1. A person's attitude toward the American’s With Disabilities Act can be directly observed.
F
Attitudes are latent, or hypothetical, constructs and because of this, they are not directly observable.
PTS: 1 DIF:
...
1. A person's attitude toward the American’s With Disabilities Act can be directly observed.
F
Attitudes are latent, or hypothetical, constructs and because of this, they are not directly observable.
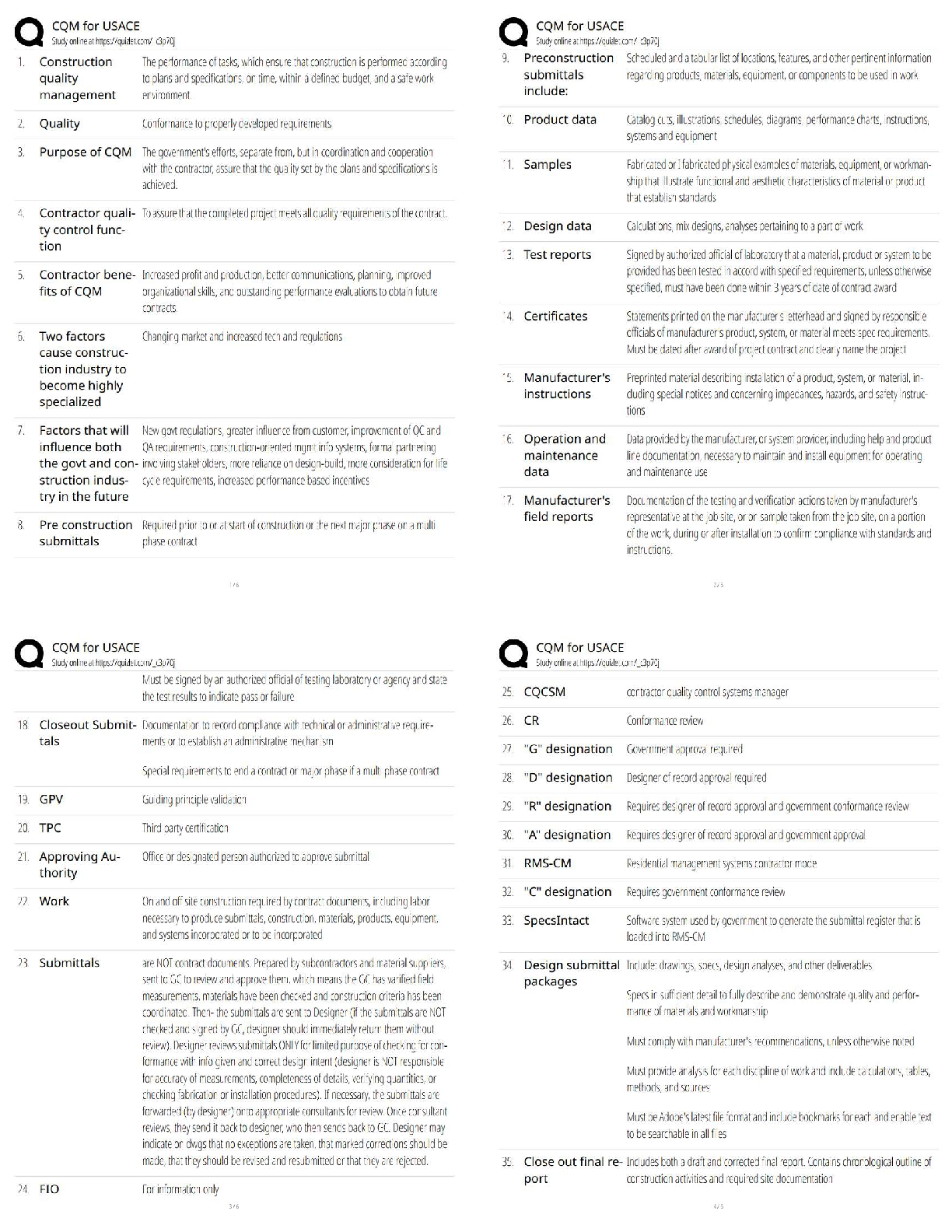
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 311 OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
2. Attitudes are thought to have three components: affective, cognitive, and behavioral.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
3. A person's knowledge about a brand is part of the affective component of that person's attitude toward that brand.
F
The cognitive component represents a person’s awareness and knowledge of the brand.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311 OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
4. Researchers have limited options for measuring attitudinal concepts..
F
Researchers face a wide variety of choices in measuring attitudinal concepts.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 312 OBJ: LO: 14-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
5. A rating task asks the respondent to estimate the magnitude or the extent to which some characteristic exists.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 313
OBJ: LO: 14-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
6. Attitude can be measured using a two-point response scale.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 314
OBJ: LO: 14-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
7. If a Likert scale statement on five-point scale is recoded, a 4 would be recoded as a 2.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 316
OBJ: LO: 14-04 NAT: AACSB Analytic| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
8. A composite scale is made up of multiple items to represent a latent construct.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 316
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
9. The semantic differential scale uses unlabeled response categories between two bipolar opposite adjectives.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 317
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
10. Semantic differential scales can be scored by: -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 317
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
11. Business researchers generally assume that the semantic differential provides ratio data.
F
Business researchers generally assume that the semantic differential provides interval data
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 318 OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
12. An image profile can be developed based on semantic differential data.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 318
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
13. A numerical scale is similar to a Likert scale except that is uses numbers instead of verbal descriptions as response options to identify response positions.
F
A numerical scale is similar to a semantic differential except that is uses numbers instead of verbal descriptions as response options to identify response positions.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 319 OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
14. The Stapel scale is more difficult to administer in a phone interview than a semantic differential scale.
F
The Staple scale is easier to administer over the telephone.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 320 OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
15. The constant-sum scale demands that respondents divide points among several attributes to indicate their relative importance.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 320
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
16. In a linear scale, a respondent's score is the length in millimeters from one end of the scale to the point marked on the scale by the respondent.
F
This is called a graphic rating scale.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 321 OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
17. A variation of the graphic ratings scale is the ladder scale.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 321
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
18. A Thurstone scale is widely used in business research because of its simplicity.
F
Its current popularity is low because the construction of a Thurstone scale is fairly complex process that requires two stages, making it time-consuming and costly.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 322 OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
19. Ranking measurements of attitudes provide interval data.
F
Ranking provides ordinal data.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 324 OBJ: LO: 14-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
20. If a researcher wants to compare five brands of toothpaste on the basis of their flavor using the paired comparison method, the researcher must ask each respondent to make five comparisons.
F
Each respondent must make 10 comparisons, which calculated by [5(5-1)/2].
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 325 OBJ: LO: 14-05
NAT: AACSB Analytic| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
21. Sorting tasks require that respondents indicate their attitudes or beliefs by arranging items on the based of perceived similarity or some other attribute.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 325
OBJ: LO: 14-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
22. A unidimensional rating scale is any measure of attitudes that asks respondents about a single concept in isolation.
F
This is a monadic rating scale.
PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 327 OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
23. A balanced rating scale has a neutral point, or point of indifference, at the center of the scale.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
24. Researchers use forced-choice scales to minimize the number of blank answers.
F
Forced-choice scales increase the number of nonresponses.
PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 328 OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
25. Most psychological concepts are latent constructs and generally require multiple items.
T PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 329
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
MULTIPLE CHOICE
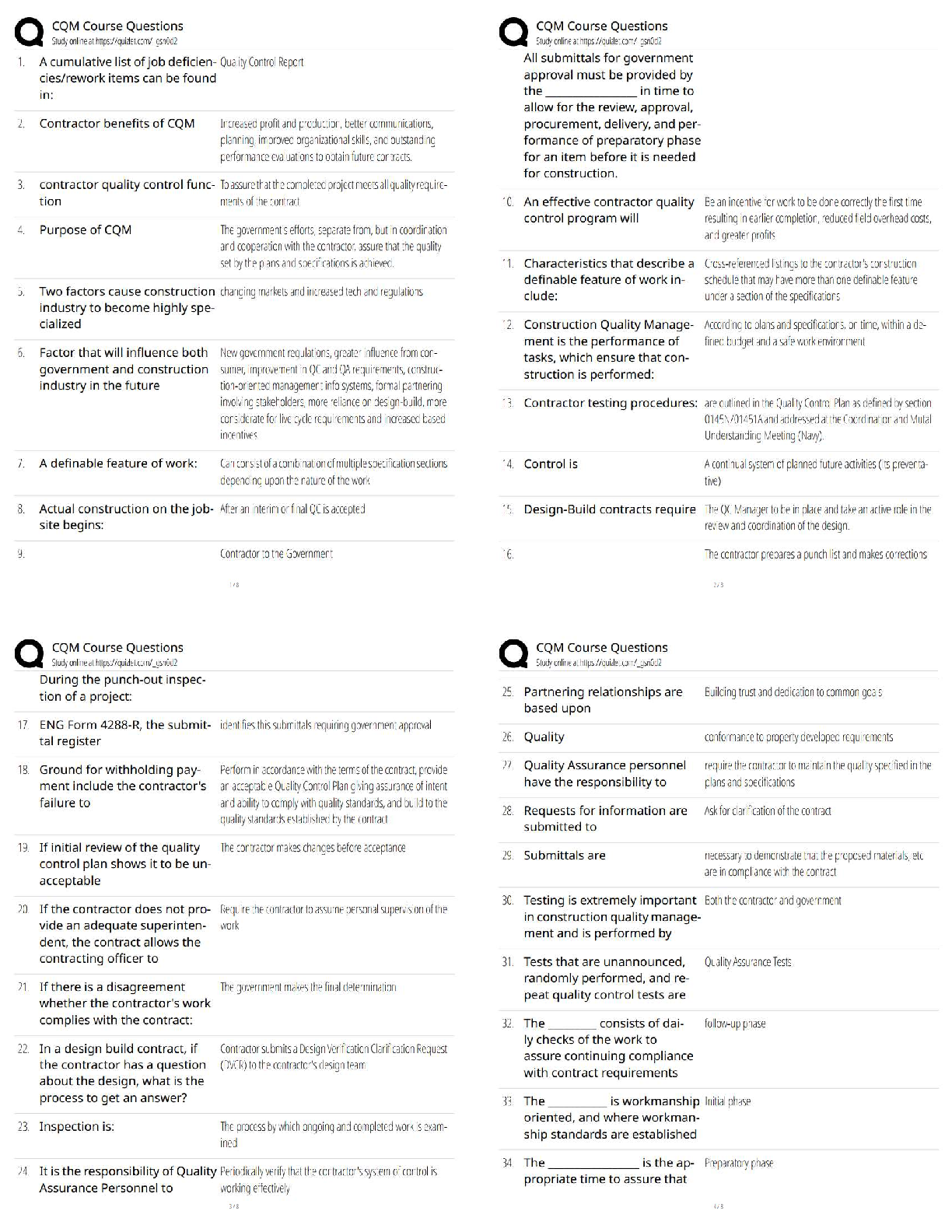
1. A(n) _____ is an enduring disposition to consistently respond in a given manner to various aspects of the world.
a. attitude
b. concept
c. expectation
d. construct
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
2. All of the following are basic components of attitude EXCEPT _____.
a. cognitive component
b. affective component
c. behavioral component
d. latent component
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
3. Which attitude component represents a person’s awareness and knowledge of the relative matter?
a. affective
b. cognitive
c. behavioral
d. personal
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
4. Hank believes that the price of his tech company’s stock will increase because the entire technology sector is experiencing rapid growth. This belief represents which component of Hank’s attitude?
a. affective
b. behavioral
c. cognitive
d. personal
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
5. Which component of attitude refers to an individual’s general feelings or emotions toward an object?
a. subjective
b. cognitive
c. affective
d. conative
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
6. "I love my job" is an example of which component of an attitude toward one’s job?
a. affective
b. behavioral
c. cognitive
d. perceptive
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
7. Which component of attitude reflects a predisposition to action by reflecting an individual’s intentions?
a. behavioral component
b. absolute component
c. cognitive component
d. affective component
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
8. "I plan to buy a new DVD player sometime in the next three months" is an aspect of which component of an attitude?
a. cognitive
b. affective
c. behavioral
d. personal
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
9. Variables that are not directly observable but are measurable through indirect indicators, such as verbal expression or overt behavior, are called _____.
a. secondary variables
b. indirect constructs
c. hypothetical constructs
d. unrealized constructs
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 311
OBJ: LO: 14-01
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
10. When a respondent is asked to place each shopping mall in a list of four local shopping malls in the order in which she prefers to shop at each mall, this is an example of a ______ task.
a. rating
b. ranking
c. sorting
d. semantic differential
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 313
OBJ: LO: 14-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
11. When a respondent is given a set of 3" x 5" cards containing the current advertising slogan for a brand or product on each card and is asked to place the cards into two piles: (1) Recognize this slogan and can identify the brand/product and (2) Do not recognize the slogan, this is an example of a ______ task.
a. rating
b. ranking
c. constant-sum
d. sorting
D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 313
OBJ: LO: 14-02
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
12. When a respondent is asked either to agree or to disagree with the statement: "The CEO is doing a good job of managing the affairs of the corporation," this type of question produces______ data.
a. ordinal
b. nominal
c. ratio
d. interval
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 314
OBJ: LO: 14-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
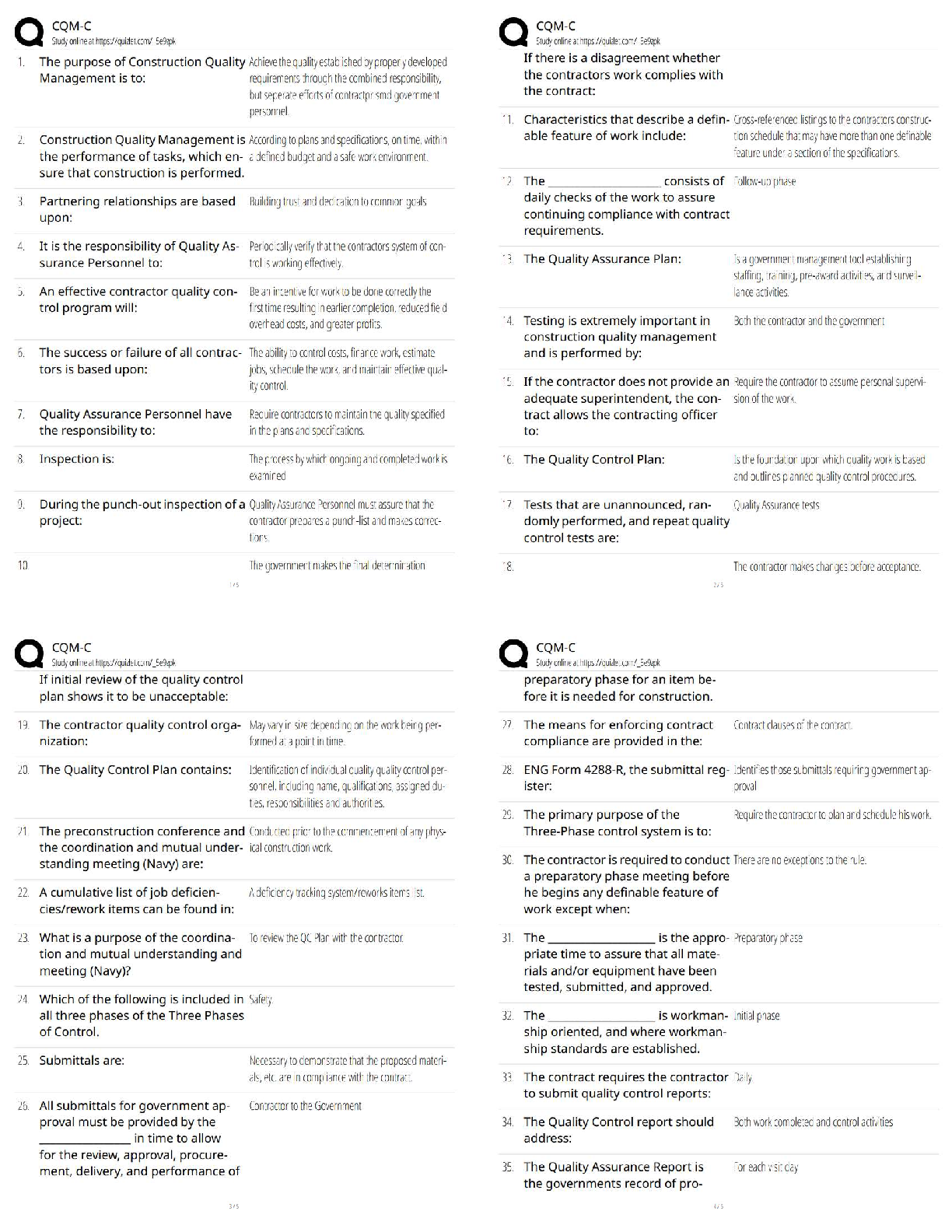
13. When a respondent is asked: "How often do you travel on business in a six-month period?" and is asked to indicate her answer by circling one of the following: never, rarely, sometimes, often, very often, this is an example of a _____ scale.
a. semantic differential
b. Likert
c. category
d. constant-sum
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 314
OBJ: LO: 14-03
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
14. Which type of scale asks respondents to indicate their attitudes by checking how strongly they agree or disagree with carefully constructed statements, ranging from very positive to very negative attitudes toward some object?
a. constant-sum
b. Likert
c. Stapel
d. graphic rating
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 315
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
15. What type of scale is the following?
The international accounting standards are an improvement over the current accounting standards.
Strongly Strongly
Agree Agree Neutral Disagree Disagree
a. semantic differential
b. constant-sum
c. Thurstone
d. Likert
D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 315
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
16. How many choices do researchers commonly use when using Likert scales?
a. two
b. three
c. five
d. ten
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 316
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
17. _____ is a method of making sure all the items forming a composite scale are scored in the same direction.
a. Scoring
b. Reverse coding
c. Consistent coding
d. Composite scoring
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 316
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
18. A researcher used five Likert items to make up an attitude toward cross-functional teams in the workplace. Two of the items were worded negatively, so the research changed the values of those items by subtracting their value from 6. What is this researcher doing?
a. reverse coding
b. cross-validating
c. data reduction
d. inverting the items
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 316
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
19. Which type of scale has respondents describe their attitude using a series of bipolar rating scales?
a. Likert
b. constant-sum
c. semantic differential
d. Thurstone
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 317
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
20. What type of scale is the following?
Contemporary ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ Traditional
a. Likert
b. graphic rating
c. Thurstone
d. semantic differential
D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 317
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
21. Which of the following is a graphic representation of semantic differential data for competing brands, products, or stores to highlight comparisons?
a. image profile
b. perceptual map
c. Likert profile
d. comparative profile
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 318
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
22. Which type of scale is similar to a semantic differential except that it uses numbers, instead of verbal descriptions, as response options to identify response positions?
a. quantitative scale
b. summated scale
c. Stapel scale
d. numerical scale
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 319
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
23. A _____ scale is a measure of attitudes that consists of a single adjective in the center of an even number of numerical values.
a. Stapel
b. unidimensional
c. numerical
d. differential
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 319
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
24. What type of scale is the following when female shoppers are asked to rate Macy's department store in terms of its women's apparel items?
Macy's
+3
+2
+1
Price
-1
-2
-3
a. semantic differential
b. Stapel
c. paired comparison
d. constant-sum
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 319
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
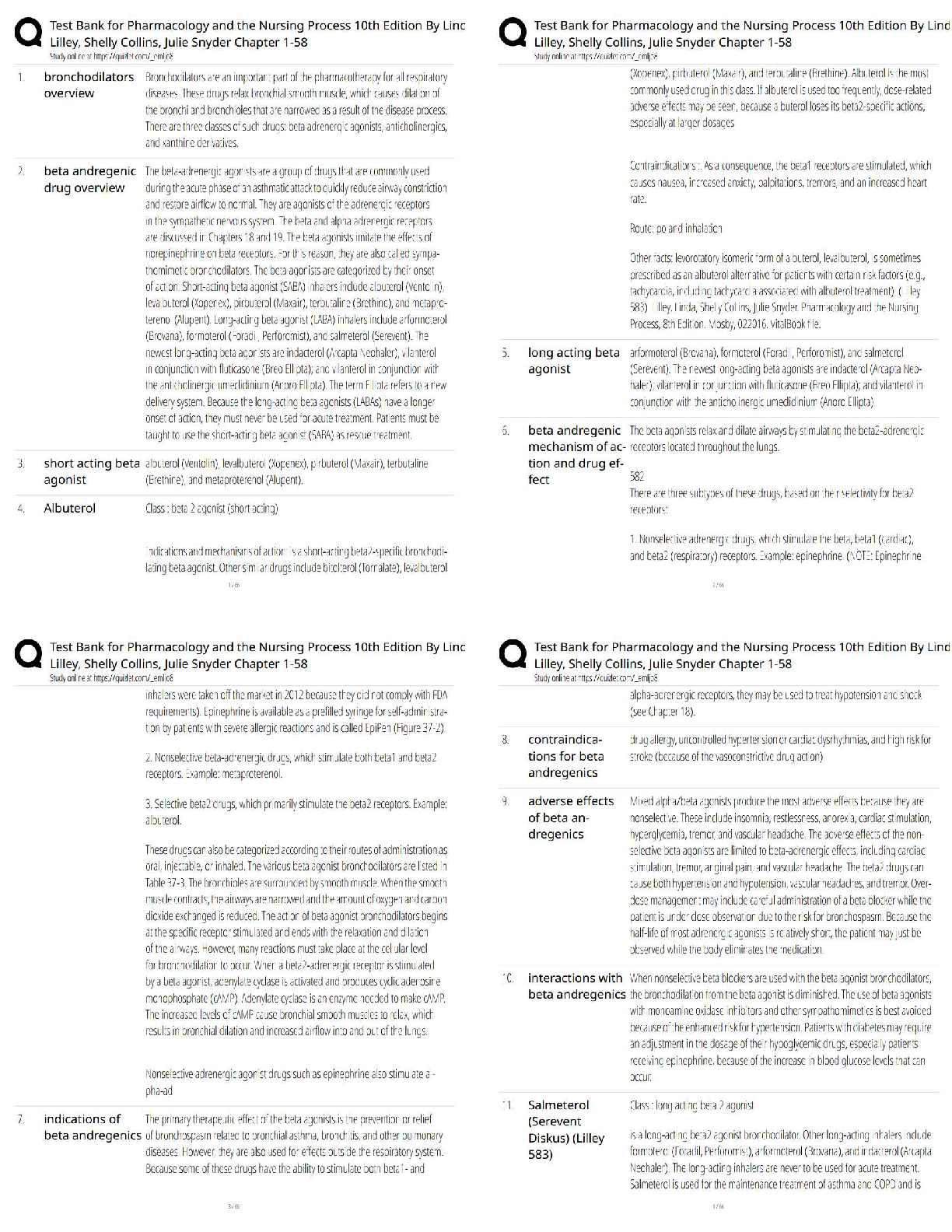
25. A type of scale that demands that respondents divide points among several attributes to indicate their relative importance is called a _____.
a. constant-sum scale
b. Likert scale
c. Stapel scale
d. semantic differential
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 320
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
26. What type of scale is the following?
United Parcel Service (UPS) would like you to distribute 50 points among the following in terms of how important each aspect is to you for your overnight shipping needs:
_____ Accurate billing
_____ On-time delivery
_____ Price
a. Likert
b. paired comparison
c. Thurstone
d. constant-sum
D PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 320
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
27. Which measure of attitude allows respondents to rate an object by choosing any point along a graphic continuum?
a. continuous rating scale
b. point scale
c. graphic rating scale
d. line scale
C PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 321
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
28. What type of scale is the following?
Please an X at the position on the horizontal line that most reflects your feelings regarding the atmosphere of this restaurant.
Modern _______________ Old-fashioned
a. graphic rating
b. Likert
c. linear
d. category
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 321
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
29. What type of scale is the following?
How likely are you to purchase a DVD player during the next six months?
____ Definitely will purchase
____ Probably will purchase
____ Might purchase
____ Probably will not purchase
____ Definitely will not purchase
a. Likert
b. behavioral intention
c. semantic differential
d. constant-sum
B PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 323
OBJ: LO: 14-04
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
30. What type of measurement is the following?
I would like to know your overall opinion of two brands of athletic shoes. They are Nike and New Balance. Overall, which of these two brands -- Nike or New Balance-- do you think is the better one? Or are both the same?
____ Nike is better
____ New Balance is better
____ They are about the same
a. semantic differential
b. Thurstone
c. paired comparison
d. constant-sum
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 324
OBJ: LO: 14-05
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
31. If researcher wish to compare six brands of HDTVs on the basis of quality, how many paired comparisons will be necessary?
a. 3
b. 6
c. 15
d. 30
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 325
OBJ: LO: 14-05 NAT: AACSB Analytic| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
32. All of the following are practical decisions regarding the selection of a measurement scale EXCEPT _____.
a. Is a ranking, sorting, rating or choice technique best?
b. Should a single measure of an index measure be used?
c. How large should the sample size be?
d. How many scale categories or response positions are needed to accurately measure an attitude?
C PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 326
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Comprehension
33. Any measure of attitudes that asks respondents about a single concept in isolation is referred to as a(n) _____ rating scale.
a. monadic
b. unidimensional
c. primary
d. singular
A PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
34. Which type of scale is the following?
Now that you have been at your job for one year, how satisfied are you?
Very Very
Satisfied 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Dissatisfied
a. Thurstone
b. monadic rating
c. constant-sum
d. behavioral intention
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
35. What type of scale asks a respondent to rate a concept, such as a brand, in comparison with a benchmark (i.e., a competing brand) explicitly used as a frame of reference?
a. comparative rating scale
b. monadic rating scale
c. semantic differential
d. ladder scale
A PTS: 1 DIF: Easy REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
36. In which type of scale is a neutral point, or point of indifference, at the center of the scale?
a. synergistic
b. symmetrical
c. unbalanced
d. balanced
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
37. Which type of scale is the following?
____ Very Satisfied
____ Satisfied
____ Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied
____ Dissatisfied
____ Very dissatisfied
a. balanced
b. Thurstone
c. unbalanced
d. semantic differential
A PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
38. Which type of fixed-alternative rating scale has more response categories at one end than the other, resulting in an unequal number of positive and negative categories?
a. biased rating scale
b. skewed rating scale
c. obtuse rating scale
d. unbalanced rating scale
D PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 327
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
39. Which type of scale is the following?
____ Satisfied
____ Neither satisfied nor dissatisfied
____ Dissatisfied
____ Very dissatisfied
a. Thurstone
b. unbalanced
c. paired comparison
d. balanced
B PTS: 1 DIF: Hard REF: p. 328
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Application
40. When a respondent is required to choose one of the fixed alternatives, what type of scale is being used?
a. semantic differential
b. forced-choice
c. non-forced-choice
d. symmetric
B PTS: 1 DIF: Moderate REF: p. 328
OBJ: LO: 14-06
NAT: AACSB Reflective Thinking| CB&E Model Research| Blooms Knowledge
COMPLETION
1. An enduring disposition to respond consistently to an aspect of the world is called a(n) ______.
2. The component of attitude that represents the action that corresponds to a certain type of attitude is a(n) _____ component.
3. Attitudes are considered to be _____ constructs because they are not directly observable but are measurable through indirect indicators.
4. When respondents are asked to order brands of cosmetics in terms of their prices (from high to low), this is an example of a(n) ______ task.
5. When respondents are asked to indicate the magnitude of a characteristic that a brand of shampoo has, this is an example of a(n) ______.
6. When respondents are asked whether they strongly agree, agree, are neutral, disagree, or strongly disagree to a series of attitude items, this is an example of a(n) ______ scale.
7. _____ coding is a method of making sure all the items forming a composite scale are scored in the same direction.
8. _____ scales are formed by summing or averaging respondents’ reactions to indicate a latent construct.
9. A(n) ______ scale measures attitudes by using 7-point rating scales that are anchored at either end by polar opposite adjectives.
10. A(n) _____ is a graphical representation of semantic differential data for competing brands, products, or stores to highlight comparisons.
11. A(n) _____ scale is similar to a semantic differential except that it uses numbers, instead of verbal descriptions, as response options to identify response positions.
12. A(n) ______ scale measures attitudes in both their direction and their intensity simultaneously.
13. When respondents are asked to divide up a sum (e.g. 50 points) to indicate the relative importance of features on a new car, this is an example of a(n) ______ scale.
14. A scale that presents respondents with a graphic continuum is called a(n) _____ rating scale.
15. A variation of the graphic rating scale is the _____ scale.
16. A rating scale instrument similar to a semantic differential that measures the behavioral intentions of subjects toward future actions is called a(n) _____.
17. When respondents are asked to choose among four brands of detergent in such a way that they are asked to select the brand they prefer when each brand is compared with each other brand, this is a type of ______ measurement.
18. An attitude scale that asks respondents about a single concept by itself is called a(n) ______ rating scale.
19. A fixed-alternative rating scale with an equal number of both positive and negative categories, with a neutral point in the middle of the scale, is called a(n) ______ scale.
20. A fixed-alternative rating scale that has an unequal number of positive and negative categories so that the categories are "piled up" at one end of the scale is called a(n) ______ scale.
ESSAY
1. Define attitude and describe the three components that comprise it, giving an example of each with respect to your attitude toward searching for a job.
2. Compare and contrast a Likert scale with a semantic differential scale.
3. Describe a constant-sum scale and discuss when a researcher might use this type of scale. What is a flaw of this type of scale?
4. Explain how a researcher uses the paired comparison method and determine the number of paired comparisons necessary to compare four brands.
5. Define a forced-choice scale and explain why a researcher would use one and the potential negative consequence of that choice of scale.
[Show More]











.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)