Health Care > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Florida Atlantic University PCB 3063 Genetics Exam 2. 50 MCQ. (All)
Florida Atlantic University PCB 3063 Genetics Exam 2. 50 MCQ.
Document Content and Description Below
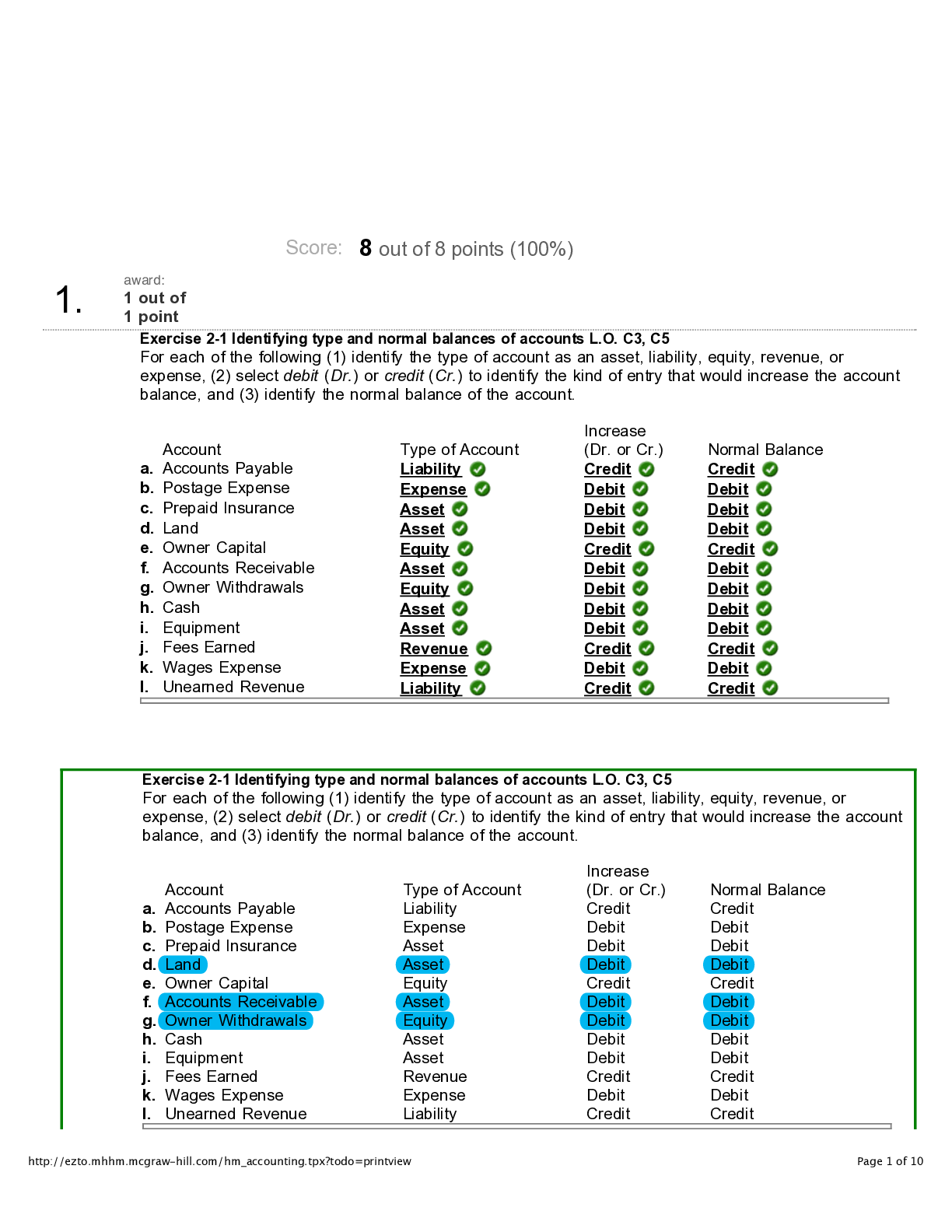
Genetics Exam 2 1. The maximum recombination frequency between two genes is A. 1% B. 100% C. 50% D. 25% E. 10% 2. Jr. Scientist has discovered a new plant species. Somatic cells from this plant... have 25 pairs of chromosomes. A very closely related species that is known to be diploid has 10 pairs of chromosomes. The new plant species is most likely __________. A. Pentaploid B. Monoploid C. Hexaploid D. Triploid E. None of the above 3. Non-viable gametes obtained from a meiotic cell that is heterozygous for a pericentric inversion result from A. Abnormal pairing of the affected chromosomes in meiosis. B. Abnormal chromosome pairing during mitosis. C. Unequal crossing over in mitosis. D. Duplication and deletion of DNA sequences due to crossing-over within the inversion. E. Spontaneous loss of the inverted portion of the chromosome. 4. The ratio of the number of observed double crossovers divided by the expected number of double crossovers is the A. Frequency of recombination B. Resistance level C. Coefficient of selection D. Coefficient of coincidence E. Interference level 5. Variations in chromosome structure can lead to which of the following? A. Evolution of new species B. The production of abnormal offspring C. Changes in the phenotype of an organism D. Variations in chromosome structure rarely have a significant effect on either the genotype or phenotype of the individual. E. Select this answer if more than one of the above choices are correct. 6. How could Jr. Scientist determine which of three linked loci is the middle locus from the progeny of a three-point testcross? A. Compare the two double crossover phenotypes with the two nonrecombinant phenotypes. B. Compare the two single crossover phenotypes. C. Compare the two double crossover phenotypes with the two single crossover phenotypes. D. Compare the two nonrecombinant phenotypes with the two single crossover phenotypes. E. Compare the two phenotypes from one single crossover to the two phenotypes of the second crossover. 7. If the sequence of one strand of DNA is 5’ AGCTAG 3’, the sequence of the complementary strand would be A. 5’ AGCTAG 3’ B. 5’ CTAGCT 3’ C. 5’ GATCGA 3’ D. 5’ GCTAGC 3’ E. 5’ TCGATC 3’ Use the following information for the next four questions. The genes curved (c, curved wings) and plexus (px, extra wing veins) are linked on the second chromosome of Drosophila. In a cross of a female who is heterozygous for al three genes with a male having the recessive phenotype for all three genes, the following progeny were counted. cn c px / cn c px 295 cn c + / cn c px 125 + + px / cn c px 120 cn + px / cn c px 10 + c px / cn c px 85 + c + / cn c px 15 + + + / cn c px 270 cn + + / cn c px 80 Total 1,000 8. The genotypes of the nonrecombinant progeny are A. cn c px / cn c px and + + px / cn c px B. cn c px / cn c px and cn + + / cn c px C. + + + / cn c px and cn c px / cn c px D. cn + px / cn c px and + c + / cn c px E. None of the above 9. The genotypes of the double crossover progeny are A. cn + px / cn c px and + c + / cn c px B. + + + / cn c px and cn c px / cn c px C. cn c px / cn c px and + + px / cn c px D. cn c px / cn c px and cn + + / cn c px E. None of the above 10. The gene order is A. cn – c – px B. c – cn – px C. px – c – cn D. Either answer A or answer C. The data does not distinguish between the two possibilities. E. None of the above is correct. 11. The map distance between px and cn is A. 16.5 cM B. 24.5 cM C. 46.0 cM D. 19.0 cM E. 27.0 cM Use the pedigree below for the next question 12. If the pedigree shown above is for an autosomal recessive characteristic, which individuals are definitely heterozygous? A. I-1, I-2, I-4, III-1 B. II-2, II-4, II-5, II-3 C. I-1, I-2, II-2, II-4, and II-5 D. I-1, I-2, II-4, II-5, III-1 E. None of the above because the pedigree is NOT consistent with an autosomal recessive trait. 13. Griffith discovered the phenomenon of transformation in 1928. In his experiments, non-infectious R type strains of S. pneumoniae became infectious following uptake of DNA from S type bacteria because A. They acquired the proteins needed for their capsule by transformation. B. They were able to make capsule protein by expression of the gene that they acquired by transformation. C. They were not easily detected by the immune system of the mouse. D. Of their susceptibility to antibiotics. E. None of the above. 14. In Drosophila, the two genes p and m are so tightly linked on an autosome that crossing-over between the genes has never been observed. If a double heterozygote with the alleles for these two genes in the trans configuration is mated with a strain that is homozygous recessive for both genes, then A. All the progeny will be p m+ / p m. B. All progeny will be p+ m+ / p m. C. 50% of the progeny will be p+ m / p m and 50% will be p m+ / p m. D. Cannot be answered without additional information. E. None of the above. 15. Assume a mouse that is heterozygous for genes A and B (that is, Aa and Bb) is used in a testcross mating. What percentage of each genotype would be expected among the offspring if these two linked genes are 10 map units apart and the heterozygote has the dominant alleles on one chromosome and the recessive alleles on the other? A. 45% of the offspring will exhibit A and b, 45% will exhibit a and B, 5% will exhibit A and B, and 5% will exhibit a and b. B. 25% of each possible combination of traits: A and B, A and b, a and B, and a and b. C. 40% of the offspring will exhibit A and B, 40% will exhibit a and b, 10% will exhibit A and b, and 10% will exhibit a and B. D. 45% of the offspring will exhibit A and B, 45% will exhibit a and b, 5% will exhibit A and b, and 5% will exhibit a and B. E. 50% of the offspring A and B and 50% of the offspring will exhibit a and b because no genetic recombination occurred. 16. The definition of lysogeny is A. The period during replication when virions are not present. B. Lysis of the host cell due to a phage. C. Incorporation (insertion) of the phage DNA into the genome of the host cell. D. When the time required to assemble new progeny phage takes an unusually long time. E. None of these. 17. What will be the result of conjugation between an E. coli F+ strain that grows on minimal medium (Strain 1) and a F- strain that cannot grow on minimal medium (Strain 2)? A. Strain 1 will become F- and still grows on minimal medium while Strain 2 will become F+ and still cannot grow on minimal medium. B. Strain 1 will remain the same while Strain 2 will become F+ and now grows on minimal medium. C. Strain 1 will remain the same while Strain 2 will become F+, but still cannot grow on minimal medium. D. Strain 1 and Strain 2 will remain the same. E. Strain 1 will remain the same while Strain 2 will stay F-, but now grows on minimal medium. 18. Why do calculated recombination frequencies between pairs of loci that are located relatively far apart underestimate the true genetic distances between loci? A. Recombination frequencies between widely separated genetic loci do not underestimate the true genetic distance. B. Double crossovers will be counted twice. C. Genetic recombination frequencies are an inaccurate method of determining genetic distances. D. The calculated recombination frequency underestimates the true crossover frequency because the double crossover progeny are not counted as recombinants. E. Because genetic maps are only accurate over short distances and, therefore, cannot be used for genes that are relatively far apart. 19. An event in which the centromere regions of two non-homologous acrocentric chromosomes become fused to form a single centromere is A. Known as a reciprocal translocation. B. Called a nonreciprocal transversion. C. Known as a Robertsonian translocation. D. Responsible for an inheritable form of Down syndrome. E. More than one of the above. 20. Recombination frequencies A. Are similar for all genes. B. Increase for more closely linked genes. C. Decrease for more widely separated genes. D. Are different, depending on whether the heterozygous genes are in the cis or trans configuration. E. Select this answer if all of the choices A-D are false. 21. Based on the pedigree shown at the right, the genetic trait being studied is most likely A. Dominant allele on the X-chromosome B. Autosomal dominant C. Recessive allele on the X-chromosome D. Autosomal recessive E. Allele on the Y-chromosome 22. Which of the following statements is NOT supported by the biochemical studies of DNA by Chargaff? A. The molar amount of adenine always equals the molar amount of thymine. B. The molar amount of guanine always equals the molar amount of cytosine. C. The molar amount of (G+C) can vary widely, depending on the source of DNA. D. The molar amount of (G+C) always equals the molar amount of (A+T). E. Select this answer if all of the answers A-D are supported by Chargaff’s experimental data. 23. Hfr bacterial cells exhibit the highest levels of gene transfer because A. Rather than existing as an isolated plasmid, the F factor is incorporated within the main chromosome where it can transfer many chromosomal genes at one time. B. They contain two distinct F factors. C. They induce the production of significantly more sex pili than normal F+ cells. D. They do not require conjugation for gene transfer. E. Select this answer if none of the choices A-D are correct. 24. The order of three genes on a chromosome is ho – dp – da. Genes ho and dp are 9.0 map units apart, and genes dp and da are 4.0 map units apart. What is the expected frequency of doublecrossovers between ho and da.? A. 0.13% B. 0.36% C. 0.24% D. 0.45% E. 0.56% 25. Which of the following is NOT an aspect of DNA that contributes to its structural stability? A. Phosphodiester linkages that connect the nucleotides B. Hydrogen bonding between the complementary bases C. Negatively charged phosphates arranged around the outside of the helix D. An extra oxygen on the 2’ carbon E. Select this answer if more than one of the choices A-D is correct. 26. The linkage phase (cis or trans) of alleles in a heterozygous parent is detectable as the A. Lowest incidence of crossing-over. B. Highest frequency of recombination. C. Largest number of map units between corresponding alleles. D. Most frequent phenotypes of the progeny. E. None of the above 27. During meiosis in a translocation heterozygote, only 50% of the gametes are viable because A. Approximately 25% of the gametes contain one normal homologue for each chromosome involved in the translocation. These gametes are viable. B. Approximately 50% of the gametes contain one normal homologue of one chromosome and one homologue with the translocation for the other chromosome. These gametes have duplicated and deleted genes and, therefore, are not viable. C. Approximately 25% of the gametes contain a balanced translocation, which is the homologue for each chromosome that has a translocation. These gametes are viable. D. While this biological phenomenon has been observed for many years, there is no explanation for it at this time. E. Select this answer if choices A, B, and C are each true. 28. The mutations cinnabar (cn, bright eye red color) and vestigial (vg, malformed wings) are linked on the second chromosome of Drosophila. The following genotypes were found among 1,000 progeny of the cross of a female heterozygous for both genes and a male who is homozygous recessive for both genes. What is the map distance between cn and vg? A. 12 map units B. 6 map units C. 8 map units D. 18 map units E. 4 map units 29. The uptake of DNA from the environment by a competent cell is called A. Conjugation B. Transformation C. Transduction D. Genetic engineering E. Transfection 30. In genetic recombination (also called crossing-over), A. The reciprocal exchange between homologous chromosomes is generally random. However, certain regions of the chromosome undergo crossing-over at higher or lower frequencies than expected for a truly random process. B. Genetic exchange occurs before chromosome replication. C. Crossing over only occurs between very tightly linked gene loci. D. The probability of its occurrence decreases with increasing distance between the genes. E. None of the above. 31. The Drosophila genes for yellow body (y), white eyes (w), and cut wings (ct) lie on the Xchromosome with w in the middle. The y gene is 2.0 cM from w while the ct gene is 10 cM from w. Out of 1,000 progeny, 2 were double-crossovers. What is the interference? A. 0% B. 33% C. 66% D. 50% E. 75% 32. A certain strain of Drosophila, when crossed to a strain having a chromosome with several linked genetic markers fails to produce progeny with a non-parental recombinant genotype. Cytological studies reveal numerous meiotic cells that contain a chromosome with two centromeres and a chromosome lacking a centromere. Which of the following chromosomal abnormalities would most likely explain these data? A. Pericentric inversion B. Chromosomal deletion C. Paracentric inversion D. Reciprocal translocation E. Either answer A or B; cannot distinguish without additional information. 33. In most instances, a heterozygote with a wild-type allele will have a phenotype that is indistinguishable from a homozygous wild-type individual. However, we sometimes find that a single functional copy of the gene does not produce enough of the gene product for the normal phenotype. These types of genes are said to be A. Incomplete recessive B. Passive aggressive C. Haploinsufficient D. Conditional mutants E. Fully penetrant 34. Which of the following is an inverted repeat? Note that the sequences are written 5’ to 3’ and only one of the two strands is shown. A. TTTTTAAAAGGGG----------CCCCTTTTAAAAA B. AACCGGAACCGG----------GGCCAAGGCCAA C. AAACCCGGG----------TTTGGGCCC D. None of the above E. More than one of the above 35. A gene mapping experiment of the E. coli chromosome was completed using several different Hfr strains. The results are diagrammed at the right. Which of the following is the most likely gene order? A. thi thr leu pro azi lac gal his B. thi leu thr azi pro lac gal his C. thi thr leu azi pro lac gal his D. thi thr leu azi pro lac his gal E. thr thi leu azi pro lac his gal 36. The results of a genetic cross are diagrammed at the right. Based on the information provided, what percentage of meiotic cells had a genetic crossover between the M and D genes? A. 12% B. 24% C. 50% D. 0% E. Cannot be determined from the information provided. 37. Three point test-crosses A. Can be used to detect double crossover events. B. Can be used to determine the genetic distance between the genes. C. Can be used to determine gene order on a chromosome. D. Answers A and B, but not C are correct. E. Answers A, B, and C are each correct. 38. The arrangement of linked genes in a double heterozygote in which both recessive alleles are present on one member of the pair of homologous chromosomes is called a A. Trans-heterozygote B. Cis-heterozygote C. Complementation group D. Parental ditype E. None of the above 39. The physical map (based on DNA sequence) of the human genome is similar for both males and females. Yet, the genetic map (based on genetic recombination) for females is about 60% larger than males. These data suggest that A. Genetic recombination frequencies are higher in females than in males. B. Genetic recombination frequencies are lower in females than in males. C. Genetic recombination does not occur in human males. D. The major laboratories doing the mapping of the human genome made numerous errors. E. Of unknown reasons. There is no explanation at this time. 40. Hershey and Chase demonstrated that DNA and not protein is the genetic material. They radiolabeled the protein of bacteriophage with 35S while the DNA was radiolabeled with 32P. The radiolabeled bacteriophage were then used to infect non-radiolabeled bacterial cells. Which of the following is true concerning the results of these experiments? A. 50% of the progeny phage had 35S-labeled proteins. B. Enzymes that degrade the DNA destroyed the transforming activity of the bacteriophage. C. Some of the 32P labeled DNA was transmitted to progeny phage. D. The transforming activity of bacteriophage was not altered with the addition of proteases or ribonucleases. E. More than one of the above is true. 41. The E. coli genetic map is measured in minutes A. Because it is based on genetic experiments involving the time required for conjugation. B. Because the chromosome is circular and a system analogous to the earth’s lines of longitude and latitude was adopted. C. For historical reasons, although the rationale for choosing this unit of genetic distance has never been clearly understood. D. Because the generation time of E. coli is so rapid (20 minutes) under optimal laboratory conditions. E. Select this answer if none of the choices A-D are true. 42. Which of the following is false concerning hydrogen bonds (H-bond)? A. The H-bond only has ~5% of the strength of a covalent bond. B. The H-bond is a weak electrostatic interaction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom, usually nitrogen or oxygen. C. H-bonds are the primary force that maintains the double-helical structure of two complementary strands of DNA. D. H-bonds are only effective over a very short distance. E. Select this answer if answers A-D are all true concerning H-bonds. 43. The frequency of meiotic cells that undergo recombination is always twice the frequency of crossing over because A. The maximum number of meiotic cells that undergo recombination is 50%. B. Genetic crossing over is a very rare event. C. Recombination does not always happen when there is crossing over. D. Each crossover involves just two of the four chromatids, which generates two recombinant chromatids and two nonrecombinant chromatids. E. Select this answer if more than one of the statements A-D is correct. 44. What term best refers to an individual with Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)? A. Triploid B. Haploid C. Polyploid D. Aneuploid E. Euploid Extra Credit 45. Red-green color blindness is a human X-linked recessive disorder. Jill has normal color vision, but her father is color-blind. Jill marries Tom, who also has normal color vision. Jill and Tom have a daughter who has Turner syndrome and is color-blind. What is the most likely reason that the daughter is color-blind? A. A normal egg with a color-blind X chromosome was fertilized by a sperm produced by a nondisjunction event during spermatogenesis, which carries no sex chromosome. B. A normal sperm with a color-blind X chromosome was fertilized by an egg produced by a nondisjunction event during oogenesis, which carries no sex chromosome. C. A normal sperm fertilized a normal egg, but sometime during embryonic development, a spontaneous mutation occurred that caused color-blindness. D. A normal sperm fertilized an egg with a color-blind X chromosome, but sometime during embryonic development, one of the X chromosomes was lost due to a spontaneous mutational event. E. A normal egg was fertilized by a normal sperm with a color-blind X chromosome. 46. Suppose you mate a male Drosophila that is heterozygous for a deletion in Chromosome 2 with a female that is heterozygous for a different deletion in Chromosome 2. Among their progeny, there are NO flies that have both chromosomal deletions – one derived from each parent. Which of the following is the most plausible explanation? A. This would be lethal because interaction of the two deleted chromosomes initiates extensive rearrangements of the genomic DNA. B. The two deletions probably overlap and result in the loss of an essential gene that lies within the deleted region that is common to both chromosomes. C. The presence of both deleted chromosomes is lethal because the total DNA content of the cell falls below the critical mass needed for viability. D. This would be an anomalous result with no plausible explanation. E. More than one of the above. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 10, 2022
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 10, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
83


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)


.png)


.png)
.png)

