Management > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Operations and Supply Chain Management –WGU C720 OA Prep Guide. Latest Version, verified. (All)
Operations and Supply Chain Management –WGU C720 OA Prep Guide. Latest Version, verified.
Document Content and Description Below
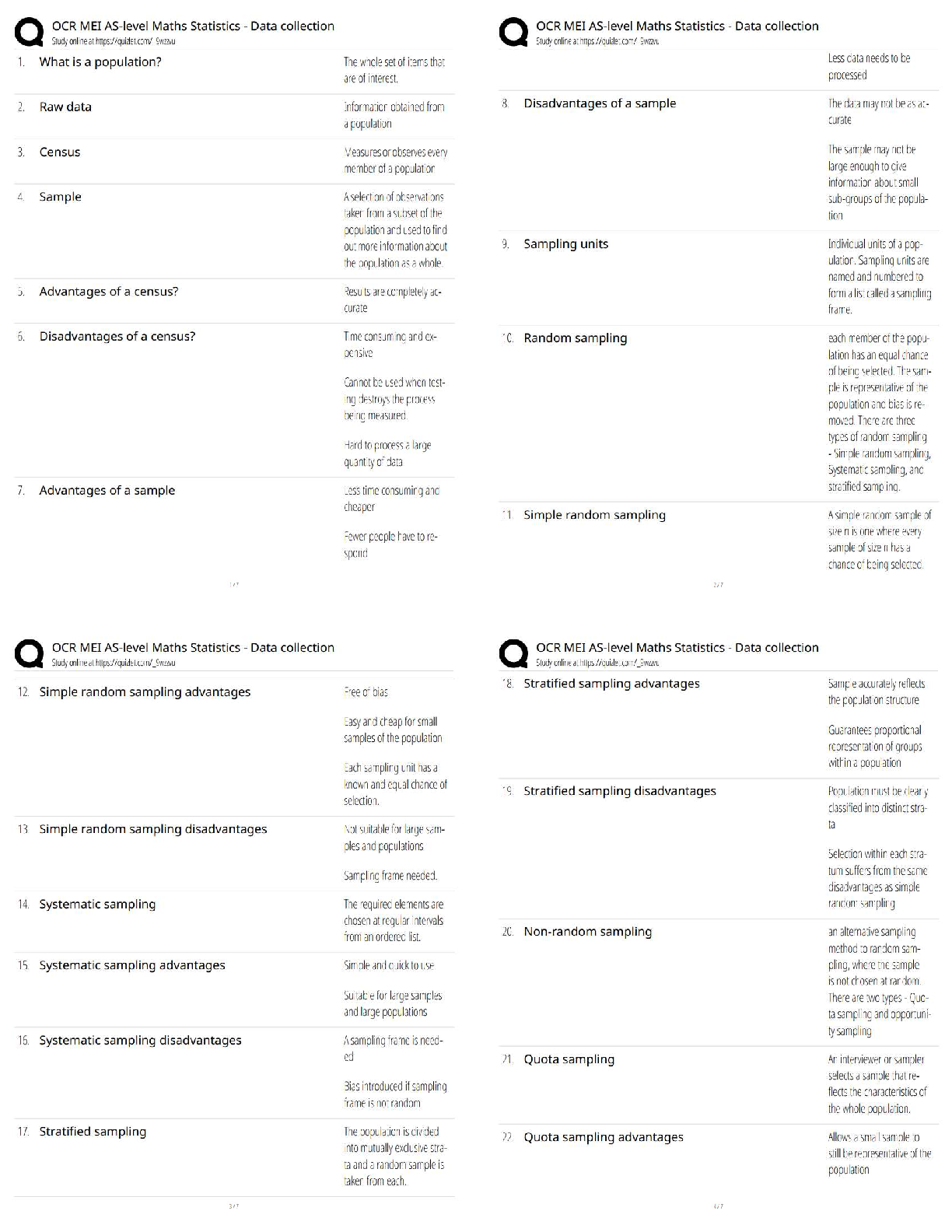
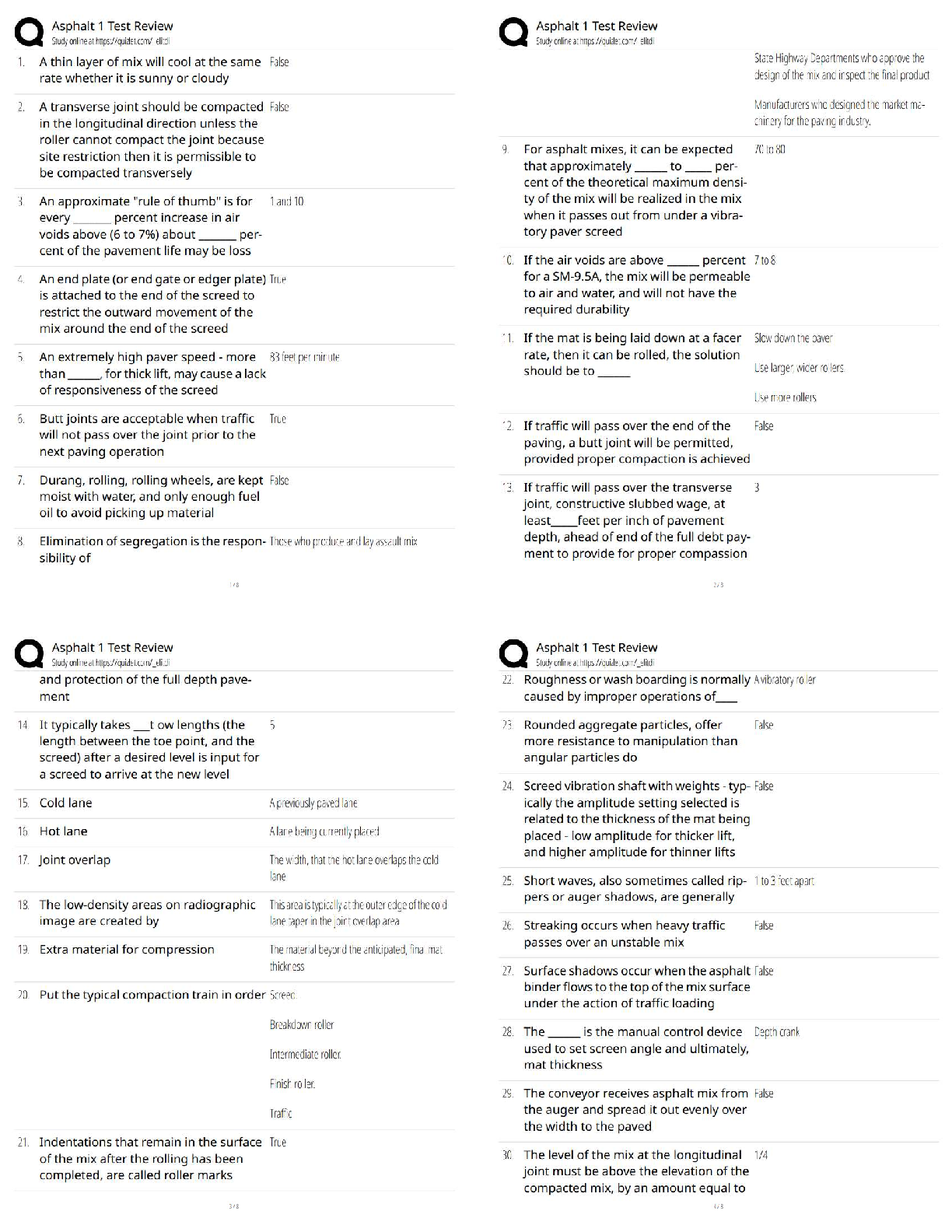
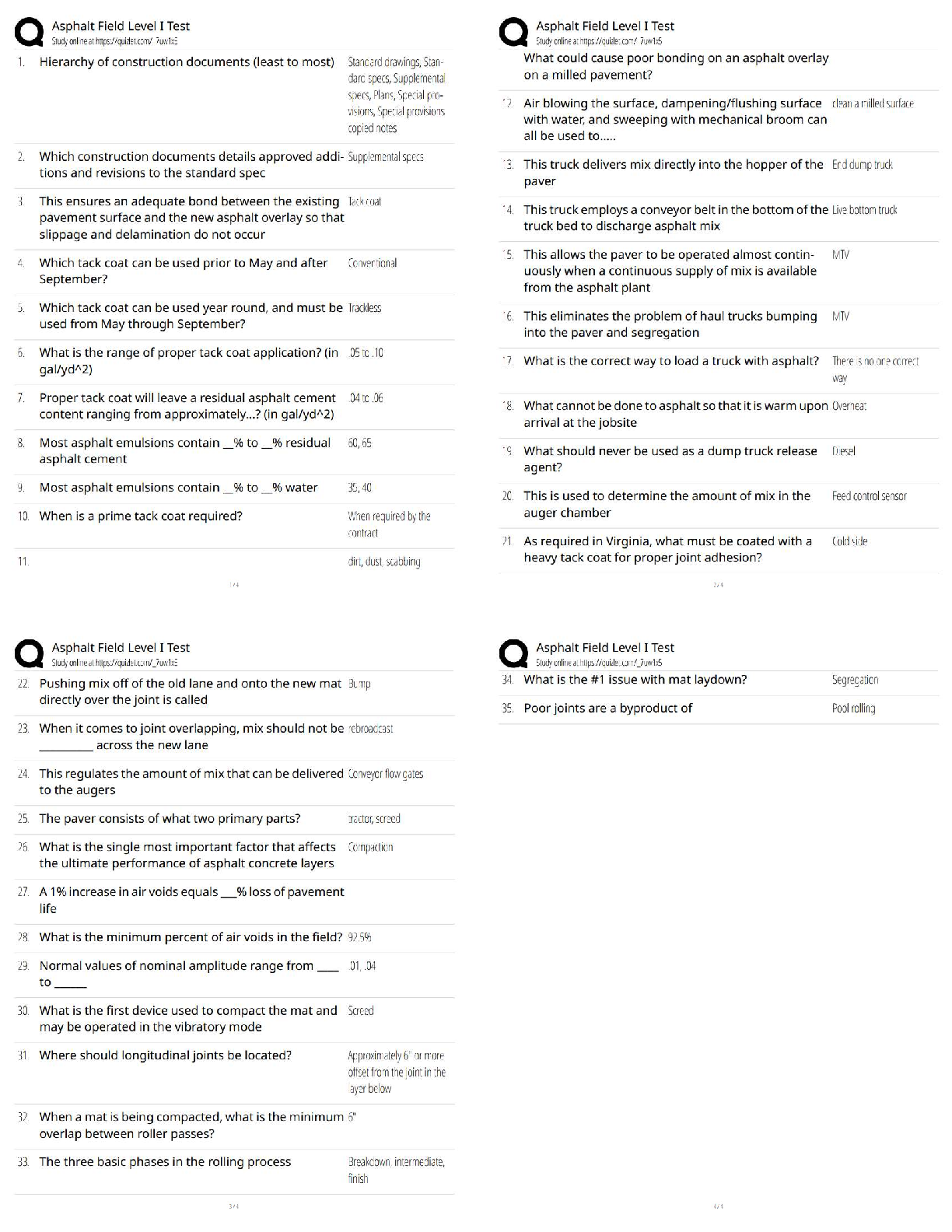
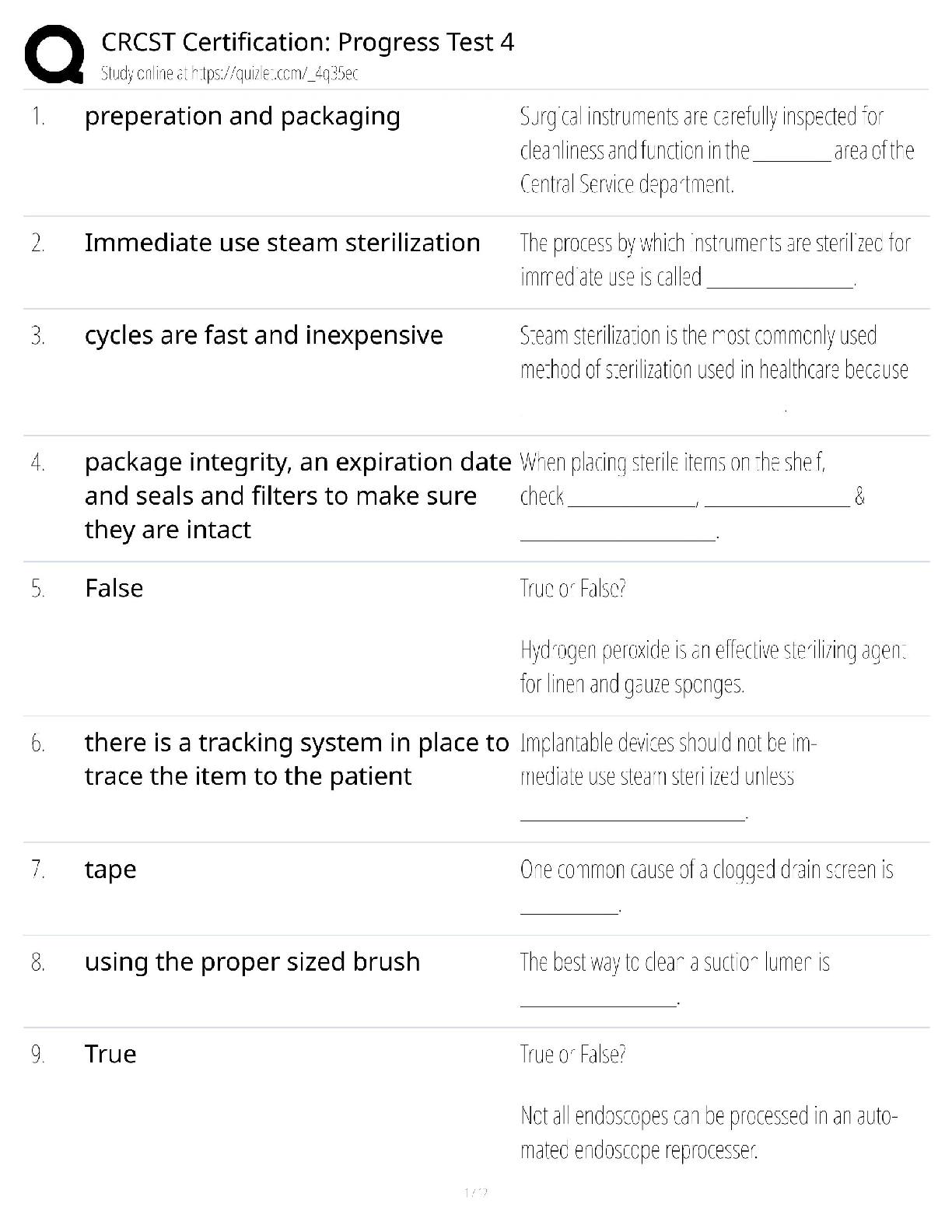
Operations and Supply Chain Management –WGU C720 OA Prep Guide. Latest Version, verified. Output - ✔✔-represent the final good or service that is produced for the consumer. are worth more ... to the consumer than the total cost of the inputs. Inputs - ✔✔-People Capital Material Energy Outputs - ✔✔-Services Goods Ethics - ✔✔-a sense of what is right and wrong that guide behavior. Unethical Business Practices - ✔✔-Anything related to fraud, wrong doing, dishonesty, etc., even if it is to protect the company, is considered ________ _________ _______. Sustainability - ✔✔-defined as the ethical issues an organization faces to balance financial performance while maintaining social responsibility standards and a responsible environmental profile. competitive advantage - ✔✔-a capability that customers value, such as short delivery lead-time or high product quality that gives an organization an edge against its competition. VIRAL uses as a framework. VIRAL - ✔✔-framework for competitive advantage. Advantage must provide: Value to consumers Inimitable - not easily imitated Rare Aptitude - capability Lifespan - sustainability to earn appropriate returns on the advantage. SWOT analysis - ✔✔-strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats can assist in future planning to achieve objectives. Strengths - ✔✔-characteristics of the business or project that lend an advantage within the scope of the study. Weaknesses - ✔✔-characteristics of a business or project that result in a disadvantage, relative to others. opporunities - ✔✔-elements that the project could exploit to its advantage. Threats - ✔✔-elements in the environment that could cause trouble for the business or project Productivity - ✔✔-is a mathematical calculation; it is the ratio of the outputs achieved divided by the inputs consumed to achieve those outputs. Inventory - ✔✔-the term for goods available for sale and raw materials used to produce goods available for sale. Can help businesses meet demand and work more efficiently. 6 types of inventory - ✔✔-Raw Materials Work-in-Process (WIP) Finished Goods Replacement Parts Inventory Supplies Transportation (Pipeline) Raw Materials Inventory - ✔✔-these parts and materials are obtained from supplies and are used in the production process. Work-in-process (WIP) inventory - ✔✔-these are partly finished parts, components, subassemblies, or modules. finished goods inventory - ✔✔-items are ready to ship to the customer. No more work is required. Replacement Parts Inventory - ✔✔-These are maintained to replace other parts in machinery or equipment as those parts wear out. Supplies Inventory - ✔✔-Parts or materials are used to support the production process but not usually a component of the product. These Items, such as lubricant and cutting tools, are consumed in the production process. Transportation (pipeline) inventory - ✔✔-the portion of inventory that is in the process of being shipped through the distribution system. Peak Demand - ✔✔-occurs in response to planned events such as advertising, publicity, or promotion. Ex. release of a popular game franchise's latest version. Seasonal Demand - ✔✔-as shoppers adjust their purchase velocity in line with holidays, especially Christmas. Unexpected Demand - ✔✔-occurs due to a usually-unexpected event. Chase demand - ✔✔-occurs when a company has to adjust production by rates to match demand by varying the workforce and using overtime. Companies vary the workforce by adding or reducing the number of employees on duty at any given time. They may choose to provide overtime by asking workers to stay on the job beyond their normally scheduled time. Safety Stock - ✔✔-cushion of inventory to protect against unexpected demand. in this way, they can continue to meet customer demand without delays. Stock-out - ✔✔-occurs when inventory is depleted. An organization may underestimate demand, experience disruptions in its supply chain or delays in production that lead to late delivery of the product. Perpetual and Periodic Inventory Systems - ✔✔-systems that companies use to track inventory. Although mostly used separately, they can also be used together. perpetual inventory system - ✔✔-Continuously monitors inventory levels. AKA continuous review system. Requires human input (cashier) and the ordering of more inventory is triggered by reorder point. periodic inventory system - ✔✔-randomly monitors inventory levels. AKA fixed order interval system. Not expensive to implement or maintain. perpetual inventory system - ✔✔--used for inventory that requires an exact inventory balance at all times. -most suitable for big businesses, large retail stores, and/or banks. -most appropriate for high value and high volume items. -best for accurate financial statements -expensive to implement and maintain. periodic inventory system - ✔✔--requires physical count to know exact inventory balances. -used when a supplier will only deliver at specific time intervals (during open window) -Most appropriate for low value and low value items -most appropriate for small businesses -inexpensive to implement and maintain. ABC analysis - ✔✔-developed to determine which inventory items should receive the highest level of control. by multiplying the dollar value of each item by its annual usage, a dollar usage value can be obtained. Pareto Principle - ✔✔-Dollar usage follows this. Frequently, only 20% of all the items account for 80% of the total dollar usage, while the remaining items frequently account for only 20% of the dollar usage. ABC Classification - ✔✔-based on focusing efforts where the payoff is highest. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) and Economic Production Quantity (EPQ) - ✔✔-two models used to help companies control the cost of ordering, receiving, and holding inventory. EOQ (Economic Order Quantity) - ✔✔--For inventory that doesn't require production. -when demand is constant and known. -when cost/unit does not depend on order quantity. -most appropriate for retail stores or companies that order finished goods. EPQ (economic production quantity) - ✔✔--For inventory that will be used in production. -when incremental ordering and depletion of inventory is allowed. -also called production order quantity. -most appropriate for manufacturing and production companies. Holding Costs - ✔✔-the costs of holding or "carrying" inventory over time. may include costs paid for storage space, interest paid on borrowed money to finance the inventory, and any losses incurred due to damage or obsolescence. Quantity Discount Model - ✔✔-a discount offered in price for ordering above a specified amount. transportation discounts - ✔✔-a discount offered on shipping costs for ordering above a specified amount. revenue sharing - ✔✔-when 2 or more companies partner and divide the profits received based on an agreement between all parties involved. Reserve capacity - ✔✔-when a company stores, or pays another company to store, excess inventory to be used for unexpected demand. Quality - ✔✔--the degree to which a specific product conforms to its design characteristics or specifications. -the amount of a specified, desired attribute. -the capacity to satisfy customers' needs. -consistently meeting or exceeding the customer's needs and expectations. -is everyones responsibility in the organization. Internal orientation of quality - ✔✔-directly measures characteristics of the product or service, such as the number of packages delivered on time or the thickness of an engine part based on manufactures specification. external orientation of quality - ✔✔-fitness for use for the customer or the capacity to satisfy customer's needs. Service Quality - ✔✔-five dimensions of quality often used by customers to judge ________ quality. reliability (service quality) - ✔✔-ability to perform the promised service dependably and accurately Five Dimensions of Service Quality - ✔✔-reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, tangibles Responsiveness - ✔✔-willingness to help customers and provide prompt service Assurance - ✔✔-the knowledge of and courtesy by employees and their ability to convey trust and confidence Empathy - ✔✔-provision of caring, individualized attention to customers. Tangibles - ✔✔-appearance of physical facilities, equipment, personnel, and communication materials, including access and effectiveness of internet-based information. Quality of Goods (8) - ✔✔-performance, features, reliability, durability, conformance, serviceability, aesthetics, perceived quality Quality of goods definition - ✔✔-the factors that comprise the quality of goods are quite different from the factors that comprise quality service. Performance - ✔✔-primary operating characteristics of a product. Features - ✔✔-secondary characteristics that supplement the product's basic functioning. Reliability (quality of goods) - ✔✔-length of time a product will function before it fails, or the probability it will function for a stated period of time. Conformance - ✔✔-The degree to which a product's design and operating characteristics meet established standards durability - ✔✔-ability of a product to function when subjected to hard and frequent use. Serviceability - ✔✔-speed, courtesy, and competence of repair aesthetics - ✔✔-how a product looks, feels, sounds, smells, or tastes perceived quality - ✔✔-image, advertising, or brand name of a product. Costs of Quality (3) - ✔✔-Failure costs, appraisal costs, and prevention costs. Failure Costs - ✔✔-can be internal to the organization or external involving the customer. appraisal costs - ✔✔-investment in measuring the quality and assessing customer satisfaction. prevention costs - ✔✔-put a stop to the quality problem. Crosby - ✔✔--used the phrase "do it right the first time" -Wrote a book in 1979, "Quality is Free" and concept of zero defects as a measurable object. -Emphasized the importance of considering all costs of quality. Juran - ✔✔--focus was on the customer's perception of quality -quality must be built on three elements: quality planning, quality control, and quality improvement. -focused on Fitness for use and Pareto Principle. Taguchi - ✔✔--Used Robust Design and Parabolic Quality Loss Function -Perfecting of Experiments to create higher quality products and processes. -argues that quality must be designed into a product. Deming - ✔✔--Had 14-point quality plan focused on Statistical Process Control (SPC) -"system" caused defects, not employees and endorsed the elimination of fear in the organization. -Modified Walter Shewart's Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) to Plan-Do-Study-Analyze (PDSA). Ishikawa - ✔✔--Developed Fishbone chart AKA cause and effect diagram. -Teamwork is essential for quality leadership. -Developed quality circles to solve problems lead by a champion (sr. manager) to oversee and approve. Benchmarking - ✔✔-a process by which a company compares its performance to the performance of other companies. Plan-Do-Check-Act Cycle - ✔✔-also referred to as the Deming Wheel or Shewart Cycle. The shape of a wheel embodies the philosophy of continuous improvement; the cycle is repeated over and over without end. Plan - ✔✔-before making any changes, be sure everything is documented and standardized. Use appropriate tools to identify problems or opportunities for improvement. Develop a plan to make changes. Do - ✔✔-Implement the plan and document any changes made. Check - ✔✔-Analyze the revised process to determine if goals have been achieved. Act - ✔✔-if the goals have been achieved, then standardize and document the changes. if the goals have not been achieved, determine why not, and proceed accordingly. Statistical Process Control (SPC) - ✔✔-the use of statistical methods to determine when a process that produces a good or service is getting close to producing an unacceptable level of defects. Statistical Process Control (SPC) (broader sense) - ✔✔-relates to the set of tips, techniques, and tools used to monitor variations in a process, determine the stability of a process, and reduce or eliminate variations that result in non-conforming products that are either defective or do not meet customer's specifications. Seven basic tools of Statistical Process Control (SPC) - ✔✔-1. Cause and Effect Diagrams / Fishbone Diagrams / Ishikawa Diagrams 2. Check sheets 3. Control Charts 4. Run Charts 5. Histograms (Box Charts) 6. Pareto Charts 7. Scatter Plot (Diagrams) Cause and Effect Diagrams - ✔✔--AKA Fishbone Diagrams or Ishikawa Diagrams -Show the impact of various inputs into the result of a -process. -help organizations isolate the root cause of the problems such as bottlenecks in their processes. Check Sheets - ✔✔--the means used to record data points in real-time at the site where the data is generated. -often first tool used to assess a process -data is often "raw", meaning it is straight from the source and without any interpretation. Control Charts - ✔✔--are graphical depictions of process output where the raw data is plotted in real time within upper (UCL) and Lower control limits ( [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 33 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

WGU C720 EXAM BUNDLE, VERIFIED.
WGU C720 Operations and Supply Chain Management, questions & Answers, rated A+ GRADED A+
By Topmark 2 years ago
$30
22
Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Mar 13, 2023
Number of pages
33
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Mar 13, 2023
Downloads
0
Views
136