Criminology > STUDY GUIDE > CRI205 Exam - University of Toronto CRI 205 (All)
CRI205 Exam - University of Toronto CRI 205
Document Content and Description Below
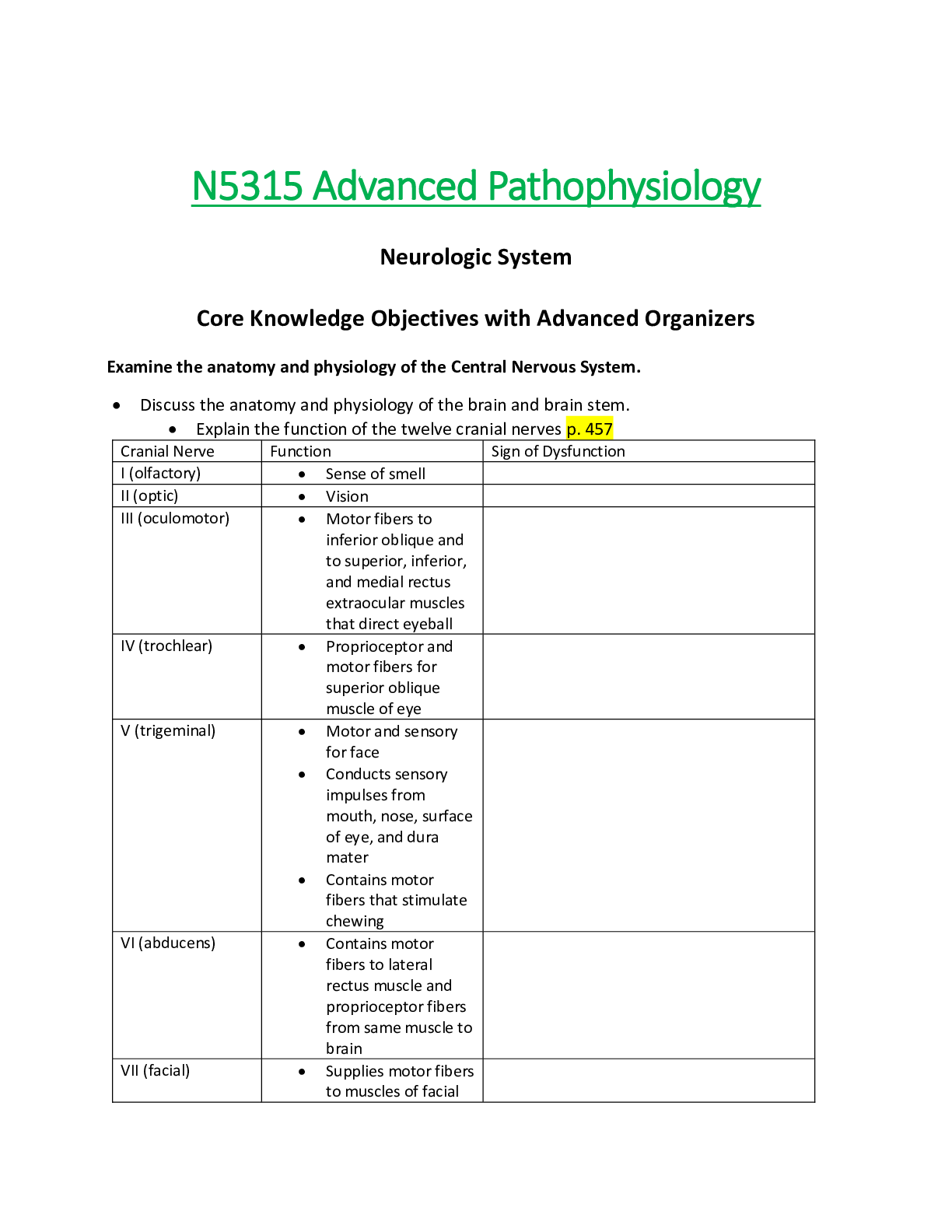
Agnew (General Strain Theory) - Strain caused by: 1) Mean-goals discrepancy: failure to achieve positively valued goals 2) Relative deprivation: disjunction of expectations/achievements 3) Loss of... positive, motivating influences: removal of positively valued stimuli 4) Presence of negative stimuli: bad friend/poverty Status Frustration - Albert Cohen Working-class: Internalized mc values: status (success) Poorly educated = cannot compete with MC kids Status-frustration = Reaction formation Subculture = opposition/devaluation of middle-class definition of success - Collard & Ohlin Opportunity Structure Job market is the problem Ideology: merit-> success Lower classes: lose to middle class, status frustration, subculture Walter Miller: Working Class Focal Concerns - Enduring working-class subculture - Frustration/blocked opportunity - Focal concerns = attention/emotional involvement - FATEST 1) Fate —> life can’t be changed, make the best of it 2) Autonomy —> don't let them push you around 3) Trouble —> life is tough/don’t run away 4) Excitement —> look for fun 5) Smartness —> look good, act sharp 6) Toughness —> manliness Sykes and Matza: Drift/Neutralization Techniques - No subculture needed/Delinquents are like others 1) Conventional: conformity/guilt/respect for law-abiding individuals 1 of 33 2) Selfish values i. denial of responsibility: beyond control ii. denial of victim: deserved it iii. denial of injury: no harm done iv. commendation of condemners v. appeal to a higher loyalty: gangs etc Chapter 7: Social Structure Theories - Focus of 20th century criminology is sociology; led by Park & Burgess to study social ecology of city —> Natural Areas: zones/neighbourhoods that develop as a result of social forces operating in urban areas, and become natural areas of crime Sociological Criminology - sociologists look at how patterns of behaviour exist with the social structure & how criminal patterns exist within society, how they predicted and controlled - concern about ecological distribution of crime, the effect of social change Economic Structure and Crime - Shift in distribution of poverty: retired people are better off 1) Inequality -> epidemic (neighbourhood quality decrease, resident problems increase) -> culture of poverty: lower class culture characterized by values/norms in conflict with conventional society, passed on through generations —> apathy, cynicism, helplessness, mistrust -> Underclass: world cut-off from society-> lacking education/skills needed to survive which increase criminality 2) Are the poor undeserving? -> people in poverty are more likely to experience high crime, poor school, excessive mortality, unemployed, single parent household—> (self-help and increase mobility = hard) 3) Unemployment and Crime -> there is little evidence that changing market conditions cause offenders to renounce crime -> crime is linked to economic deprivation -> social embeddedness (hagan) -> early behaviour patterns become stable, lifelong habits Branches of Social Structure Theory = looks at class stratification 2 of 33 1. Social disorganization theory = looks at neighbourhoods marked by culture conflict, lack of cohesiveness, transiency, anomie 2. Strain theory = looks at the conflict caused when people cannot achieve their goals through legitimate means, and are denied access to adequate opportunities and social support 3. Cultural deviance theory = criminal behaviour is in conformity to lower-class subcultural values that develop in disorganized neighbourhoods due to strain and values in conflict with conventional social norms Social Disorganization Theory (Shaw & McKay) - Crime-ridden neighbourhoods are the ones residents try to leave at the earliest opportunity; crime is a result of destructive ecological conditions in urban slums - Poverty -> Social disorganization -> Breakdown of social control -> Criminal areas -> Cultural transmission -> Criminal careers 1) Concentric Zone Theory Crime is the product of transitional neighbourhoods that manifest social disorganization and value conflict, identifies high crime rates in slum areas - late 19th century expansion -> popular to view crime as the province of inferior racial/ethnic groups, but this rooted in the anxiety over changes in the 20th (industrialization, urbanization) - William Julius Wilson —> the lowest levels of underclass as the truly disadvantaged Transitional Neighbourhoods = area undergoing a shift in popn and structure with increasing rates of popn turnover, incapable of making residents stay Concentric Zones = heaviest crime appeared in inner-city (zone 1,2) Legacy of Shaw & McKay = prominent for 75+ years; criminal activity is normal response to adverse conditions; paved way for community action and treatment programs 2) Social Ecology School - social disorganization produces criminality, and quality of community life 1 Community deterioration: deserted house/abandoned buildings attract crime-> (Messner: poverty & single parent household); (Pratt & Godsey: anomie & strain) 4. Employment opportunities: reduce stabilizing-> vulnerable to predatory(hunt) crime 5. Community fear: incivilities convince residents of disorganized areas-> high victimization odds 6. Siege mentality: result of common disorganization 7. Population turnover: change is the hallmark of inner-city areas which leads to high popn turnover 8. Community change: building of residential dwellings, decrease in socio-economic status, increase in population density-> gentr [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 33 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Dec 17, 2022
Number of pages
33
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Dec 17, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
87






.png)

.png)