TRUE/FALSE
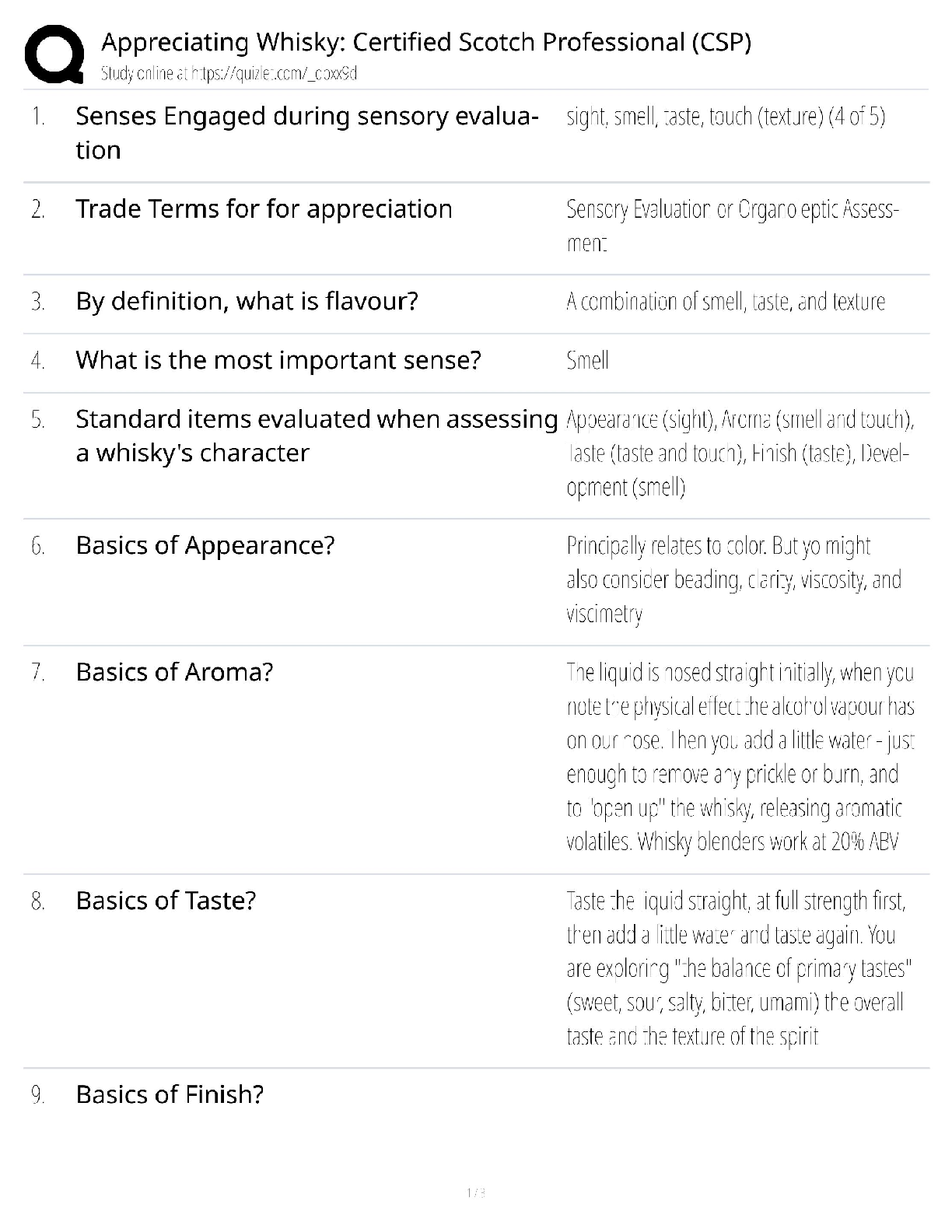
1. Effective managers learn to surface rather than avoid or suppress personal differences.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: Discover Knowledge
KEY: B
...
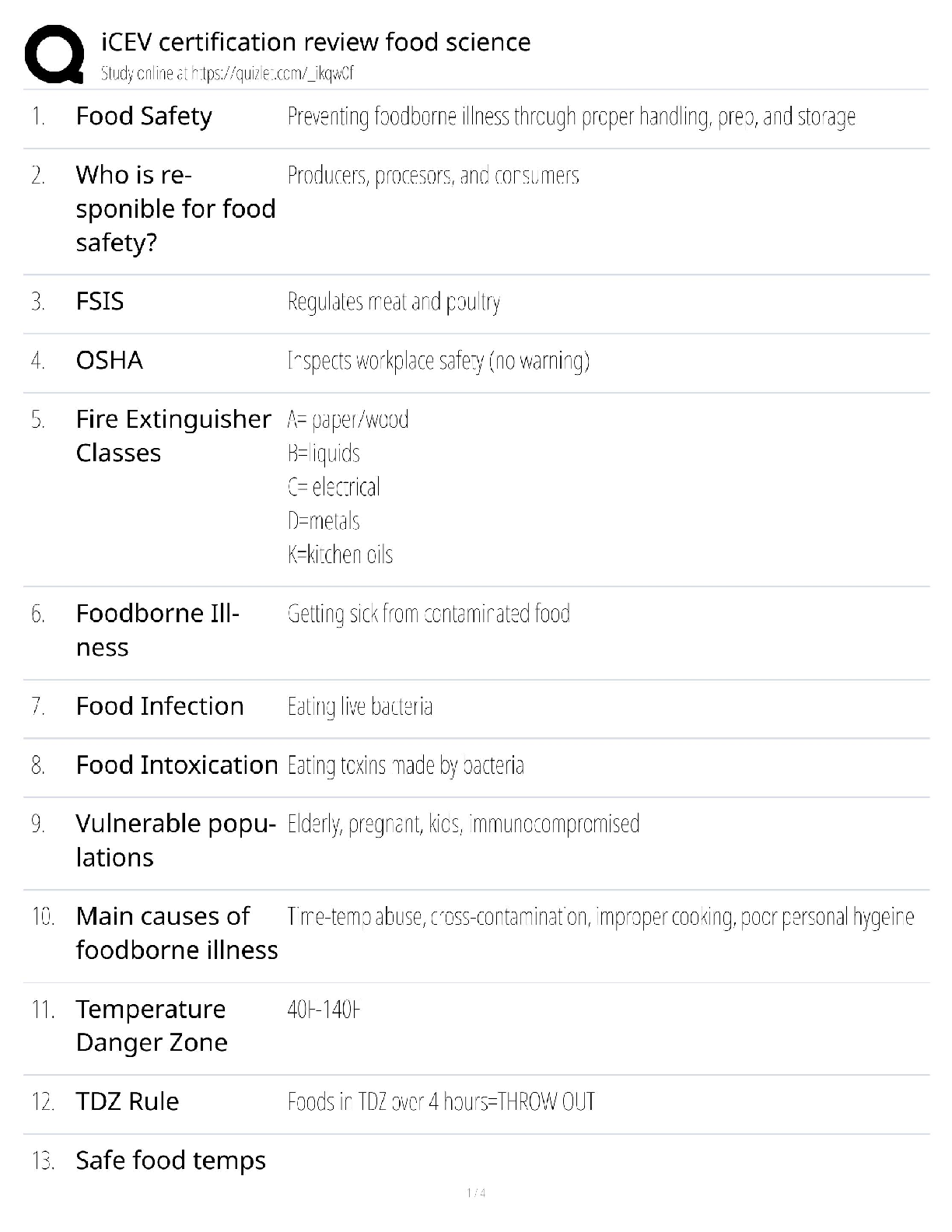
TRUE/FALSE
1. Effective managers learn to surface rather than avoid or suppress personal differences.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: Discover Knowledge
KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
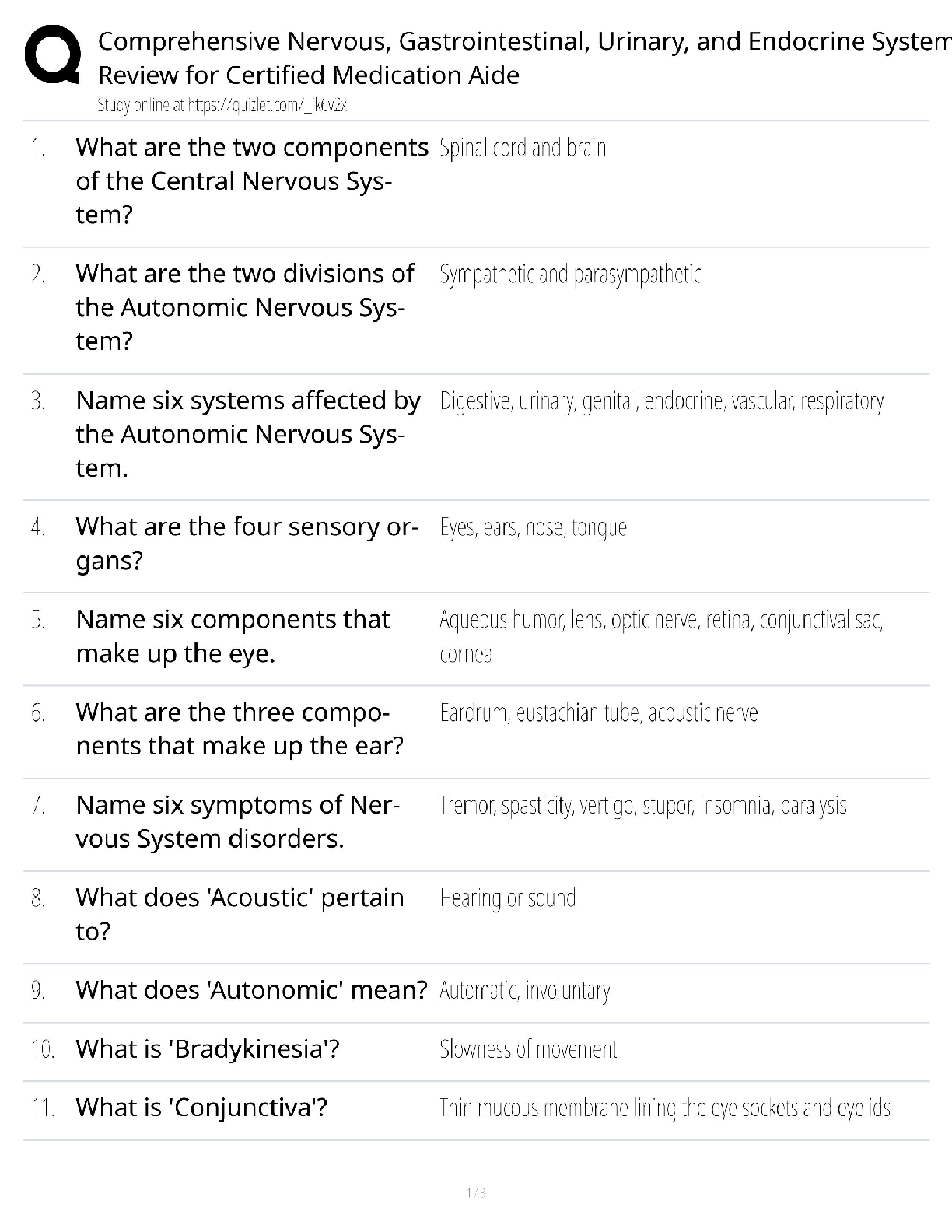
2. The manager only has the responsibility of disclosure when he engages people in a dialogue.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues
KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
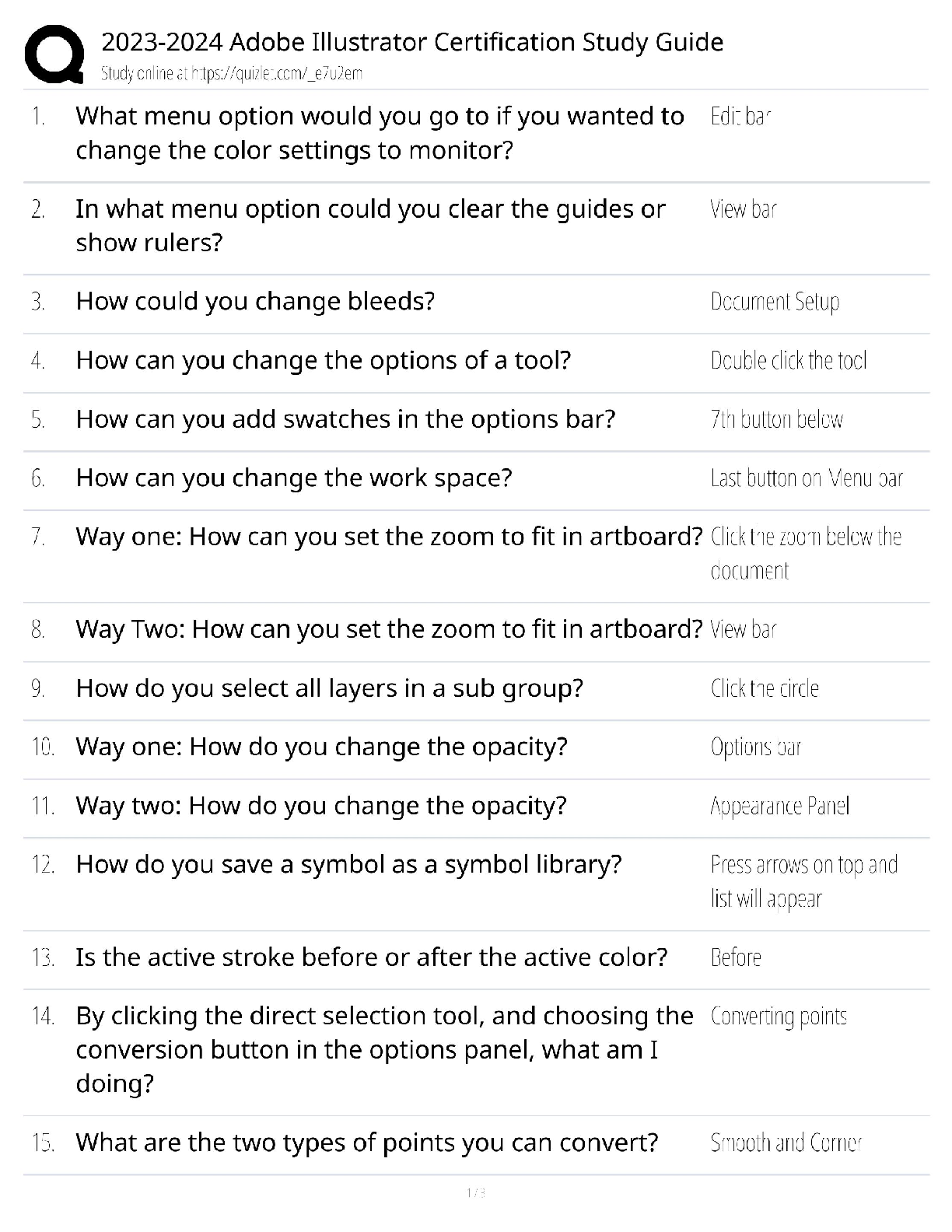
3. A conversation that is in disagreement can go one of two ways: debate/discussion or dialogue.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: Handling Difficult Conversations
KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
4. When you anticipate you will be engaging in a difficult conversation, the first thing you should do is prepare your argument.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations
KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
5. The ILETS model stands for: Introduce the topic, Listen to the other person, Empathize, Talk, Solve the Problem.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations
KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
6. When delivering bad news, you should follow the ILETS model by listening first and speaking second.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations
KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
7. Conflict refers to antagonistic interaction in which one party, in order to achieve its goals, will prevent or block the intentions or goals of another.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style?
KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
8. Bargaining is appropriate when an issue is trivial, when there is no chance of winning, or when a delay to gather more information is needed.
ANS: F PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style?
KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
9. When negotiating you should look for standards that may apply. For example, when buying a car you should look at the Kelly Blue Book.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements
KEY: Bloom's: Application
10. When a negotiator is inexperienced or feels intimidated by the other side, he or she tends to over-compromise.
ANS: T PTS: 1 DIF: Easy NAT: BUSPROG: Communication
LOC: DISC: Group Dynamics TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements
KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. The opening story talks about Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer at Microsoft. Their success depended on ____.
a. their intellect
b. the creativity of the upper level managers
c. their time management
d. the quality of communication among managers at the middle and upper levels
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Discover Knowledge KEY: Bloom's: Application
2. Which of the following forces work against positive relationships in organizations?
a. busyness c. the rush to get things done
b. distractions d. all of these
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Discover Knowledge KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
3. ____ explains the inability of groups to manage differences and achieve genuine agreement.
a. The NECX Paradox c. Pandora’s box
b. The Abilene Paradox d. The Disagreement Problem
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
4. Indeed, during meetings people may express ____ so they fit in and gain approval.
a. the opposite of their true opinion c. little opinion
b. their true opinion d. frustration
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
5. Travis is a manager at an aircraft engine repair company. There is a problem with one of the repairs that requires input from many team members. How should Travis solve the problem?
a. make the decision on his own
b. discuss with just 1 or 2 team members
c. email all the team members
d. call a meeting that involves robust dialogue
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Application
6. How do viewpoints look when robust dialogue is being used?
a. viewpoints lead in a straight line towards a decision
b. viewpoints wildly diverge then converge toward a decision
c. viewpoints circulate around to a decision
d. viewpoints converge then diverge
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
7. As a manager, which of the following should you do when engaging people in dialogue?
a. have people sit in a circle so they can be face-to-face
b. begin discussing the purpose of the dialogue
c. give each person a chance to speak without interruption
d. all of these
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
8. ___ during a dialogue means that everyone must be willing to say what is really on their minds about the subject.
a. Advocating c. Disclosure
b. Responsibility d. Inquiry
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
9. ___ during a robust dialogue means asking questions to deepen one’s understanding about what something means.
a. Advocating c. Disclosure
b. Responsibility d. Inquiry
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
10. Maxine, the shift supervisor, was upset that her team had finished 10 fewer assemblies than they were expected to finish during their shift. But before taking any action, she decided to first use inquiry, which meant she:
a. explored assumptions c. listened without defensiveness
b. listened deeply d. all of these
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Application
11. Veejay wanted to understand why so many people on his staff were running behind schedule when he felt they had sufficient time and resources to complete their projects. He called them together and asked them to explain what was happening, and then he deliberately stated conflicting opinions to push the team to discuss these varying viewpoints. Veejay was attempting to use _________ to fully understand the situation.
a. debate c. inquiry
b. dialogue d. disclosure
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Application
12. ___ requires that participants suspend their attachment to a particular point of view so that a deeper level of listening, synthesis, and meaning can emerge from the group.
a. Debate c. Inquiry
b. Dialogue d. Disclosure
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
13. A dialogue’s focus is on ____.
a. discussion c. argument rather than inquiry
b. debate d. inquiry rather than argument
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Use Robust Dialogue for Team Issues KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
14. Claudia is a manager at an architectural firm. She just gave an important project to a new employee, Justin. An experienced employee, Ayman, is mad that she didn’t give him the assignment. She did this because Ayman had previously complained about extra work. What should Claudia have done differently?
a. discussed Ayman’s complaints before she gave out the new assignment
b. given the assignment to Ayman
c. ignored Ayman’s complaints, just as she had done
d. none of these
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Handling Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Application
15. A difficult conversation can be defined as a discussion between two or more people where ___.
a. outcomes are important
b. viewpoints differ
c. emotions run high
d. all of these
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Handling Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
16. Which of the following is an example of a difficult conversation?
a. giving the boss comments about his behavior
b. discussing how an employee will complete a challenging assignment
c. discussing the game when you and your coworker root for different teams
d. all of these
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Handling Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Application
17. Beth’s performance has not been as good as it used to be lately, and her boss, Tamara, has made an appointment to discuss the situation with her. Prior to the appointment, Tamara writes down some examples, gathers some information, plans what to say, and calms herself with a few minutes of meditation. Why is Tamara doing these steps to prepare for this meeting?
a. It will put Tamara in the right frame of mind.
b. It guarantees that Beth will truly hear what Tamara is saying.
c. It will enable Tamara to use the ILETS model.
d. It will prevent Beth from getting upset during the meeting.
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Application
18. If you don’t prepare for a difficult conversation, you ___.
a. lose sleep
b. could end up with a combat mentality
c. could have free sharing of thoughts
d. all of these
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
19. Which of the following are included in the preparation phase of handing difficult conversations?
a. get in the right frame of mind c. seek first to understand
b. think learning, not combat d. all of these
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
20. The most important step of a difficult conversation is ___.
a. getting in the right frame of mind
b. using the ILETS model
c. seeking first to understand
d. for each person to truly hear the other
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
21. The example in the book about the Zen master and tea proves what point?
a. that you need to get into the right frame of mind
b. a person listening to you is like a tea cup, they can’t accept anymore ideas until they “empty their cup”
c. the Zen master likes tea
d. a person listening is like a tea cup that is half full: he can either be optimistic (half full) or pessimistic (half empty)
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Challenging
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Synthesis
22. When leading a crucial conversation, you can use a step-by-step technique called the ___ model.
a. ILATS c. ILETS
b. WEEZ d. MODELO
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
23. Another way of thinking about the “L” in the ILETS model would be:
a. introducing the topic
b. hearing what the other person is trying to say
c. feeling sympathy and understanding for the other person
d. sharing your opinions
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
24. ___ means being able to put yourself in other’s shoes, sense their emotions, and understand their perspective.
a. Talk c. Empathize
b. Professional intimacy d. Understand
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
25. If you’re having a difficult conversation, when is it possible to come to a solution?
a. when both parties know what the other party wants
b. when there is empathy
c. when both people have spoken
d. when you have asked the key questions
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
26. What is a good time and place to hold a conversation that you know will be difficult?
a. in your office when there is plenty of time
b. a neutral location when there is plenty of time
c. anytime or place is fine
d. at dinner when time is short
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
27. Which of the following is a conversation killer?
a. speaking your opinion as truth
b. acting like you’re right and the other person is wrong
c. saying “it’s your fault”
d. all of these
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
28. Suppose you have some bad news you have to deliver to your friend. After you empathize with him, you should ____.
a. listen c. share a personal experience
b. solve the problem d. all of these
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Application
29. How can you measure your success of delivering bad news?
a. by how much you compromise
b. by the other person’s understanding
c. by how much the other person thinks the decision can be reversed
d. by how long the conversation lasts
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: A Guide for Conducting Difficult Conversations KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
30. ____ refers to antagonistic interaction in which one party, in order to achieve its goals, will prevent or block the intentions or goals of another.
a. Team cohesiveness c. Conflict
b. Disagreement d. Anger
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style? KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
31. ____ refers to disagreements among people about the goals to be achieved or the tasks to be performed.
a. Task conflict c. Conflict
b. Relationship conflict d. Assertive conflict
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style? KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
32. ____ refers to interpersonal incompatibility that creates tension and personal animosity among people.
a. Task conflict c. Conflict
b. Relationship conflict d. Assertive conflict
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style? KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
33. The design team shares an open office in which all of their workstations are arranged around a central conference table in one big room. Because they are the creative talent in the company, many of the designers bring in toys, games, posters, and other items to inspire creativity. They work long hours, so there is often a lot of food, such as boxes of donuts and pizza, lying around. Most of the team members love their work environment, but Kerri hates what she calls the “disgusting mess.” This is an example of which type of conflict?
a. Task conflict c. Workplace conflict
b. Relationship conflict d. Assertive conflict
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style? KEY: Bloom's: Application
34. Malik is frustrated because his new shift supervisor, Hannah, has ignored his requests and scheduled him to work on Tuesday evening when he has a biology class. When he tries to discuss it with Hannah, she barks at him, “I don’t care about your classes. I need someone to work that night, and you’re it!” Hannah’s style could best be described as:
a. Dominating c. Bargaining
b. Avoiding d. Accommodating
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style? KEY: Bloom's: Application
35. The ___ style of handling interpersonal conflict can be described by the following attitude: “I tell others my ideas, seek out their ideas, and search for a mutually beneficial solution”
a. dominating c. avoiding
b. collaborating d. accommodating
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: What is Your Conflict Handling Style? KEY: Bloom's: Application
36. ___ is a formal process of discussion used to reach an agreement between parties in conflict.
a. Resolution c. Negotiation
b. Collaboration d. Accommodation
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
37. What is the number one way to achieve a successful negotiation?
a. planning c. being forceful
b. being nice d. setting your initial price high
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
38. When negotiating, what is the first thing you need to decide?
a. how much time you want to invest c. how much effort you want to invest
b. what is most important to you d. what is the minimum you will accept
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
39. The next best option is called ____.
a. negotiation standard (NS)
b. the alternative (A)
c. the best alternative to a negotiated agreement (BANTA)
d. the 2nd level negotiation (2NDLN)
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
40. Let’s say you are negotiating for a new car. You do not know the dealer personally and will probably never talk to him again after the sale. What approach to the negotiation should you have?
a. BANTA
b. consider the relationship you have with the dealer
c. compromise with the dealer
d. fight hard for the deal you want because the financial outcome is most important
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Application
41. You have been offered a new job you really want, and you are now negotiating your compensation package. You believe the hiring manager is being honest when she says she simply cannot pay the full salary that you’ve asked for. So instead, you ask if she’d be willing to give you three extra paid vacation days if you agree to the lower salary she has offered. What approach are you taking?
a. integrative c. BANTA
b. distributive d. win-lose
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Application
42. When the ___ approach is used, one party gets something he wants and the other party gives up something he has.
a. integrative c. BANTA
b. distributive d. win-lose
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
43. What negotiation approach is described by the following situation: Sean has some extra cash and he wants to buy a new car. Sarah is desperate for cash so she puts her car up for sale, and Sean exploits this to get a great price.
a. integrative c. BANTA
b. distributive d. win-lose
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Application
44. Which approach is the preferred style of negotiation?
a. integrative c. BANTA
b. distributive d. win-lose
ANS: B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
45. It is generally best to ___ when it is time to consider offers.
a. make the first offer c. make a high initial offer
b. make mutual offers d. let the other party go first
ANS: D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
46. It is always better to concentrate on you and the other party’s ____.
a. stated position c. underlying interests
b. mutual benefit d. time management
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Comprehension
47. In a negotiation, you should focus on ____.
a. why the other side wants what it wants
b. the price the other side wants
c. the amount to other side wants
d. the characteristics the other side wants
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Challenging
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Synthesis
48. How can you learn more about your opponent’s position?
a. asking questions c. both ask questions and be quiet
b. being quiet d. being forceful
ANS: C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Analysis
49. When a negotiator is inexperienced or feels intimidated by the other side, he tends to ____.
a. over-compromise c. be quiet
b. under-compromise d. be forceful
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
50. When people get angry or upset during a negotiation, they ____.
a. typically get over it quickly c. become more quiet
b. ask more questions d. are more arrogant
ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate
NAT: BUSPROG: Reflective Thinking LOC: DISC: Leadership Principles
TOP: Negotiation Strategies for Reaching Agreements KEY: Bloom's: Knowledge
SHORT ANSWER
1. If you own a company and there is a conflict among a few top managers, how should you deal with this?
2. What is the difference between robust dialogue and typical group decision making?
3. Why are skills for team dialogue and difficult conversations among individuals so important for managers?
4. When having a negotiation, what is the key step and why?
ESSAY
1. Explain the two routes a conversation can take when there is a lack of understanding or disagreement.
2. Explain the five steps of the ILETS model for conducting difficult conversations and why they’re each important.
3. Explain the five interpersonal conflict handling styles with regards to cooperativeness and assertiveness. Give a situation where each one should be used.
[Show More]











.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)