Human Resource Management > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Principles of Human Resource Management 2017: Assignment 1. 100% (All)
Principles of Human Resource Management 2017: Assignment 1. 100%
Document Content and Description Below
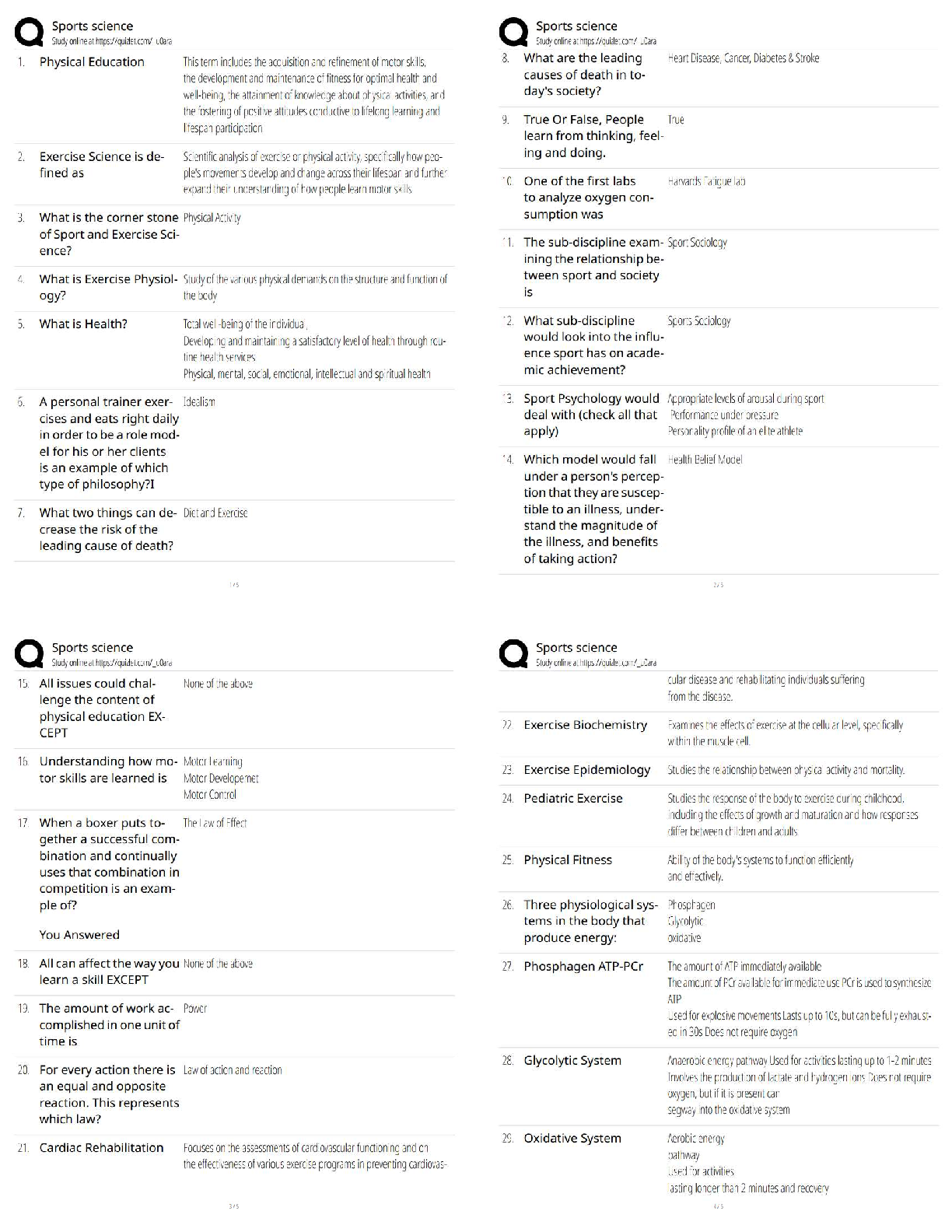
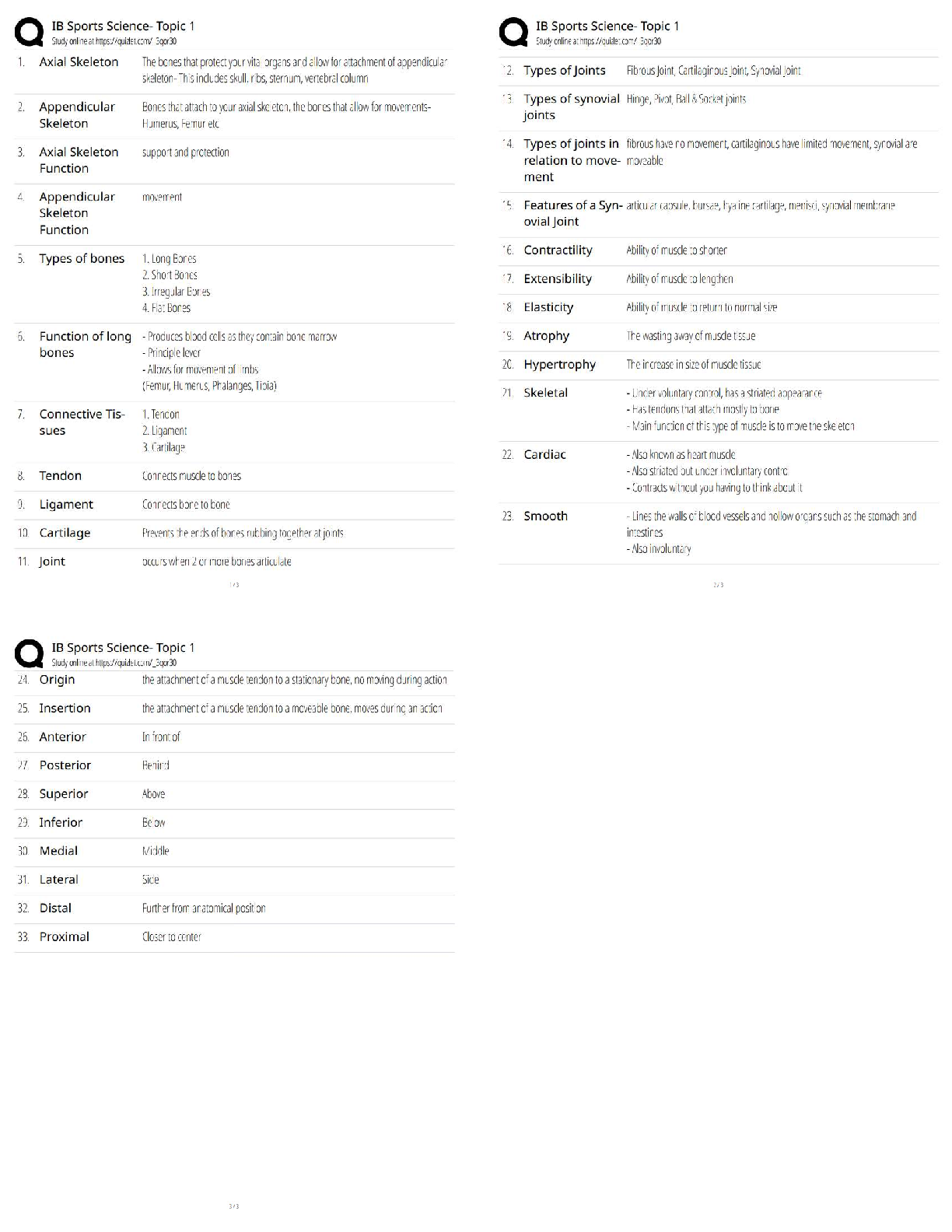
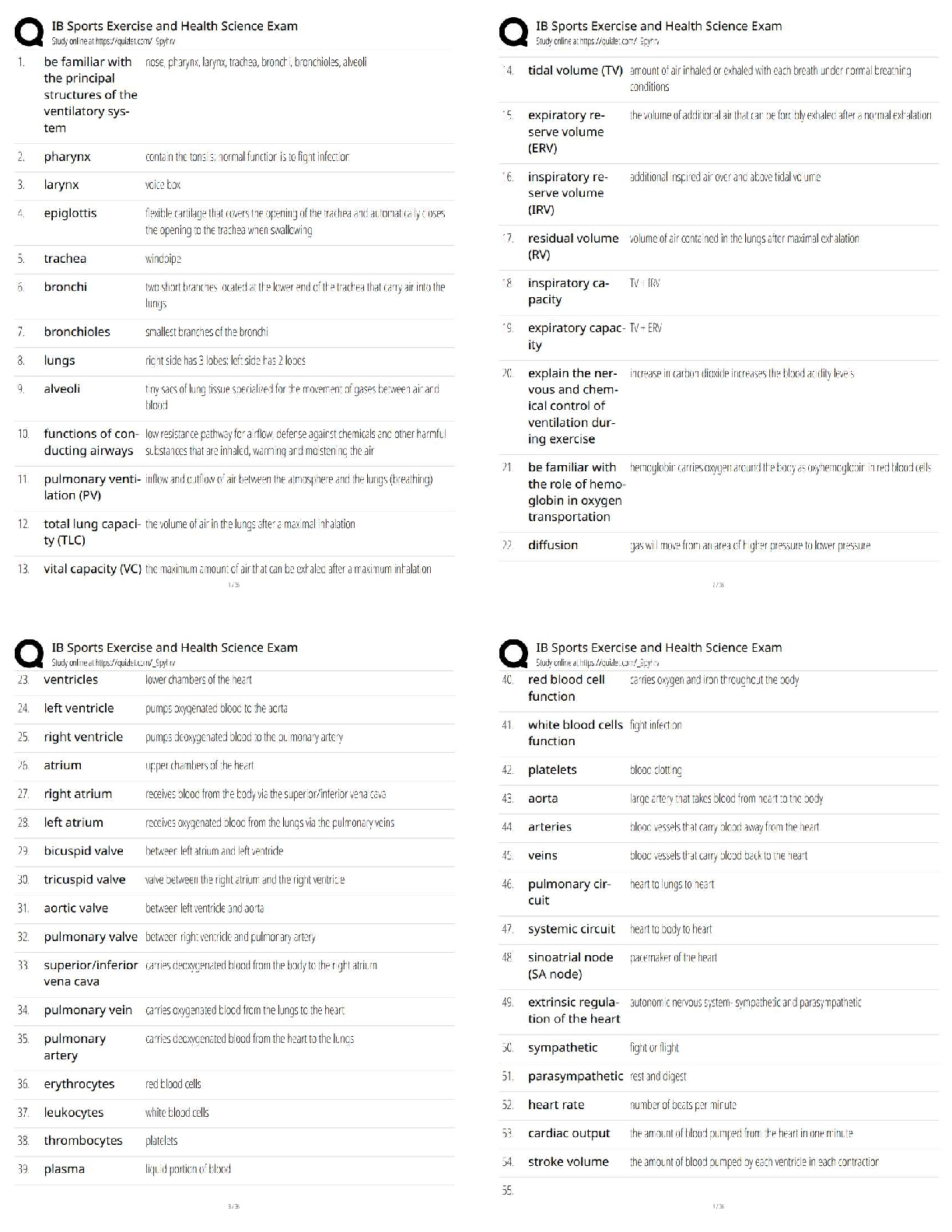
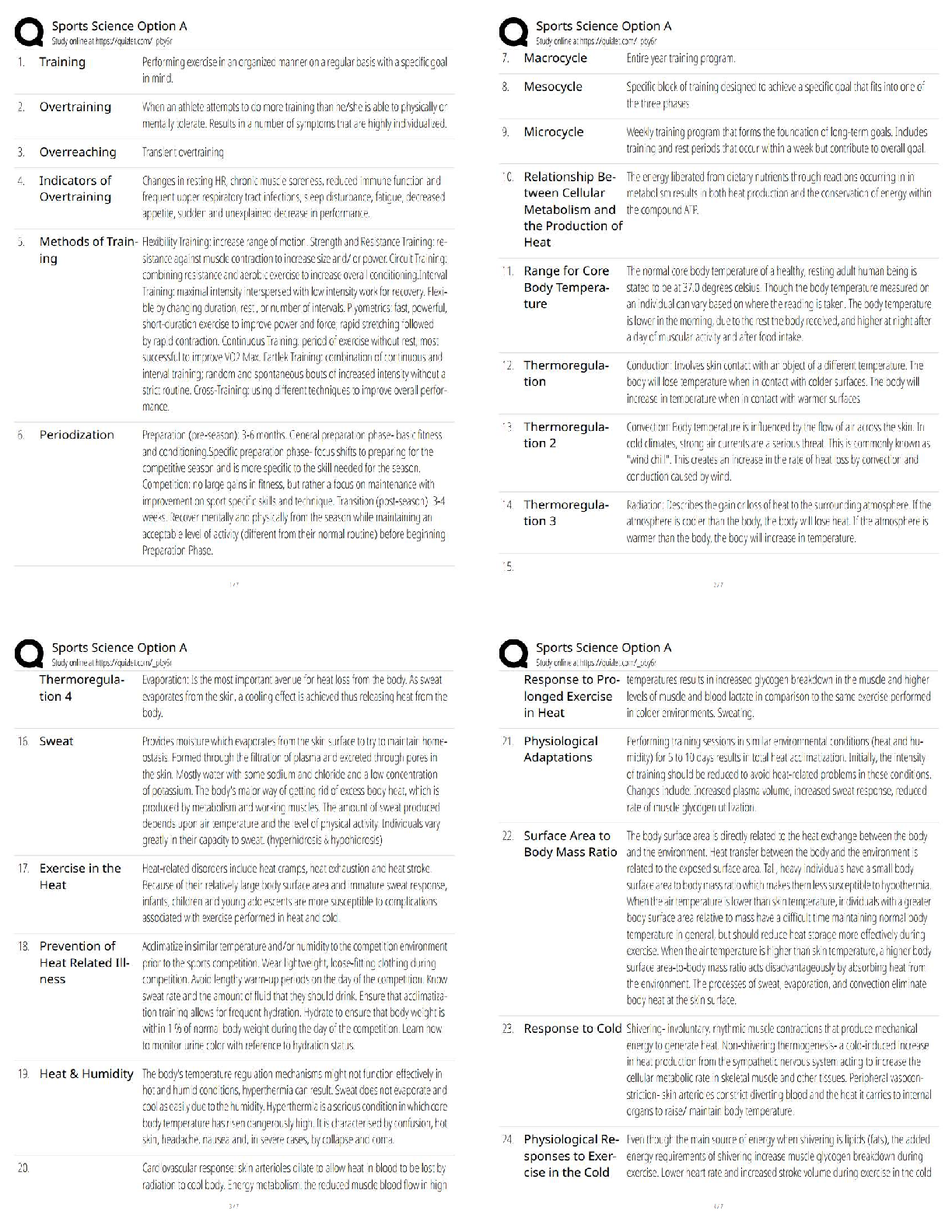
1. An employee in an organization who personally takes all official papers from one department to another in that organization is an example of: a. A manager b. A leader c. A line employee d. A s ... taff employee 2. The cook in the kitchen of a restaurant is an example of: a. A manager b. A leader c. A line employee d. A staff employee 3. An organization that prefers management led employment conditions and planning of people resources is said to be involved in: a. Personnel management b. Human resource management c. Change management d. None of the above 4. An organization that views employees as a cost to be controlled is said to be involved in: a. Personnel management b. Human resource management c. Change management d. None of the above 5. Appreciating and rewarding employees who work well helps with: a. Employee staffing b. Employee recruitment c. Employee retention d. Employee development 6. Helping employees improve their knowledge, skills, and competencies helps with: a. Employee staffing b. Employee recruitment c. Employee retention d. Employee development 7. Retirement of employees falls under the category of: a. Training and career development b. Employee separation c. Performance appraisal d. Employee compensation8. Examination of the benefits work brings to the ongoing business processes is known as: a. Job analysis b. Work flow analysis c. Job description d. Job specification 9. Analyzing business processes with the explicit intention to change them leading to a reduction in resource consumption and enhancement of production is known as: a. Training and development b. Human resource development c. Business process analysis d. Business process re-engineering 10.An organization whose structure is determined by the kind of expertise its employees have and the type of work they do as opposed to how long they have been in the organization may be characterized as a: a. Vertical organization b. Flat organization c. Virtual organization d. Boundaryless organization -----------------------------Principles of Human Resource Management 2017: Assignment 2 1. Workers that have full time jobs and enjoy special benefits and privileges are known as: a. Special workers b. Contingent workers c. Core workers d. Contract workers 2. Workers that are hired only when a special job is required to be completed and only during the time that that job is being worked on, are known as: a. Special workers b. Contingent workers c. Core workers d. Contract workers 3. A type of work schedule that results in the reduction of workdays per week but an increase in the number of hours of work per day so that the total number of work hours per week remains the same is known as: a. Flexible work hours b. Compressed workweek c. Balanced work hours d. None of the above 4. A type of work schedule that results in a division of work schedules into core time and flexible time to help employees balance their work and personal lives is known as: a. Flexible work hours b. Compressed workweek c. Balanced work hours d. None of the above 5. Breaking down of work into smaller tasks that are repetitive and can be considered as individual units of work is known as: a. Work rearrangement b. Work elimination c. Work simplification d. None of the above 6. Rearranging tasks in an effort to cut down on tasks that one can do without and maximize the output of tasks that are really required, is known as: a. Work rearrangement b. Work elimination c. Work simplification d. None of the above 7. An integral step of work without which the assigned output cannot be achieved, is known as: a. Task b. Jobc. Duty d. Responsibility 8. A group of units of work that form a significant activity leading to the desired activity of the organization is known as: a. Task b. Job c. Duty d. Responsibility 9. Turnover costs of separation include: a. Pre-employment testing b. Exit interview c. Recruiter fees d. Orientation and training 10.Turnover costs of hiring include: a. Pre-employment testing b. Exit interview c. Recruiter fees d. Orientation and training ------------------------ -----------------------------1. Which of the following qualifies as a career? Principles of HRM 2017: Assignment 3 a. A one time project with the UNICEF b. c. A lifetime position as the accountant of a rich businessman A series of progressive positions in Indian Oil Corporation d. None of the above 2. Which of the following poses a challenge to career management? a. Decisions regarding salaries of employees b. c. Decisions regarding new product development The choice of training of employees given to employees versus their supervisors d. None of the above 3. A large multinational organization needs a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager prepares several documents. A table containing a list of required educational qualifications of the available managers and the actual qualifications and experience of the available managers, and the gaps between the two would count as: a. b. Instructional design Needs analysis c. Evaluation d. None of the above 4. A large multinational organization needs a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager prepares several documents. The list of training programs for these managers would count as: a. Needs analysis b. c. Evaluation Instructional design d. None of the above 5. A large multinational organization needs a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager prepares several documents. The list of methods to measure the impact of would count as: a. Needs analysis b. Instructional design c. d. None of the above Evaluation 6. A large multinational organization needs a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager prepares several documents. The document containing the list of managers requiring advanced training in implementing the new Enterprise Resource Planning software for the new factory would count as a. Organizational analysis b. Task analysisc. d. None of the above Person analysis 7. A large multinational organization needs a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager prepares several documents. The document describing the match between what the organization needs in the long term and what the available employees can produce, and the gap between the two, would count as: a. b. Task analysis Organizational analysis c. Person analysis d. None of the above 8. A large multinational organization needs a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager prepares several documents. The document describing the demands and requirements of the new positions would count as: a. Organizational analysis b. c. Person analysis Task analysis d. None of the above 9. A large multinational organization brings together a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. For this, the Human Resources manager designs a training program to help the newly appointed employees think out of the box. This type of training would be called: a. b. Diversity training Creativity training c. Crisis training d. None of the above 10.A large multinational organization brings together a team of managers to run a new factory being set up in Ahmedabad. The Human Resources Manager realizes that the newly appointed employees need help dealing with colleagues coming from a variety of social, educational, and ethnic backgrounds. The type of training designed to achieve this would be called: a. Creativity training b. c. Crisis training Diversity training d. None of the above1. Layoffs are a form of: Principles of HRM 2017: Assignment 4 a. Voluntary separation b. c. Contractual separation Involuntary separation d. None of the above 2. The death of a person by heart attack while still in service is a form of: a. Voluntary separation b. c. Contractual separation Involuntary separation d. None of the above 3. Resigning from a job is a form of: a. b. Involuntary separation Voluntary separation c. Contractual separation d. None of the above 4. Similarity of salaries between equally qualified, equally experienced, and equally skilled employees in different organizations is a form of: a. b. Internal equity External equity c. Fair equity d. None of the above 5. Similarity of salaries between equally qualified, equally experienced, and equally skilled employees within the same organization is a form of: a. External equity b. c. Fair equity Internal equity d. None of the above 6. Each member of the sales team in an organization receives the same basic salary, but the additional compensation they receive is based on the quantum of sales they make. This is an example of: a. Capability pay b. c. Fixed pay Variable pay d. None of the above 7. Each member of the sales team in an organization receives the same basic salary, and the same percentage of bonuses irrespective of the quantum of sales they make. This is an example of: a. Capability pay b. Variable pay c. d. None of the above Fixed pay8. The salary of the front line employees in Organization A is higher than their peers in similar organizations in other cities because Organization A has a hard time finding skilled front line employees in the city where it is located. Considering this, the salary structure of Organization A may be said to have been decided upon: a. The Distributive Justice Model b. c. Egalitarianism The Labor Market Model d. None of the above 9. Supervisors in Organization B encourage their employees to go for training that can help their professional development. The policies of Organization B are also very supportive of further training of their current employees and also provides financial assistance for training to the extent possible. However, the management realizes that this can result in employees moving out of the organization for better jobs. This situation denotes: a. Training needs b. c. Recruitment crunch Training paradox d. None of the above 10.A school for formula one car racing drivers does not want to risk the lives of its trainees. So, it has created a laboratory in which the trainees can practice under supervision on a model of a race car and feel what it feels like to drive one without actually being on the race track, till they are ready to try out an actual race car. This is an example of: a. Job instruction training b. Programmed learning c. d. None of the above Vestibule training1. An employee fears that if she reports her boss’s unwelcome personal advances towards her, she may lose her job, even though her boss has never said this explicitly. This is an example of: Principles of HRM: Assignment 5 a. b. Coercion Adverse impact c. Disparate treatment d. Affirmative action 2. A manager announces openly that anyone reporting his misdemeanour in the office will be dealt with more strictly that the ones who choose to ignore his bad behavior. This is an example of: a. Adverse impact b. Coercion c. d. Affirmative action Disparate treatment 3. A manager forces his subordinate to withdraw her complaint against his inappropriate behavior by bullying her and shouting at her in front of the entire office. This is an example of: a. Adverse impact b. c. Disparate treatment Coercion d. Affirmative action 4. An organization requires that all applicants for the position of a maintenance engineer at a construction site at the periphery of a nuclear plant have M. Tech. degrees in Civil Engineering. This is an example of: a. Business necessity b. Discrimination c. d. Affirmative action Bonafide occupational qualification 5. An organization requires that all applicants for the position of a maintenance engineer at a construction site at the periphery of a nuclear plant have at least three years of experience with maintenance operations of civil engineering sites in high risk areas. This is an example of: a. b. Discrimination Business necessity c. Bonafide occupational qualification d. Affirmative action 6. Ethical theory that assumes that after the formation of basic rules of acceptable social behavior, different points of view will exist, and should be allowed to coexist, is known as: a. b. Ethical relativism Pluralismc. Absolutism d. None of the above 7. Ethical theory that assumes that there are no universal rights and wrongs and that the decision for right and wrong depends upon the culture and context the decision maker makes the decision in, is known as: a. Absolutism b. c. Pluralism Ethical relativism d. None of the above 8. Utilitarian ethics deals with: a. b. Decision about right and wrong based on the end result Decision about right and wrong based on the cost-benefit analysis c. Decision about right and wrong based on the opinion of the person in charge of the situation d. None of the above 9. Whistleblowing is not a good idea when: a. b. You do not have someone senior to back you up You do not have complete and convincing documentation c. You do not have a whistle d. None of the above 10.An organization needs to cut down on its expenses. Towards this end, it decides to lay off a few senior executives so it can save the jobs of a larger number of junior executives. Since these employees are being laid off despite their stellar performance, the organization decides to give them a year’s worth of health insurance and a seven day trip for two to Europe in addition to what is promised through their contract. This is an example of: a. Unemployment insurance b. c. Job sharing Supplemental unemployment benefit d. Bonus ------------------1. Tight deadlines at work are an example of: Principles of HRM 2017: Assignment 6 a. b. Hindrance stressors Challenge stressors c. Personal stressors d. Interpersonal stressors 2. Office politics is an example of: a. Challenge stressor b. c. Personal stressor Hindrance stressor d. Interpersonal stressor 3. Which of the following is an example of an employees’ union? a. A group of people taking meals together b. A group of people working together on a project c. d. A group of people managing an organization A group of people committed to and working together on issues regarding their welfare as employees 4. A situation in which the management views the employees’ union as an opponent and prepares to deal with any opposition they may present to the working of the organization, is known as: a. Labor union strategy b. c. Union acceptance strategy Labor relations strategy d. Union friendly strategy 5. A situation in which the management and employees’ union work together to solve common goals and draw upon their resources to help each other, is known as: a. Labor union strategy b. Labor relations strategy c. d. Union friendly strategy Union acceptance strategy 6. Bargaining topics including discussion about the minimum pay scales of employees are classified as: a. b. Permissive bargaining topics Mandatory bargaining topics c. Illegal bargaining topics d. None of the above 7. Bargaining topics including discussion about the special leave that some employees need to take care of their children during their board examinations, are classified as: a. Mandatory bargaining topics b. c. Illegal bargaining topics Permissive bargaining topicsd. None of the above 8. Bargaining topics including discussion about policies regarding preferential treatment for people following a specific religion in the workplace are classified as: a. Mandatory bargaining topics b. Permissive bargaining topics c. d. None of the above Illegal Bargaining topics 9. Grievances regarding inability of the concerned administrator to follow a specific procedure due to his inability to understand the complex language of the conditions of employment, are known as: a. b. Grievances due to employee indiscipline Contract interpretation grievances c. Contract administration grievances d. None of the above 10. A situation in which the bargaining parties are unable to resolve their conflict is known as: a. Deadlock b. Wildcat c. Lockout d. Impasse ______________________1. An Indian organization purchases land in The Phillippines, and develops its infrastructure from scratch along the lines of its set ups in India. This is an example of: Principles of HRM 2017: Assignment 7 a. A wholly owned subsidiary employing the Brownfield strategy for entry into international business b. c. A wholly owned subsidiary acquiring a business that is already set up in a foreign country A wholly owned subsidiary employing the Greenfield strategy for entry into international business 2. An Indian organization purchases an abandoned set of buildings in Australia, and renovates them along the lines of its set ups in India. This is an example of: a. b. A wholly owned subsidiary employing the Greenfield strategy for entry into international business A wholly owned subsidiary employing the Brownfield strategy for entry into international business c. A wholly owned subsidiary acquiring a business that is already set up in a foreign country 3. An Indian organization buys a dying business in England and revives it under the banner of its Indian name while retaining most of its English footprint. This is an example of: a. A wholly owned subsidiary employing the Brownfield strategy for entry into international business b. A wholly owned subsidiary employing the Greenfield strategy for entry into international business c. 4. A multinational organization allows its employees in their foreign subsidiary to handle their problems at their own end and intervenes only when they approach the head office for help. This is an example of: A wholly owned subsidiary acquiring a business that is already set up in a foreign country a. Guide and advise approach to management of labor relations in multinational enterprises b. c. Strategic planning approach to labor relations in multinational enterprises Hands off approach to labor relations in multinational enterprises 5. A multinational organization expects its employees in their foreign subsidiary to report to the head office about their day to day affairs and the head office participates in all their decision making activities. This is an example of: a. b. Hands off approach to labor relations in multinational enterprises Guide and advise approach to management of labor relations in multinational enterprises c. Strategic planning approach to labor relations in multinational enterprises6. To get ahead of its competitors, an organization adds new features to its product offerings that are not offered by its competitors. This is an example of: a. Cost reduction strategy b. Enhancement strategy c. 7. To get ahead of its competitors, an organization routinely organizes a series of sales in its factory outlets, where its products are priced at 20% to 40% below the market price. This is an example of: Innovation strategy a. b. Enhancement strategy Cost reduction strategy c. Innovation strategy 8. To get ahead of its competitors, an organization starts using better raw material to manufacture its products and offers them at the same price as before. This is an example of: a. Cost reduction strategy b. c. Innovation strategy Enhancement strategy 9. According to the cybernetic model of strategic HRM, with reference to behaviour management as a responsibility of strategic HRM, an organization ensures that the salaries of its employees are commensurate with their output. This is an example of: a. Competence utilization b. c. Behavioral coordination Behavioral control 10.With reference to the types of networks in networked organizations, an organization that survives on a team of expert firms networking with each other to complete a project, is utilizing: a. An interactive network b. An individual network c. An interwoven network -------------------------------Principles of HRM 2017: Assignment 8 1. With reference to the just cause standard of discipline, notification refers to: a. b. Reasonable relation of the rule that was violated to the safe and efficient operations of the organization Forewarning to the employee of the disciplinary consequences of his or her conduct c. Impartial inquiry into the action deemed inappropriate d. None of the above 2. With reference to the just cause standard of discipline, the term ‘reasonable rule’ refers to: a. Forewarning to the employee of the disciplinary consequences of his or her conduct b. c. Impartial inquiry into the action deemed inappropriate Reasonable relation of the rule that was violated to the safe and efficient operations of the organization d. None of the above 3. With reference to the just cause standard of discipline, fair investigation refers to: a. Forewarning to the employee of the disciplinary consequences of his or her conduct b. Reasonable relation of the rule that was violated to the safe and efficient operations of the organization c. d. None of the above Impartial inquiry into the action deemed inappropriate 4. With reference to the just cause standard of discipline, proof of guilt refers to: a. Evenhanded application of the rules, orders & penalties of the disciplinary action b. Reasonable relation of the disciplinary action and/ or punishment to the seriousness of the rule violated c. 5. With reference to the just cause standard of discipline, reasonable penalty refers to: Provision of substantial evidence through the investigation regarding the action requiring disciplinary action a. Evenhanded application of the rules, orders & penalties of the disciplinary action b. c. Provision of substantial evidence through the investigation regarding the action requiring disciplinary action Reasonable relation of the disciplinary action and/ or punishment to the seriousness of the rule violated 6. With reference to the just cause standard of discipline, absence of discrimination refers to: a. Evenhanded application of the rules, orders & penalties of the disciplinary actionb. Reasonable relation of the disciplinary action and/ or punishment to the seriousness of the rule violated c. Provision of substantial evidence through the investigation regarding the action requiring disciplinary action 7. Which of the following is an example of positive discipline? a. Verbal warning – written warning – suspension – discharge b. c. Immediate fine every time a mistake is made Counselling sessions – assignment of a mentor – adjustment of timeschedules – training – feedback – final warning – discharge 8. Which of the following is an example of the hot stove rule? a. Verbal warning – written warning – suspension – discharge b. Counselling sessions – assignment of a mentor – adjustment of timeschedules – training – feedback – final warning – discharge c. 9. Which of the following is an example of progressive discipline? Immediate fine every time a mistake is made a. b. Counselling sessions – assignment of a mentor – adjustment of timeschedules – training – feedback – final warning – discharge Verbal warning – written warning – suspension – discharge c. Immediate fine every time a mistake is made 10.Which of the following scorecards ties all major activities and perspectives of an organization’s operations to the vision and strategy of the organization: a. b. Basic Input Process Output Scorecard Balanced scorecard c. Causal Chain Scorecard [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 15, 2020
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 15, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
102






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)