Nursing: Notes 2 - Labor & delivery
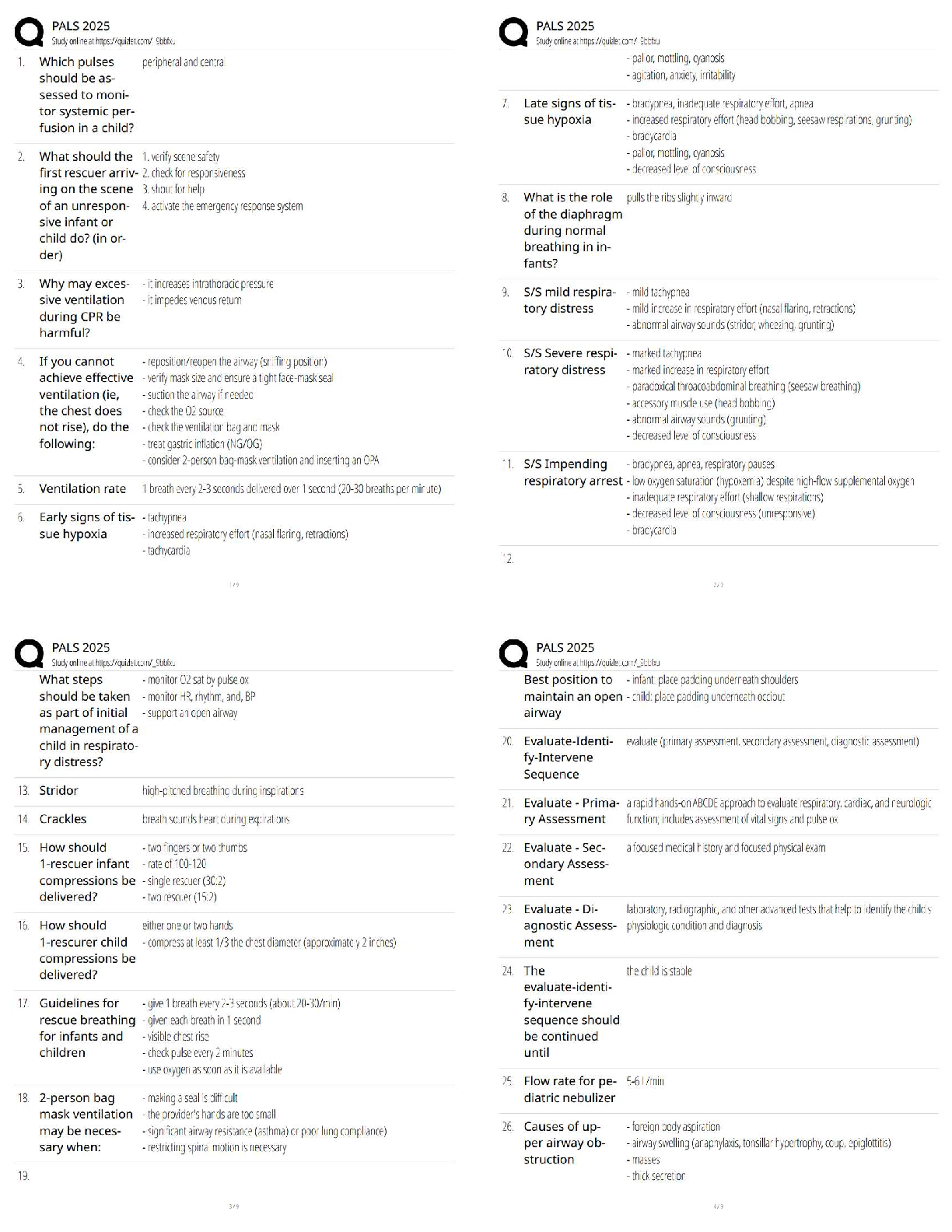
Learning Objectives for Labor & Delivery
Chapter 14 (start on pg. 336)
Discuss the different childbirth education programs and discuss the differences of each
Goal is to hel
...
Nursing: Notes 2 - Labor & delivery
Learning Objectives for Labor & Delivery
Chapter 14 (start on pg. 336)
Discuss the different childbirth education programs and discuss the differences of each
Goal is to help pt make good choices; in order to do that, they need to understand the birthing process
• Programs available:
o Early pregnancy (“early bird”) classes – early fetal development, physiologic & emotional changes of pregnancy, human sexuality, nutritional needs of mother & fetus
Differentiate the differences in the health care providers. Discuss the pros and cons of each. Identify what sort of client can go to each.
• It may be necessary to help the pt make an informed decision about who to see, based on the presence of
• Doula – nonmedical labor & support person
• Birth plan – tool to help pt explore options & make choices
Discuss the different birth setting choices. Be able to identify the pros and cons of each setting.
• Hospital – 99% in the U.S. choose this
• Birth center – for low risk pregnancy only; often free-standing, usually close to hospital
• Home birth – client in control of birth, less chance of infection. Risk is no emergency equipment
Chapter 16
Be able to identify and describe the factors that affect labor. This includes normal and what would make them abnormal.
Definition of labor: contractions with cervical change
Five P’s:
• Passenger (fetus & placenta) – the way the passenger moves through the birth canal is determined by these factors:
o Head – sutures & fontanels make the skull flexible enough for the bones to slightly overlap
o Presentation – which part of the fetus enters the pelvic inlet first?
o Lie – t
o Attitude –
o Position
Denoted by 3-part abbreviation
o Station
• Passageway – birth canal
o Assessment performed during
Baby must be able to perform cardinal moves - (K) 377
o Types of pelvis – review chart on pg. 374
Platypelloid (flat)
• Powers (contractions)
o Primary powers = contractions
Responsible for effacement & dilation of cervix & descent of fetus
• Effacement – shortening & thinning of the cervix during 1st stage labor
• Position of the mother
o Encourage mother to find positions comfortable to her
• Psyche (or psychological response)
o Is mom ready to have baby? Mentally prepared?
Be able to identify the signs preceding labor.
• Lightening (when fetal presenting part descends into the true pelvis) - @2wks before term
Identify the mechanism of labor and the adaptations of the fetus through the birth canal.
Stages of labor (4)
1. From onset of contractions to full dilation (longest stage)
a. Latent (0-3 cm), 6 to 8 hours – affect talkative, excited, anxious (euphoria)
b. Active (4-7 cm), 3 to 6 hours – affect more introspective (increased seriousness)
Mechanism of labor (cardinal movements)
a. Engagement & Descent
b. Flexion
Fetal physiologic adaptation to labor
• Fetal heart rate (110-160 bpm normal) shows temporary accelerations & slight early decelerations in
Discuss the maternal physiologic changes. Identify normal and abnormal for the following systems.
• Cardiovascular – increases (about 50% above baseline); should return to baseline w/in first postpartum hour
• Respiratory – increases
• Renal – proteinuria of 1+ is a normal finding (d/t muscle tissue breakdown from physical work of labor)
o Voiding difficulties; may be d/t…
• Integumentary – stretching of vaginal introitus – minute tears in skin occur, even with episiotomy
• Musculoskeletal - increased muscle activity
• Neurologic – pain! (see Stages of Labor for sensorial changes)
• Gastrointestinal – decreased motility & absorption, N/V is common
• Endocrine
o Progesterone decreases, estrogen, oxytocin, & prostaglandins increase.
o Metabolism increases
o Blood glucose levels may decrease (w/ the work of labor)
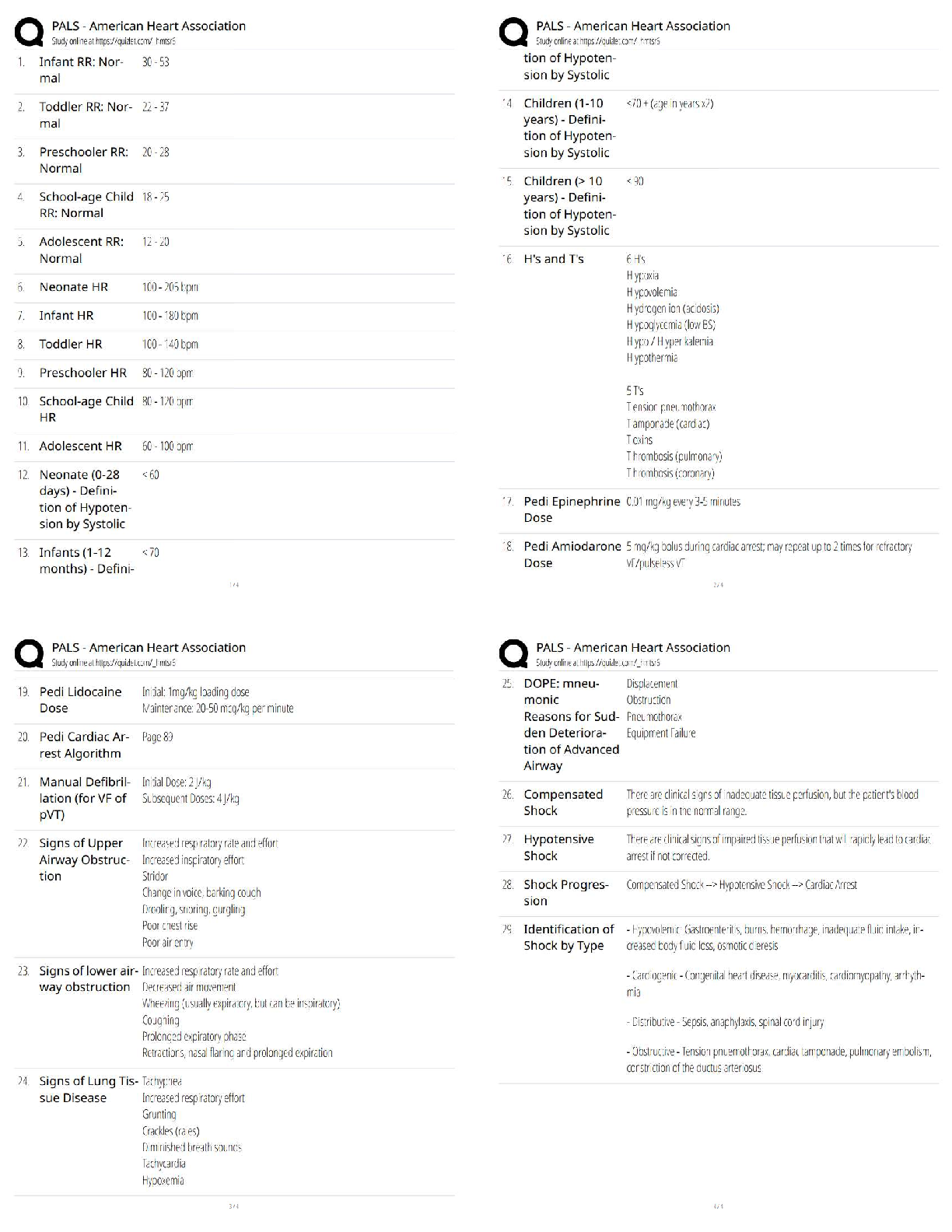
Chapter 17
• Pain is relative to who you are. Whatever the pt says is pain is what it is for them.
o Distraction techniques are used to reduce or block the capacity of nerve pathways to transmit pain
Discuss the different cultural differences in expression of pain. Page 383
• Chinese women may not exhibit reactions to pain, although exhibiting pain during childbirth is acceptable. They consider accepting something when it is first offered as impolite; therefore, pain interventions must be offered more than once. Acupuncture may be used for pain relief.
• Arab or Middle Eastern women may be vocal in response to labor pain. They may prefer medication for pain relief.
• Japanese women may be stoic in response to labor pain, but they may request medication when pain becomes severe.
• Southeast Asian women may endure severe pain before requesting relief.
• Hispanic women may be stoic until late in labor, when they may become vocal and request pain relief.
• Native-American women may use medications or remedies made from indigenous plants. They are often stoic in response to labor pain.
• African-American women may express pain openly. Use of medication for pain relief varies.
Discuss the nonpharmacologic pain management, the nursing care and describe when each would be appropriate.
What nurses can do alone (be aware that what works in one pt or even one stage of labor may not work in another):
• Cutaneous – tactile
o Effleurage – slow, light stroking touch (belly, arms, thigh, chest)
Other forms that the nurse would need help or training for:
• TENS unit – electrodes placed on spine provide low-intensity electrical impulses/stimuli - does not
Pharmacologic pain management
(K) when to give, what method is used, and who can have/not have:
Differentiate and discuss the medications and indications of use for sedatives and analgesics as well as anesthetics.
Sedatives – used in prolonged latent stage – relieve anxiety & induce sleep
Analgesia – alleviates or decreases pain w/ no loss of consciousness (nurse can give)
• IV preferred – or IM or pt can use PCA
Discuss the action, indication dosage, adverse effects and contraindications of the following medications
Rev. pg. 392
All narcotics – work best in early part of active labor
Opioid Agonist Analgesics
• Meperidine (Demerol) – don't give if cardiac problems
Opioid Agonist-Antagonist Analgesics
• Major advantage is their ceiling effect for respiratory depression; higher doses don't produce additional
Opioid Antagonist
• Narcan – always have on hand
• Can give IM or IV
Discuss the indications, contraindications, side effects and nursing care for the following nerve blocks. (Given by provider)
• These are the “caines” (lidocaine, Marcaine, xylocaine, etc.)
o Check for allergies
• Local
o An injection along the inside of the perineum
• Spinal – one time injection
assess VS, EFM, fluid balance
• Epidural – continuous infusion
Don't need to know where to inject, but (K) the care
promote safety – pt shouldn’t ambulate alone
• CSE
o Combined spinal/epidural
o Also called a walking epidural
Discuss use of Nitrous Oxide (laughing gas) as well as the indications, contraindications and nursing care.
Discuss when a general anesthesia would be used in labor and delivery. Discuss the indications, contraindications and nursing care for a patient undergoing general anesthesia.
• Used for emergencies – rapid birth needed! Rarely for vag births & only about 10% of C/S
o NPO
o Pt will need pain med soon after regaining consciousness
o Assess readiness to see baby; be ready with information
Pitocin – stimulates uterine contractions & aids in milk letdown. For the induction & augmentation of labor.
If too long, too close, or uterus doesn’t relax, uterus can rupture; can also cause placental abruption and fetal distress
• Nursing considerations:
Stop oxytocin immediately if non-reassuring fetal heart tones or overstimulation of uterus or >5
If normal FHR… If abnormal FHR…
• Give 500 mL LR bolus
• Turn pt on side
• If uterine activity not normal within 10 min, • • Immediately D/C oxytocin
• 500 mL LR bolus
• Turn pt on side
• If no response, start O2
• If still no response, consider sub-Q terbutaline
To resume oxytocin after resolution of tachysystole:
• If D/C’d <20 to 30 min, resume at half the former rate
• If D/C’d >30 to 40 min, resume at initial start dose
Mag sulfate
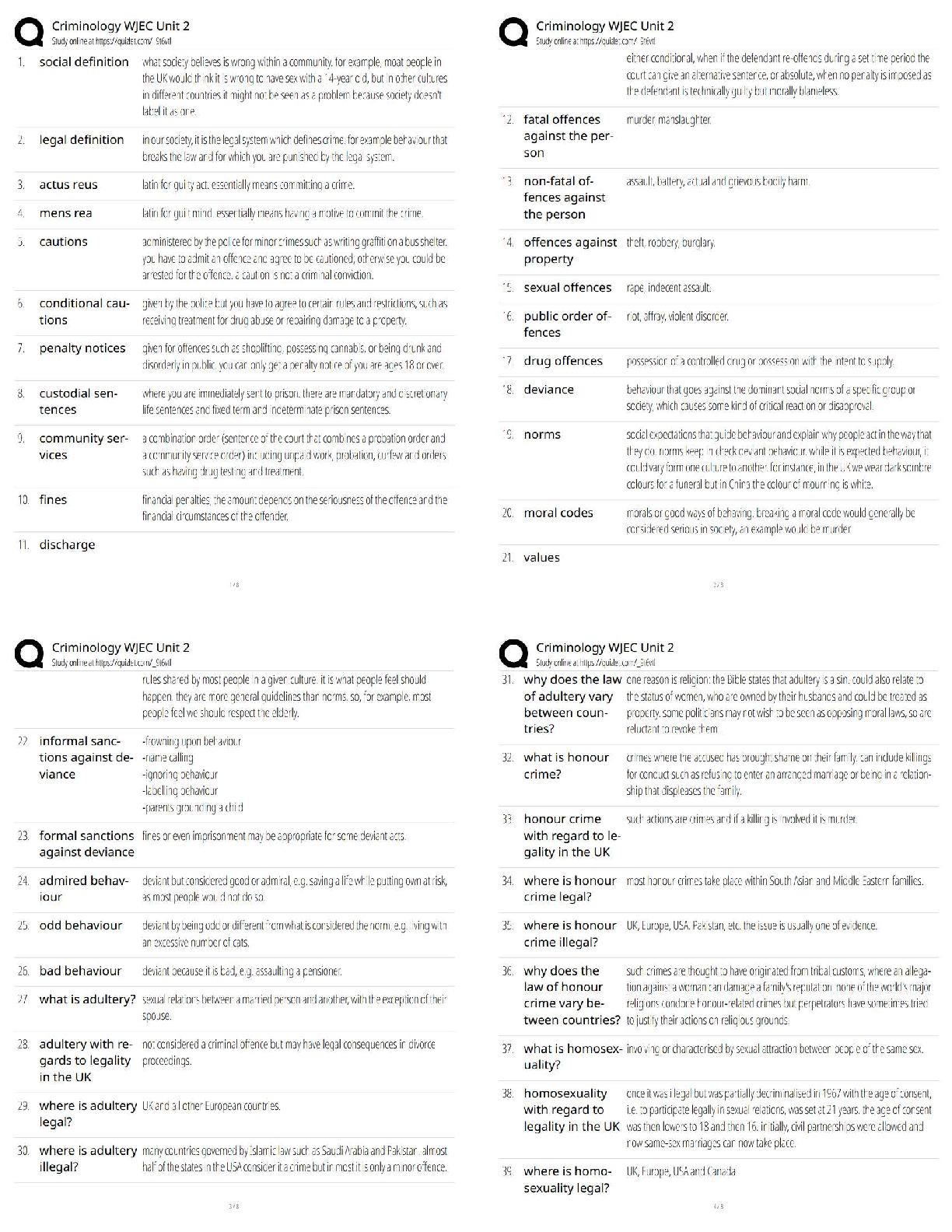
Chapter 18
Discuss the basis of fetal monitoring
Purpose: to see how baby is doing
• Monitoring of fetal response to labor
NICHD (National Institute of Child Health and Human Development) fetal monitoring classifications
• Category 1 – Normal; requires no specific action
results in metabolic acidosis
Describe the normal uterine contractions patterns and the nursing care for the following. In addition describe the clinical significance of any variation to normal with the medical/nursing care.
Normal process of labor
• Frequency – from beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next
o normal 2-5 contractions per 10 min (frequency increases as labor progresses)
Describe the different monitoring techniques and when they would be used
Compare and contrast the difference between Internal and external fetal monitoring.
• Intermittent Auscultation
• EFM
o External
Bands on mom’s belly hold devices that detect FHR and UC
Describe the basic fetal heart tone patterns.
• Baseline heart rate
o 110 to 160 (slightly higher in preterm baby)
• Variability
o Irregular waves or fluctuations – doesn’t include accelerations or decelerations
Marked (>25 bpm)
Define, describe the causes, clinical significance and the nursing care for the following fetal heart rate patterns.
• Tachycardia
• Bradycardia
Depends on cause
• Not specifically related to fetal oxygenation
• Often fetal cardiac problem
Periodic & episodic changes in FHR
• Accelerations
o Abrupt increase in FHR of at least 15 bpm for at least 15 seconds, with return to baseline in <2 min
Can be 10 bpm for 10 seconds if <32 wks gestational age
o Considered an indication of fetal wellbeing
• Early decelerations
• Late decelerations
o FHR dips after contraction starts, returns to baseline after the contraction is over
• Variable decelerations
o V, W, or U shaped abrupt dip within the contraction
time from start of decrease until nadir of the deceleration no more than 30 seconds
• Prolonged deceleration
• Decrease in variability! Usually d/t hypoxemia
• Progressive increase or decrease in baseline (bradycardia, tachycardia)
Montevideo units – a method of measuring uterine performance during labor
• Use with internal monitors
Things to remember:
Chapter 19
Describe the admitting process and information needed for the client in the labor and delivery suite
Triage – for pt coming in to the maternity ward (remember EMTALA, legally a doctor must certify pt is NOT in labor True
Describe the expected maternal progress in the first stage of labor. Cervical status and time period
Describe and apply to care during the assessment on admission and during the 1st stage all three phases) of labor. Include VS, UA, FHT.
Describe the nursing care and apply the nursing care including: hygiene, intake, output, positioning and supportive care through the first state of labor.
Nursing responsibilities in stage 1
What diagnostic tests will be performed in labor?
What other support people can support a woman in labor?
Describe the nursing management for a client in the second stage of labor. Include VS, care medications, time period, positioning – review pg. 455
What is the Ritgen maneuver?
What is the Ferguson Reflex?
What injuries can happen during the second stage of labor?
Laceration
Episiotomy
What is the nursing care for the 3rd stage of labor?
What is the nursing care for the 4th stage of labor?
Chapter 32
Compare and contrast the dysfunctional labor patterns. Include contractions, cervical status and nursing care.
What are the emergencies that can happen during labor? What is the nurses’ responsibility and care during all of the emergencies?
Uterine abnormalities
Inadequate uterine relaxation
• When resting tone is not < 10 mmHg
Inversion of uterus
Uterine rupture
Hypotonic uterine dysfunction
Hypertonic Uterine dysfunction
Preterm
Post-term birth (>42 wks)
Compare and contrast the different Dystocia include causes, medical and nursing interventions.
Causes:
Pelvic
• When pelvic contractures reduce the capacity of the pelvis
Soft tissue
• Obstruction of birth passage by anatomic abnormality (something besides the bony pelvis)
CPD
• When mom’s uterus is disproportionate to size of fetus – baby can’t fit
Malposition (pg. 775)
• Most deliveries are ROA or LOA, but when fetal head is positioned LOP or ROP (most common
Malpresentation
• Types of Breech (pg. 776)
o Three types (see picture)
What is the care for an obese woman in labor and during delivery and the immediate post-partum period?
• BMI > 30
• Greater risk for venous thromboembolism & C/S
Describe the following Obstetric procedures. Be able to identify the use, medical and nursing care for the following.
Version
• Turning baby from a breech or side-lying presentation to a vertex presentation
Amnioinfusion
• Infusion of isotonic fluid - (K) what isotonic fluid is
• Done in situations of cord compression or oliohydramnios
Amniotomy – rupturing membranes artificially – AROM
o Document (time of rupture, etc.)
Induction, Augmentation (see section on Pitocin)
Use of Cervical ripening agents. Include what is the bishop’s score
Cervical ripening agents
Other cervical ripening methods
• Hydroscopic dilator
o Acupuncture (has been found to be effective)
Operative vaginal birth
(Forceps-assisted; Vacuum assisted)
Cesarean birth
Scheduled or emergency
• Reasons: failure to progress, CPD, placental abnormalities, malpresentation, prolapsed cord, fetal distress, genital herpes
• Nursing
VBAC (pg. 794, box 32.11)
• Cannot do with classical incision; must have previously had low transverse incision (1 or 2 C/S)
TOL
• “Trying” labor for 4 to 6 hours to see if vag birth is safe for pt
Describe the etiology, clinical manifestations as well as the medical and nursing interventions for the following obstetric emergencies.
Meconium stained amniotic fluid
Shoulder dystocia
• Cause usually CPD or macrosomia
• Nursing
• Helpful maneuvers
Prolapsed cord
• When cord lies below presenting part
Precipitous Labor and Delivery
• Labor lasting less than 3 hours
Fetal demise
• Baby dies in utero during labor – very traumatic
Conditions
Pregnancy induced hypertension (care pg. 662)
• If mild PIH, no meds
CV disease
We want these women to deliver fast and pain-free
Gestational DM (Review Intrapartum portion only, pg. 698, 4 paragraphs)
o No morning insulin
o Epidural anesthesia preferred (b/c hypoglycemia can be detected more easily if pt awake)
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)