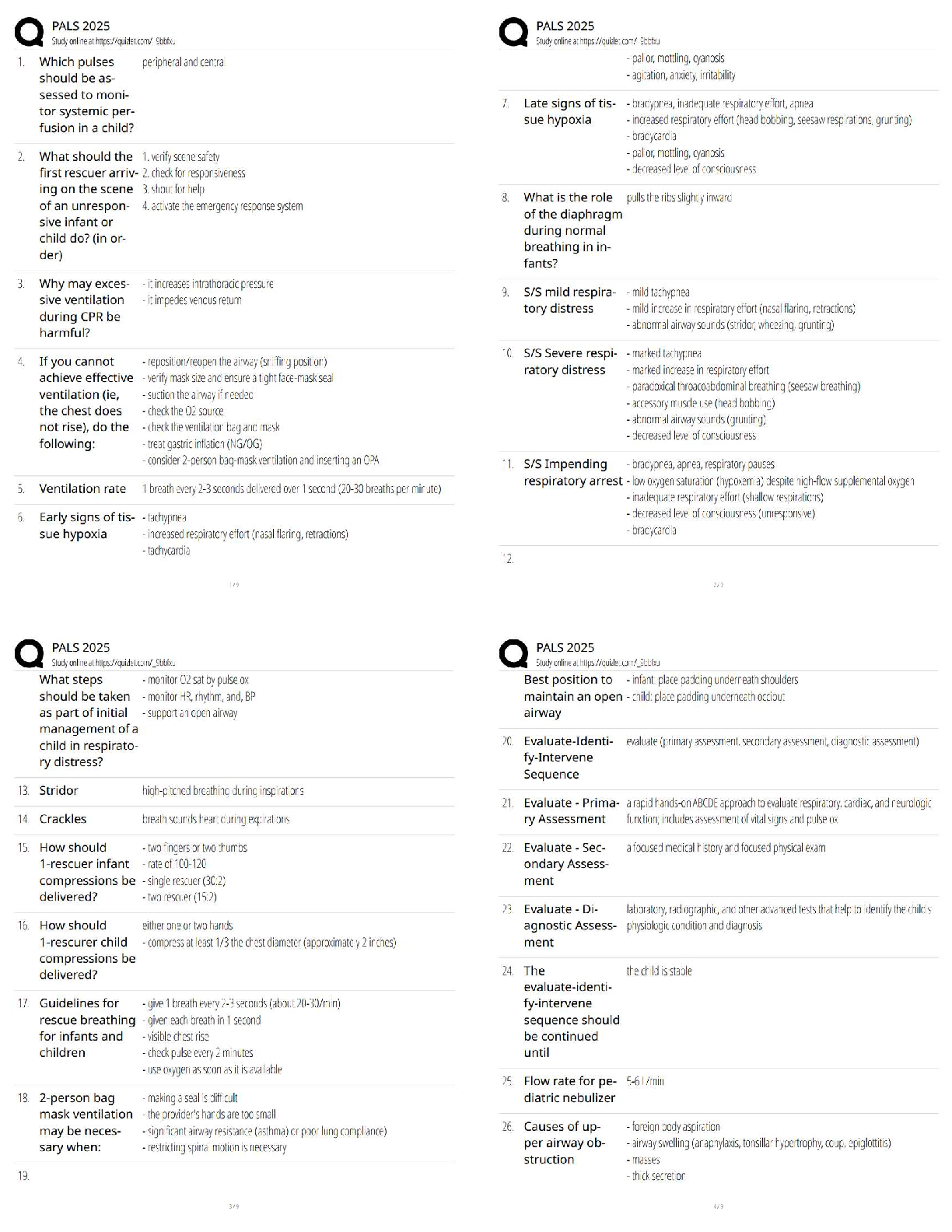
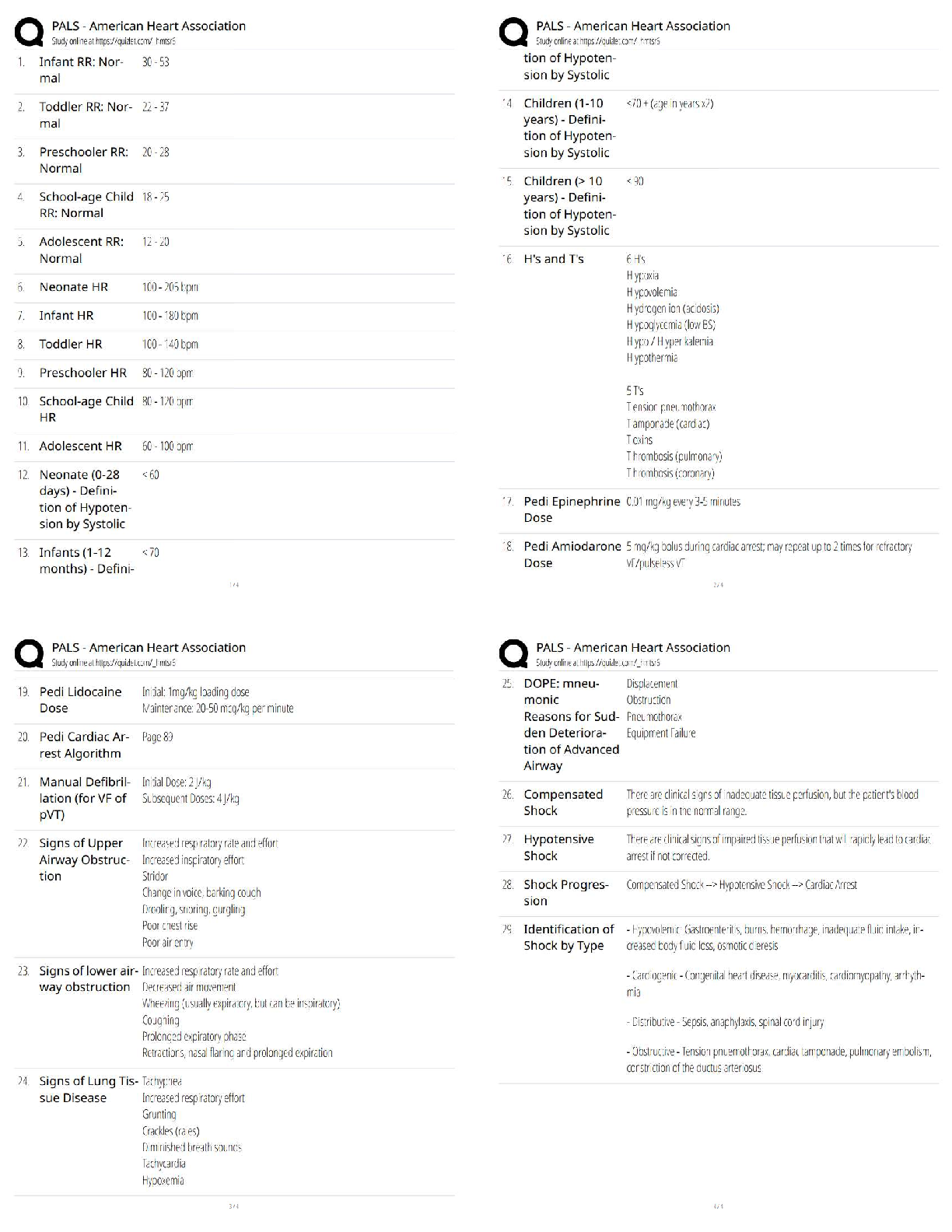
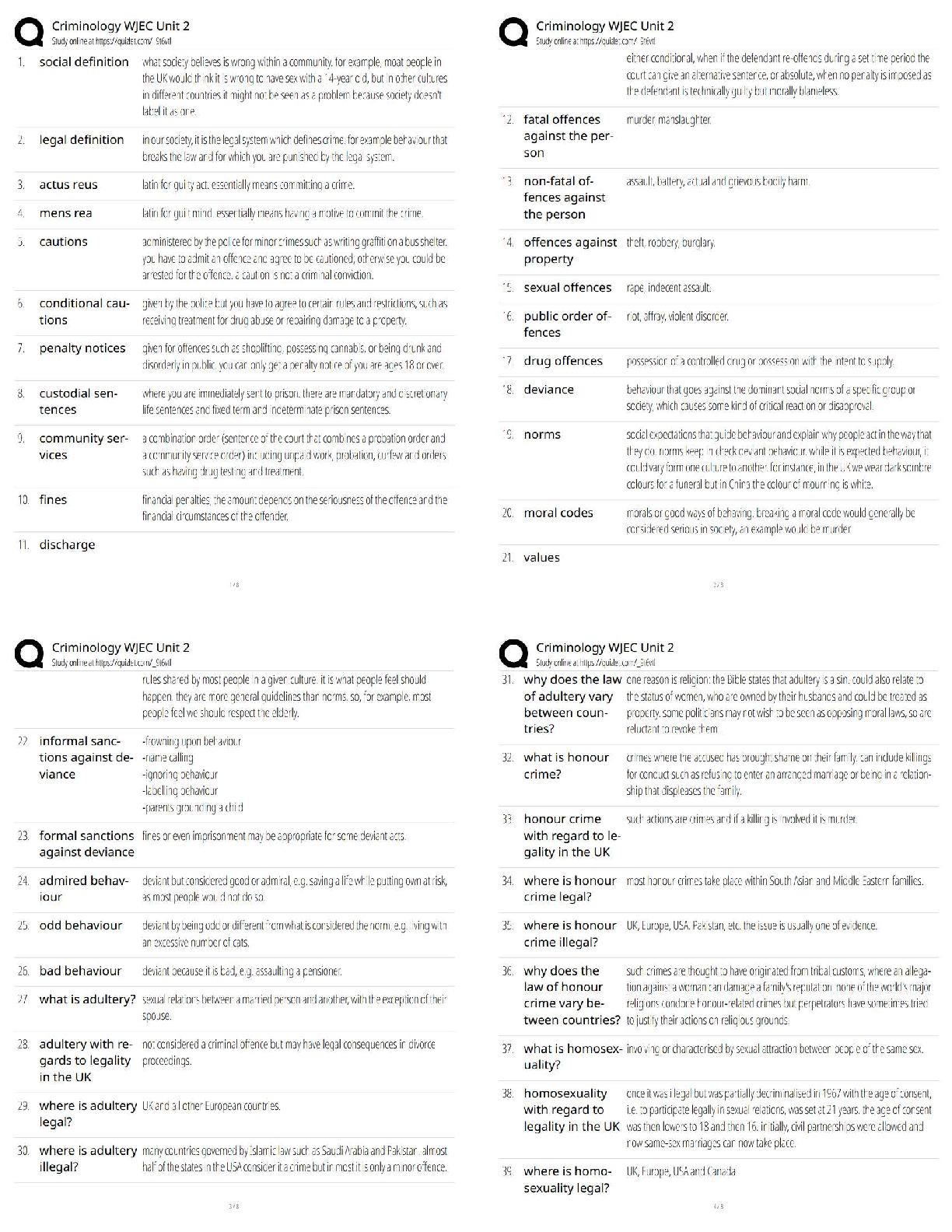
The nurse is caring for a client admitted with shock secondary to severe gastrointestinal bleeding. Once the client is stabilized, what intervention should the nurse do next?
1 Monitor the peripheral pulses.
2 Check
...
The nurse is caring for a client admitted with shock secondary to severe gastrointestinal bleeding. Once the client is stabilized, what intervention should the nurse do next?
1 Monitor the peripheral pulses.
2 Check the level of consciousness.
3 Take a blood sample for laboratory tests.
4 Control the bleeding with a pressure dressing.
A client has a functional transection of the spinal cord at C7-8, resulting in spinal shock. Which clinical indicators does the nurse expect to identify when assessing the client immediately after the injury? Select all that apply.
11Spasticity
2Incontinence
3 Flaccid paralysis
4 Respiratory failure
5 Lack of reflexes below the injury
A female client who is receiving intravenous antibiotic therapy at home for treatment of toxic shock syndrome is visited by a home health nurse. What statement indicates to the nurse that the client understands the teaching regarding future care?
1 "I will call the clinic if I get a rash."
2 "I will call the clinic if the menstrual cramps return."
3 "I now know how to insert my diaphragm ly."
4 "I now know how to perform tampon hygiene."
A nurse is caring for a client with a pneumothorax who has a chest tube in place. What should the nurse do when caring for this client?
1 Encourage range of motion to the client's arm on the affected side
2 Administer the prescribed cough suppressant at the prescribed times
3 Empty and measure the drainage in the collection chamber each shift
4 Apply clamps below the insertion site when getting the client out of bed
A client with a pneumothorax has a chest tube inserted and attached to a closed chest drainage system. The client asks, "Why is the tube in my chest hooked up to a contraption with water in it?" How does the nurse explain the function of the water?
1 Promotes pleural drainage via gravity
2 Measures the pressures in the chest wall
3 Prevents reflux of air back into the chest
4 Ensures bubbling in the water-seal chamber
While walking in a hallway, a client with a chest tube becomes confused and pulls the chest tube out. What is the nurse's immediate action?
1 Place the client in the supine position
2 Spread a clamp in the insertion site to hold the site open
3 Obtain a sterile Vaseline gauze to cover the opening
4 Cover the opening with the cleanest material available
A client who sustained serious burns now has a stress ulcer. Which clinical indicators of shock should the nurse immediately report to the primary healthcare provider? Select all that apply.
1 Weakness
2 Diaphoresis
3 Tachycardia
4 Cold extremities
5 Flushed skin tone
A client is in profound (late) hypovolemic shock. The nurse assesses the client’s laboratory values. What does the nurse know that clients in late shock develop?
1 Hypokalemia
2 Metabolic acidosis
3 Respiratory alkalosis
4 Decreased Pco2 levels
The nurse is caring for a client who had a massive myocardial infarction and developed cardiogenic shock. Which clinical manifestations support these diagnoses? Select all that apply.
1 Rapid pulse
2 Deep respirations
3 Warm, flushed skin
4 Increased blood pressure
5 Decreased urinary output
A client is admitted to the emergency department with the diagnosis of a possible spinal cord injury. The nurse should monitor the client for what clinical manifestations of spinal shock? Select all that apply.
1 Bradycardia
2 Hypotension
3 Spastic paralysis
4 Bladder dysfunction
5 Increased pulse pressure
A client who had a myocardial infarction develops cardiogenic shock despite treatment in the emergency department. Which client responses are related to cardiogenic shock? Select all that apply.
1 Tachycardia
2 Restlessness
3 Warm, moist skin
4 Decreased urinary output
5 Bradypnea
During the progressive stage of shock, anaerobic metabolism occurs. The nurse expects that initially the anaerobic metabolism will cause what?
1 Metabolic acidosis
2 Metabolic alkalosis
3 Respiratory acidosis
4 Respiratory alkalosis
What is the term for shock associated with a ruptured abdominal aneurysm?
1 Vasogenic shock
2 Neurogenic shock
3 Cardiogenic shock
4 Hypovolemic shock
The nurse is caring for a client who is experiencing cardiogenic shock. Which assessment findings support this diagnosis? Select all that apply.
1 Polyuria
2 Dyspnea
3 Diaphoresis
4 Tachycardia
5 Hypertension
A nurse is caring for a client who has had multiple myocardial infarctions and has now developed cardiogenic shock. Which clinical manifestation supports this diagnosis?
1 Cold, clammy skin
2 Slow, bounding pulse
3 Increased blood pressure
4 Hyperactive bowel sounds
A client is in cardiogenic shock. Which explanation of cardiogenic shock should the nurse include when responding to a family member's questions about the condition?
1 An irreversible phenomenon
2 A failure of the circulatory pump
3 Usually a fleeting reaction to tissue injury
4 Generally caused by decreased blood volume
A client is admitted with full-blown anaphylactic shock that developed due to a type 1 latex allergic reaction. Which findings will the nurse observe upon assessment? Select all that apply.
1 Stridor
2 Fissuring
3 Hypotension
4 Dyspnea
5 Cracking of the skin
Which bacteria causes toxic shock syndrome in female clients?
1 Treponema pallidum
2 Streptococcus faecalis
3 Staphylococcus aureus
4 Neisseria gonorrhoeae
The nurse is conducting triage under mass casualty conditions. Which tag should the nurse use for a client who is experiencing hypovolemic shock due to a penetrating wound?
1 Red
2 Black
3 Green
4 Yellow
Victims of a mine explosion are admitted to the emergency department. The nurse finds that the victims were exposed to dynamite and have injuries caused by a supersonic overpressurization shock wave. Which is the priority nursing intervention in this situation?
A Administering whole blood as needed
B Administering intravenous antibiotics as ordered
C Assessing for liver, long bones, and eyes immediately
D Assessing for lung, gastrointestinal tract, and middle ear injuries immediately
A client undergoes a bowel resection. When assessing the client 4 hours postoperatively, the nurse identifies which finding as an early sign of shock?
1 Respirations of 10
2 Urine output of 30 mL/hour
3 Lethargy
4 Restlessness
To prevent septic shock in the hospitalized client, what should the nurse do?
1 Maintain the client in a normothermic state.
2 Administer blood products to replace fluid losses.
3 Use aseptic technique during all invasive procedures.
4 Keep the critically ill client immobilized to reduce metabolic demands.
The nurse notifies the primary healthcare provider that a client has been admitted to the high-risk unit in her thirty-sixth week of gestation. She is bleeding, has severe abdominal pain and a rigid fundus, and is demonstrating signs of impending shock. Which intervention should the nurse prepare for?
1 A high-forceps birth
2 An immediate cesarean birth
3 Insertion of an internal fetal monitor
4 Administration of an oxytocin infusion
A healthcare provider in the emergency department identifies that a client is in cardiogenic shock. Which type of drug does the nurse anticipate will be prescribed?
1 Loop diuretic
2 Cardiac glycoside
3 Sympathomimetic
4 Alpha-adrenergic blocker
A nurse assesses a client who is experiencing profound (late) hypovolemic shock. When monitoring the client's arterial blood gas results, which response does the nurse expect?
1 Hypokalemia
2 Metabolic acidosis
3 Respiratory alkalosis
4 Decreased carbon dioxide level
A nurse is caring for a client with severe burns. The nurse determines that this client is at risk for hypovolemic shock. Which physiologic finding supports the nurse’s conclusion?
1 Decreased rate of glomerular filtration
2 Excessive blood loss through the burned tissues
3 Plasma proteins moving out of the intravascular compartment
4 Sodium retention occurring as a result of the aldosterone mechanism
A nurse is obtaining an admission history for a client who is scheduled for surgery to repair a ruptured abdominal aneurysm. Which type of shock should the nurse monitor for in this client?
1 Obstructive
2 Neurogenic
3 Cardiogenic
4 Hypovolemic
A client receiving a blood transfusion that was just initiated reports urticaria and difficulty breathing. The heart rate has increased, the blood pressure is falling, and the client is becoming extremely apprehensive. Which type of shock does the nurse suspect the client is experiencing?
1 Septic shock
2 Cardiogenic shock
3 Neurogenic shock
4 Anaphylactic shock
On the morning of surgery a client is admitted for resection of an abdominal aortic aneurysm. While awaiting surgery, the client suddenly develops symptoms of shock. Which nursing action is priority?
1 Prepare for blood transfusions.
2 Notify the surgeon immediately.
3 Make the client nothing by mouth (NPO).
4 Administer the prescribed preoperative sedative.
A client is experiencing hypovolemic shock with decreased tissue perfusion. Which information should the nurse consider when planning care?
1 The body initially attempts to compensate by releasing more red blood cells.
2 The body initially attempts to compensate by maintaining peripheral vasoconstriction.
3 The body initially attempts to compensate by decreasing mineralocorticoid production.
4 The body initially attempts to compensate by producing less antidiuretic hormone (ADH).
Which complication of anaphylactic shock in the adolescent client is most important for the nurse to detect early?
1 Urticaria
2 Tachycardia
3 Restlessness
4 Laryngeal edema
A client is diagnosed with gastric cancer, and a subtotal gastrectomy is performed. After surgery the client begins to hemorrhage. What clinical findings support the nurse's conclusion that the client is experiencing hypovolemic shock? Select all that apply.
1 Oliguria
2 Bradypnea
3 Diaphoresis
4 Tachycardia
5 Hypertension
A client has a colon resection with an anastomosis. What assessments by the nurse support a suspicion of impending shock? Select all that apply.
1 Oliguria
2 Lethargy
3 Irritability
4 Hypotension
5 Slurred speech
During the progressive stage of shock, anaerobic metabolism occurs. Which complication should the nurse anticipate in this client?
1 Metabolic acidosis
2 Metabolic alkalosis
3 Respiratory acidosis
4 Respiratory alkalosis
Identify the component of a pulmonary catheter used to measure pulmonary artery (PA) pressures and sample mixed venous blood.
A nurse prepares a client for insertion of a pulmonary artery catheter. What information can be obtained from monitoring the pulmonary artery pressure?
1 Stroke volume
2 Venous pressure
3 Coronary artery patency
4 Left ventricular functioning
A client with the diagnosis of myocardial infarction is admitted to the intensive care unit, and a pulmonary artery catheter is inserted for hemodynamic monitoring. Therapy is administered to maintain the pulmonary artery wedge pressure at 16 to 20 mm Hg to optimize stroke volume. The client's pulmonary artery wedge pressure increases to 24 mm Hg. What does the nurse consider as the most likely reason for this change?
1
Decreased afterload
2
Decreased heart rate
3
Increased stroke volume
4
Increased intravascular volume
46%of students nationwide answered this question ly.
View Topics
40. 3204949242
Confidence: Pretty sure
Stats
Issue with this question?
40.
A client with a suspected pulmonary embolism is scheduled for a spiral computed tomography scan. Which intervention should the nurse perform when preparing the client for the test?
1
Check the client’s blood glucose levels.
2
Obtain informed consent from the client.
3
Assess if the client is allergic to shellfish.
4
Instruct the client to remove his or her dentures.
64%of students nationwide answered this question ly.
View Topics
41. 3204942833
Confidence: Pretty sure
Stats
Issue with this question?
41.
Which diagnostic test would the nurse consider to be the gold standard for diagnosis of pulmonary embolism?
1
Pulmonary angiography
2
Helical computed tomography (CT)
3
Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scans
4
Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CT-PA)
View Topics
42. 3203947233
Confidence: Pretty sure
Stats
Issue with this question?
42.
What points should be considered when a client with a respiratory disorder undergoes a spiral-computed tomography (CT) scan to diagnose a pulmonary embolism? Select all that apply.
1
The test involves the administration of a contrast medium.
2
Clients should have their hydration levels assessed.
3
Clients are instructed to lie still on a hard table.
4
Clients are served shellfish before the test.
5
A client’s serum creatinine level is evaluated after the test.
View Topics
43. A client is receiving warfarin for a pulmonary embolism. Which drug is often contraindicated when taking warfarin?
1
Atenolol
2
Ferrous sulfate
3
Chlorpromazine
4
Acetylsalicylic acid
44.
A nurse is caring for a variety of clients. In which client is it most essential for the nurse to implement measures to prevent pulmonary embolism?
1
A 59-year-old who had a knee replacement
2
A 60-year-old who has bacterial pneumonia
3
A 68-year-old who had emergency dental surgery
4
A 76-year-old who has a history of thrombocytopenia
45.
A nurse is caring for a group of clients on a medical-surgical unit. Which client has the highest risk for developing a pulmonary embolism?
1
An obese client with leg trauma
2
A pregnant client with acute asthma
3
A client with diabetes who has cholecystitis
4
A client with pneumonia who is immunocompromised
46.
The nurse is caring for a client who has undergone a total hip replacement. The nurse recognizes which clinical manifestations that indicate a pulmonary embolism? Select all that apply.
1
Sudden chest pain
2
Flushing of the face
3
Elevation of temperature
4
Abrupt onset of shortness of breath
5
Pain rating increase from 2 to 8 in the hip
48.
A nurse is caring for a client who has chest tubes inserted to treat a hemothorax that resulted from a crushing chest injury. While planning care for a stationary chest tube drainage system, which purpose of the first chamber will the nurse consider?
1
Collect drainage
2
Ensure adequate suction
3
Maintain negative pressure
4
Sustain a continuance of the water seal
50.
During the first 36 hours after the insertion of chest tubes, when assessing the function of a three-chamber, closed-chest drainage system, the nurse identifies that the water in the underwater seal tube is not fluctuating. What initial action should the nurse take?
1
Take the client's vital signs.
2
Inform the healthcare provider.
3
Turn the client to the unaffected side.
4
Check the tube to ensure that it is not kinked.
A client has chest tubes attached to a chest tube drainage system. What should the nurse do when caring for this client?
1
Clamp the chest tubes when suctioning.
2
Palpate the surrounding area for crepitus.
3
Change the dressing daily using aseptic technique.
4
Empty the drainage chamber at the end of the shift.
52.
A client is shot in the chest during a holdup and is transported to the hospital via ambulance. In the emergency department, chest tubes are inserted, one in the second intercostal space and one at the base of the lung. What does the nurse expect the tube in the second intercostal space to accomplish?
1
Remove the air that is present in the intrapleural space
2
Drain serosanguineous fluid from the intrapleural compartment
3
Permit the development of positive pressure between the layers of the pleura
4
Provide access for the instillation of medication into the pleural space
53.
A client who sustained trauma to the chest as a result of an injury has chest tubes inserted and is attached to a closed chest drainage system. When caring for this client, what should the nurse do?
1
Palpate the area around the tubes for crepitus
2
Clamp the chest tubes when suctioning the client
3
Empty the drainage chamber at the end of the shift
4
Change the client's dressing daily using aseptic technique
54.
The team leader is making client assignments. Which team member should be assigned a client with a tracheostomy, chest tube, and blood transfusion?
1
Charge nurse
2
Registered nurse (RN)
3
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP)
4
Licensed practical nurse/licensed vocational nurse (LPN/LVN)
55.
A nurse is providing immediate postoperative care to a client who had a lung resection for a malignancy. The client has a closed chest tube drainage system connected to suction. Which assessment finding requires additional evaluation by the nurse?
1
A column of water 20 cm high in the suction control chamber
2
75 mL of bright red blood in the drainage collection chamber
3
An intact occlusive dressing at the insertion site
4
Constant bubbling in the water seal chamber
56.
A client's chest tube has accidentally dislodged. What is the nursing action of highest priority?
1
Place the client in a left side-lying position.
2
Apply oxygen via nonrebreather mask.
3
Apply a petroleum gauze dressing over the site.
4
Prepare to reinsert a new chest tube.
57.
A client tells the nurse that the client's chest tube is scheduled to be removed soon. Before it is removed, what is the nurse aware of?
1
The drainage system will be disconnected from the chest tube.
2
A chest x-ray will be performed to determine lung re-expansion.
3
An arterial blood gas will be obtained to determine oxygenation status.
4
The client will be sedated 30 minutes before the procedure.
59.
A nurse is caring for a client with a pneumothorax who has a chest tube attached to a closed chest drainage system. If the chest tube and closed chest drainage system are effective, what type of pressure will be reestablished?
1
Neutral pressure in the pleural space
2
Negative pressure in the pleural space
3
Atmospheric pressure in the thoracic cavity
4
Intrapulmonic pressure in the thoracic cavity
61.
The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client who had a chest tube removed. To promote respiratory exchange, what should the nurse add to the plan of care?
1
Careful monitoring for crepitus
2
Bed rest with range-of-motion exercises
3
Coughing and deep breathing every hour
4
Covering the chest tube site with a sterile dressing
62.
What is the primary responsibility of a nurse when caring for a client with a chest tube attached to a three-chamber underwater-seal drainage system?
1
Ensure maintenance of the closed system
2
Maintain mechanical suction to the system
3
Encourage the client to deep breathe and cough
4
Keep the client in the dorsal recumbent position
A client sustains a stab wound to the chest, and a chest tube is inserted. Later the client's chest tube appears to be obstructed. Which is the most appropriate nursing action?
1
Instruct the client to cough
2
Clamp the tube immediately
3
Prepare for chest tube removal
4
Arrange for a stat chest x-ray film
64.
A nurse is caring for a client with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) who develops a pneumothorax and has a chest tube inserted. Which primary purpose of the chest tube will the nurse consider when planning care?
1
Lessens the client's chest discomfort
2
Restores negative pressure in the pleural space
3
Drains accumulated fluid from the pleural cavity
4
Prevents subcutaneous emphysema in the chest wall
65.
A client with a chest tube is to be transported via a stretcher. When transporting the client, what should the nurse do?
1
Keep collection device attached to mechanical suction
2
Keep chest tube clamped distal to the water-seal chamber
3
Keep collection device below the level of the client's chest
4
Keep chest tube end covered with sterile gauze pads taped to the client
66.
A client is admitted to the hospital for a surgical resection of the lower left lobe of the lung. After surgery the client has a chest tube to a closed chest drainage system. What should the nurse do to determine if the chest tube is patent?
1
Milk the chest tube toward the drainage unit
2
Check the amount of bubbling in the suction control chamber
3
Observe for fluctuations of the fluid in the water-seal chamber
4
Assess for extent of chest expansion in relation to breath sounds
67.
A nurse is caring for a client with a chest tube. How will complete lung expansion be determined before removal of the chest tube?
1
Return of usual tidal volume
2
Decreased adventitious sounds
3
Absence of additional drainage
4
Comparison of chest radiographs
68.
The client has just had a chest tube inserted. How should the nurse monitor for the complication of subcutaneous emphysema?
1
Palpate around the tube insertion sites for crepitus
2
Auscultate the breath sounds for crackles and atelectasis
3
Observe the client for the presence of a barrel-shaped chest
4
Compare the length of inspiration with the length of expiration
69.
The nurse is caring for a client with a pneumothorax and chest tube. To evaluate the effectiveness of a chest tube, the nurse assesses for which finding?
1
Productive coughing
2
Return of breath sounds
3
Increased pleural drainage in the chamber
4
Constant bubbling in the water-seal chamber
70.
A client is admitted to the postanesthesia care unit after a segmental resection of the right lower lobe of the lung. A chest tube drainage system is in place. When caring for this tube, what should the nurse do?
1
Raise the drainage system to bed level and check its patency
2
Clamp the tube when moving the client from the bed to a chair
3
Mark the time and fluid level on the side of the drainage chamber
4
Secure the chest catheter to the wound dressing with a sterile safety pin
View Topics
71.
A client with a spontaneous pneumothorax asks, "Why did they put this tube into my chest?" Which information should the nurse provide about the purpose of the chest tube?
1
It checks for bleeding in the lung.
2
It monitors the function of the lung.
3
It drains fluid from the pleural space.
4
It removes air from the pleural space.
The nurse is caring for a client who had a wedge resection of a lobe of the lung and now has a chest tube with a three-chamber underwater drainage system in place. Which main purpose of the third chamber of the underwater drainage system should the nurse consider when planning care?
1
Acts as a drainage container
2
Provides an airtight water seal
3
Controls the amount of suction
4
Allows for escape of air bubbles
A client has a closed chest drainage system in place. What should the nurse do to determine the amount of chest tube drainage?
1
Refer to the date and time markings on the outside of the collection chamber.
2
Aspirate the drainage from the collection chamber.
3
Replace the existing system with a new one to access the drainage in the existing system.
4
Clamp the chest tube and empty the fluid from the collection chamber.
74.
Immediately after a thoracentesis, a client's right lung collapses. A chest tube is inserted and is attached to a three-chamber closed drainage system. What does the nurse assess about the fluid when the chest tube is functioning properly?
1
Remains constant in the chest drainage chamber.
2
Is bubbling gently in the chest drainage chamber.
3
Is bubbling vigorously in the suction control chamber.
4
Rises in the tube of the water-seal chamber during inspiration.
75.
A client has a chest tube for a pneumothorax. The nurse finds the client in respiratory difficulty, with the chest tube separated from the drainage system. What should the nurse do?
1
Obtain a new sterile drainage system.
2
Use two clamps to close the drainage tube.
3
Place the client in the high-Fowler position.
4
Reconnect the client's tube to the drainage system.
76.
After thoracic surgery, a client has a chest tube connected to a water-seal drainage system that is attached to suction. When excessive bubbling is observed in the water-seal chamber, what should the nurse do?
1
Strip the chest tube catheter
2
Check the system for air leaks
3
Decrease the amount of suction pressure
4
Recognize that the system is functioning ly
77.
A chest tube with an attached closed-drainage system is inserted into a client who was stabbed in the chest. Which is an important nursing intervention when caring for this client?
1
Observe for fluid fluctuations in the water-seal chamber.
2
Obtain a prescription for morphine to minimize agitation.
3
Apply a thoracic binder to prevent excessive tension on the tube.
4
Clamp the tubing securely to prevent a rapid decline in pressure.
79.
A nurse is caring for a client who experienced a crushing chest injury. A chest tube is inserted. Which observation indicates a desired response to this treatment?
1
Increased breath sounds
2
Increased respiratory rate
3
Crepitus detected on palpation of the chest
4
Constant bubbling in the drainage collection chamber
80.
The nurse is providing postoperative care to a client with cancer of the lung who had a lobectomy. The client has a chest tube attached to suction. Which assessment finding includes a complication?
1
Clots in the tubing during the first postoperative day
2
Bloody fluid in the drainage-collection chamber on the first postoperative day
3
Subcutaneous emphysema on the second postoperative day
4 Decreased bubbling in the water-seal chamber on the third postoperative day
81.
A nurse is caring for a client with a pneumothorax who has a chest tube in place with a closed drainage system. Which of these actions by the nurse is ?
1
Strip the chest tube periodically.
2
Administer the prescribed cough suppressant at the scheduled times.
3
Empty and measure the drainage in the collection chamber each shift.
4
Keep the drainage system lower than the level of the client's chest.
82.
The nurse is caring for a client after the client’s open heart surgery (coronary artery bypass grafting [CABG]). Serosanguineous fluid drains from the client’s chest tube. The nurse expects what volume of drainage from the tube during the first 24 hours after the surgery?
1
100 to 300 mL
2
400 to 500 mL
3
750 to 900 mL
4
800 to 1000 mL
83.
A client who had thoracic surgery is admitted to the postanesthesia care unit. What should the nurse do after the chest tube is attached to a disposable plastic water-seal drainage system?
1
Ensure the security of the connections from the client to the drainage unit.
2
Empty the drainage container and measure and record the amount once a day.
3
Verify that there is vigorous bubbling in the wet suction control compartment.
4
Check that the fluid level in the water-seal compartment increases with expiration.
An emergency nursing staff member is performing defibrillation/cardioversion and special resuscitation for clients who sustained injuries in a tsunami. Which certification does the emergency nursing staff member possess?
1
Basic Life Support(BLS)
2
Certified Emergency Nurse (CEN)
3
Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)
4
Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
85.
In addition to atrial fibrillation, which cardiac dysrhythmia exhibited by a client does the nurse determine may be converted to sinus rhythm by cardioversion?
1
Cardiac standstill
2
First degree heart block
3
Supraventricular tachycardia
4
Frequent premature complexes
86.
A client is admitted to the coronary care unit with atrial fibrillation and a rapid ventricular response. The nurse prepares for cardioversion. What nursing action is essential to prevent the potential danger of inducing ventricular fibrillation during cardioversion?
1
Energy level is set at its maximum level.
2
Synchronizer switch is in the "on" position.
3
Skin electrodes are applied after the T wave.
4
Alarm system of the cardiac monitor is functioning simultaneously.
88.
A client with burns is hospitalized in the emergency department and advised to get an electrocardiogram (ECG) done. Which type of burn injury has the client most likely sustained?
1
Flame burn
2
Chemical burn
3
Electrical burn
4
Radiation burn
89.
The nurse is managing a client who underwent cardiac bypass surgery. Which healthcare member can be safely delegated the task of monitoring electrocardiography?
1
Nurse aide
2
Certified technician
3
Cross-trained technician
4
Licensed vocational nurse (LVN)
90.
Electrocardiography (ECG) is scheduled for an infant who has tetralogy of Fallot. The mother asks the nurse what type of test this is and why it is done. What is the best response by the nurse?
1
"It’s a type of x-ray that shows us the size of the baby’s heart."
2
"Electrical activity in the baby’s heart is recorded, then printed on graph paper."
3
"It’s an ultrasound procedure that produces images of the structures in the baby’s heart."
4
"Contrast material is injected into the baby’s vein to visualize the flow of blood through the heart."
92.
Before a client has a cardiac catheterization, an electrocardiogram (ECG) is performed, and hypokalemia is suspected. The nurse expects that the diagnosis will be confirmed by which diagnostic test?
1
Complete blood count
2
Serum potassium level
3
X-ray film of long bones
4
Blood cultures times three
93.
A client is brought to the emergency department with chest pain. The client asks why an electrocardiogram (ECG) has been prescribed. What does the nurse explain that the ECG will do?
1
Indicates acutely impaired blood flow to the heart muscle
2
Detect altered heart sounds
3
Determine the flow of blood to the heart muscle
4
Evaluate the spatial relationship of structures within the heart
94.
The nurse observes the following pattern on a client’s electrocardiogram (ECG) strip. What dysrhythmia does the nurse identify?
1 Asystole
2 Atrial flutter
3 Ventricular fibrillation
4 Premature ventricular complex
95.
A client is admitted to the emergency department with chest pain and shortness of breath. An electrocardiogram indicates that the client is experiencing a myocardial infarction. An emergency cardiac catheterization is scheduled. What information should the nurse include in the preprocedure teaching?
1
Mild sedation is maintained during the procedure.
2
The procedure will take approximately 15 minutes to complete.
3
Ambulation is encouraged shortly after the procedure.
4
It will take approximately 24 hours to determine whether blockage is present.
A client experiences crushing chest pain and is brought to the emergency department. When assessing the electrocardiogram (ECG) tracing, the nurse concludes that the client is experiencing premature ventricular complexes (PVCs). Which abnormalities of the ECG support this conclusion?
1
Irregular rhythm, abnormally shaped P wave, and normal QRS
2
Irregular rhythm, absence of a P wave, and wide and distorted QRS
3
Regular rhythm, more than 100 beats per minute, normal P wave, and normal QRS
4
Regular rhythm, 100 to 250 beats per minute, absent P wave, and wide and distorted QRS
97.
The nurse is interpreting an electrocardiogram rhythm. What part of the electrical pattern represents ventricular contraction?
1
P wave
2
T wave
3
PR interval
4
QRS interval
98.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is performed before a client is to have a cardiac catheterization, and hypokalemia is suspected. What does the nurse expect the primary healthcare provider to prescribe to confirm the presence of hypokalemia?
1
A complete blood count
2
A serum electrolyte level
3
An arterial blood gas panel
4
An x-ray film of long bones
A nurse attaches electrocardiogram (ECG) leads to a client who is admitted to the hospital for chest pain. When monitoring the ECG strip, the nurse identifies that depolarization of the atria is occurring when which waveform in the illustration is present?
1 A
2 B
3 C
4 d
100.
A client who had several episodes of chest pain is scheduled for an exercise electrocardiogram (ECG). Which explanation should the nurse include when teaching the client about this procedure?
1
"This is a noninvasive test to check your heart’s response to physical activity."
2
"This test is the definitive method to identify the actual cause of your chest pain."
3
"The findings of this test will be of minimal assistance in the treatment of angina."
4
"The findings from this minimally invasive test will show how your body reacts to exercise."
101.
An electrocardiogram is prescribed for a client complaining of chest pain. The nurse recognizes which as an early finding of an infarcted area of the heart?
1
Flattened T waves
2
Absence of P waves
3
Elevated ST segments
4
Disappearance of Q waves
102.
A client who is suspected of having had a silent myocardial infarction has an electrocardiogram (ECG) prescribed by the primary healthcare provider. While the nurse prepares the client for this procedure, the client asks, "Why was this test prescribed?" Which is the best reply by the nurse?
1
"This test will detect your heart sounds."
2
"This test will reflect any heart damage."
3
"This procedure helps us change your heart’s rhythm."
4
"The ECG will tell us how much stress your heart can tolerate."
104.
A client arrives at the emergency room complaining of chest pain and dizziness. The client has a history of angina. The primary healthcare provider prescribes an electrocardiogram (ECG) and lab tests. A change in which component of the ECG tracing should the nurse recognize as the client actively having a myocardial infarction (MI)?
1
QRS complex
2
S-T segment
3
P wave
4
R wave
105.
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is prescribed for a client who reports chest pain. Which early finding does the nurse expect on the lead over the infarcted area?
1
Flattened T waves
2
Absence of P waves
3
Elevated ST segments
4
Disappearance of Q waves
106.
A client presents to the emergency department with weakness, dizziness, and difficulty breathing. The nurse performs an electrocardiogram (ECG) and notices this arrhythmia. Which arrhythmia is the client exhibiting?
1 Atrial fibrillation (AF)
2 Ventricular tachycardia (VT)
3 Junctional tachycardia
4 Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)