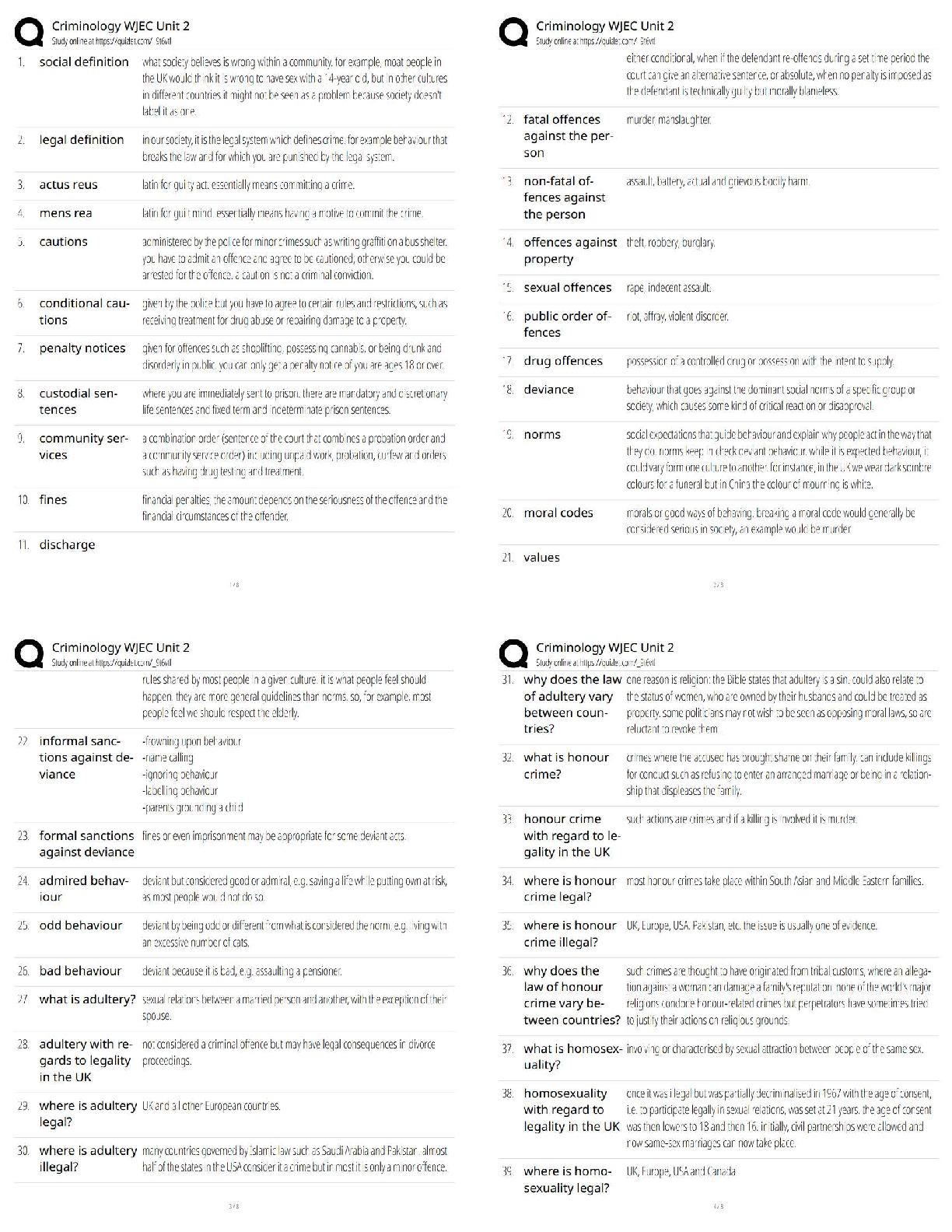
1.A nurse is implementing a plan of care for a client who has a wound infection. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform first?
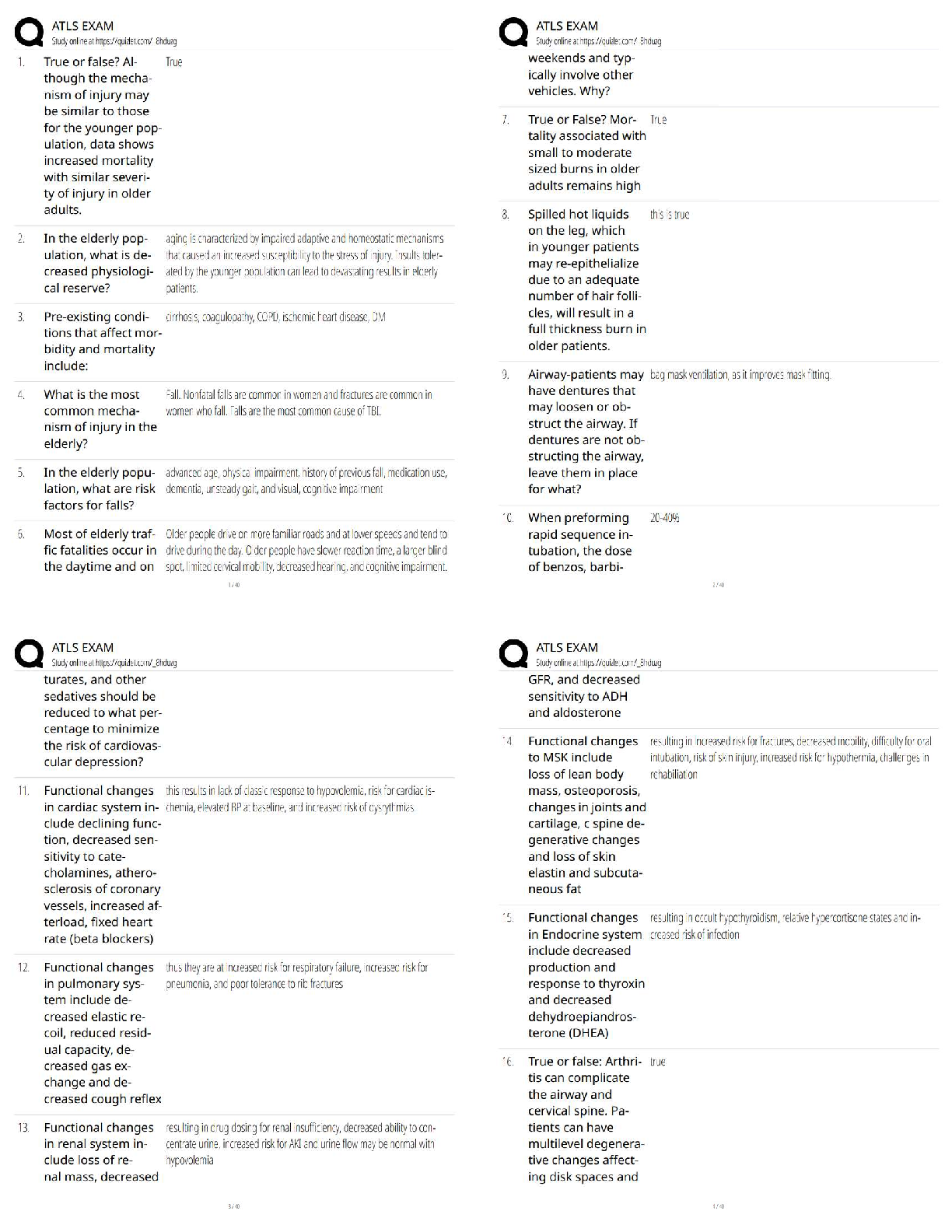
A.Administer antibiotic medication.
B.Obtain a wound specimen for culture.
...
1.A nurse is implementing a plan of care for a client who has a wound infection. Which of the following actions should the nurse perform first?
A.Administer antibiotic medication.
B.Obtain a wound specimen for culture.
C.Review WBC laboratory findings.
D.Apply a dressing to the wound.
2.A nurse is caring for a client who has a urinary tract infection and a history of recurrence of this type of infection. The client asks why the provider has not yet prescribed an antibiotic. The nurse should explain that the provider has to wait for the results of which of the following laboratory tests to identify which antibiotic to prescribe?
A.Gram stain
B.Culture
C.Sensitivity
D.Specific gravity
3.A nurse is preparing information for the unit’s nurses about the effectiveness of antimicrobial therapy for clients who have bacterial infections. Which of the following host factors should the nurse include as conditions that affect antimicrobial effectiveness? (Select all that apply.
A. meningitis
B.Pacemaker
C.Endocarditis
D.Pneumonia
E.Pyelonephritis
4.A nurse is caring for a group of clients who are receiving antimicrobial therapy. Which of the following clients should the nurse plan to monitor for manifestations of antibiotic toxicity?
A.An adolescent client who has a sinus infection
B.An older adult client who has prostatitis
C.A client who is postpartum and has mastitis
D.A middle adult client who has a urinary tract infection
5.A charge nurse is teaching a group of nurses about the importance of prophylactic antimicrobial therapy. Which of the following information should the charge nurse include in the teaching? (Select all that apply.)
A.Administer prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to clients who report exposure to a sexually transmitted infection.
B.Administer prophylactic antimicrobial therapy to clients who are having orthopedic surgery.
C.Instruct clients who have a prosthetic heart valve about the need for prophylactic antimicrobial therapy before dental work.
D.Consult the provider for prophylactic antimicrobial therapy for clients who have recurrent urinary tract infections.
E.Instruct clients to request prophylactic antimicrobial therapy immediately when they have an upper respiratory infection.
ATI CHAPTER 44ANTIBIOTICS AFFECTINGThE BACTERIAL CELL WALL
1.A nurse in an outpatient facility is preparing to administer nafcillin Im to an adult client who has an infection. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? (Select all that apply.)
A.Select a 25‑gauge, ½‑inch needle for the injection.
B.Administer the medication deeply into the ventrogluteal muscle.
C.Ask the client about an allergy to penicillin before administering the medication.
D. monitor the client for 30 min following the injection.
E.Tell the client to expect a temporary rash to develop following the injection.
2.A nurse is preparing to administer cefotaxime IV to a client who has a severe infection and has been receiving cefotaxime for the past week. Which of the following findings indicates a potentially serious adverse reaction to this medication that the nurse should report to the provider?
A.Diaphoresis
B.Epistaxis
C.Diarrhea
D.Alopecia
3.A nurse is obtaining a medication history from a client who is to receive imipenem‑cilastatin IV to treat an infection. Which of the following medications the client also receives puts him at risk for a medication interaction?
A.Regular insulin
B.Furosemide
C.Valproic acid
D.Ferrous sulfate
4.A nurse is caring for a client who has a cerebrospinal fluid infection with gram‑negative bacteria. Which of the following cephalosporin antibiotics should the nurse expect to administer IV to treat this infection?
A.Cefaclor
B.Cefazolin
C.Cefepime
D.Cephalexin
5.A nurse is preparing to administer penicillin V to a client who has a streptococcal infection. The client tells the nurse that she has difficulty swallowing tablets and doesn’t “do well” with liquid or chewable medications because the taste gags her, even when the a nurse mixes the medication with food. The nurse should request a prescription for which of the following medications?
A.Fosfomycin
B.Amoxicillin
C.Nafcillin
D.Cefaclor
ATI CHAPTER 45ANTIBIOTICS AFFECTING PROTEIN SYNThESis
1.A nurse is teaching a client about taking tetracycline to treat a GI infection due to Helicobacter pylori. Which of the following statements should the nurse identify as an indication that the client understands the instructions?
A.“I will take this medication with 8 ounces of milk.”
B.“I will let my doctor know if I start having diarrhea.”
C.“I can stop taking this medication when I feel completely well.”
D.“I can take this medication just before bedtime.”
2.A nurse is administering gentamicin by IV infusion at 0900. The medication will take 1 hr to infuse. When should the nurse plan to obtain a blood sample for a peak serum level of gentamicin?
A.1000
B.1030
C.1100
D.11303.
A nurse is caring for a client who is starting a course of gentamicin IV for a serious respiratory infection. For which of the following manifestations should the nurse monitor as an adverse effect of this medication? (Select all that apply.)
A.Pruritus
B. hematuria
C. muscle weakness
D.Difficulty swallowing
E.Vertigo
4.A nurse is caring for a client who has subacute bacterial endocarditis and is receiving several antibiotics, including streptomycin Im. For which of the following manifestations should the nurse monitor as an adverse effect of this medication?
A.Extremity paresthesias
B.Urinary retention
C.Severe constipation
D.Complex partial seizures
5.A nurse is caring for a client who is undergoing preparation for extensive colorectal surgery. Which of the following oral antibiotics should the nurse expect to administer specifically to suppress normal flora in the GI tract?
A. kanamycin
B.Gentamicin
C.Neomycin
D.Tobramycin
ATI CHAPTER 46URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
1.A nurse reviewing a client’s medication history notes an allergy to sulfonamides. This allergy is a contraindication for taking which of the following medications? (Select all that apply.)
A. hydrochlorothiazide
B. metoprolol
C.Acetaminophen
D.Glipizide
E.Furosemide
2.A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for nitrofurantoin. Which of the following information should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.)
A.Observe for bruising on the skin.
B.Take the medication with milk or meals.
C.Expect brown discoloration of urine.
D.Crush the medication if it is difficult to swallow.E.Expect insomnia when taking it.
3.A nurse is teaching a female client who has a severe UTI about ciprofloxacin. Which of the following information about adverse reactions should the nurse include? (Select all that apply.)
A.Observe for pain and swelling of the Achilles tendon.
B.Watch for a vaginal yeast infection.
C.Expect excessive nighttime perspiration.
D.Inspect the mouth for cottage cheese‑like lesions.
E.Take the medication with a dairy product.
4.A nurse is planning discharge teaching for a female client who has a new prescription for trimethoprim‑sulfamethoxazole. Which of the following information should the nurse include?
A.Take the medication even if pregnant.
B. maintain a fluid restriction while taking it.
C.Take it on an empty stomach.
D.Stop taking it when manifestations subside.
5.A nurse is planning to administer ciprofloxacin IV to a client who has cystitis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
A.Administer a concentrated solution.
B.Infuse the medication over 60 min.
C.Infuse the solution through the primary IV fluid’s tubing.
D.Choose a small peripheral vein for administration.
ATI CHAPTER 47MYCOBACTERIAL, FUNGAL, AND PARASITIC INFECTIONs
1.A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus, pulmonary tuberculosis, and a new prescription for isoniazid. Which of the following supplements should the nurse expect to administer to prevent an adverse effect of INh?
A.Ascorbic acid
B.Pyridoxine
C.Folic acid
D.Cyanocobalamin
2.A nurse is infusing IV amphotericin B to a client who has a systemic fungal infection. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects of this medication?
A. hypoglycemia
B.Constipation
C.Fever
D. hyperkalemia
3.A nurse is administering IV amphotericin B to a client who has a systemic fungal infection. The nurse should monitor which of the following laboratory values? (Select all that apply.
)A.Serum calcium
B.Serum amylase
C.Serum potassium
D. hematocrit
E.Serum creatinine
4.A nurse is teaching a client who is beginning a course of metronidazole to treat an infection. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse instruct the client to stop taking metronidazole and notify the provider?
A. metallic taste
B.Nausea
C.Ataxia
D.Dark‑colored urine
5.A nurse is teaching a client who has active tuberculosis about his treatment regimen. The client asks why he must take four different medications. Which of the following responses should the nurse make?
A.“Four medications decrease the risk for a severe allergic reaction.”
B.“Four medications reduce the chance that the bacteria will become resistant.”
C.“Four medications reduce the risk for adverse reactions”
D.“Four medications decrease the chance of having a positive tuberculin skin test.”
CH 48 ATI
1.A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for combination oral NRTIs (abacavir, lamivudine, and zidovudine) for treatment of hIV. Which of the following statements should the nurse include?
A.“These medications work by blocking hIV entry into cells.”
B.“These medications work by weakening the cell wall of the hIV virus.”
C.“These medications work by inhibiting enzymes to prevent hIV replication.”
D.“These medications work by preventing protein synthesis within the hIV cell.”
2.A nurse is caring for a client who takes several antiretroviral medications, including the NRTI zidovudine, to treat hIV infection. The nurse should monitor for which of the following adverse effects of zidovudine? (Select all that apply.)
A.Fatigue
B.Blurred vision
C.Ataxia
D. hyperventilation
E.Vomiting
3.A nurse is caring for a client who is taking ritonavir, a protease inhibitor, to treat hIV infection. The nurse should monitor for which of the following adverse effects of this medication?
A.Increased TSh level
B.Decreased ALT level
C. hypoglycemia
D. hyperlipidemia
4.A nurse is caring for a client who has a new prescription for enfuvirtide to treat hIV infection. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the adverse reactions of this medication? (Select all that apply.)
A.Bleeding
B.Pneumonia
C.Cerebral edema
D.Localized erythema
E. hypotension
5.A nurse is administering IV acyclovir to a client who has varicella. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
A.Administer a stool softener.
B.Decrease fluid intake following infusion.
C.Infuse acyclovir over 1 hr.
D. monitor for a for hypotension
6.A nurse is teaching a client who is beginning highly active antiretroviral therapy (hAART) for hIV infection about ways to prevent medication resistance. Which of the following information should the nurse teach the client about resistance?
A.Taking low dosages of antiretroviral medication minimizes resistance.
B.Taking one antiretroviral medication at a time minimizes resistance.
C.Taking medication at the same times daily without missing doses minimizes resistance.
D.Changing the medication regimen when adverse effects occur minimizes resistance
What drug should be prescribed for a patient who has Streptococcal Pharyngitis and is allergic to Penicillin?
Erythromycin
ATI online
1. Patient taking rifampin(rifadin) and is also on oral contraceptive should be instructed to...
2. Extra caution in a patient taking acyclovir (Zovirax) who is also...
3. Monitor these lab tests in a TB patient taking cephalexin (Keflex)
4. Patient should report these effects while taking isoniazid (inh) for TB
5. Actions to take when IV insertion site is warm and reddened after the administration of cefotetan to treat bacterial meningitis.
6. Monitor this lab value when a patient is taking acyclovir (Zovirax).
7. Sputum culture results in MRSA. Which drug should be administered?
8. Report the following effect of ciproflaxacin (cipro) when taking prednisolone (prelone) for uti and RA?
9. Include these instructions when a patient receiving amoxicillin (amoxil) and notices a rash and wheezing.
10. Low dose of aztreonam (azactam) for a patient who has a respiratory tract infection and also has what?
11. Patient taking tetracycline orally to treat chlamydia should report severe blood-tinged diarrhea as it is suspected to be..
12. Patient taking imipenem (primaxin) to treat a bacterial infection. Recognize side effect.
13. Include these instructions for a patient taking chloroquine (Aralen) to prevent malaria
14. Report this effect when taking nitrofurantion (macrodantin) for UTI
15. Medications that cause an effect on a patient who drinks alcohol and takes disulfiram (Antabuse)
16. Report this effect when taking ketoconazole to treat a fungal infection.
17. These drugs warfarin (Coumadin ) trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (bactrim) to treat UTI put a patient at an increase risk for...
18. Use with caution in a patient who is taking metronidazole (flagyl) but also has...
19. Give these medications before giving amphotericin B IV
20. Nystatin (mycostatin) oral instructions
21. Question the use of this drug when a patient is taking gentamicin to treat systemic infection.
22. Recommend this for a patient experiencing dyspepsia while taking ciproflaxacin (cipro)
23. Monitor for this effect of a patient taking erythromycin.
24. Monitor for this in a patient taking gentamicin to treat an infection
CH. 34
1. Superinfections are an adverse effect common to all anti-biotic therapy. Which of the following best describes a superinfection?
1. An initial infection so overwhelming that it requires multiple anti microbial drugs to treat successfully
2. Bacterial resistance that creates infections that are difficult to treat and that are often resistant to multiple drugs
3. Infections requiring high-dose antimicrobial therapy with increased chance of organ toxicity
4. The overgrowth of normal body flora or or opportunistic organisms such as viruses and yeast no longer held in check by normal, beneficial flora.
2. A client will be discharged after surgery with a prescription for penicillin. When planning at-home instructions, what will the nurse include?
1. Penicillin can be taken while breast feeding
2. The entire prescription must be finished
3. All penicillins can be taken without regard to eating
4. Some possible side effects include abdominal pain and constipation
3. A client has been prescribed tetracyclin. When providing information regarding this drug, the nurse should include what information about tetracycline?
1. It is classified as a narrow spectrum antibiotic with minimal adverse effects
2. It is used to treat a wide variety of disease processes
3. It has been identified to be safe during pregnancy
4. It is contraindicated in children younger than 8 years
4. What information should be included in the client’s education regarding taking ciprofloxacin (Cipro)?
1. The drug can cause discoloration of the teeth
2. Fluid intake should be decreased to prevent urine retention
3. Any heel or lower leg pain should be reported immediately
4. The drug should be taken with an antacid to reduce gastric effects
5. A client has been diagnosed with tuberculosis and is prescribed Rifater (combination of pyrazinamide with isoniazid and rifampin). While the client is on this medication, what teaching is essential? (select all that apply)
1. "It is crucial to continue therapy for at least 6 to 12 months"
2. "Two or more drugs are used to prevent tuberculosis bacterial resistance"
3. "These drugs may also be used to prevent tuberculosis "
4. "No special precautions are required"
5. "After 1 month of treatment, the medication will be discontinued"
6. A 32-year-old female has been started on amozicillin (Amoxil, Trimox) for severe UTI. Before sending her home with this prescription, the nurse will provide which instruction?
1. Teach her to wear sunscreens
2. Ask her about oral contraceptive use and recommend an alternative method for the education of the ampicillin course
3. Asses for hearing loss
4. Recommend taking the pill with some antacid to prevent GI upset
CH. 35
1. A client has been diagnosed with a fungal nail infection. The health care provider has prescribed griseofulvin (Fulvicin). The nurse will include which of the following in her teaching to the client?
a. Notify the provider if symptoms of infection worsen.
2. A client with type 2 diabetes treated with oral antidiabetic medication is receiving oral fluconazole (Diflucan) for treatment of chronic tinea cruris (jock itch). The nurse instructs the client to monitor blood glucose levels more frequently because of what potential drug effect?
a. Fluconazole (Diflucan) interacts with certain antidiabetic drugs, causing hypoglycemia.
3. A client with a severe systemic fungal infection is to be given amphotericin B (Fungizone). Before starting the amphotericin infusion, the nurse premedicates the client with acetaminophen (Tylenol), diphenhydramine (Benadryl), and prednisone (Deltasone). What is the purpose of premedicating the client prior to the amphotericin?
a. It decreases the risk of hypersensitivity reactions to the amphotericin.
4. A client was prescribed chloroquine (Aralen) prior to a trip to an area where malaria is known to be endemic. the nurse will instruct the client to remain on the drug for up to 6 weeks after returning and the client asks why this is necessary. What is the nurse's best response?
a. "It continues to kill any remaining malarial parasites that may have been acquired during the trip that are in your red blood cells."
5. A 32-year-old female client is started on metronidazole (Flagyl) for treatment of a trichomonas vaginal infection. What must the client eliminate from her diet for the duration she is on this medication?
a. Alcohol
6. Metronidazole (Flagyl is being used to treat a client's Giardia lamblia infection, a protozoal infection of the intestines. Which of the following are appropriate to teach this client?
a. -Metronidazole may leave a metallic taste in the mouth.
-The urine may turn dark amber brown while on the medication.
-Taking the metronidazole with food reduces GI upset.
-Current sexual partners do not require treatment for this infection.
Ch 36
1. A client is started on efavirenz (Sustiva) for HIV. What should the nurse teach the client about this drug?
a. Efavirenz (Sustiva) will not cure the disease but may significantly extend the life expectancy.
2. A client with HIV has been taking lopinavir with ritonavir (Keletra) for the past 8 years and has noticed a redistribution of body fat in the arms, legs, and abdomen (lipodystrophy). The nurse will evaluate this client for what other additional adverse effects associated with this drug?
a. –Hyperglycemioa
-Pancreatitis
-Hepatic failure
3. Which of the following findings would suggest that myelosuppression is occurring in a client who is taking zidovudine (Retrovir)?
a. Decrease in platelet count
4. A client has received a prescription for zanamivir (Relenza) for flulike symptoms. The client states, "I think I'll hold off on starting this. I don't feel that bad yet." What is the nurse's best response?
a. "To be effective, it must be started within 48 hours after the onset of symptoms."
5. The nurse is teaching a community health class to a group of young adults who have recently immigrated to the United States about preventing hepatitis B (HBV). What is the most effective method of preventing an HBV infection?
a. HBV vaccine (Engerix-B)
6. A client has been diagnosed with genital herpes and has been started on oral acyclovir (Zovirax). What should be included in the teahing instructions for this client?
a. -Increase fluid intake up to 2 L per day.
b. -Report any dizziness, tremors, or confusion.
c. -Use barrier methods such as condoms for sexual activity.
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)