EML4321 Manufacturing Engineering HW-7
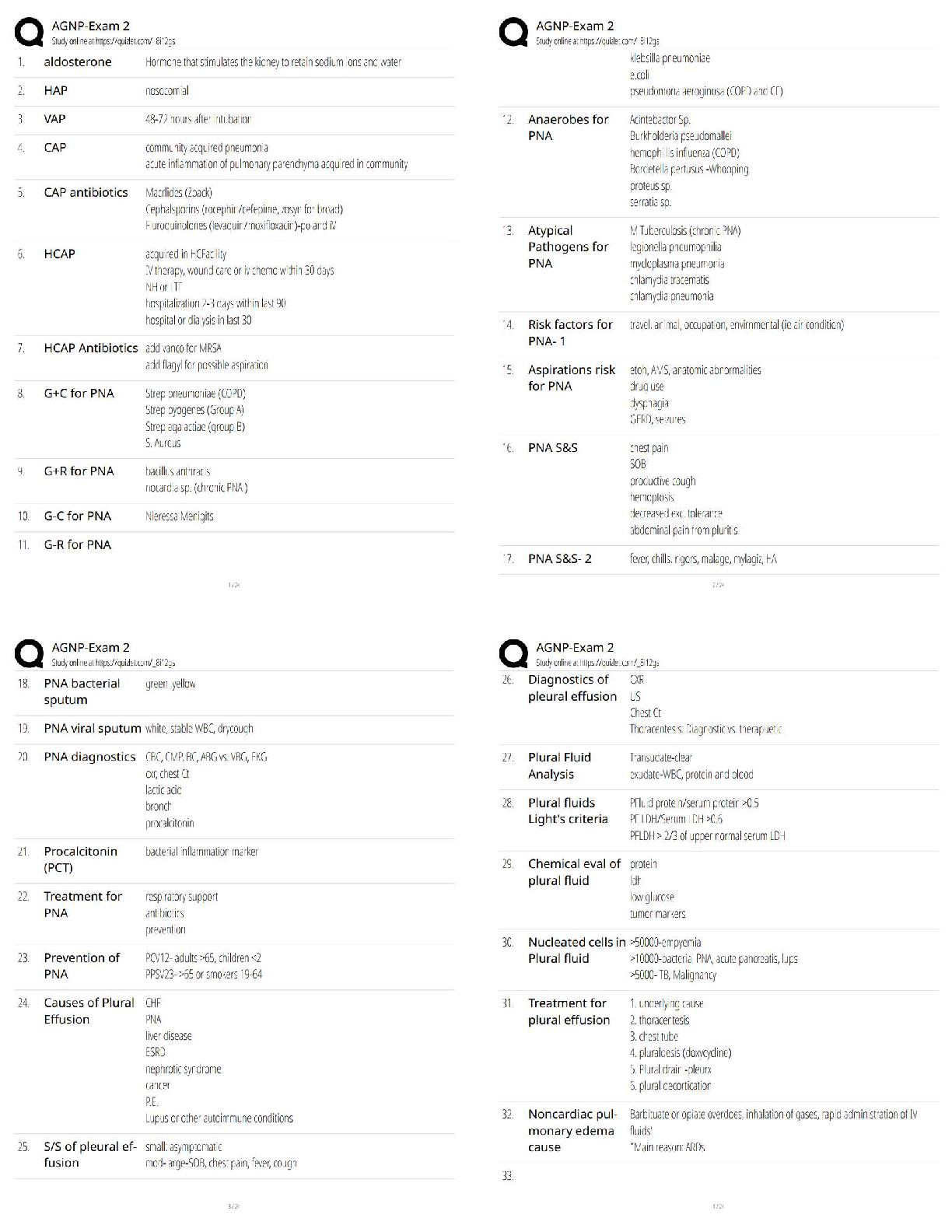
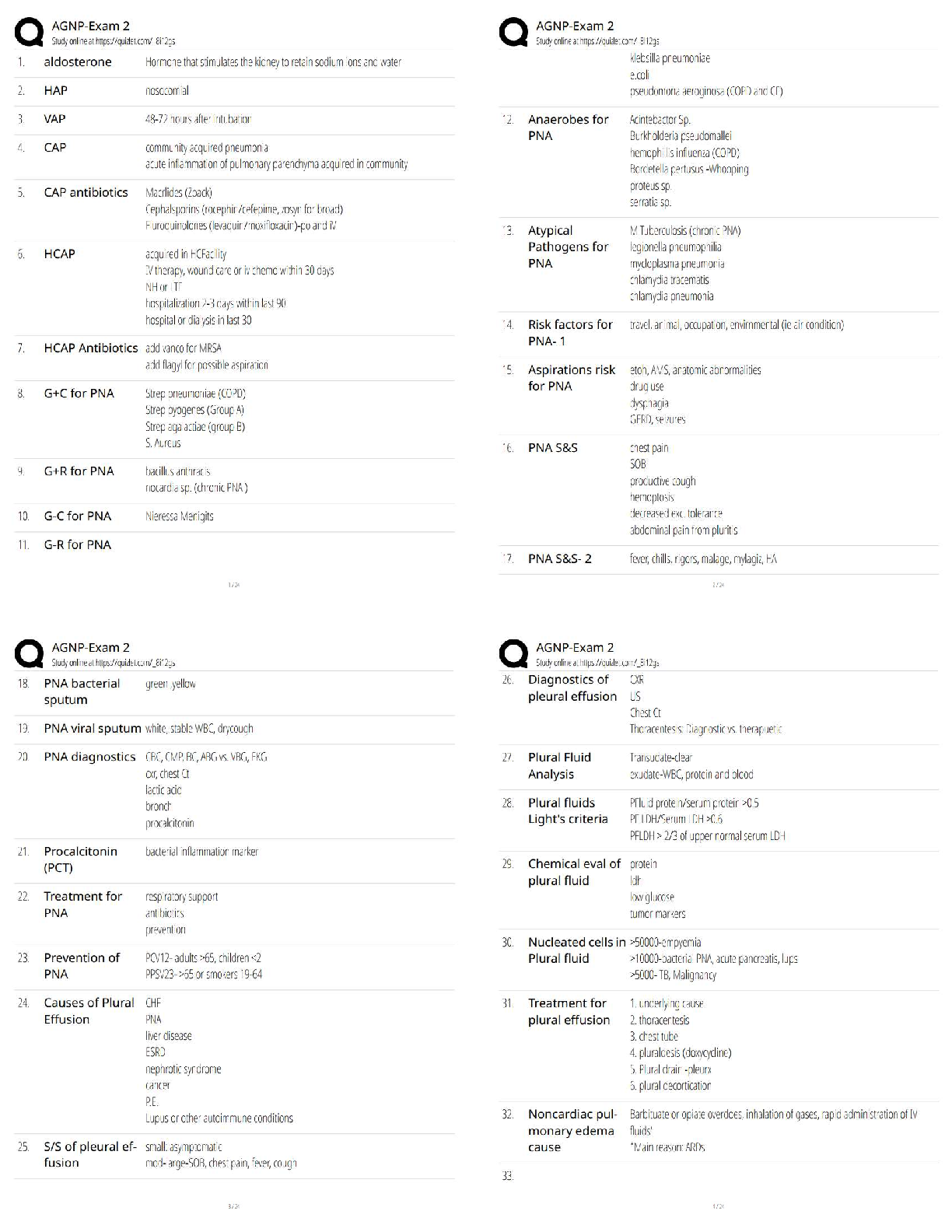
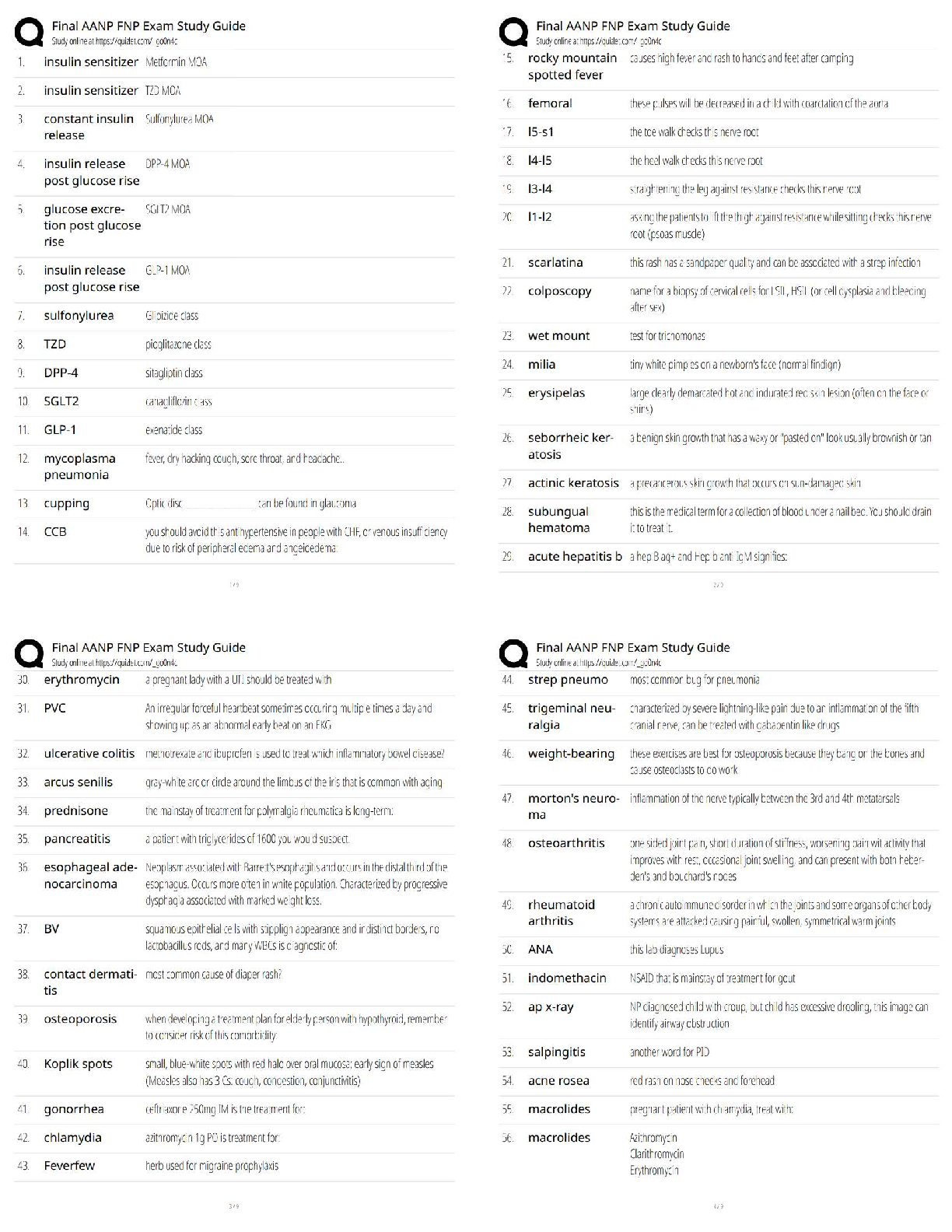
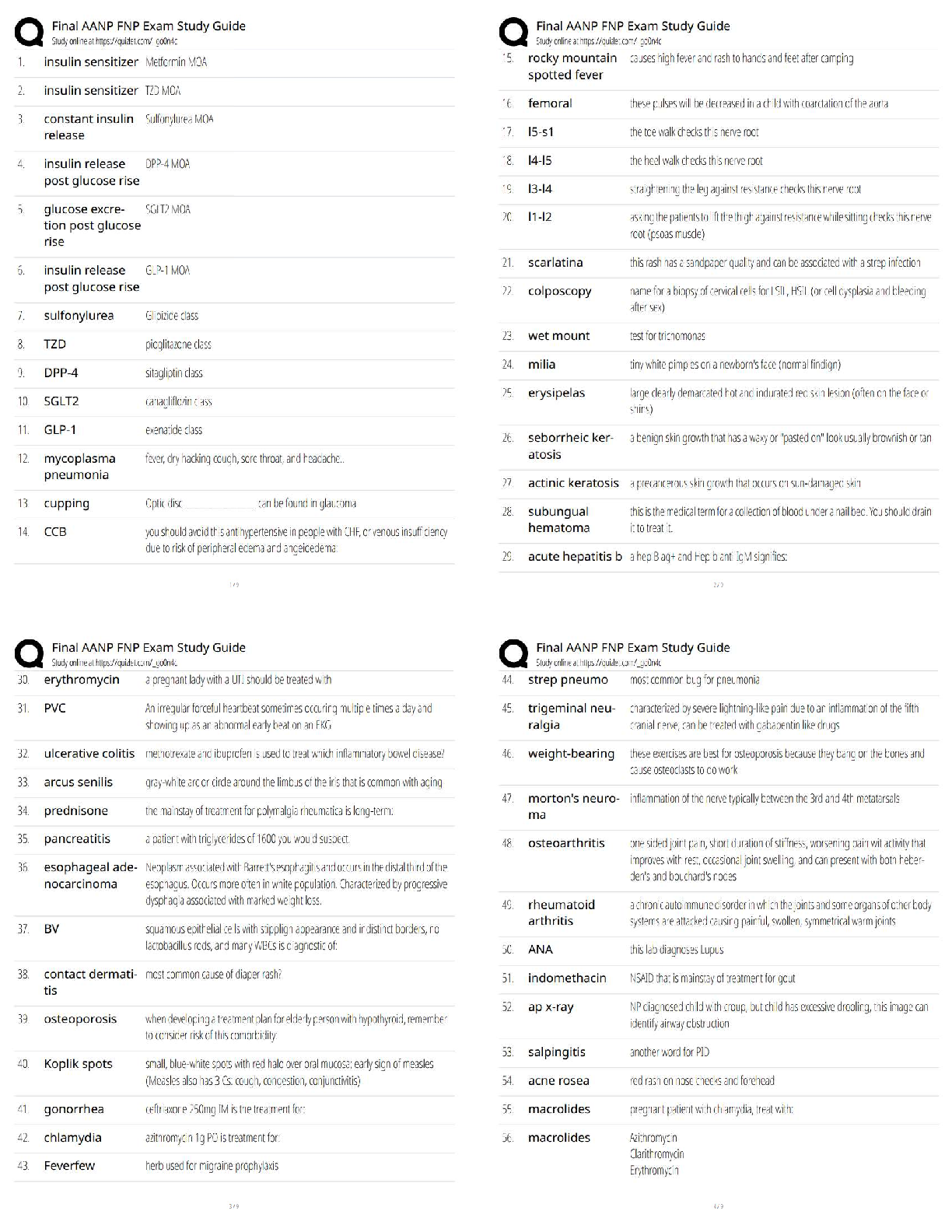
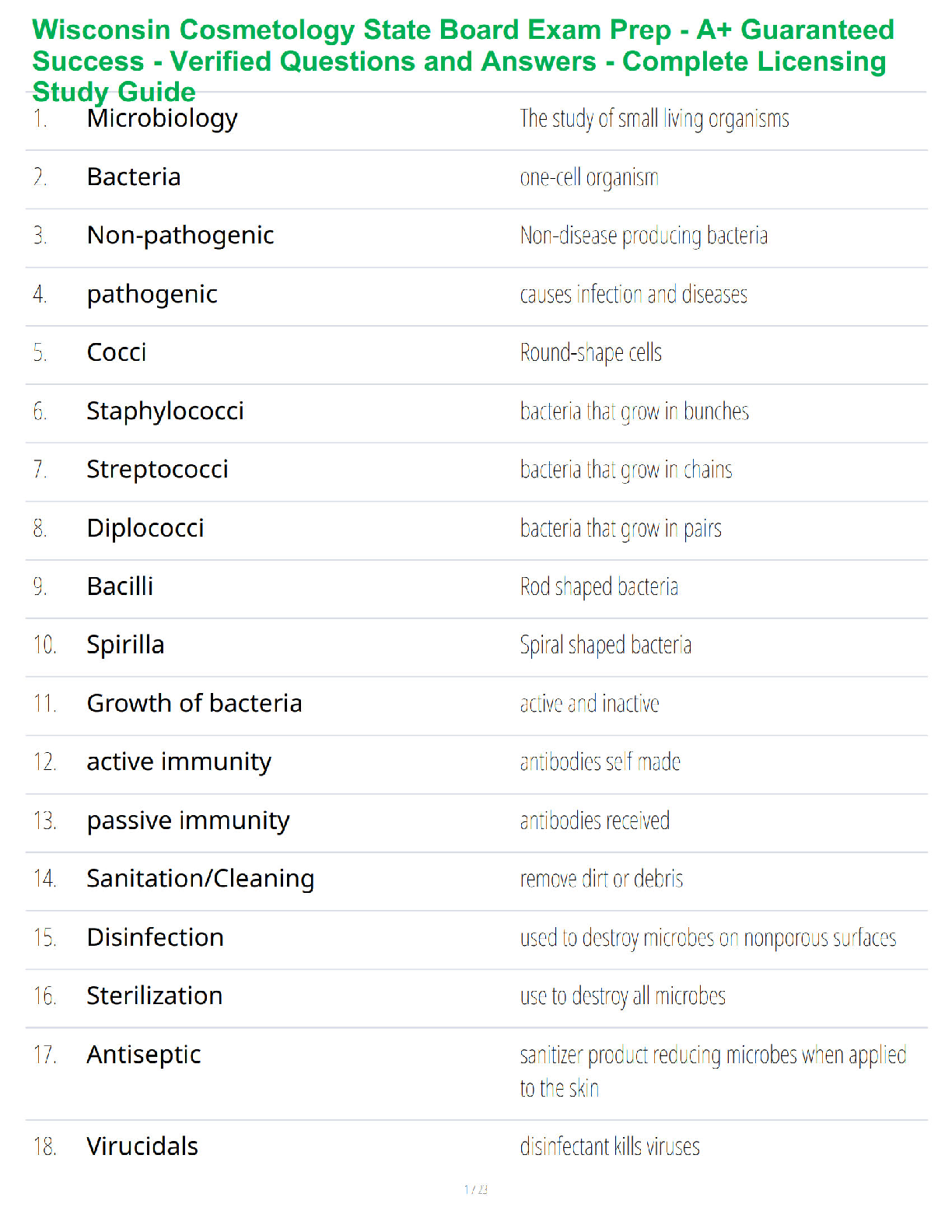
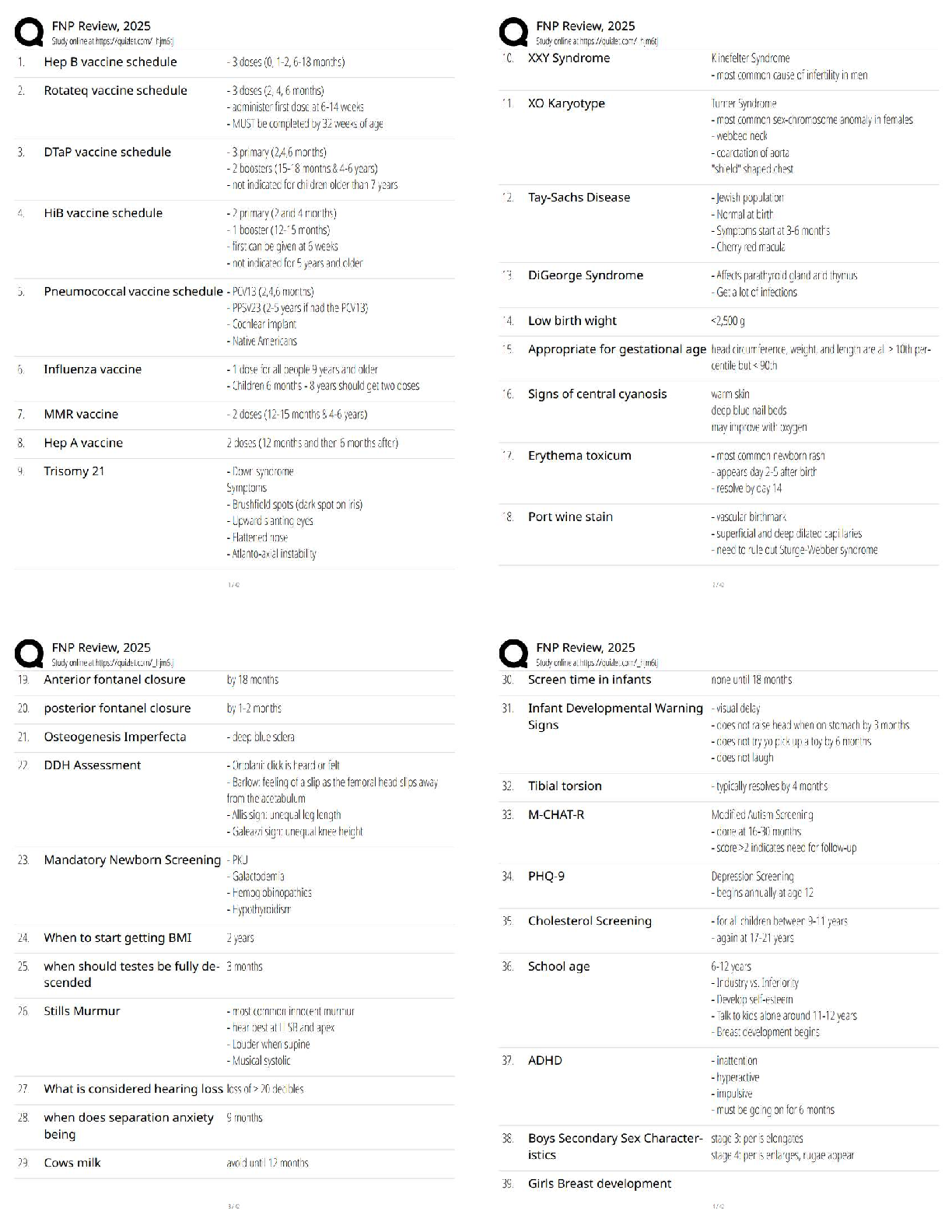
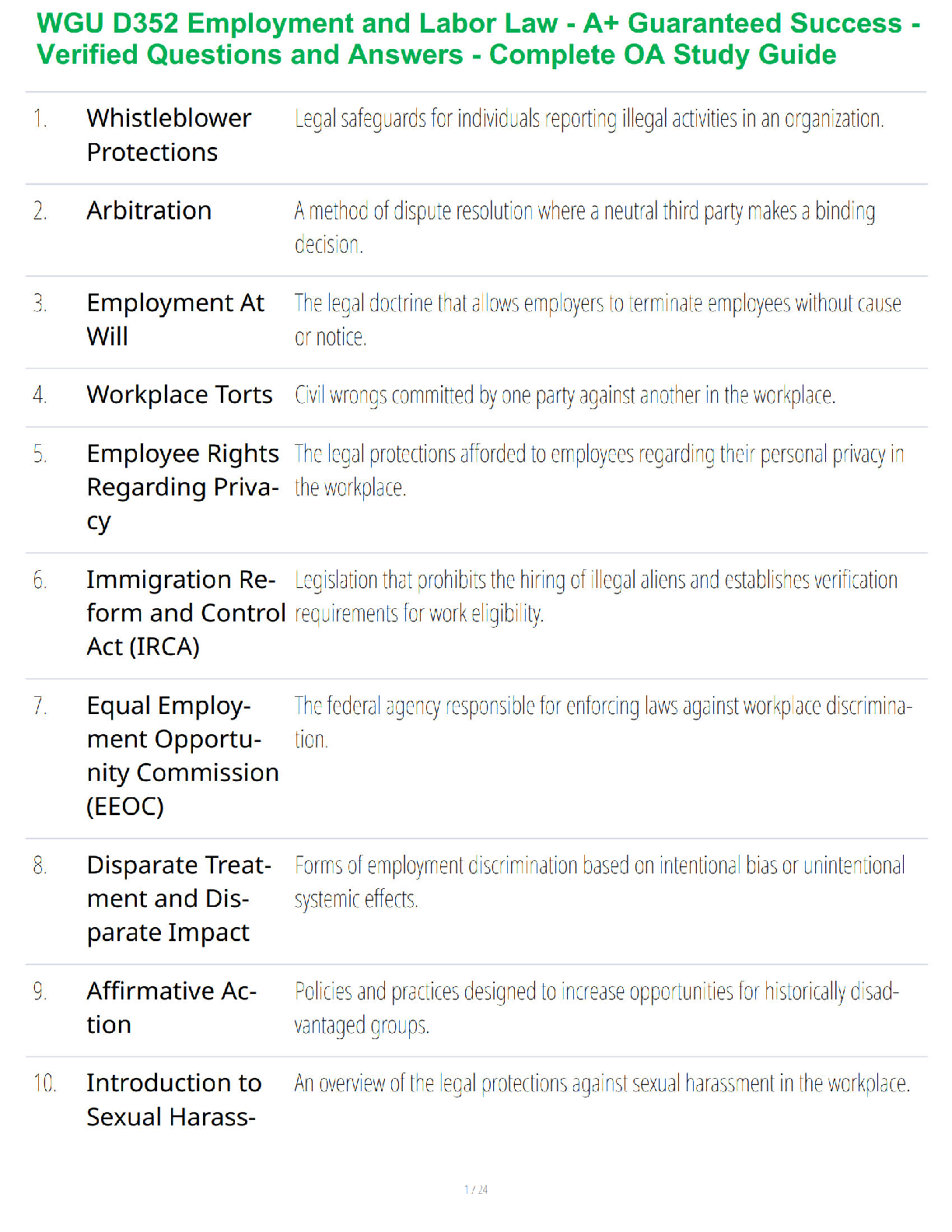
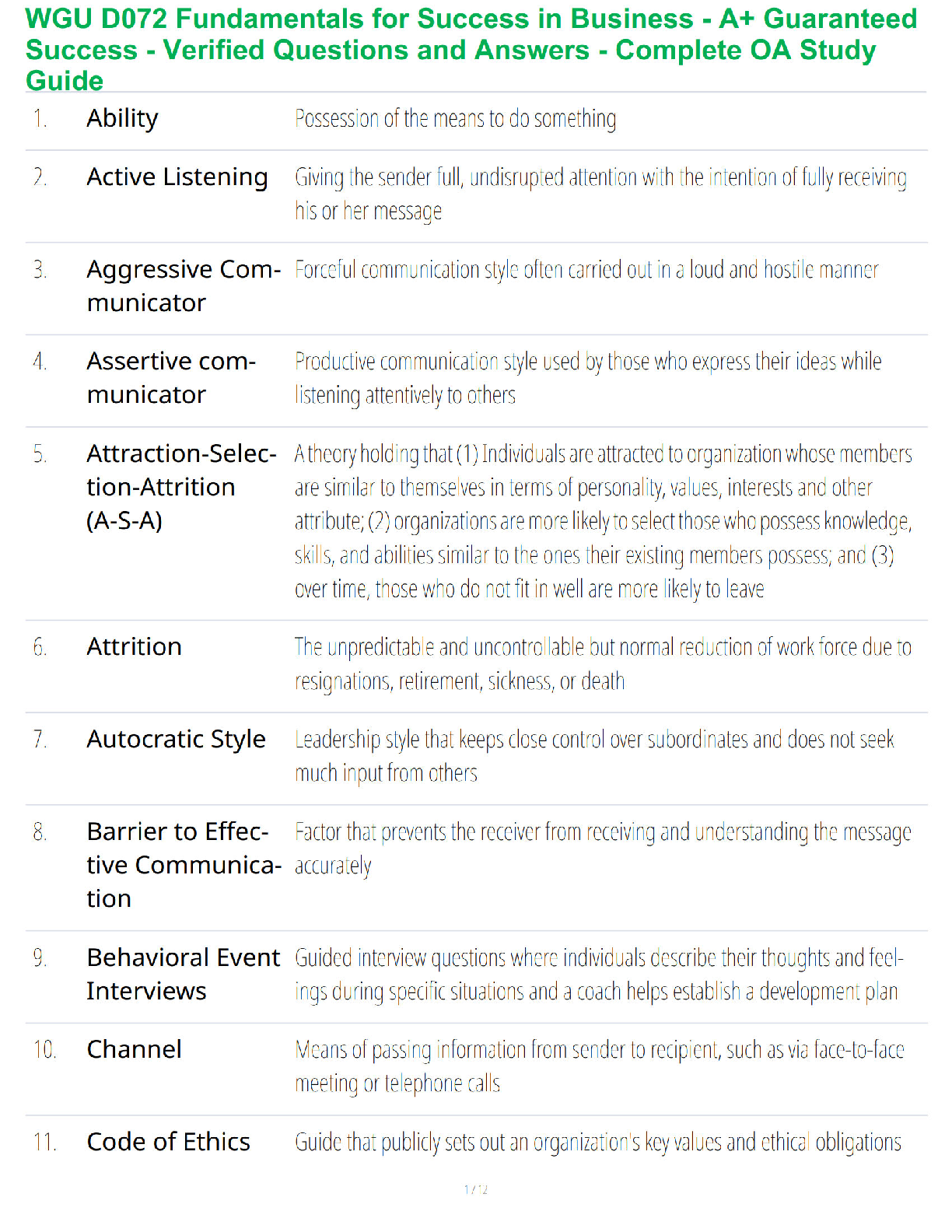
Q1. In an orthogonal cutting operation, the tool has a rake angle of 15°. The chip thickness before the cut is 0.30 mm and the cut yields a deformed chip thickness of 0.65 mm.
Cal
...
EML4321 Manufacturing Engineering HW-7
Q1. In an orthogonal cutting operation, the tool has a rake angle of 15°. The chip thickness before the cut is 0.30 mm and the cut yields a deformed chip thickness of 0.65 mm.
Calculate:
(a) The shear plane angle and
(b) The shear strain for the operation.
Q2. Which one of the four types of chip would be expected in a turning operation conducted at low cutting speed on a brittle work material?
Q3. Identify the two forces that can be measured in the orthogonal metal-cutting model:
Q4. According to the Merchant equation for shear angle, if all other factors remain the same, an increase in rake angle would have which of the following results (two best answers)?
Q5. Why is the maximum temperature in cutting is located at about the middle of the tool-chip interface? (Hint: Note that there are two principal sources of heat: the shear plane and the tool-chip interface.)
Q6. In a dry cutting operation using a tool with a 5° rake angle, the measured forces were cutting force Fc = 1330 N and thrust force Ft = 740 N. When a cutting fluid was used, these forces were Fc = 1200 N and Ft = 710 N. What is the change in the friction angle resulting from the use of a cutting fluid?
Q7. Draw a simple diagram of forces acting on a cutting tool in an orthogonal cutting and derive Eq. (8.25) on page 470 in the textbook.
Q8. Consider an orthogonal cutting operation using a tool with a rake angle of 5° and the coefficient of friction is 0.5. Using the Merchant equation for the shear angle, determine the percentage increase in chip thickness when the friction is doubled. Assume that the depth of cut and the rake angle are constant.
Q9. An orthogonal cutting operation on a steel workpiece is being carried out in which the depth of cut t0 = 0.13 mm, the cutting speed V = 2 m/s, the rake angle α = 5°, and the width of cut of w = 2.5 mm. It is observed that the chip thickness tc = 0.58 mm, the cutting force Fc = 890 N and the thrust force Ft = 600 N. Calculate the shear angle [deg], coefficient of friction µ, shear stress τ [MPa] and shear strain γ on the shear plane, chip velocity Vc [m/s], and shear velocity Vs [m/s], specific energies for friction uf [MNm/m3] and shear us [MNm/m3], and total specific energy ut [MNm/m3]. Do not use Equations [8.20] through [8.23] in the textbook.
Q10. Which of the following cutting conditions has the greater effect on mean temperature in turning on a lathe?
(a) Cutting speed
(b) Feed
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)