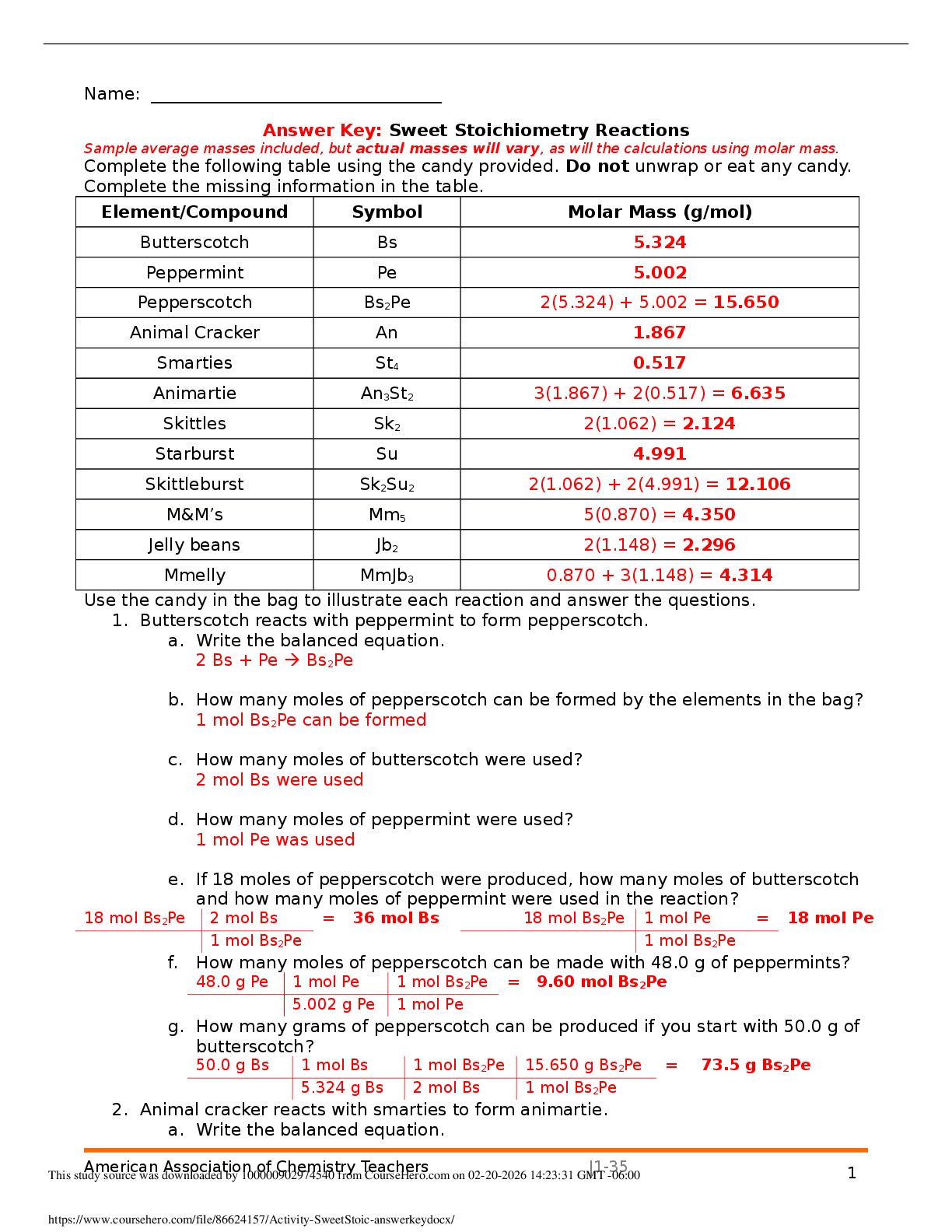
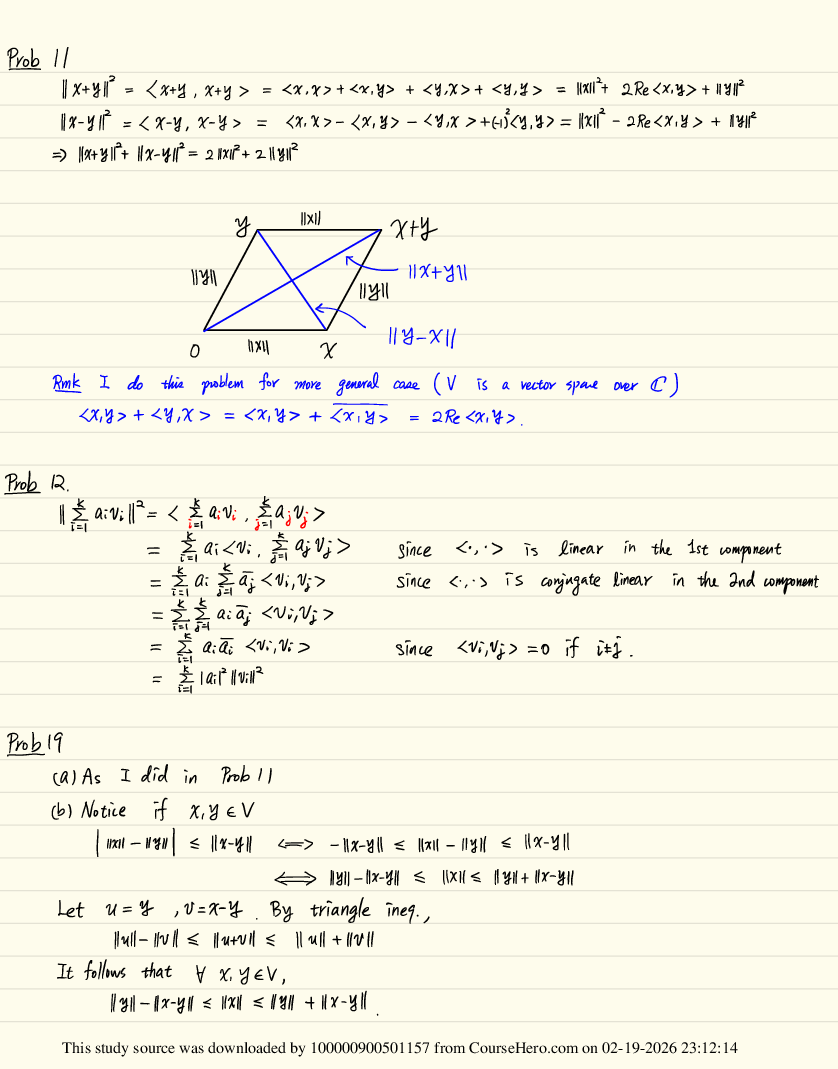
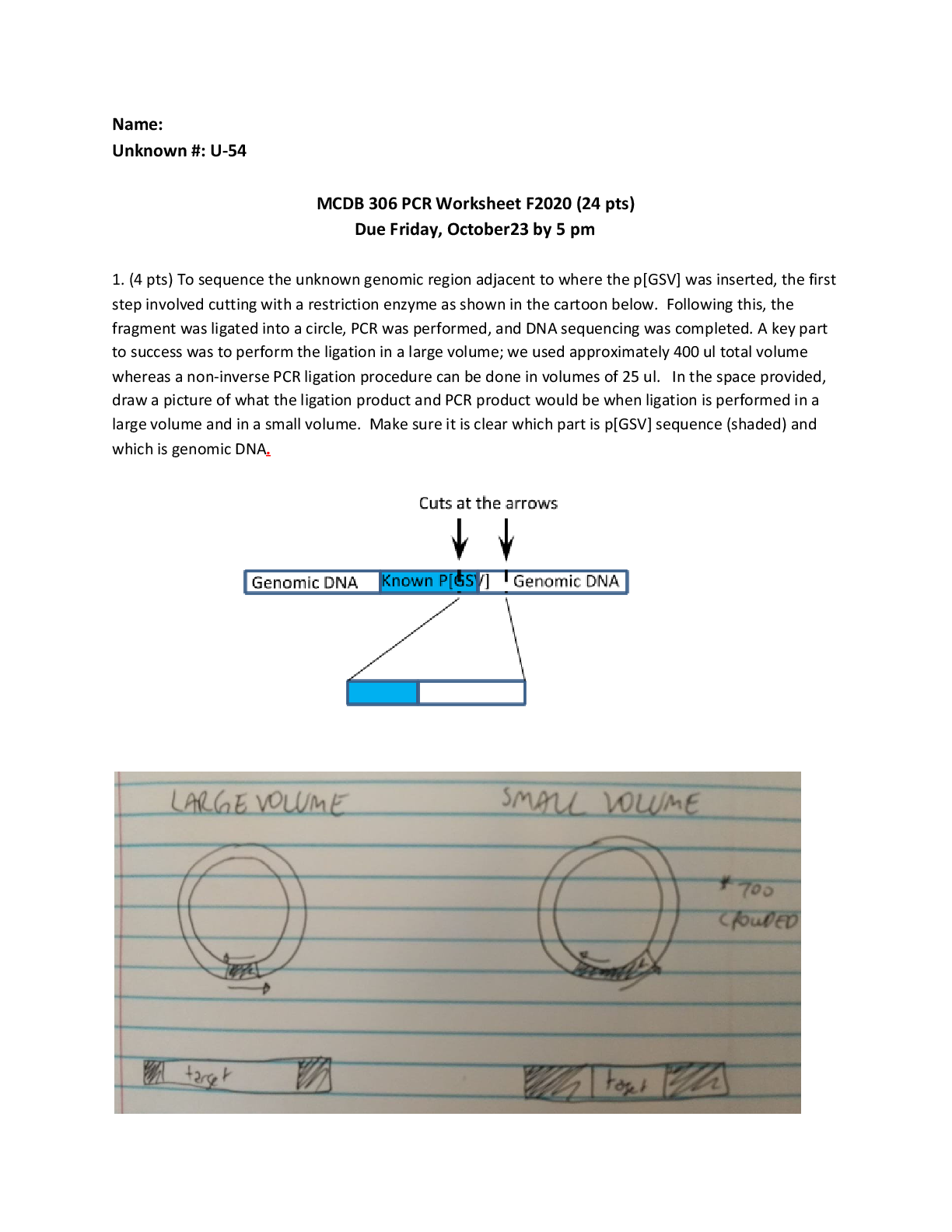
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. What contains enzymes and other factors that protect the conjunctiva from microbial invasion?
a. Skin
b. Tears
c. Upper lid
d. Lower lid
B
The tears that keep the conjunctiva moist conta
...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
1. What contains enzymes and other factors that protect the conjunctiva from microbial invasion?
a. Skin
b. Tears
c. Upper lid
d. Lower lid
B
The tears that keep the conjunctiva moist contain many enzymes and other factors (IgG, IgM, -lysin, lysozyme, lactoferrin) that protect the conjunctiva from microbial invasion.
REF: 957 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation
2. A layer of tears blankets the cornea to provide all of the following except:
a. waste elimination.
b. optical clarity.
c. lubrication.
d. nutrition.
A
A layer of tears (the tear film) blankets the cornea to provide optical clarity, lubrication, and nutrition.
REF: 957 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
3. Which of the following make up the majority of indigenous ocular microbial flora?
a. Mobiluncus and Lactobacillus
b. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus and Corynebacteria
c. Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus and Lactobacillus
d. Moraxella and Corynebacteria
B
Coagulase-negative staphylococci and Corynebacteria spp. make up 80% to 90% of indigenous flora recovered from uninflamed eyes.
REF: 957 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
4. All of the following factors determine whether a pathogen can cause disease in the eye except:
a. characteristics of the invading organism.
b. health of normal flora.
c. integrity of underlying tissue.
d. host’s immune system.
B
Because of their location, external ocular structures and surfaces such as the conjunctivae and cornea are frequently challenged by a variety of microorganisms. Whether an infection or damage ensues depends on the structure, immune status of the host, integrity of the underlying tissues, character of the invading organism, and host’s immune system.
REF: 957 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
5. All of the following are common risk factors associated with ocular infection except:
a. age.
b. sex.
c. personal hygiene.
d. social economic status.
C
Risk factors associated with ocular infections are age, sex, race, socioeconomic status, behavior, geographic location, occupation, and underlying disease.
REF: 957 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
6. In a warm climate, what organism is the most frequently isolated pathogen?
a. Haemophilus influenzae
b. Neisseria meningitidis
c. N. gonorrhea
d. Staphylococcus aureus
D
In warm climates, S. aureus is the most frequently isolated pathogen, whereas Streptococcus pneumoniae may be the most common isolate in areas with cooler temperatures.
REF: 959 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
7. What organism causes neonatal conjunctivitis, lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV), and trachoma?
a. Chlamydia trachomatis
b. Streptococcus trachomatis
c. Staphylococcus aureus
d. Neisseria meningitidis
A
C. trachomatis causes a myriad of ocular infections, including neonatal conjunctivitis, inclusion conjunctivitis, LGV, and trachoma.
REF: 960 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation
8. All of the following viruses cause acute viral conjunctivitis except:
a. adenovirus.
b. caliciviruses.
c. herpesviruses.
d. enteroviruses.
B
Acute viral conjunctivitis infections are attributed mainly to adenoviruses, herpesviruses, or enteroviruses.
REF: 961 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
9. What parasite is responsible for causing a form of blindness in West Africa?
a. Hookworm
b. Pinworm
c. Loa loa
d. Whipworm
C
Loa loa, the eye worm, is one of the leading causes of blindness in West Africa.
REF: 962 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation
10. Blepharitis is inflammation of the:
a. conjunctiva.
b. sclera.
c. lacrimal gland.
d. lid margins.
D
Blepharitis, inflammation of the lid margins, and inflammation of the conjunctivae are not mutually exclusive. Conjunctivitis usually presents as a blepharoconjunctivitis.
REF: 962 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
11. What condition is considered a true ocular emergency?
a. Conjunctivitis
b. Blepharitis
c. Microbial keratitis
d. Yellowing of the sclera
C
Microbial keratitis is considered a true ocular emergency. Few organisms can invade the intact cornea.
REF: 963 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
12. What compromises vision and must be treated aggressively with antimicrobials or surgery?
a. Epithelial infection
b. Infection in Bowman’s zone
c. Stromal infection
d. Perforation of Descemet’s membrane
D
Perforation of Descemet’s membrane compromises vision and must be treated aggressively with antimicrobials or surgical intervention.
REF: 963 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation
13. What is the leading cause of infectious blindness and ocular morbidity in the United States?
a. Epstein-Barr virus
b. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
c. Human papillomavirus (HPV)
d. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
D
Herpes simplex viruses are the leading cause of infectious blindness and ocular morbidity in the United States and other industrialized countries.
REF: 964 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation
14. A patient who makes her own saline solution for her contact lenses is examined at her physician’s office because she has a blood red, infected right eye. The physician performs bacterial, fungal, and viral cultures, all of which are negative. What is the most probable cause of this infection?
a. Acanthamoeba spp.
b. Entamoeba spp.
c. Trypanosoma spp.
d. Leishmania spp.
A
Acanthamoeba spp. are the most frequent isolates. Homemade saline solution associated with contact lens wear was the original identified risk factor. Amebic keratitis is often mistaken for viral or fungal keratitis, and a diagnosis of amebic keratitis is made only when all other cultures (bacterial, fungal, and viral) are negative.
REF: 965 OBJ: Level 3: Synthesis
15. Which condition is a medical emergency in children?
a. Chronic sinusitis
b. Lacrimitis
c. Preseptal cellulitis
d. Orbital cellulitis
C
Preseptal cellulitis is infection of the eyelids and soft tissues surrounding the orbit. It is a medical emergency in children. Infection can lead to blindness or death if not treated immediately and aggressively in all age groups.
REF: 966 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
16. Microorganisms can gain entry into orbital tissue in all the following ways except:
a. surgery.
b. eyelid infections.
c. dental caries.
d. carrying organisms on facial skin.
D
Microorganisms can gain entry into the orbital tissue through trauma or injury to the eyelids or orbit resulting from surgery, infections of the eyelids and adjacent skin, upper respiratory tract infections, and dental caries.
REF: 966 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
17. What is the most common infection of the lacrimal gland?
a. Blepharitis
b. Dacryocystitis
c. Canaliculitis
d. Conjunctivitis
B
Inflammation of the lacrimal or tear sac—dacryocystitis—is the most common infection of the lacrimal apparatus. Infections are usually associated with obstruction of the nasolacrimal sac.
REF: 967 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
18. What are the most frequent etiologic agents of endophthalmitis?
a. Staphylococcus epidermidis
b. Staphylococcus saprophyticus
c. Staphylococcus aureus
d. Escherichia coli
A
S. epidermidis and other coagulase-negative staphylococci are the most frequent pathogens of endophthalmitis.
REF: 968 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
19. All the following diseases are associated with uveitis except:
a. juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
b. HIV.
c. Reiter’s syndrome.
d. systemic lupus.
B
Connective tissue diseases, such as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, Reiter’s syndrome, and systemic lupus, are associated with uveitis.
REF: 966 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
20. Retinitis with what organism is common in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients?
a. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
b. Arenavirus
c. Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
d. Herpes simplex virus (HSV)
C
CMV retinitis is the second most common condition in patients with full-blown AIDS and can affect both eyes, even in the absence of systemic disease.
REF: 969 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
21. When performing ophthalmic cultures, all of the following are required for best results except the:
a. specimen should be collected on a transport swab.
b. sample should be plated directly when possible.
c. specimen requisition must be filled out completely.
d. ophthalmologist must communicate with the personnel performing the culture.
A
The ophthalmologist must communicate with the laboratory scientists performing the microbiologic evaluation of the specimen to ensure isolation of ocular pathogens. It should be noted whether the patient is a contact lens wearer. For best results, ocular materials must be inoculated directly onto the appropriate media. Scant recovery is the norm when transport swabs are submitted for recovery of ocular pathogens.
REF: 971 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
22. Bacteria that cause keratitis associated with contact lenses often initiate infection through which of the following?
a. Biofilm formation
b. Growth in the contact lens
c. Attachment to the lens
d. Contamination of the fluid coating the lens
A
Contamination of the soft contact lenses is usually caused by failure to follow manufacturer’s recommended procedures or poor hygiene. Organisms attach to and form biofilm.
REF: 975 OBJ: Level 2: Interpretation
23. What is the most common route of administration for ophthalmic drugs?
a. Topical
b. Intravenous
c. Intramuscularly
d. Oral
A
The routes of administration of ophthalmic drugs include topical (which is the most common and may include drops or ointments), periocular, intracameral, and intravitreal.
REF: 961 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
24. Nosocomial transfer of which virus may occur during optometry examinations through contaminated tonometer tips?
a. Adenovirus
b. Caliciviruses
c. Herpesviruses
d. Enteroviruses
A
Nosocomial transmission of adenoviruses may occur during ocular examinations, as the virus can persist in solutions or on tonometer tips.
REF: 961 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
25. Bacterial keratitis associated with contact lenses in warmer climates is commonly caused by which of the following organisms?
a. Corynebacterium spp.
b. Staphylococcus aureus
c. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
d. Viridans streptococci
C
Keratitis associated with contact lenses is being documented with increasing frequency. Gram-negative rods (especially P. aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens) are common isolates in southern Florida and other warm climates, whereas S. aureus is the most frequent in other parts of the country and cooler regions. Acanthamoeba spp., mycobacteria other than M. tuberculosis, and gram-positive cocci have also been recovered.
REF: 975 OBJ: Level 1: Recall
[Show More]












.png)
.png)
.png)