Philosophy > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > CLEX Quinn Pond Nursing 479 | University of Arizona. All Fully Answered/Explained (All)
CLEX Quinn Pond Nursing 479 | University of Arizona. All Fully Answered/Explained
Document Content and Description Below
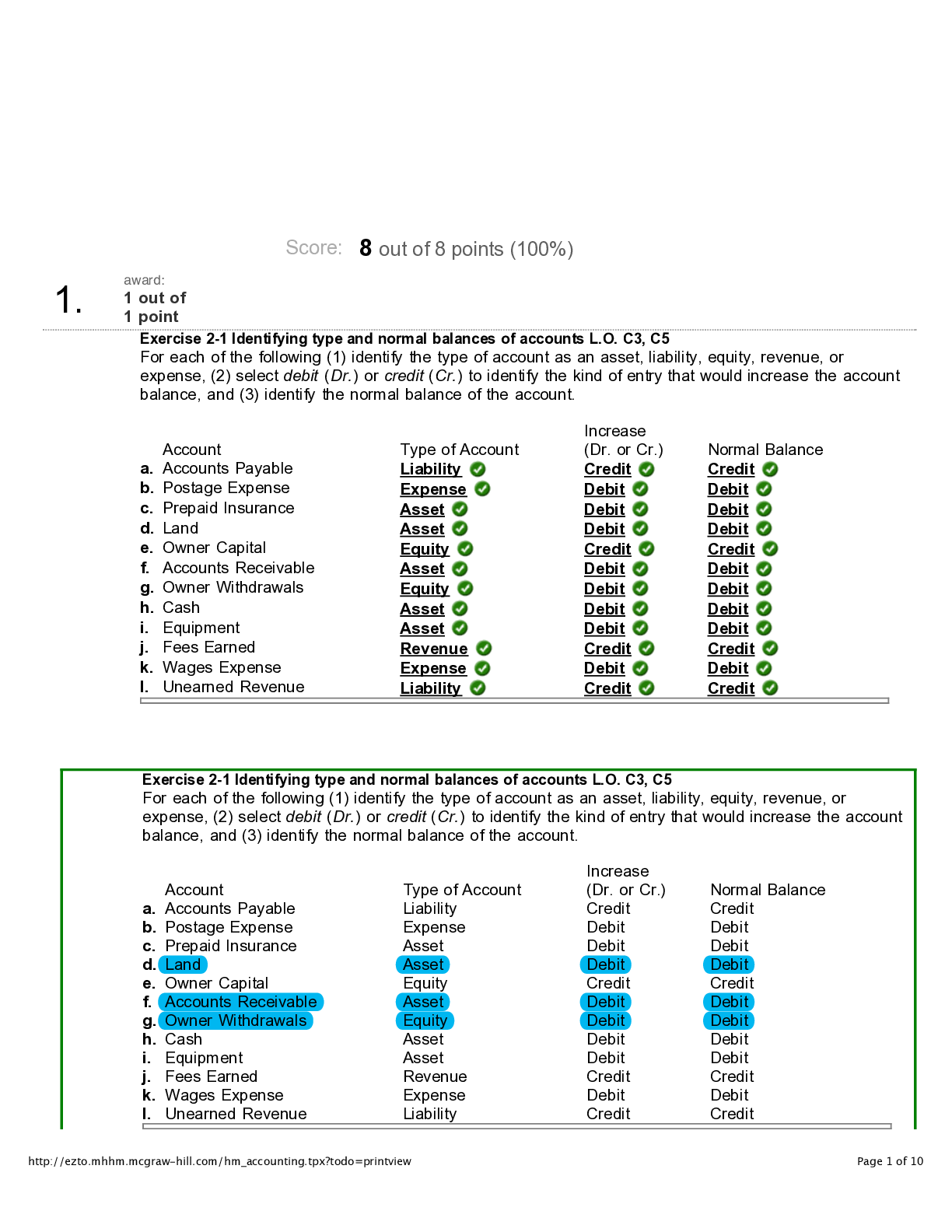
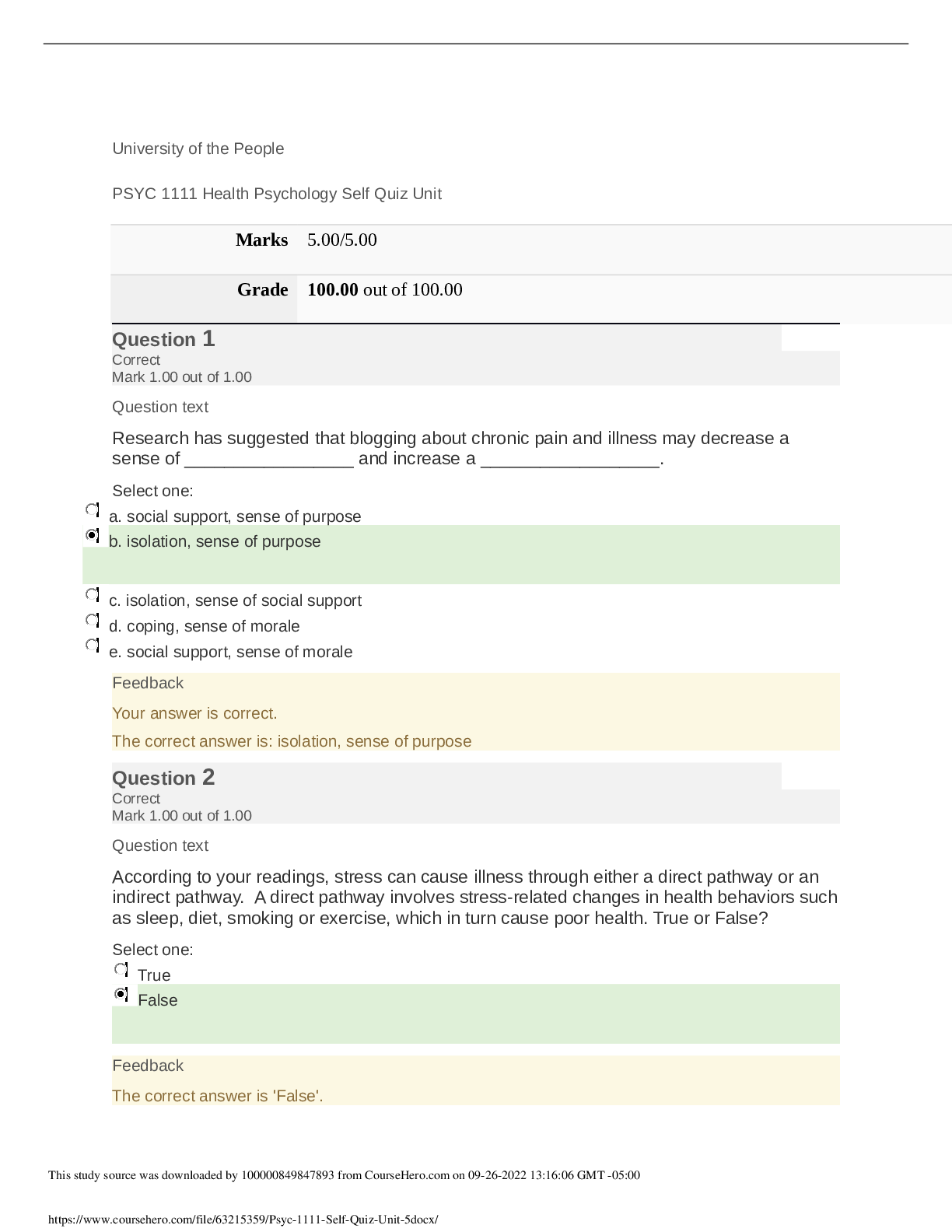
N Blood Pressure 120/80 Heart rate 60-100 bpm SPO2 95-100%88-92% for COPD pts Temperature 36.5-37.5 C98.6-100.4 F Respiration rate 12-20 rpm Therapeutic acetaminophen levels 10-30 mcg/mL ... Therapeutic carbamazepine levels 5-12 mcg/mL Therapeutic digoxin levels 0.5-2 ng/mL Therapeutic gentamicin levels 5-10 mcg/mL Therapeutic lithium levels 0.5-1.2 mEq/L Therapeutic magnesium sulfate levels 4-7 mg/dL Therapeutic phenobarbital levels 10-30 mcg/mL Therapeutic phenytoin levels 10-20 mcg/mL Therapeutic salicylate levels 100-250 mcg/mL Therapeutic valproic acid levels 50-100 mcg/mL Rule of 9s: Head 9% Rule of 9s: Arms 18% (9% each) Rule of 9s: Back 18% Rule of 9s: Chest 18% Rule of 9s: Legs 36% (18% each) Rule of 9s: Genitalia 1% Fluid resuscitation formula 4 mL x BSA (% of body burned) x kg Give half in the first 8 hours and remaining half over 16 hours Potassium (K) 3.5-5.0 mEq/L Sodium (Na) 135-145 mEq/L Calcium (Ca) 8.5-10.5 mg/L Chloride (Cl) 95-105 mEq/L Magnesium (Mg) 1.5-2.5 mEq/L Phosphorus (Phos) 2.5-4.5 mg/dL Red blood cells (RBC) 4.5-5.0 million White blood cells (WBC) 5K-10K Platelets (Plt) 200K-400K Hemoglobin (Hgb) 12-16 g (female)14-18 g (male) pH 7.34-7.45 Bicarbonate (HCO3) 22-28 mEq/L PaO2 80-100% Glucose 70-100 mg/dL4-6 mmol/L A1C .<7% Specific gravity 1.010-1.030 Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 7-22 mg/dL Creatinine 0.6-1.35 mg/dL LDH 100-190 units/L Trigylcerides 40-50 mg/dL Total cholesterol 130-200 mg/dL Bilirubin .<1.0 mg/dL Protein 6.2-8.1 g/dL Albumin 3.4-5.0 g/dL PTT 20-36 secondsIf on heparin 1.5-2.5x normal PT 9-11 seconds INR 0.9-1.82-3 if on Warfarin How many mL in 1 tsp? How many mL in 1 tbsp? How many mg in 1 g? How many mcg in 1 g? How many mL in 1 oz? How many oz in 1 cup? How many lbs in 1 kg How many mcg in 1 mg? Positioning for NG tube placement? Positioning for hypotension? Positioning for labor or un-reassuring FHR? Position for tube feeding with decreased LOC? Position for epidural puncture? Positioning for lumbar puncture? Positioning for after myringotomy? Positioning for after cataract surgery? Positioning for after thyroidectomy? Positioning for detached retina? Positioning for enema? Positioning for autonomic dysreflexia/hyperflexia? Positioning for paracentesis? Positioning for after liver biopsy? Positioning for SOB? Positioning for MI? Positioning for head injury? Positioning for after total hip replacement? Positioning for infant with spina bifida? Positioning for prolapsed cord? Positioning for after lumbar puncture? Positioning for infant with Cleft Lip? Positioning to prevent dumping syndrome? Positioning for above knee amputation? Positioning for below knee amputation? Positioning for after supratentorial surgery (incision for behind hairline)? Positioning for after infratentorial surgery? Positioning for chest tube insertion? Contact precautions Droplet precautions Airborne precautions Precautions for multi-drug resistant organisms? Precautions for respiratory infections? Precautions for skin infections (varicella zoster, cutaneous diphtheria, herpes simplex, impetigo, pediculosis, scabies) Precautions for wound infections? Precautions for enteric infections (C. diff)? Precautions for eye infections? Precautions for sepsis? Precautions for Scarlet Fever? Precautions for Streptococcal pharyngitis? Precautions for Parvovirus B19? Precautions for pneumonia? Precautions for pertussis? Precautions for influenza? Precautions for Diphtheria (pharyngeal)? Precautions for epiglotitis? Precautions for Rubella? Precautions for Mumps? Precautions for meningitis? Precautions for mycoplasma or meningeal pneumonia? Precautions for Adenovirus Precautions for Measles Precautions for TB? Precautions for Varicella Zoster? Antidote for Warfarin? Antidote for opioid overdose? Antidote for Digoxin? Antidote for magnesium? Antidote for Tylenol? Antidote for Benzodiazepine? Antidote for insulin? Antidote for cholinergic crisis? Placement for aortic valve auscultation Placement for pulmonic valve auscultation Placement for Erb's point auscultation Placement for tricuspid valve auscultation Placement for mitral valve auscultation Normal BNP .<100 pg/mL Normal PR interval 0.12-0.20 seconds Normal QRS complex .<0.12 seconds Normal amount of chest tube drainage .<100 mL/hr Amount of weight gain that should be reported with heart failure Normal MAP 70-105 mmHg MAP calculation (SBP + (2DBP))/3 Normal ejection fraction 55-70% RICE RestIceCompressionElevation Chvostek's sign Tapping on facial nerve causing the lip on the same side to twitch, which is seen in tetany caused by hypocalcemia Trousseau's sign Carpopedal spasm when a BP cuff is inflated for 3 minutes, which is a sign of tetany caused by hypocalcemia Clear liquid diet Clear fat-free broth, bouillon, jello, popsicles, clear fruit juice (apple, grape), carbonated beverages, coffee, tea Full liquid diet Strained/blended cream soups, custards, pudding, refined cooker cereals, all fruit juice, ice cream, frozen yogurt, sherbet, milkshakes Soft diet Soups, ground and finely diced meats, flaked fish, pancakes, biscuits, muffins, pasta, rice, mashed potatoes, cooked/canned fruits and vegetables, peanut butter, scrambled eggs How many calories need to be reduced/burned to loss 1 lb? What are Maslow's hierarchy of needs (1-3) from most important to least? What are Maslow's hierarchy of needs (4-5) from most important to least? ABCDE skin assessment Glasgow coma scale 3-15 GCS: Motor response GCS: Verbal response GCS: Eye-opening 4. Spontaneous3. In response to sounds2. In response to pain1. No response Cranial nerves I. OlfactoryII. OpticIII. OculomotorIV. TrochlearV. TrigeminalVI. AbducensVII. FacialVIII. VestibulocochlearIX. GlossopharyngealX. VagusXI. Spinal accessoryXII. Hypoglossal Positioning for thoracentesis Sitting up with arms and shoulders on bedside table Side-lying with HOB elevated Nasal cannula Delivers 1-6 L/minFiO2 24-44% Simple face mask Delivers 5-8 L/minFiO2 40-60% Venturi mask Delivers 4-10 L/minFiO2 24-55% Partial rebreather mask Delivers 6-15 L/minFiO2 70-90% Non-rebreather mask FiO2 60-100%Flow rate determined by bag inflation Relationship between sodium and potassium Inverse relationship (high Na = low K) Relationship between calcium and phosphorus Inverse relationship (high Ca = low Phos) Relationship between Calcium and vitamin D Similar relationship (high Ca = high Vitamin D) Relationship between Magnesium and Calcium Similar relationship (low Mg = low Ca) Relationship between Magnesium and Potassium Similar relationship (low Mg = low K) Relationship between Magnesium and Phosphorus Inverse relationship (low Mg = high Phos) CAUTION Change in bowel/bladder habitsA sore that won't healUnusual bleeding/dischargeThickening/lumpIndigestion/difficulty swallowingObvious change in wart/moleNagging cough/hoarseness 6 P's of compartment syndrome PainPressureParesthesiaPallor (late)Puslelessness (late)Paralysis (late) Normal pupil size 3-5 mm PaCO2 35-45 mmHg Respiratory acidosis pH: lowHCO3: normalPaCO2: high Partially compensated respiratory acidosis pH: lowHCO3: highPaCO2: high Respiratory alkalosis pH: highHCO3: normalPaCO2: low Partially compensated respiratory alkalosis pH: highHCO3: lowPaCO2: low Metabolic acidosis pH: lowHCO3: lowPaCO2: normal Partially compensated metabolic acidosis pH: lowHCO3: lowPaCO2: low Metabolic alkalosis pH: highHCO3: highPaCO2: normal Partially compensated metabolic alkalosis pH: highHCO3: highPaCO2: high Reversal of hyperkalemia with EKG changes Calcium gluconate Reversal of hyperkalemia without EKG changes Insulin with dextrose Positioning for air embolism Left lateral trendelenburg Virchow's triad Blood stasis + endothelial damage + hyper-coagulability = thrombosis Central venous pressure (CVP) 2-8 mmHgReflects fluid volume problems Signs of refeeding syndrome PPM; low Phosphorus, Potassium, and/or Magnesium Lab values associated with liver dysfunction Causes of respiratory acidosis Causes of respiratory alkalosis Causes of metabolic acidosis Causes of metabolic alkalosis How should a cane be held? Moving up/down stairs with cane/crutches Normal sinus rhythm Normal sinus rhythm Atrial fibrillation Atrial fibrillation Premature ventricular contractions (PVC); unifocal Prematur ventricular contractions (PVC); multifocal Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach) Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib) Atrial flutter Atrial flutter Premature atrial contraction (PAC) Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Accelerated junctional rhythm Accelerated junctional rhythm Junctional escape rhythm Junctional escape rhythm Junctional tachycardia 1st degree heart block 1st degree heart block 2nd degree heart block type 1 (Wenckebach) 2nd degree heart block type 1 (Wenckebach) 2nd degree heart block type 2 (Mobitz II) 3rd degree heart block Signs of hypoglycemia Signs of hyperglycemia What diseases are caused by a previous Strep infection? Confirmation of active TB Order of assessment for infants, toddlers, and young children (in general) Infant milestones: 1 month Infant milestones: 2-3 months Infant milestones: 4-5 months Infant milestones: 6-9 months Infant milestones: 10-12 months Toddler milestones: 18 months Toddler milestones: 2 years Toddler milestones: 3 years Preschooler physical development Infant physical development Erickson's theory of development: Infancy Birth-18 months; Trust vs mistrust Erickson's theory of development: Early childhood 18 months-3 years; Autonomy vs Shame & doubt Erickson's theory of development: Late childhood 3-6 years; Initiative vs Guilt Erickson's theory of development: School age 6-12 years; Industry vs Inferiority (developing social, physical and learning skills) Erickson's theory of development: Adolescence 12-20 years; Identity vs Role confusion Erickson's theory of development: Early adulthood 20-35 years; Intimacy vs Isolation Erickson's theory of development: Middle adulthood 35-65 years; Generativity vs Stagnation Erickson's theory of development: Later adulthood 65 years-death; Integrity vs Despair Toddler's physical development Height: 3 inches/yearWeight: 4-6 lbs/ Tetrology of Fallot VSDPulmonary stenosisOverriding aortaRight ventricular hypertrophy Chest tube drainage for children Less than <5-10 mL/kg in 1 hour Urine output for children 1-2 mL/kg/hr Positioning after tonsillectomy Prone or side lying Vaccines contraindicated for immunocompromised MMR, Varicella, Rotavirus 3 C's of esophageal atresia and tracheoesophageal fistula Coughing, choking, cyanosis Cushing's triad Bradycardia, slowed respirations, widened pulse pressure (indicate increased ICP) FLACC scale Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolibility Vaccines given at birth Hepatitis B Vaccines given at 1 month Hepaatitis B Vaccines given at 2 months Inactivated poliovirus Vaccines given at 4 months Vaccines given at 6 months DTaPHaemophilus influenzae type B Vaccines given at 12-15 months Haemophilus influenzae type Vaccines given at 15-18 months DTaP Vaccines given at 18-33 months HepA Vaccines give at 4-6 years DTaPInactivated poliovirus (IPV)MMRVaricella Vaccines given at 11-12 years MMR (if not received at 4-6 years)TdapMeningococcal (MCV4) with a booster at 16HPV Precautions for RSV Contact Classic signs of nephrotic syndrome Massive proteinuriaHypoalbuminemiaEdemaIncreased lipid levels How many mL of fluid equals 1 kg of weight gain? 1000 mL [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 21 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$6.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Feb 04, 2020
Number of pages
21
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Feb 04, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
110


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)