Economics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Questions and Answers > Ohio University, Main Campus ECON 305 Final Study Guide: CONTAINS: Game Theo (All)
Questions and Answers > Ohio University, Main Campus ECON 305 Final Study Guide: CONTAINS: Game Theory and Business Strategy (1 – 49), Strategies Over Time, Strategies Over Time, Managerial Decision Making Under Uncertainty (87 – 150), AND Asymmetric Information (151 - )
Document Content and Description Below
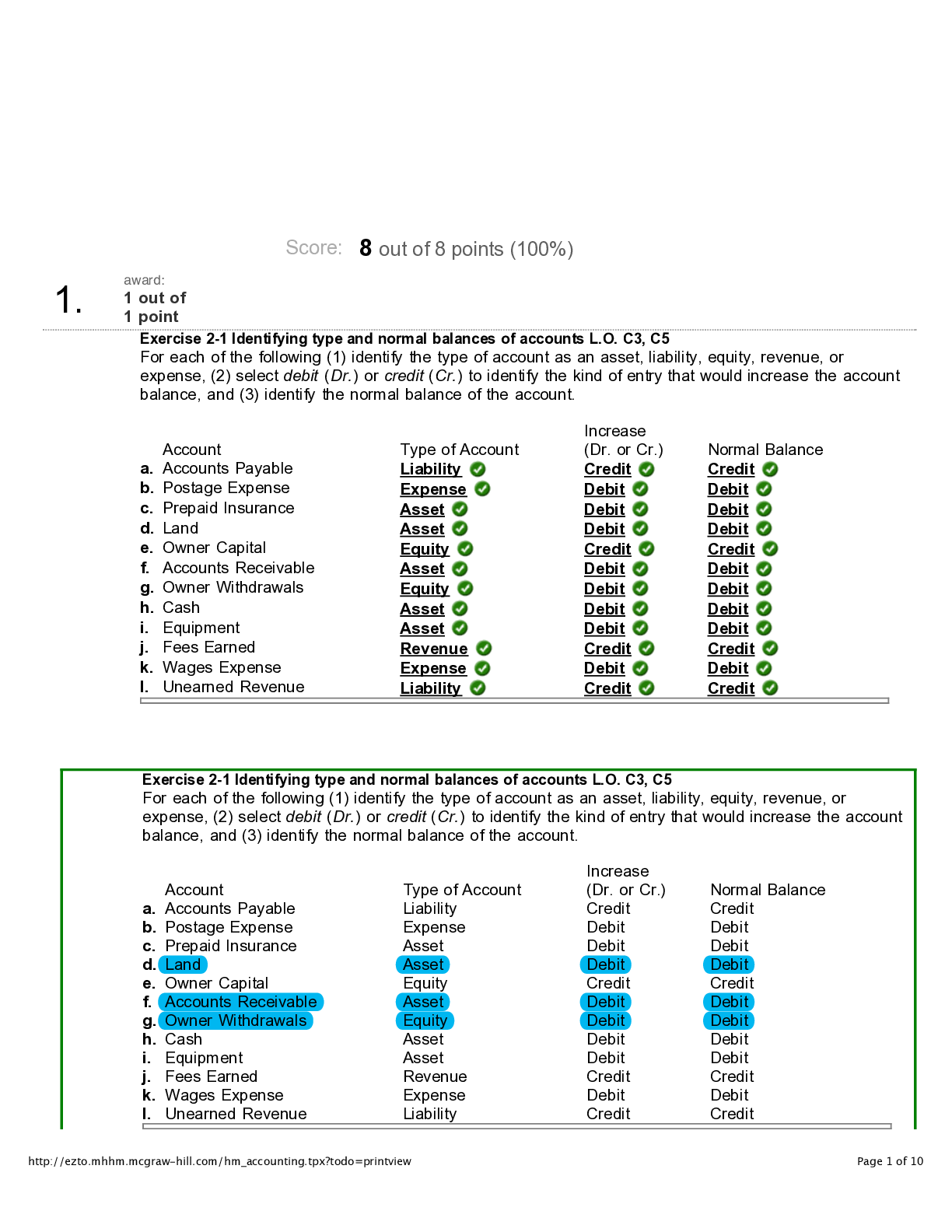
Ohio University, Main Campus ECON 305 Final Study Guide Sample Questions for the Final Exam For: Lecture 9 Chapter 12 – Game Theory and Business Strategy (1 – 49) Lecture 10: Chapter 12 – St... rategies Over Time Lecture 11: Chapter 14 – Managerial Decision Making Under Uncertainty (87 – 150) Lecture 12: Chapter 15 – Asymmetric Information (151 - ) SAMPLE QUESTIONS 1. Common knowledge in game theory A. is information known by all players. B. is required for static games. C. does not impact the outcome of the game, since everyone has the information. D. is information known by most people in a country. 2. Which of the following is a simultaneous decision game? A. rock-paper-scissors (Roshambo) C. chess B. tic-tac-toe D. poker 3. A dominated strategy A. exists when one firm is weaker than another. B. is a characteristic of games with multiple Nash equilibria. C. only occurs in a mixed strategy scenario. D. is one that is never used by a rational actor. 4. A dominant strategy can best be described as A. a strategy that leaves every player in a game better off. B. a strategy taken by a dominant firm. C. a strategy that is optimal for a player no matter what an opponent does. D. the strategy taken by a firm in order to dominate its rivals. 5. A payoff matrix A. shows the payoffs to each firm for each possible outcome. B. is optional in game theory. C. details the actions each firm takes. D. shows the payoffs (i.e. bribes) required to government officials for firms undertaking specific actions. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 6. When both firms have dominant strategies A. there is a prisoners' dilemma. B. the outcome is called a dominant strategy solution. C. there are multiple Nash equilibria. D. joint profits are maximized. 7. The term prisoners' dilemma refers to a game in which A. the payoff from both players playing their dominant strategies is the same for each player. B. the payoff from both players playing their dominant strategies is not the highest payoff possible. C. there are no Nash equilibria. D. there are no dominant strategies. 8. A Nash equilibrium occurs when A. the efficient allocation of resources is achieved by setting marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. B. players choose their best strategy given the strategies chosen by others. C. a monopolist is forced to produce the efficient level of output. D. oligopolists cooperate with each other. 9. The figure below shows the payoff to two airlines, A and B, of serving a particular route. If the two airlines must decide simultaneously, which one of the following statements is TRUE? A. Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium. B. Since firm B's decision is unpredictable, firm A's decision is unpredictable. C. Firm B will not enter because it knows firm A will. D. Since firm B has no dominant strategy, its decision is unpredictable. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 10. The above figure shows the payoff to two airlines, A and B, of serving a particular route. If the two airlines must decide simultaneously, what happens if the government imposes a $20 per firm tax on firms that service this route? A. Neither firm entering is a Nash equilibrium. B. Only firm A will enter. C. Neither firm has a dominant strategy. D. Not entering is a dominant strategy for both firms. 11. The figure below shows a payoff matrix for two firms, A and B, that must choose between selling basic computers or advanced computers. Firm B's dominant strategy A. is to make basic computers. B. is to adopt firm A's strategy. C. is to make advanced computers. D. does not exist in this game. 12. Which of the following statements is TRUE about a non-cooperative game? A. When two players each have a dominant strategy, joint profits may not be maximized. B. When players use their best responses, joint profits are maximized. C. When two players each have a dominant strategy, joint profits are maximized. D. When two players each have a dominant strategy, joint profits may is never maximized. 13. Your economics professor has decided that your class will not be graded on a curve but on an absolute scale. Therefore, it is possible for every student in the class to get an "A." Your grade will not depend in any way on your classmates' performance. Based on this information, you decide that you should study economics three hours each day, regardless of what your classmates do. In the language of game theory, your decision to study three hours each day is: A. a minimax strategy. C. a dominant strategy. B. a maximin strategy. D. a Prisoner's dilemma. | 14. | Which of the following is true for the game in Scenario 3? Scenario 3 Consider the following game: A. Neither company has a dominant strategy. B. Zport's dominant strategy is the sun roof. C. Zport's dominant strategy is the low-profile tires. D. Moto's dominant strategy is the free maintenance. 15. In the game in Scenario 3, equilibrium Scenario 3 Consider the following game: A. is for Moto to offer free maintenance and Zport to offer a sunroof. B. is for Moto to offer a CD changer and Zport to offer low-profile tires. C. is for Moto to offer free maintenance and Zport to offer low-profile tires. D. does not exist in pure strategies. 16. In the game in Scenario 6, what is the Nash equilibrium? Scenario 6 Consider the following game: Payoffs are in millions of dollars. A. The strategy pair associated with -$.5, -$.5. B. The strategy pair associated with $1, -$1. C. The strategy pair associated with $2, -$.5. D. The strategy pair associated with -$100, -$1. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 17. How many Nash equilibria are there in this payoff matrix? A. 1 C. 2 B. 4 D. 3 Ø 18. If player 1 has a dominant strategy, then player 2 A. must also have a dominant strategy. B. will not be able to reach an optimal solution to the game. C. may or may not have a dominant strategy. D. will block this dominant strategy and force player 1 to another strategy. 19. In a two-player game in which each player has four options, how many outcomes can there be? A. 16 C. 8 B. 64 D. 4 Sample Questions for the Final Exam 20. Refer to Figure 13-4. Which of the following is true? Two rival oligopolists in the athletic supplements industry, the Power Fuel Company and the Brawny Juice Company, have to decide on their pricing strategy. Each can choose either a high price or a low price. Figure13-4 shows he payoff matrix which reports the profits that each firm can expect to earn, depending on the pricing strategy that each adopts. Use the Figure to answer the following question(s). Figure 13-4 A. Power Fuel does not have a dominant strategy. B. Brawny Juice does not have a dominant strategy. C. Brawny Juice's dominant strategy is to select a high price. D. Power Fuel's dominant strategy is to select a low price. Ø 21. Refer to Figure 13-2. Ming and Henri each run one of two dry cleaning facilities in the town of Scaraby. Both are considering offering free pickup and delivery services. Figure 13-2 below shows he payoff matrix containing the expected quarterly profits for each firm. Use this Figure to answer the following question(s). Does Henri have a dominant strategy? If yes, what is it? A. No, he does not a dominant strategy - his best outcome depends on what Ming does. B. Yes, he has a dominant strategy and it is to offer free pickup and delivery. C. Yes, he has a dominant strategy and it is not to offer free pickup and delivery. D. No, he does not a dominant strategy - his strategies are all dominated by Ming’s. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 22. Refer to Figure 13-3. There are two mobile home manufacturers in Nevada, Sturdy Homes (S) and My Haven (M). Sturdy Homes has been in the market for a long time and must now compete with newcomer, My Haven. Suppose that Sturdy Homes believes that My Haven will match any price it sets. Use Figure 13-3 to answer the following question(s) and assume throughout that Sturdy Homes believes that My Haven will match any price it sets. Figure 13-3 What price will My Haven select after Sturdy Homes sets its price at $10,000 and what is My Haven's expected profit? A. price = $8,000; expected profit = $4 million B. price = $8,000; expected profit = $6 million C. price = $10,000; expected profit = $5 million D. price = $12,000; expected profit = $3 million Ø 23. Communication between players prior to the start of a game that does NOT affect the payoffs is called A. a binding verbal contract. C. pareto efficient. B. ineffective bargaining. D. cheap talk. 24. "Cheap talk" is considered cheap because A. firms avoid the costs of hiring lawyers. B. a firm can say anything, but may actually do something different. C. communications via phone or email these days has a cost that is close to zero. D. the cost of talking is far outweighed by the gains to be made in coordinating efforts. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 25. Not all games with two or more Nash equilibria can be solved with pre-play communication because A. cheap talk may be illegal under anti-trust laws. B. if there's an incentive for one or more players to lie, then cheap talk lacks credibility. C. pareto criterion might not be defined. D. Both A and B 26. When firms select the solution that is better for all parties, the ________ is satisfied. A. Pareto Criterion C. Nash equilibrium condition B. pure strategy requirement D. coordination game requirement 27. A mixed strategy may A. lead identical firms to choose different actions. B. be part of a Nash equilibrium. C. be a set of probabilities of selecting each possible action. D. All of the above. 28. When neither player has a dominant strategy A. at least one Nash equilibrium exists. B. the game cannot be analyzed. C. no Nash equilibrium exists. D. game theory will not provide information. 29. A strategy in which a player uses probabilities to decide which strategy to use is called a A. mixed strategy. C. pure strategy. B. Pareto strategy. D. coin flip strategy. 30. If a game has a pure strategy Nash equilibrium then A. it does not have a mixed strategy equilibrium. B. it might also have a mixed strategy equilibrium. C. no player has a dominant strategy. D. at least one player has a dominant strategy. 31. A maximin strategy A. involves a random choice between two strategies, one which maximizes potential gain and one which minimizes potential loss. B. maximizes the gain of one player, but minimizes the gain of the opponent. C. maximizes the minimum gain that can be earned. D. minimizes the maximum gain that can be earned. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 32. Andre Agassi, a star tennis player, is playing the number one player in the world, Roger Federer. Before the match, Agassi decided that he would serve 20 percent of his serves to Federer's backhand, 30 percent of his serves to Federer's forehand, and 50 percent of his serves straight at Federer. In the language of game theory, this is known as: A. a mixed strategy. C. a maximin strategy. B. a dominant strategy. D. a pure strategy. 33. In a Nash equilibrium, A. each player has a dominant strategy. B. players may or may not have dominant strategies. C. no players have a dominant strategy. D. the player with the dominant strategy will win. E. at least one player has a dominant strategy. 34. In the example of coordination problems between Google and Motorola Mobility, one method to solve the problems was A. to undertake a merger or acquisition. B. form a joint venture. C. for one firm to subcontract with the other. D. All of the above. 35. If a game contains private information, then A. players will decide not to play the game. B. firms will engage in cheap talk to coordinate their actions. C. third-party negotiations are necessary to resolve the information gap. D. the game's outcome is affected. 36. If decision makers have limited ability to calculate profits from all possible combinations of options, they are said to have A. bounded rationality. C. Pareto inefficiency. B. a maximin problem. D. dementia. 37. A maximin strategy A. maximizes the minimum joint profits of the players. B. minimizes the maximum payoff. C. maximizes the payoff of one player, but minimizes the payoff of the other. D. maximizes the minimum payoff. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 38. If you take a maximin strategy A. then both players are doing the best they can given the payoffs in the game. B. you are irrational according to economic definition. C. you are getting the best possible outcome given that the other player does the thing that's worst for you. D. you are ensuring that the other player gets the worst possible outcome. 39. In the above table, if the players do not have complete information on their rival's payoffs and use a maximin strategy A. firm A produces a High Quality product and firm B produces a Low Quality product. B. the equilibrium choice is the same as using a regular, best response strategy. C. firm A produces a Low Quality product and firm B produces a High Quality product. D. both firms produce a High Quality product. 40. In a bargaining game, players A. are forced to negotiate, as in a mediation. B. voluntarily negotiate. C. are engaging in illegal activity. D. have to share the surplus equally. 41. A Nash bargaining solution A. is derived from a Nash equilibrium. B. gives a solution in both cooperative and non-cooperative games. C. is not the same as a Nash equilibrium. D. None of the above. 42. A disagreement point is A. the outcome that occurs if there is no agreement in a bargain. B. the point in a negotiation where the players cannot reach an agreement. C. a way of keeping score in a negotiation. D. an item of contention between the two bargaining players. Sample Questions for the Final Exam 43. One possible source of inefficiency in bargaining is A. that there are multiple Nash equilibria. B. that the bargaining process takes time. C. bounded irrationality. D. that the Nash product may be indeterminant. 44. In the reality TV show Storage Wars, people bid on the contents of repossessed storage units without being able to evaluate the contents. This is an example of a ________ auction. A. private value C. second-price B. common value D. Dutch 45. In an English auction A. the winning bidder pays the amount bid by the person with the second highest bid. B. the price increases until nobody else will raise the bid. C. bidders put their bids in a sealed envelope. D. the price decreases until someone bids. 46. The individual with the highest valuation of the good will win in which of the following auctions? A. Sealed Bid Auction C. Dutch Auction B. English Auction D. All of the above. 47. In a first-price sealed-bid auction, the winner pays A. its own, highest bid. C. the amount bid by the runner-up. B. the common value. D. the average of the three highest bids. 48. In a second-price auction, the winner pays A. the average of the top two bids. B. the amount bid by the runner-up. C. the second-to-last bid he/she made. D. the winning bid minus 1 cent. 49. A private auction is an auction in which A. individuals have their own valuation of the good but don't know everyone else's. B. only one good is auctioned off. C. individuals know their own value of the good and everyone else's valuation, too. D. many auctions are auctioned off at the same time. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 119 pages
.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 06, 2022
Number of pages
119
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
59



.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)