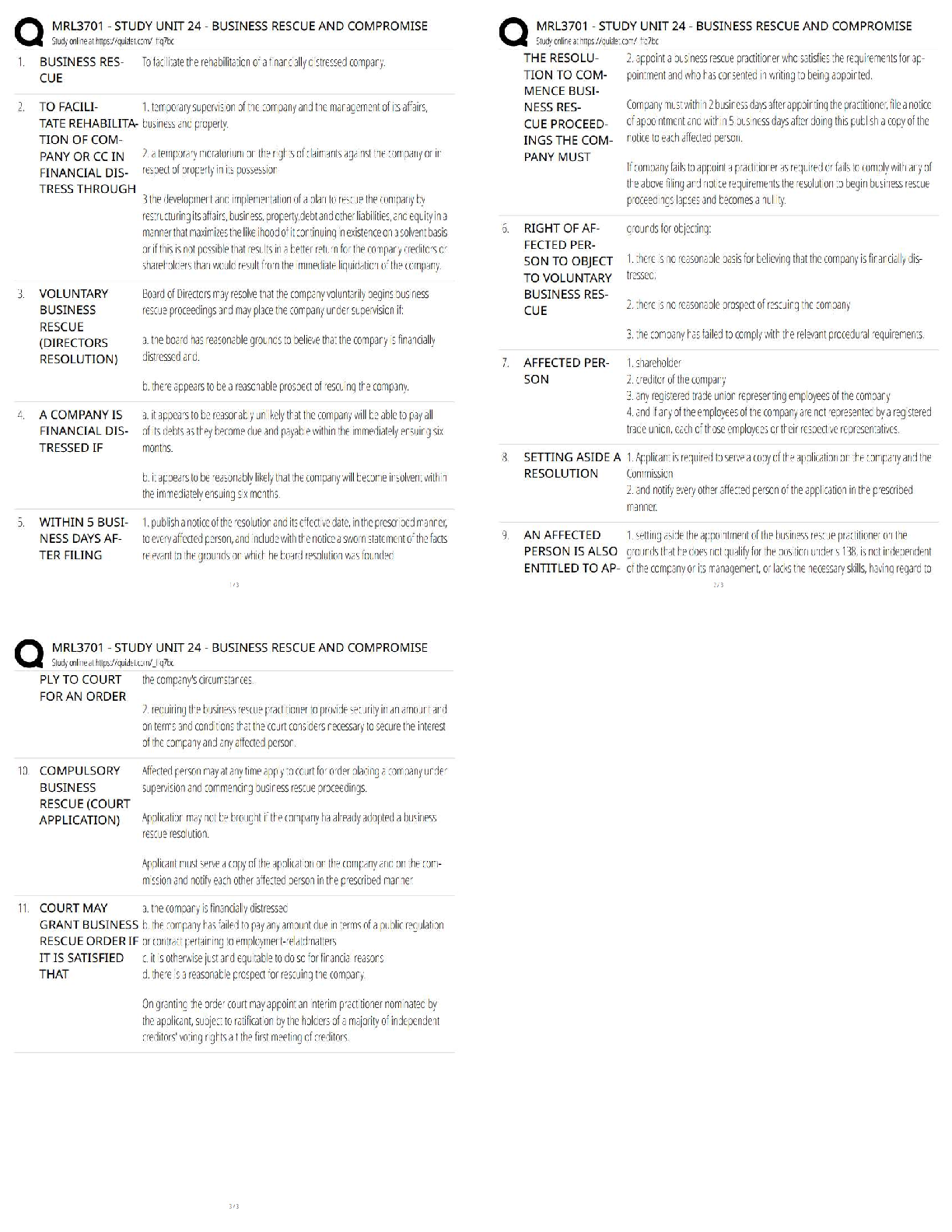
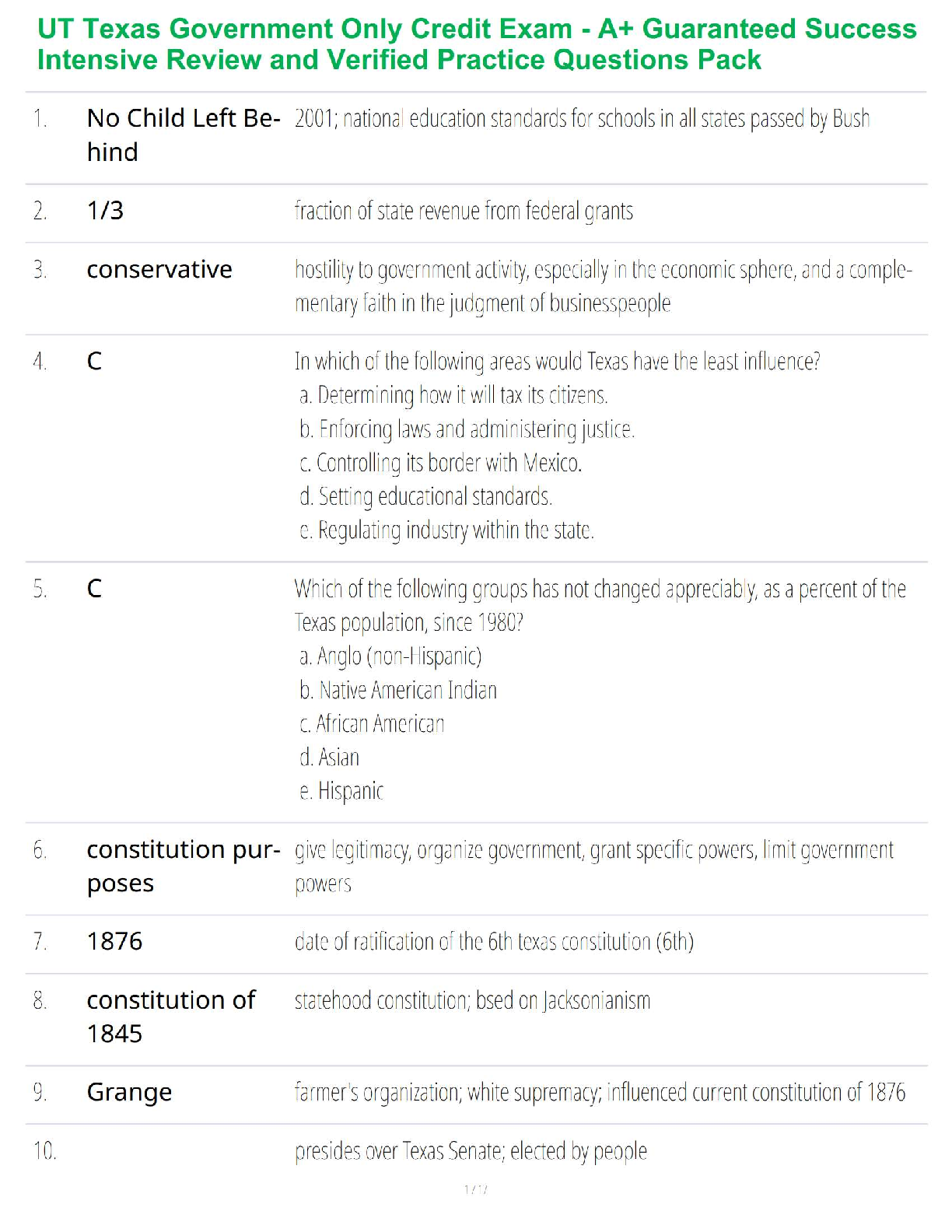
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. A formal, logical explanation of some events that includes descriptions of how things relate to one another is called a(n) _____.
a. hypothesis
b. theory
c. causal statement
d. empirical study
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 38
OBJ: LO: 03-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
2. Psychologists explain that humans’ better recall of information that is presented visually compared to information presented verbally is due to the fact that the information is stored both visually and verbally. Because it is stored using this dual-coding process, it is easier to retrieve from memory. This formal logical explanation of this phenomenon is an example of a(n) _____.
a. theory
b. construct
c. operationalization
d. abstraction
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 38
OBJ: LO: 03-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
3. What are the two goals of theory?
a. speculating and confirming
b. understanding and predicting
c. deducting and inducting
d. abstracting and concretizing
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 38
OBJ: LO: 03-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
4. A(n) ____ is a generalized idea about a class of objects that has been given a name.
a. variable
b. theory
c. node
d. construct
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 39
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
5. Which of the following is considered the basic unit for theory development?
a. concept
b. proposition
c. hypothesis
d. variable
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 39
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
6. Self-efficacy, which is a generalized idea about how humans perceive their own abilities, is an example of a(n) _____.
a. hypothesis
b. proposition
c. concept
d. abstraction
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 39
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
7. The organization of concepts in sequence from the most concrete and individual to the most general is called the _____.
a. conceptual hierarchy
b. ladder of abstraction
c. conceptual progression
d. operationalization of constructs
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 40
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
8. In theory development, which of the following is the level of knowledge expressing a concept that exists only as an idea or a quality apart from an object?
a. empirical level
b. primary level
c. conceptual level
d. abstract level
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 40
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
9. At what level do we “experience” reality?
a. empirical level
b. abstract level
c. primary level
d. secondary level
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 40
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
10. A concept that is not directly observable or measurable but can be estimated through proxy measures is called a(n) _____.
a. indirect construct
b. secondary construct
c. higher order construct
d. latent construct
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 40
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
11. Empathy is a concept that is not directly observable or measurable but is measured through other measures, such as an individual’s thoughts and behaviors toward others. This is an example of a(n) _____.
a. latent construct
b. empirical construct
c. secondary construct
d. higher order construct
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 40
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
12. Which of the following is a statement explaining the logical linkage among certain concepts by asserting a universal connection between concepts?
a. hypothesis
b. proposition
c. construct
d. theory
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 41
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
13. “Employees dressed professionally will perform better than those dressed casually” is an example of a _____.
a. theory
b. proposition
c. hypothesis
d. variation
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 41
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
14. Which of the following means that something has been examined against reality using data?
a. causality
b. manipulation
c. empirical testing
d. spurious association
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 41
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
15. When a researcher collects data to test the hypothesis that consumers will be more satisfied if a business offers compensation after the consumer complains, we say that _____ testing is being conducted.
a. validation
b. confirmation
c. observational
d. empirical
D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 41
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
16. Anything that may assume different numerical values is considered a(n) _____.
a. variable
b. construct
c. item
d. data point
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 42
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
17. Which of the following is an empirical assessment of a concept?
a. hypothesis
b. variable
c. construct
d. item
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 42
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
18. When the data from an empirical study are consistent with a research hypothesis, we say that the hypothesis is _____.
a. confirmed
b. conclusive
c. supported
d. true
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 42
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
19. The process of identifying the actual measurement scales to assess the variables of interest is called _____.
a. operationalizing
b. synthesizing
c. verifying
d. conceptualizing
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 42
OBJ: LO: 03-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
20. _____ is the logical process of deriving a conclusion about a specific instance based on a known general premise or something known to be true.
a. Deductive reasoning
b. Inductive reasoning
c. Latent reasoning
d. Abstract reasoning
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 43
OBJ: LO: 03-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
21. The logical process of establishing a general proposition on the basis of observation of particular facts is known as _____.
a. deductive reasoning
b. generalized reasoning
c. inductive reasoning
d. conceptual reasoning
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 44
OBJ: LO: 03-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
22. If all the trees a person has seen in his life have been green and therefore he concludes that all trees are green, which type of reasoning is he using?
a. deductive reasoning
b. inductive reasoning
c. generalized reasoning
d. conceptual reasoning
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 44
OBJ: LO: 03-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
23. A researcher is testing the hypothesis stating a positive relationship between business owners’ level of risk tolerance and the insurance coverage for the business. To test this, the researcher uses a set of prescribed procedures for establishing and connecting theoretical statements about these two constructs, for analyzing empirical evidence gathered through surveys, and for predicting future behavior. This researcher is following the _____.
a. hypothetical method
b. scientific method
c. deductive method
d. inductive method
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 44
OBJ: LO: 03-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
24. Which of the following is a step involved in the application of the scientific method?
a. statement of hypotheses
b. formulation of concepts and propositions
c. analysis and evaluation of data
d. all of these choices
D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 44
OBJ: LO: 03-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
25. What is the LAST step in the application of the scientific method?
a. assessment of relevant existing knowledge of a phenomenon
b. proposal of an explanation of the phenomenon and statement of new problems raised by the research
c. design of research to test the hypothesis
d. acquisition of meaningful empirical data
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 44
OBJ: LO: 03-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
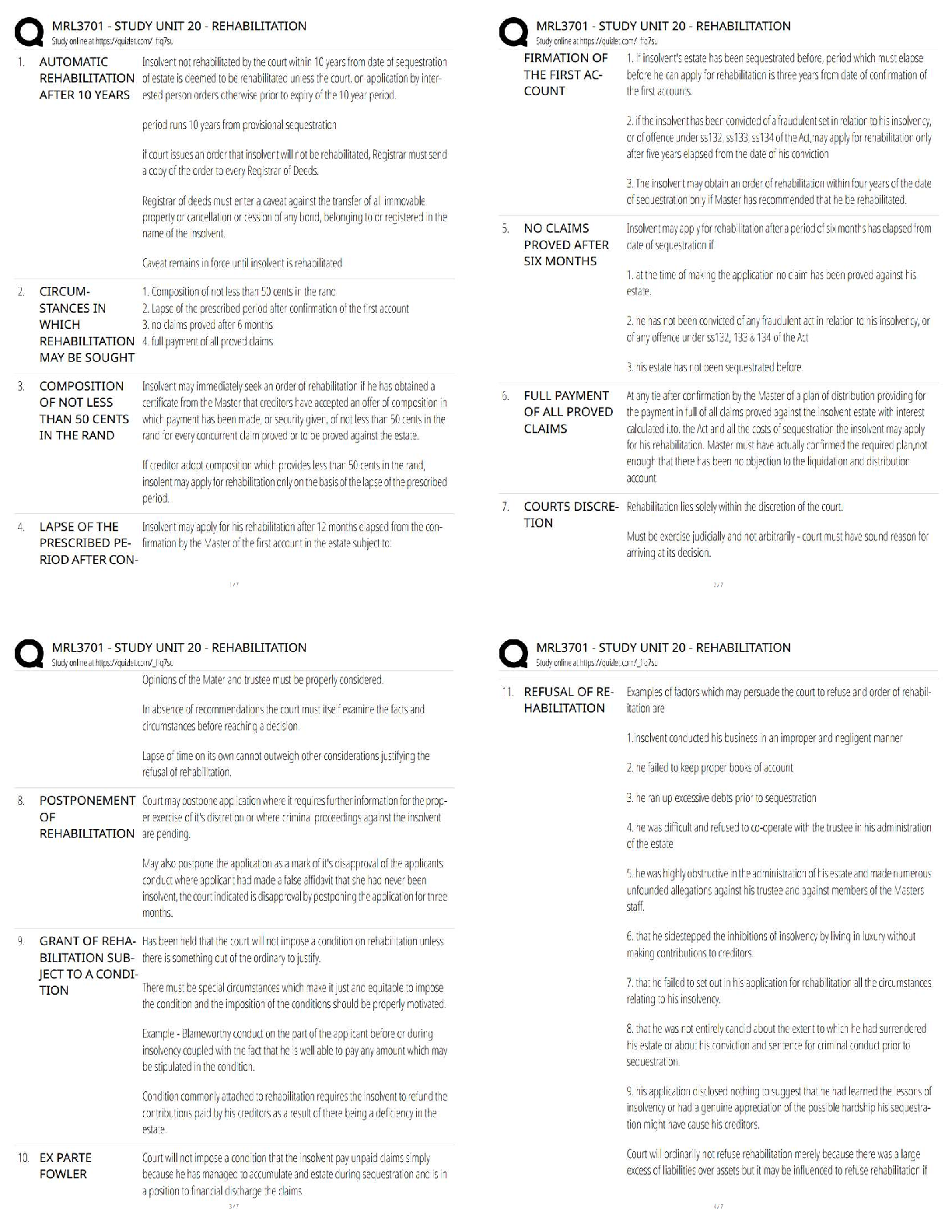
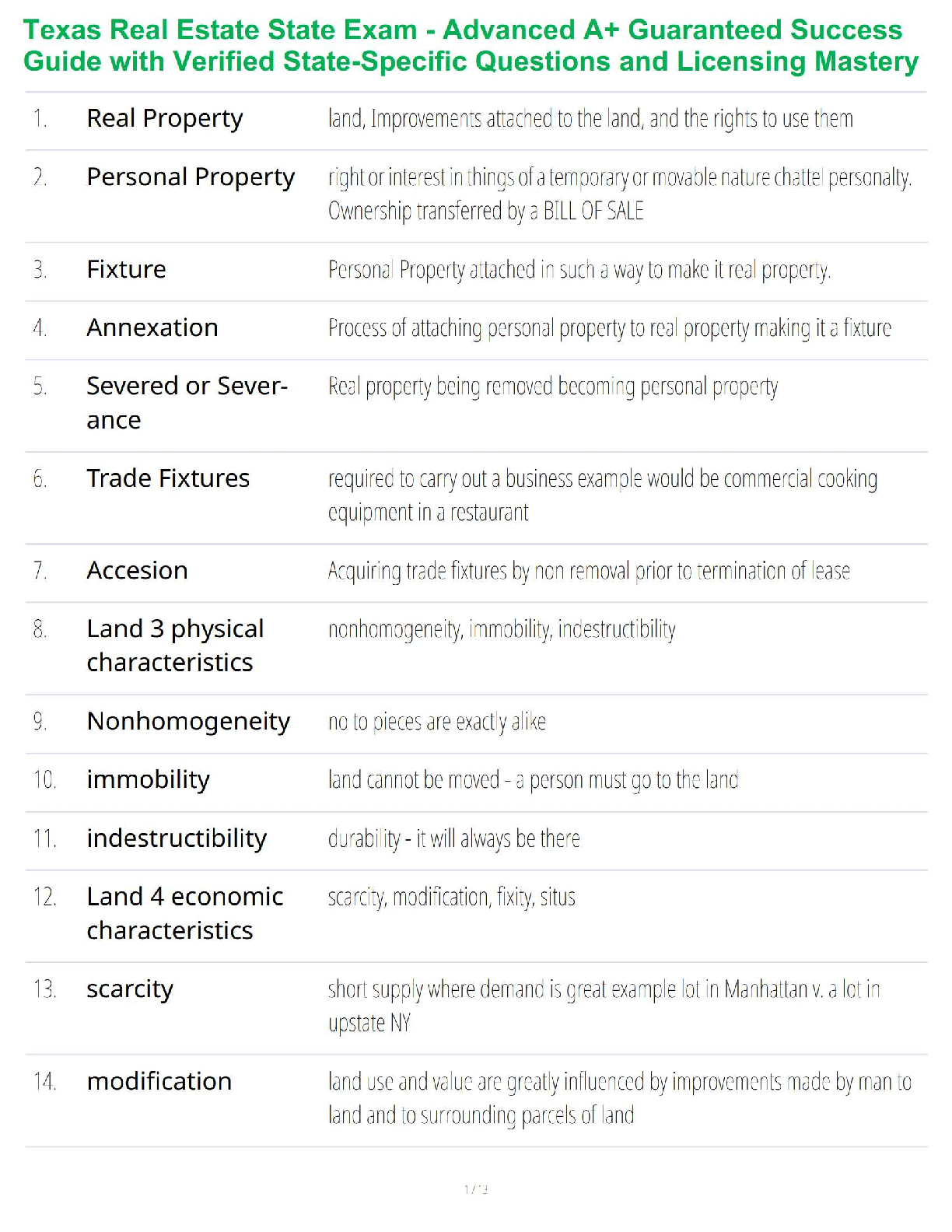
COMPLETION
1. A formal, logical explanation of some events that includes predictions of how things relate to one another is known as a(n) _____.
2. The two purpose of theory are understanding and _____.
3. _____ are the building blocks of theory.
4. The organization of concepts in sequence from the most concrete and individual to the most general is called the _____.
5. In theory development, the level of knowledge expressing a concept that exists only as an idea or a quality apart from an object is the ____ level.
6. A concept that is not directly observable or measurable, but can be estimated through a proxy measure is known as a(n) _____ construct.
7. Statements explaining the logical linkage among certain concepts by asserting a universal connection between concepts are called _____.
8. A(n) _____ is a formal statement explaining some outcome and is testable.
9. _____ involves applying statistics to data to test hypotheses.
10. When the data are inconsistent with a hypothesis, we say the hypothesis is _____,
11. If it is hypothesized that higher levels of compensation will positively influence workers’ intention to stay with a company, level of compensation measured in dollars and intentions to stay using a scale are examples of _____.
12. A researcher is using income, education, and zip code as an indication of social class. This process of identifying the actual measurement scales to assess social class is called _____.
13. Going from the general to the specific is done in _____ reasoning.
14. _____ reasoning establishes a general proposition on the basis of observation of particular facts.
15. A set of prescribed procedures for establishing and connecting theoretical statements about events, for analyzing empirical evidence, and for predicting events yet unknown is called the _____.
ESSAY
1. What is a theory and a hypothesis, and what role do they play in marketing research?
2. Explain the difference between a concept and a variable and give an example of each.
3. How does a hypothesis differ from a proposition? Give an example of each.
4. Discuss the types of reasoning researchers use to build theories.
5. List the steps a researcher will likely follow when applying the scientific method to develop and test theories
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)