Physics > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > PH MISCweek 13 virtual lab/ PH MISC Week 13 virtual lab DIFFRACTION AND INTERFERENCE (All)
PH MISCweek 13 virtual lab/ PH MISC Week 13 virtual lab DIFFRACTION AND INTERFERENCE
Document Content and Description Below
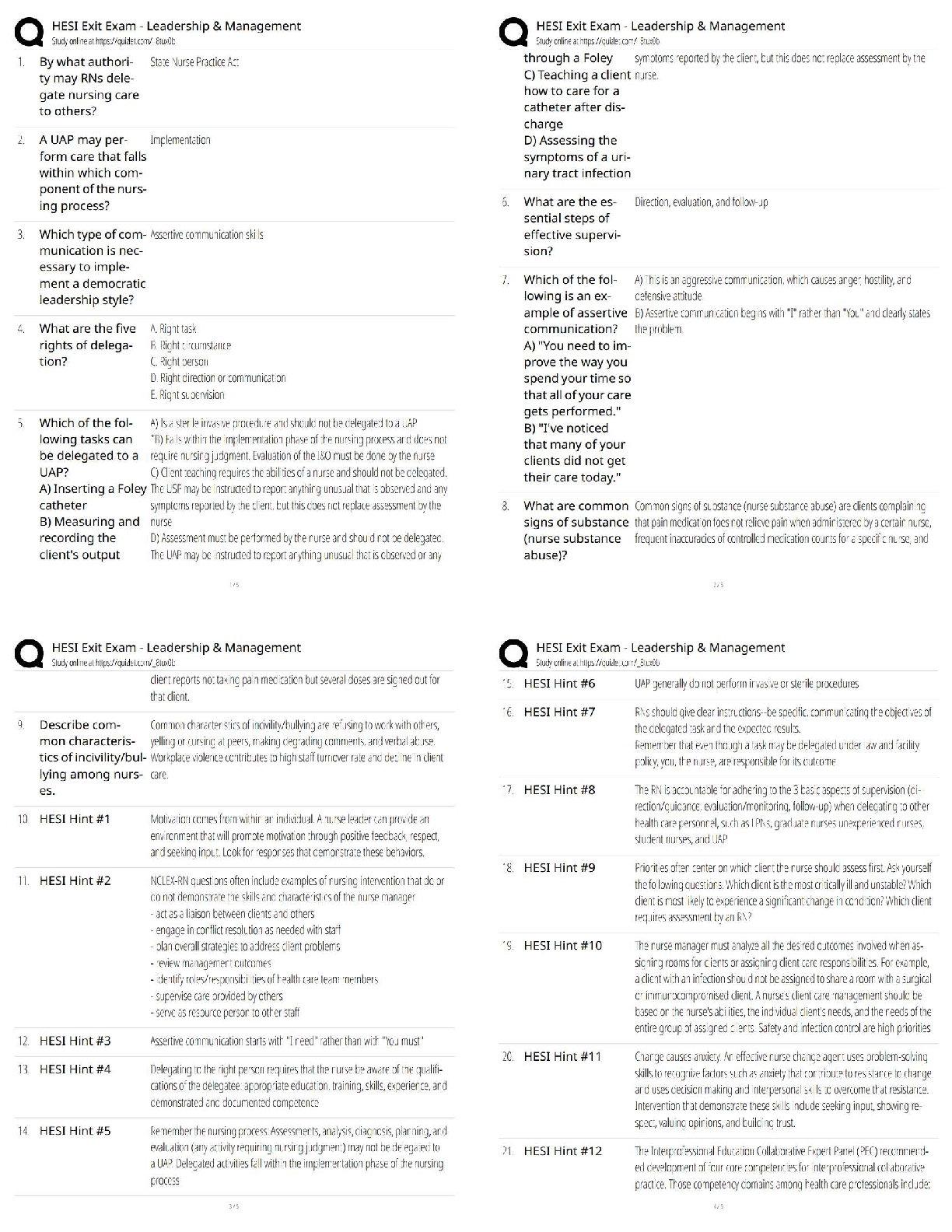
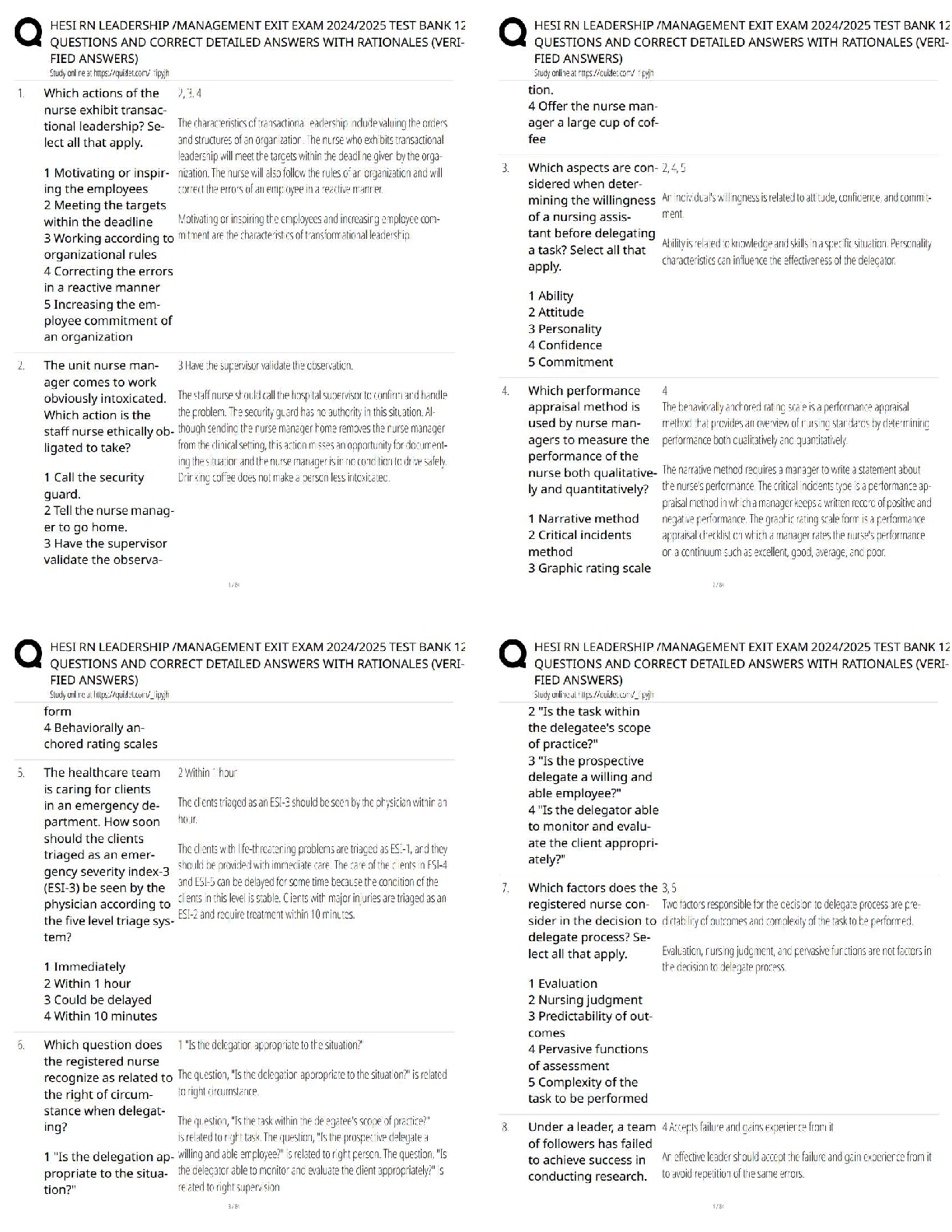
PH MISC Week 13 virtual lab DIFFRACTION AND INTERFERENCE Introduction When waves momentarily overlap, they temporarily add their amplitudes without affecting the original waves. This interfere ... nce can be seen when two wave sources are used and their overlaps viewed. You will view this phenomenon in parts I and II of this lab. When a wave strikes a barrier, some of the energy will bend around the barrier and spread out. This is known as diffraction. In part III of the lab, you will view the results of splitting a single wave source with a narrow slit, and then observe as the new waves created at the slit interfere. The interference pattern that results is symmetrical. The bands of constructive interference are referred to as maxima. Double Slit Theory When interference of light occurs as it passes through two slits, the angle from the central maximum (bright spot) to the side L maxima in the interference pattern is given by d sin θ = nλ (n=0,1,2,3, …) where "d" is the slit separation, θ is the angle from the center of the pattern to the nth maximum, λ is the wavelength of the light, and n is the order (0 for the central maximum, 1 for the first side maximum, 2 for the second side maximum ...counting from the center out). Simple trig arrives us at tan θ = x /L Theta is a small angle thus: sin θ ≈ tan θ = x /L Accordingly : ? ≈ ? ? ? ? Part I: Waves a) Observe the water waves created in the faucet analogy. The darker areas are areas of higher amplitude. b) Adjust frequency and amplitude and observe the characteristics of the waves. c) Discuss the changes in the waves as the amplitude is changed; frequency is changed. d) Change the source to the laser. Choose red light and side view. Choose slow and turn on the laser. Select and drag the sensor graph mechanism to the region of the waves. Click pause and place the electrodes so the white sensor is centered on a bright region and the dark sensor is centered on an adjacent dark region. (as shown) Click play. How would you describe the relationship of the phase of the graphs generated? e) Click pause and place the sensors so the white one is centered on a bright region and the dark one is centered on an adjacent bright region. Click play. How would you now describe the relationship of the phase of the graphs generated? f) Repeat for green light and blue light and discuss the similarities and differences for theses colors. g) Click on interference at the bottom to add a second drip to the simulation. Use two faucets. Observe the interference of the two water waves. h) Describe and comment on the interference of the two waves art II: Interference Please note the waves take some time to settle out – be patient a) Change the simulation to laser slow light emission from a single-light source. (remain on the interference tab, but only turn on one laser) b) Observe the wavelength of red light and then move the wavelength slider to blue light. Comment on the actual wavelength of blue light versus red light. c) Click screen to show how the light would look if viewed on a screen. Add a second light source and view the interfering waves and the pattern they create on the screen. Describe and comment on the pattern on the screen. d) Click Intensity – this graph quantifies the energy that is incident upon the screen. Vary the simulation to answer the following: i. What effect does amplitude have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? ii. What effect does source spacing have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? iii. What effect does wavelength have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? Part III: Diffraction a) Click on slits at the bottom. Click on the laser light. Add a 2-slit barrier to the simulation and allow click on screen and intensity. Observe the interference pattern created when the characteristics of the simulation are adjusted. You may have to adjust amplitude when other elements of the simulation are changed to observe the graph. i. What effect does a larger amplitude have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? ii. What effect does a shorter wavelength have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? iii. What effect does a larger barrier-to-screen distance have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? iv. What effect does a smaller slit width have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? v. What effect does a smaller slit separation have on the maxima separation in the interference pattern? Conclusion Questions and Calculations: 1. Why would a helicopter passing over or near a TV antenna cause a garbled or unusable TV signal? 2. The simulation uses monochromatic light. If white light was used instead, what would be seen on the screen? 3. As wavelength of the incident light increases (blue red) what happens to the maxima separation? 4. Two thin slits with separation of .0250 mm are placed over monochromatic orange laser light at 610.nm. What is the small angle measurement from the central maximum to the first maximum? (PSYW) 5. A beam of green light is split by thin double slit with separation of 0.0500 mm and incident upon a screen some distance away. The angles of the first and second maximums are 0.584º and 1.17 º respectively. What is the wavelength of the green light? (PSYW) 6. A single, monochromatic indigo light source is shined through an etched, flat prism with a slit separation of .0250 mm. The resulting interference pattern is viewed on a screen 1.25 m away. The third maximum is found to be 6.6 cm from the central maximum. What is the wavelength of the indigo light? (PSYW) 7. Where are the first and second maxima in question 6? (PSYW) 8. When the two additive colors blue (475 nm) and green (510 nm) are incident in equal magnitudes upon a white screen, the subtractive color cyan results. Consider two beams, one blue and one green. The blue beam is shined through a double-slit diffraction grating with slit distance of 0.0400 mm and then displays an interference pattern on a screen 1.00m away. If the green beam is then shined from the same position as the blue beam, what size diffraction grating slit width would be required for the green beam so only a cyan interference pattern would be seen on the screen? (PSYW) [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 5 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jan 22, 2021
Number of pages
5
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jan 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
34






.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)