Biology > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 24: Chlamydia, Rickettsia and Similar Organisms. All Answers (All)
Chapter 24: Chlamydia, Rickettsia and Similar Organisms. All Answers
Document Content and Description Below
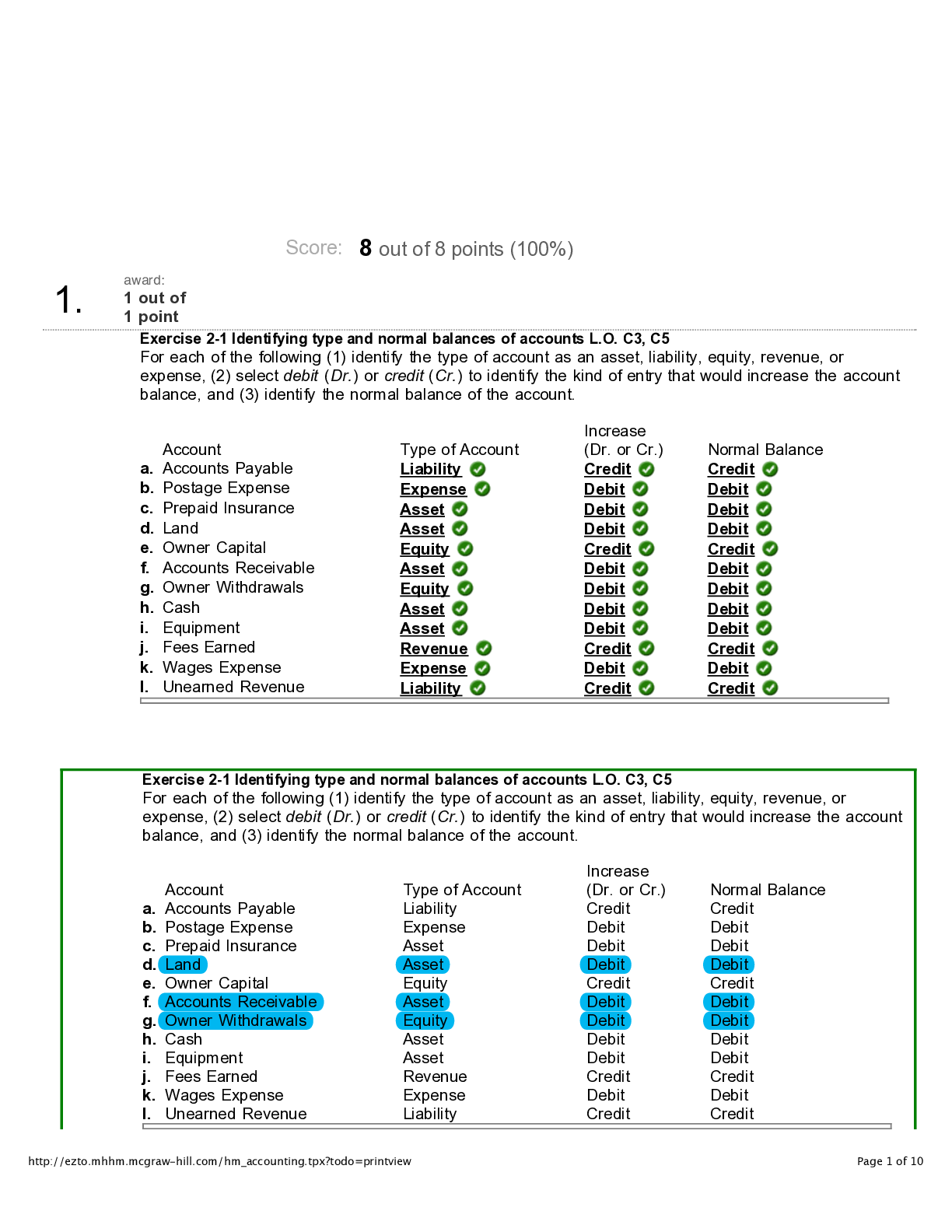
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What organisms are considered obligate intracellular parasites? a. Chlamydia b. Mycoplasma c. Ureaplasma d. Haemophilus A Chlamydia spp. are deficient in energy metab... olism and are therefore obligate intracellular parasites. REF: 539 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 2. What organism’s unique life cycle contains an elementary body and a reticulate body? a. Haemophilus b. Chlamydia c. Ureaplasma d. Mycoplasma B The unique life cycle of Chlamydia involves two distinct forms: an elementary body (EB), which is infectious, and a reticulate body (RB), which is noninfectious. REF: 539 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 3. What has an outer membrane similar to that of many gram-negative bacteria, with the most prominent feature being the major outer membrane protein? a. Haemophilus b. Reticulate body c. Elementary body (EB) d. Intracellular parasites C The EB has an outer membrane similar to that of many gram-negative bacteria. The most prominent component of this membrane is the major outer membrane protein. REF: 539 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation 4. Chlamydia trachomatis is the infectious agent in all the following conditions in humans except: a. trachoma. b. urogenital infections. c. lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV). d. pharyngitis. D C. trachomatis has been divided into three biovars: trachoma, LGV, and mouse pneumonitis. These biovars are responsible for trachoma (a severe eye infection), Lymphogranuloma venereum (an invasive urogenital tract disease), and urogenital infections. REF: 539 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 5. What disease, caused by Chlamydia trachomatis, is considered a sexually transmitted disease where the organisms enter the lymph nodes near the genital tract, resulting in bubo formation and ultimately rupturing the lymph node? a. Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV) b. Trachoma c. Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) d. Conjunctivitis A In LGV, the patients have inguinal and anorectal symptoms. The bacteria enter the lymph nodes near the genital tract and produce a strong inflammatory response that often results in bubo formation and subsequent rupture of the lymph node. REF: 540 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation 6. All of the following are urogenital infections in men, produced by Chlamydia trachomatis except: a. epididymitis. b. orchitis. c. prostatitis. d. nongonococcal urethritis (NGU). B C. trachomatis infections in adult men include NGU, epididymitis, and prostatitis. REF: 541 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 7. A young man goes to his physician complaining of a discharge from his penis. The physician collects a slide for Gram stain and a swab for culture and sends them to the laboratory. The Gram stain is prepared and read: greater than 25 wbc/hpf, no bacteria seen. The culture results after 48 hours show no growth. What is the most probable diagnosis and the organism responsible? a. Urethritis, Streptococcus pneumonia b. Epididymitis, Moraxella c. Nongonococcal urethritis, Neisseria meningitidis d. Nongonococcal urethritis, Chlamydia trachomatis D Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common sexually transmitted bacterial pathogen in the United States. In 2010, a total of 1,307,893 cases of genital infections were reported, but many infections are undiagnosed and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates 2 to 3 million new cases occur annually in the United States. C. trachomatis will not show up on Gram stains or grow on culture media. C. trachomatis will elicit an inflammatory response, so white blood cells will be present in the discharge, but no bacteria. REF: 541 OBJ: Level 3: Synthesis 8. Chlamydia trachomatis produces all the following conditions in adult women except: a. pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). b. salpingitis. c. bacterial vaginosis. d. endometritis. C Infections in adult women include urethritis, follicular cervicitis (meningitidis, hypertrophic cervical erosion), endometritis, proctitis, salpingitis, PID, and perihepatitis. Salpingitis can lead to scarring and dysfunction of the ova ductile transport system, resulting in infertility or ectopic pregnancy. In the United States, this is a major cause of sterility. REF: 541 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 9. Infants can contract all the following chlamydial infections when passing through the birth canal except: a. conjunctivitis. b. nasopharyngeal infections. c. pneumonia. d. endocarditis. D Infants suffering from chlamydial infection can experience conjunctivitis, nasopharyngeal infections, and pneumonia. REF: 541 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 10. What is the most commonly used test technique to detect Chlamydia trachomatis infection? a. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) b. Nucleic acid probes c. Cell culture d. Cytologic methods A The most commonly used rapid antigen assay for the detection of C. trachomatis is the EIA. The cytologic and cell-culture methods are inherently labor intensive and time consuming. REF: 543 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 11. What method is used to confirm a positive Chlamydia trachomatis enzyme immunoassay (EIA)? a. Cytologic methods b. Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) c. Cell culture d. Nucleic acid probes B The EIA cannot be confirmed using nucleic acid probes because the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values are about the same as the EIA test, so DFA is used. REF: 542 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 12. Why are antibody detection methods for Chlamydia trachomatis infection severely limited in the knowledge they provide the physician? a. Because C. trachomatis is an intracellular parasite, the body does not produce antibodies against it. b. Only IgE antibodies are produced against C. trachomatis. c. Many people have antibodies from previous infections, and local infections do not cause great increases in antibody levels. d. All of the above. C Many individuals have chlamydial antibodies from previous infections, and because chlamydial infections tend to be localized, they do not cause the traditional fourfold rise in antibody titer between acute and convalescent specimens. REF: 544 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation 13. Guidelines for testing and reporting the results of Chlamydia trachomatis testing on patients include all the following except: a. testing specifically using profiles. b. reporting which tests were and were not performed. c. reporting unusual observations. d. performing a routine culture in addition to all the tests for Chlamydia. D Guidelines for reporting results include agreeing in advance with the obstetrics/gynecology and emergency departments on which organisms are associated with which clinical syndrome, then testing accordingly, using profiles, reporting which tests were and were not performed for each patient profile, and reporting unusual observations. REF: 545 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 14. What organism has been established as a risk factor for Guillain-Barré syndrome? a. Chlamydophila pneumoniae b. C. trachomatis c. C. psittaci d. C. urealyticum A C. pneumoniae is recognized as an important respiratory pathogen. It is known to be the cause of acute respiratory disease, pneumonia, and pharyngitis. It also has been isolated from patients with otitis media with effusion, pneumonia with pleural effusion, and aseptic pharyngitis. Infection with C. pneumoniae has been established as a risk factor for Guillain-Barré syndrome, an immunologically mediated neurologic disease. REF: 545 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 15. What testing method is the method of choice for detecting antibodies to Chlamydophila pneumoniae? a. Direct fluorescent antibody (DFA) b. Serologic tests c. Cell culture d. Enzyme immunoassay (EIA) B Given the difficulty and lack of standardization for isolation of C. pneumoniae, serologic tests have been the method of choice for diagnosis. The present method of choice is the micro-IF assay, which is more sensitive and specific than complement fixation. REF: 546 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 16. What disease does Chlamydophila psittaci cause in humans? a. Conjunctivitis b. Endocarditis c. Parrot fever d. Bird flu C C. psittaci is the cause of psittacosis, also known as ornithosis or Parrot fever. REF: 547 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 17. A 4-day-old infant shows symptoms of conjunctivitis. A Giemsa stain of the conjunctival scraping shows perinuclear cytoplasmic inclusions. This organism is most likely: a. C. trachomatis serovars A, B, Ba, C. b. C. trachomatis serovars D-K. c. C. trachomatis serovars L1, L2, L3. d. C. pneumoniae. B Serovars D through K are associated with inclusion conjunctivitis, a milder eye infection, and urogenital infections. Traveling through an infected birth canal, infants can be infected with Chlamydia spp. Chlamydial infection in an infant delivered by cesarean section is rare, and infection from seronegative mothers has not been reported. Infants suffering from chlamydial infection can experience conjunctivitis, nasopharyngeal infections, and pneumonia. REF: 539 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 18. What organism causes Rocky Mountain spotted fever? a. Rickettsia prowazekii b. R. typhi c. R. canada d. R. rickettsii D The most severe of the rickettsial infections, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, is caused by R. rickettsii. REF: 547 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 19. What organism causes endemic typhus? a. Rickettsia typhi b. R. canada c. R. rickettsii d. R. prowazekii A Endemic typhus is caused by R. typhi. The arthropod vector is the oriental rat flea and the rat is the reservoir. REF: 548 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 20. What organism causes epidemic louse-borne typhus? a. Rickettsia typhi b. R. canada c. R. rickettsii d. R. prowazekii D Epidemic louse-borne typhus is caused by R. prowazekii. REF: 549 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 21. What organism causes human monocytic ehrlichiosis and uses the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum) as its primary vector? a. Neorickettsia sennetsu b. Ehrlichia chaffeensis c. Anaplasma phagocytophilum d. Leptotrombidium deliensis B Ehrlichia chaffeensis causes human monocytic ehrlichiosis (HME), which occurs in the United States, Europe, Africa, and South and Central America. In the United States, most cases are found in the southeastern and south central states, as well as in the Mid-Atlantic States. Oklahoma, Missouri, and Arkansas account for about 35% of the cases. REF: 550 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation 22. All of the following diseases are associated with Chlamydia trachomatis except: a. Undulant fever. b. Urethritis. c. Conjunctivitis. d. Lymphogranuloma venereum. A Chlamydia trachomatis, which was initially associated with trachoma, is also known to cause conjunctivitis, urethritis, lymphogranuloma venereum, and a number of non-gonococcal urogenital infections. REF: 541 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 23. Diseases caused by rickettsial organisms are typically transmitted to man by: a. ingestion of contaminated food. b. an arthropod vector. c. animal bites. d. inhalation of aerosols. B Most of the members of the rickettsial group are arthropod-borne, obligately intracellular pathogens that can grow only in the cytoplasm of host cells. These bacteria have become extremely well adapted to their arthropod hosts. REF: 547 OBJ: Level 1: Recall 24. Fifty years after his release from a concentration camp, a man develop signs and symptoms of typhus. He has no known contacts or source of disease exposure at this time; however, he may have had it in 1945. What is the most likely current diagnosis? a. Oroya fever b. Q fever c. Rocky Mountain spotted fever d. Brill Zinsser syndrome D Brill-Zinsser disease, also called recrudescent typhus, is seen in patients who have previously had louse-borne typhus. R. prowazekii lies dormant in the lymph tissue of the human host until the infection is reactivated. Brill-Zinsser disease is a milder disease than louse-borne typhus, and death is rare. REF: 549 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 7 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 23, 2020
Number of pages
7
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 23, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
65


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)