*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > CRT/RRT (NBRC) | EXAM REVIEW 100% Correct Questions and Answers (All)
CRT/RRT (NBRC) | EXAM REVIEW 100% Correct Questions and Answers
Document Content and Description Below
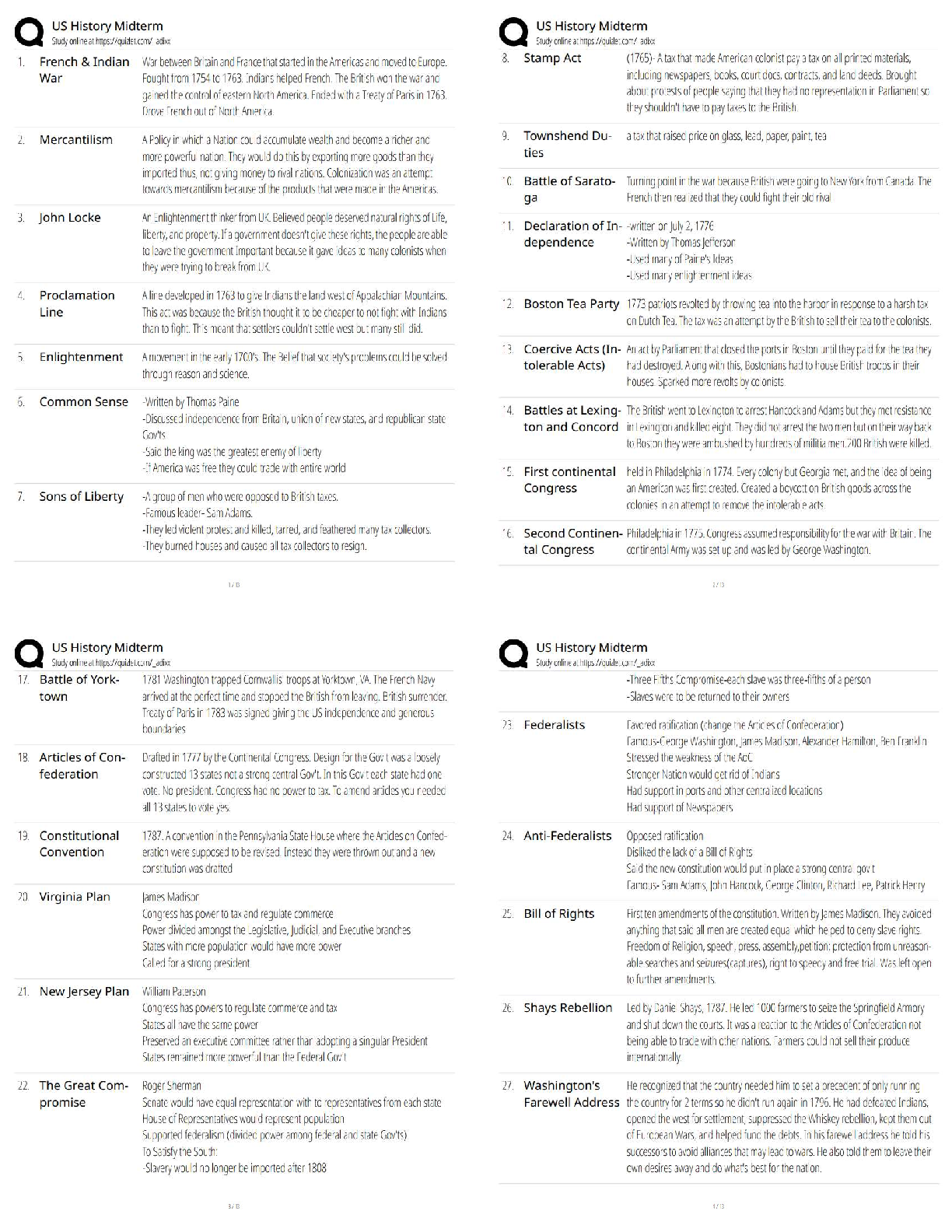
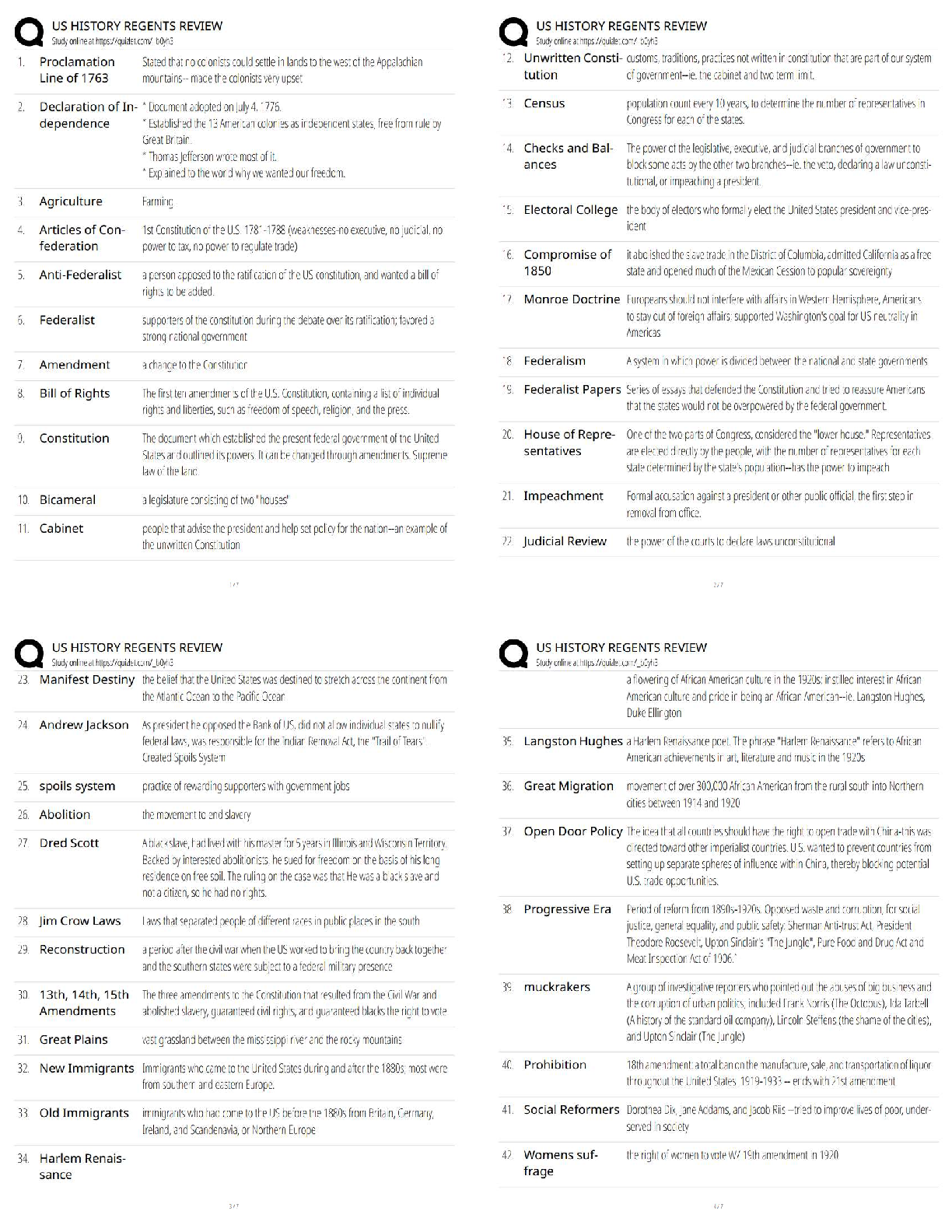
FULL EXAM REVIEW CRT/RRT (NBRC) 100% Correct Questions and Answers Ascites - accumulation of fluid in the abdomen caused by LIVER FAILURE Venous distention - -occurs with CHF -seen with obstruc ... tive patients (seen in exhalation phase) Capillary refill - -indication of peripheral circulation -Normal < 3 seconds Jaundice skin color - -increase in bilirubin. -mostly in face and trunk Bradypnea (oligopnea) - -decreased respiratory rate (<12bpm) variable depth and irregular rhythm Hyperpnea - -increased rate, depth, with regular rhythm Cheyne-Stokes - -gradually increasing then decreasing rate and depth in a cycle lasting from 30 - 180 secs, with apnea up to 60 secs -increased ICP, meningitis, overdose Biots - -increased rate and depth with irregular periods of apnea -CNS problem, head/brain injury Kussmaul's - -increased rate, depth, irregular rhythm, breathing sounds labored -Raspy voice Apneustic - prolonged gasping inspiration followed by extremely short, insufficient expiration -respiratory center problems, trauma, tumor cachectic - muscle atrophy/loss of muscle tone retractions - -chest moves inward during inspiratory efforts instead of outward -blocked airway in adults = INTUBATE -RDS in infants Character of cough - -dry, non-productive cough may indicate tumor in the lungs or asthma -productive cough may indicate infection evidence of difficult airway - -short receding mandible (chin) -enlarged tongue (macroglossia) -bull neck -limited neck range-of-motion pulsus paradoxus - -pulse/blood pressure varies with respiration. may indicate severe air trapping (status asthmaticus or cardiac tamponade) tactile fremitus - -vibrations felt by hand on chest wall -vocal fremitus: voice vibrations on the chest wall -pleural rub fremitus: grating sensation due to roughened pleural spaces -Rhonchial fremitus(palpable rhonchi): secretions in airways Crepitus - -bubbles of air under skin that can be palpated and indicates subcutaneous emphysema Resonant percussion - -hollow sound -normal lungs Flat percussion - -heard over sternum, muscles, or areas of atelectasis Dull percussion - -heard over fluid-filled organs such as heart or liver (thudding) -pleural effusion or pneumonia Tympanic percussion - -heard over air-filled stomach. -drum-like sound and when heard over lung = increased volume Hyperresonant - -found where pneumothorax or emphysema is present. -booming sound vesicular breath sounds - normal sounds in lungs bronchial breath sounds - -normal sounds over airways. -breath sounds over lungs indicate LUNG CONSOLIDATION Egophony - -patient instructed to say E and sounds like A. -lung consolidation Bronchophony / whisphered pectoriloquy - -increased intensity or transmission of the spoken voice and indicate CONSOLIDATION or PNEUMONIA -increase in spoken voice = consolidation -decrease in spoken voice = obstructon, pneumo, emphysema Rales - -crackles -secretions/fluid [Show More]
Last updated: 1 year ago
Preview 5 out of 33 pages

Loading document previews ...
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

TMC Practice Exam B Kettering 160 Question Mock Board Exam , TMC Practice Exam A and B, TMC practice exam, NBRC Mock TMC, 188 NBRC TMC Review Exam, TMC Mechanical Ventilation, FULL EXAM REVIEW CRT/RRT (NBRC), RRT EXAM , (A Graded) Questions and answers (with complete solution)
TMC Practice Exam B Kettering 160 Question Mock Board Exam Answered Updated for class of Fall 2022 TMC Practice Exam A Updated 2022 (Graded A+) TMC practice exam Updated 2022 (Graded A+) TMC...
By Professor Lynne 3 years ago
$16
10
Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 09, 2022
Number of pages
33
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 09, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
372